Netskope Threat Research Labs recently posted an article, detailing the CloudPhishing Fan-out resulting from Decoy PDF documents. We are observing a growing trend in the use of such PDF decoys that use Cloud Storage services to carry out not only phishing attacks but also infect user devices with malware such as Remote Administration Tools (RATs). These latest threats are taking advantage of many companies’ “default allow” policy for Cloud Storage services and also the use of popular PDF readers. In our research, we identified several PDF decoys using popular Cloud Storage services like Google Drive, OneDrive (and OneDrive for Business), Box, and Dropbox for downloading malicious payloads. We also identified the usage of URL redirection services for retrieving malicious payloads hosted in Cloud Storage services.
In one particularly clever example, the attack delivers a too-small image of a document, and offers the user a magnifier to trick him/her into clicking on a document, as shown in Figure 1.
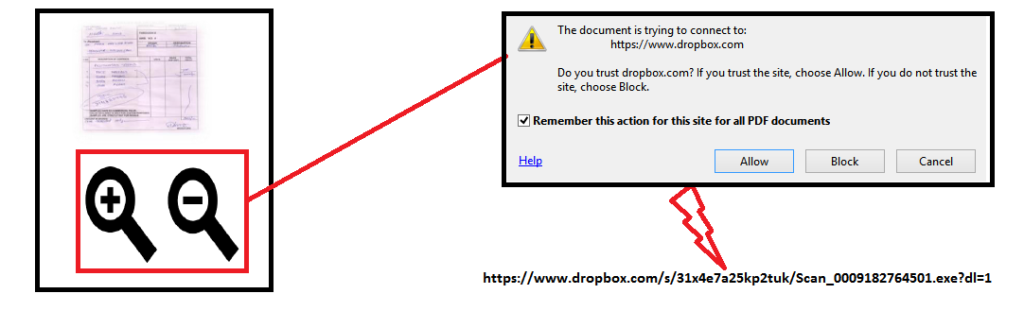
Figure 1: Enticing document delivered when the user clicks the magnifier
On clicking the “zoom in/out” magnifier option in Figure 1, the victim is pointed to a malicious payload hosted in Dropbox. At the time of analysis, the Dropbox link was down and not serving malware.
The above illustrates one of the tactics and we have been observing a number of similar themed PDF decoys as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Messages displayed to trick users into launch PDF decoy documents
In the following sections of this blog we will detail two cases in which the PDF decoys used Cloud Storage services to download malicious payloads. The malicious payloads resident in the Cloud Storage services as well as an attempt to download them are detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.Gen.20002647 and Backdoor.Generckd.3640291.
Delivery of PDF Decoys via E-mail and Cloud Storage services
During our analysis, we found PDF decoys being sent as email attachments to users at various enterprises. Some organizations tend to save email attachments in Cloud Storage services to reduce email storage, collaborate with clients and colleagues more efficiently, and send and receive large email attachments with greater speed and ease. If a PDF decoy gets synced to the Cloud Storage service and then others sync it to their devices in order to collaborate, that can create a dangerous fan-out effect. See how the attack chain also causes a fan-out effect for email attachments within shared users in the cloud, and how enterprises can protect themselves using Netskope Threat Protection, in Figure 3.
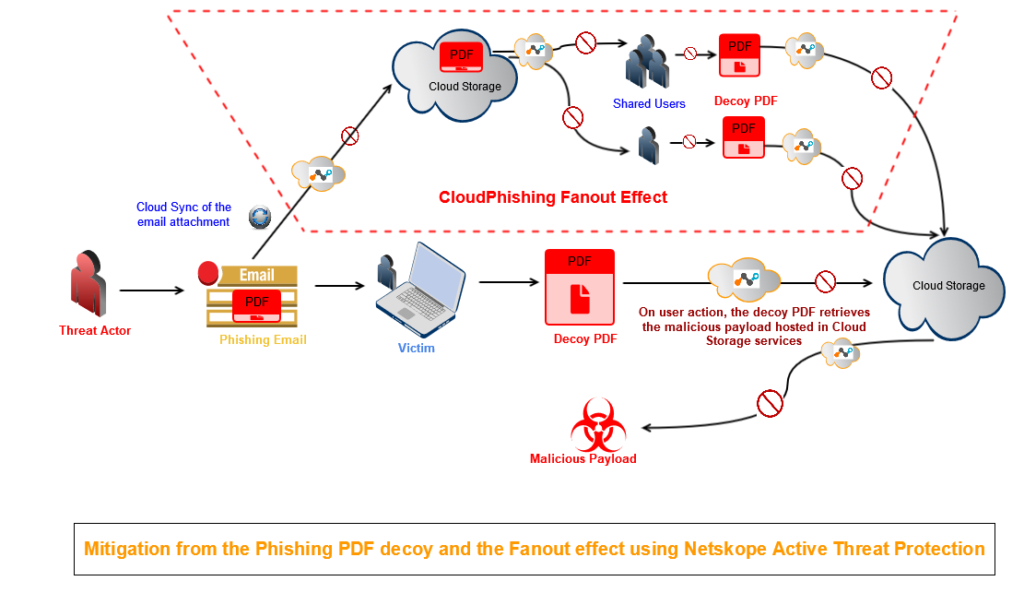
Figure 3: Protection using Netskope Threat Protection
Saving email attachments and collaborating on them in the cloud without regular supervision results in a secondary propagation vector of the decoy document creating a severe impact to an organization.
