Netskope Threat Research Labs discovered a parasitic Monero mining malware campaign named xbooster that was successful in generating close to $100,000 USD using multiple Monero accounts. The attack kill chain used Amazon Web Services (AWS) and pay-per-install” (PPI)/ “pay-per-click” (PPC) model modus operandi. Since the attack kill chain uses both the cloud and web, it makes it hard to detect the full scope of an attack and perform complete remediation. Netskope for Web detects xbooster malware as Application.Downloader.Sasquor.Gen.1 and the payloads as Generic.Application.CoinMiner.1.02762A18, Gen:Variant.Zusy.280450 and Trojan.GenericKD.30600286.
During the last week of April, Netskope detected several Monero parasitic miners that used AWS for hosting the payloads and exfiltrating the victim’s host details. The malware campaign dubbed ‘xbooster’, shared many similarities with Zminer, discovered and detailed by us last year.
This blog provides a preliminary overview of coin miners, the cryptocurrency Monero, and xbooster. We will be posting a follow-up blog detailing the technical analysis of xbooster, the different xbooster strains, and the monero earnings of the associated accounts.
Cryptocurrencies – coin miners
Cryptocurrency has exponentially grown since inception starting with Bitcoin. Almost 1600 cryptocurrencies have evolved in this space and has attracted widespread adoption across the globe because of a blend of the wide range of acceptance and popularity, in addition of mining and generating coins using computing power.
Most importantly, features like decentralization and anonymity have induced threat actors and cybercriminals to use them for transactions and also for parasitic coin miners. The implementation of SMB wormed attacks that subsequently install coin miners for scaling mining operations in large scale has yielded profitable business to the attackers.
The most interesting twist for browser-based coin miner is the consumption of victims’ resources (CPU / memory) when the website is visited, as an alternative provision to bombarding annoying and enticing ads. These coin operations can seamlessly mine in a corporate environment as the machines and workstations have robust hardware and abundant resources that provide faster and efficient scaling.
Why Monero coin miner?
Of all the mining-based currency models, Monero miner is most commonly used and deployed by threat actors. Monero is a preferred choice because of the following:
- Privacy – Monero supports Stealth Addresses and Ring Confidential Transactions to apply privacy to every single transaction
- Faster Block Computation – Traditionally Monero blocks are produced at an average of every 2 minutes, and Bitcoin blocks are produced at an average of every 10 minutes
- Mining – Monero provides an egalitarian mining process and also the feasibility of CPU mining and browser-based mining for generating coins yielding a profitable revenue to its users
The valuation of a Monero coin is nearing $250. According to the website cryptocompare.com, the mining metrics of Monero is shown in Figure 1.
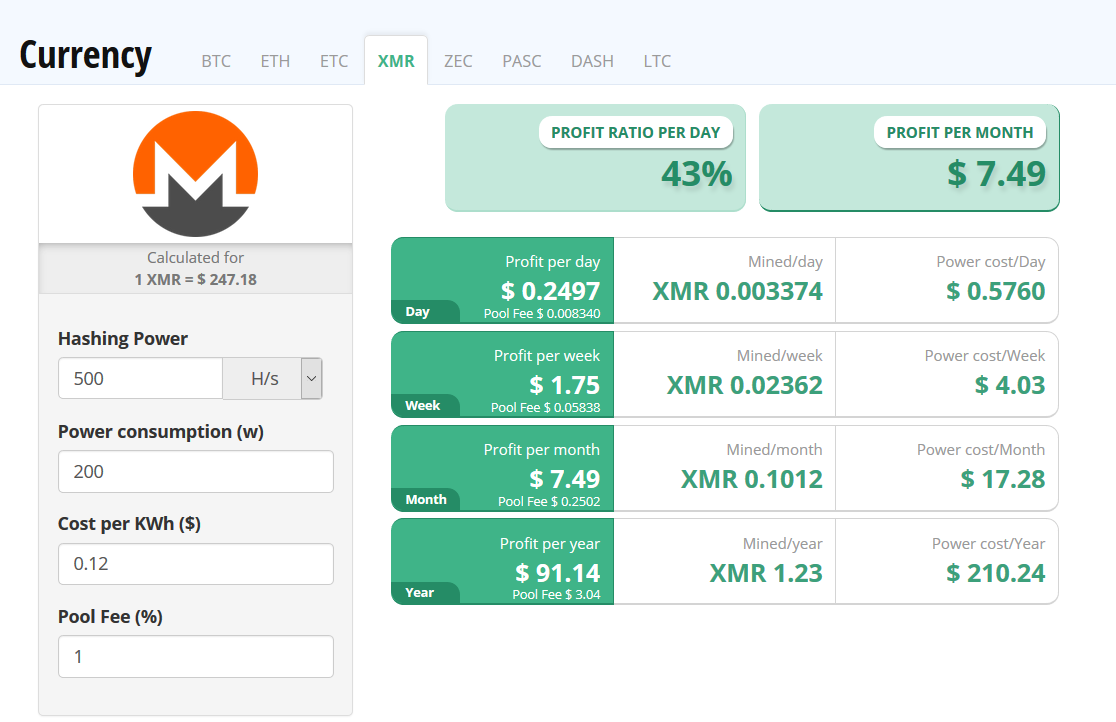
Figure 1: Mining metrics of Monero (XMR)
On the same note, according to the website minergate.com, Monero is currently the most profitable CPU mining coin as shown in Figure 2.