PDF decoys using Cloud Storage services for downloading malicious payloads with UUE extension
As part of our research, we found several PDF decoys arriving in email that are capable of downloading additional payload files with the UUE extension. As an example, in one case we observed an email with attachment was sent to a contact at a multinational company as shown in Figure 4.
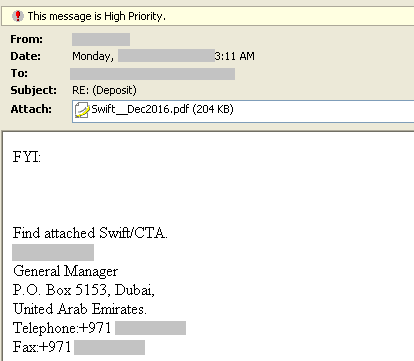
Figure 4: PDF decoy sent as an email attachment
The email attachment contained a PDF decoy named, Swift__Dec2016.pdf. Upon opening the PDF decoy and clicking anywhere in the document, a malicious RAR compressed archive with the UUE extension, named Swift_Dec2016_pdf.uue, hosted in Dropbox is downloaded to the victim’s machine. The compressed archive, Swift_Dec2016_pdf.uue, contains an executable file called Swift_Dec2016_pdf.exe. This compressed archive file resident in the cloud storage as well as the download activity by a user are detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.Gen.20002647. This activity is shown in Figure 5.
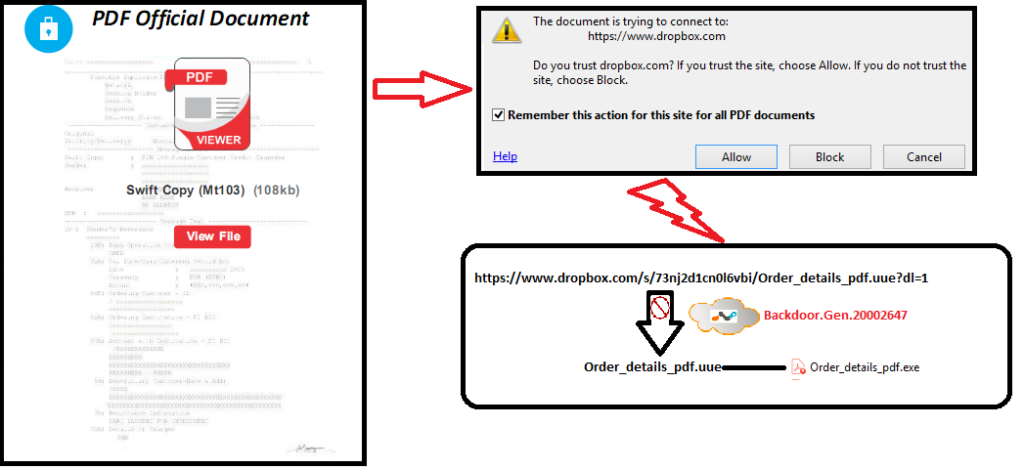
Figure 5: Swift__Dec2016.pdf retrieving the malicious payload from Dropbox
UUE file extension
Generally, UUE files are binary files that have been encoded, so they can be transmitted as text. Traditional compression tools like WinRAR and WinZip support the decoding of the UUE file format. Since RAR decompression is also supported by these tools, the malicious RAR compressed archive with a UUE extension detonates successfully when the victim inadvertently executes the file. We suspect that the malware author used the UUE file format with the intention of bypassing network security devices.
PDF decoys use URL redirection services to point to Cloud Storage services that deliver malicious payloads
As we continued our research, we identified several PDF decoys that connected to Cloud Storage services via URL redirection services. An example of a PDF decoy that we observed using a URL redirection service to download the malicious payload hosted in Cloud Storage services is shown in Figure 6.
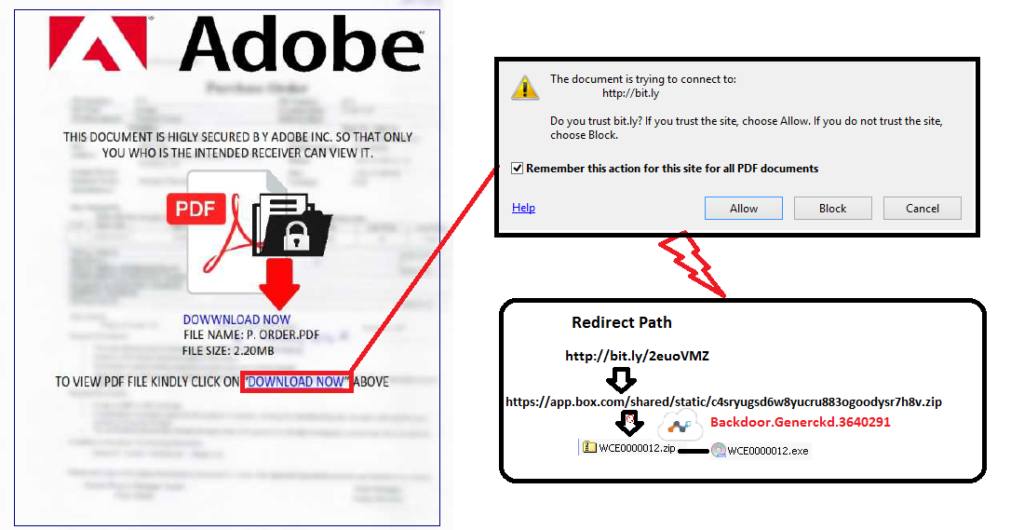
Figure 6: PDF decoy using a URL redirection and Cloud Storage service
Figure 6 illustrates that, on clicking the “DOWNLOAD NOW” hyperlink, the victim is displayed with a bit.ly URL redirection link, which fetches the malicious payload hosted in Box. This malicious payload file WCE0000012.exe that is resident in the cloud storage as well as the download activity by a user are detected by Netskope Threat Protection as as Backdoor.Generckd.3640291.
Annotations in PDF Decoys
While looking into the two decoy PDFs, we found several malicious links present in the files. These links were used as annotations for several iterations like updating and editing with the same PDF decoy. An important observation was the usage of the URL shortener links and the Cloud Storage links in the annotations.
Annotation in Swift__Dec2016.pdf
The annotations seen in Swift__Dec2016.pdf are shown in Figure 7.
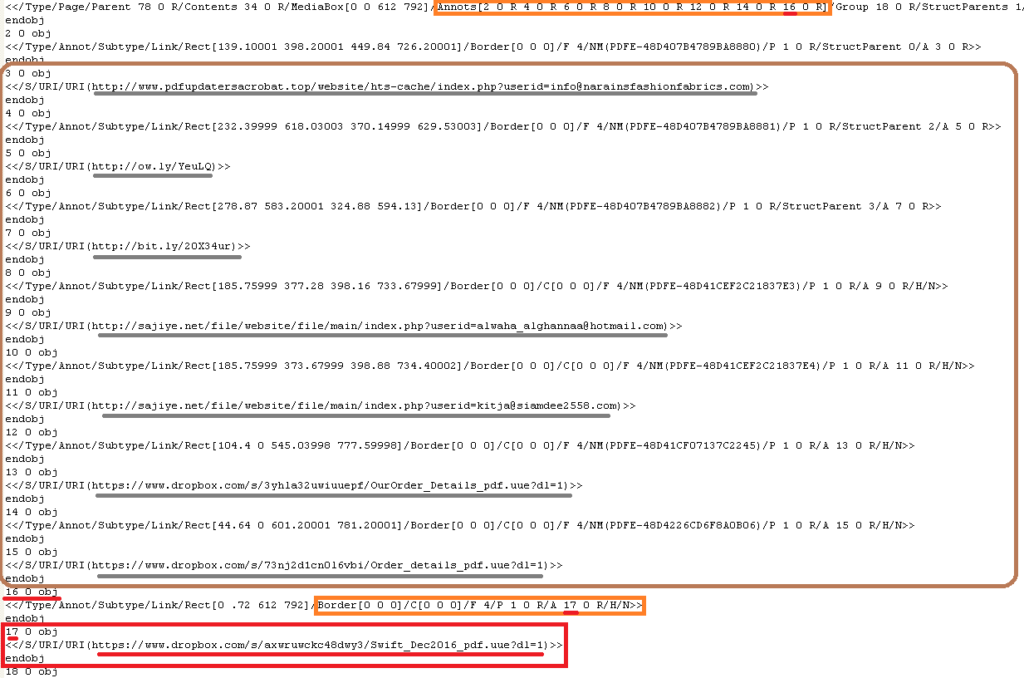
Figure 7: Links in the annotations of Swift__Dec2016.pdf
Figure 7 illustrates that the decoy PDF uses the Dropbox link in the 17th object for downloading the malicious payload. The links in Swift__Dec2016.pdf were annotated using the RAD PDF annotator, as shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8: Annotations using RAD PDF annotator
Annotation in the second PDF Decoy
We also found several bit.ly URL redirection service URLs’ annotations using Nitro Pro. An excerpt of the annotations seen in the decoy is shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: Annotations seen in the second PDF decoy
The last updated link in the annotation is used by the PDF decoy for downloading the malicious payload.
The annotations in the PDF decoys indicate that the attack campaign artifacts are simply being reused by the malware author to rapidly adapt to malicious file takedowns by Cloud Storage services.
Analysis of the malicious Payload
The malicious payloads downloaded from the two PDF decoys had the same behavior and functionality. Both of the binaries are self-extracting cabinet executables that drop an AutoIT compiled executable on installation, as shown in Figure 10.
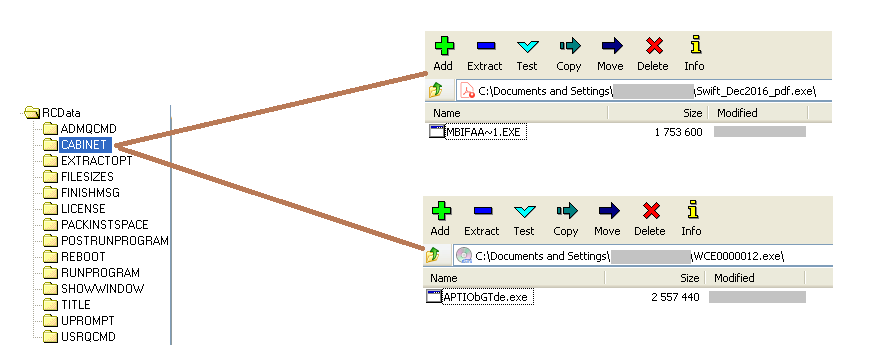
Figure 10: Executables dropped by the self-extracting cabinet installers
The binaries are detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.Agnt.ND and Gen:Variant.Strictr.115561. The binaries inject code into %windir%\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\RegAsm.exe on execution, as shown in Figure 11.
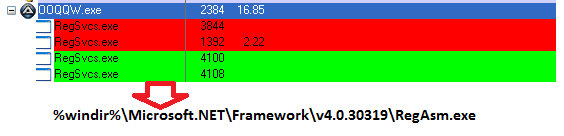
Figure 11: Injected code in RegAsm.exe
After extracting the script from the AuotoIT executables, we came to know that the AutoIT executables were wrapped with a Remote Administration Tool (RAT) named NanoCore. The Analysis of this AutoIT-wrapped executable with NanoCore has been already documented by several researchers. The wrapped NanoCore binaries are .NET executables packed with the Eazfuscator Obfuscator. The presence of NanoCore RAT strings and functionality after de-obfuscating the binary are shown in Figure 12.
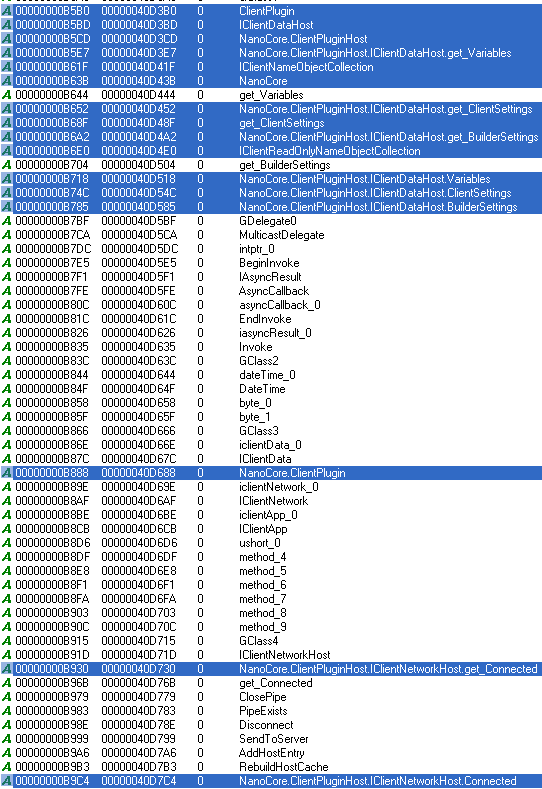
Figure 12: Strings present in the deobfuscated NanoCore binary
The samples we analyzed contacted the C&Cs at 212.83.131[.]214 and princek[.]ignorelist[.]com
NanoCore RAT
NanoCore is a commercially available RAT, effectively used with the intention of taking control of Windows machines.
The features offered by the NanoCore RAT as mentioned on their the website are shown in Figure 13.

Figure 13: Features offered by NanoCore RAT
The functionality and working of the NanoCore RAT on the website are shown in Figure 14.
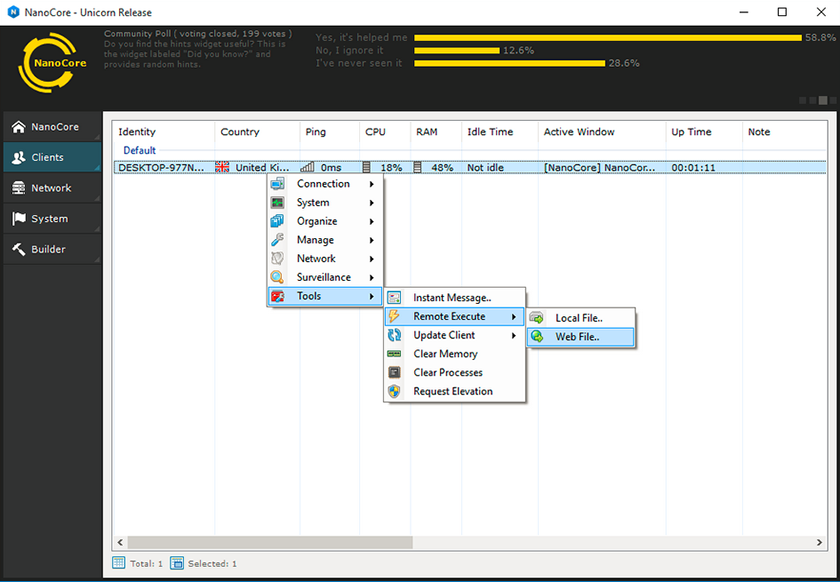
Figure 14: Functionality and working of NanoCore RAT
Due to a wide range of features offered, several cracked versions of this RAT have been leaked, serving an effective use case for threat actors. NanoCore started to be in the limelight when one of the leaked versions was reported to be used in the targeted attack campaigns against energy companies in Asia and the Middle East.
Conclusion
The usage of cloud services for hosting and delivering malware is being rapidly adopted by threat actors. A clear evidence is evident from the growing trend of the PDF decoys for retrieving malicious payloads. Enterprises need novel approaches for detecting suspicious or malicious files in the cloud. Using a threat-aware cloud access security broker (CASB) that includes threat protection, such as Netskope Threat Protection, can aid in remediating threats and staying agile. Netskope has worked with the cloud storage providers, Dropbox and Box to take down the URLs hosting the malicious payloads. We will continue to closely monitor the developments of the PDF decoys using Cloud Storage services and update our findings with more interesting developments.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate all threats in sanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware solution like Netskope Threat Protection along with the Netskope Active Platform and Netskope Introspection
- Detect and remediate all threats being downloaded from unsanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware solution like Netskope Threat Protection along with Netskope Active Platform
- Administrators should actively track the usage of unsanctioned cloud services and enforce DLP policies to control files and data entering and leaving your corporate environment
- Users should regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Users should enable the “View known file extensions” option in Windows machines
- Users should uncheck the option “Remember this action for this site for all PDF documents” in the PDF reader software
- Whenever you receive a hyperlink, hover the mouse over it to ensure it’s legitimate
- Users should actively track URL links added to the “Always Allow” list in PDF reader software
- Users should avoid executing any file unless you are very sure that it is benign
- Administrators should warn users to avoid opening untrusted attachments, regardless of those attachments’ extensions or file names
- Users should keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Zurück
Zurück 























 Read the blog
Read the blog