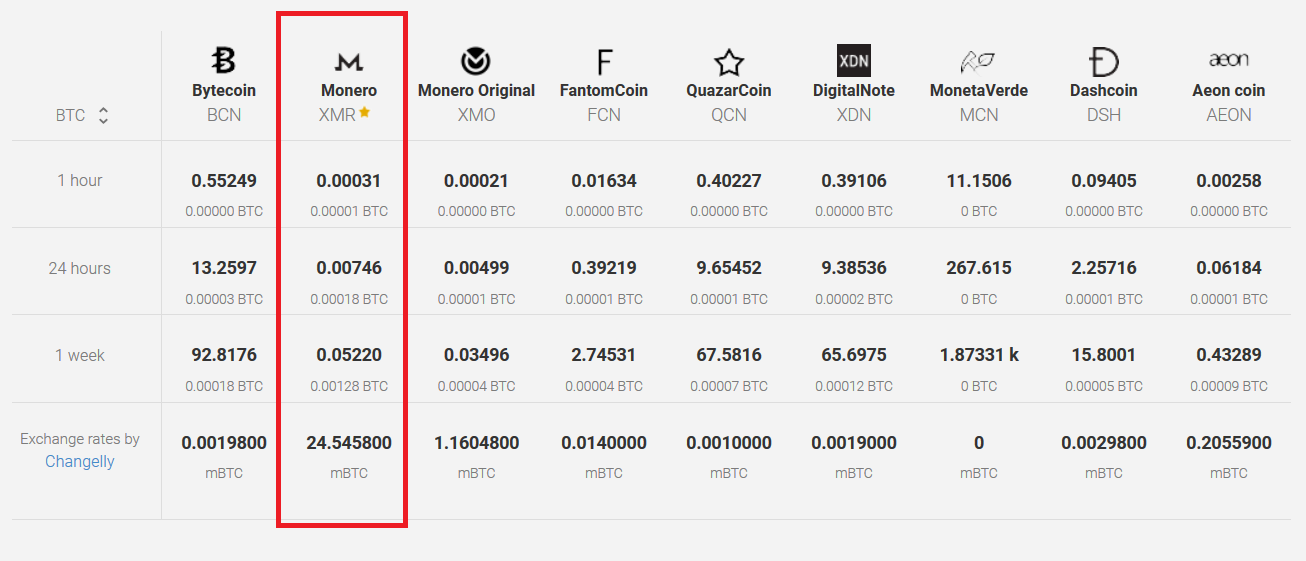
Figure 2: Comparison of CPU miners
Comparison of Xbooster and Zminer
Zminer is a mining malware that downloaded the payloads from Amazon S3 to a victim’s machine and also used a C&C registered to Amazon for exfiltrating the victim’s host details.
Unlike Zminer, which downloaded the stage payloads and also exfiltrated the victim’s host details from AWS, xbooster dropped the initial payloads from its resource. The resource is a password protected zip file which is unzipped during runtime. These payloads use the machine’s computing resources to perform coin mining. The dropped xbooster payloads then use AWS for downloading the next stage payload and also exfiltrating the victim’s host details. Though the initial version of the xbooster binaries dropped the miner payloads from the resource, the latest variants are downloading a zip file containing the miner payloads from Amazon S3.
Although Zminer and Xbooster shared many common similarities, one major difference is the choice of the miner. Xbooster used xmrig miner while Zminer used Claymore CryptoNote CPU Miner for a 32 bit Windows operating system or nheqminer for a 64 bit Windows operating system.
Xbooster Attack Kill chain – Depiction
The visual depiction of the attack kill chain of the xbooster Monero miner that we first observed is shown in Figure 3.
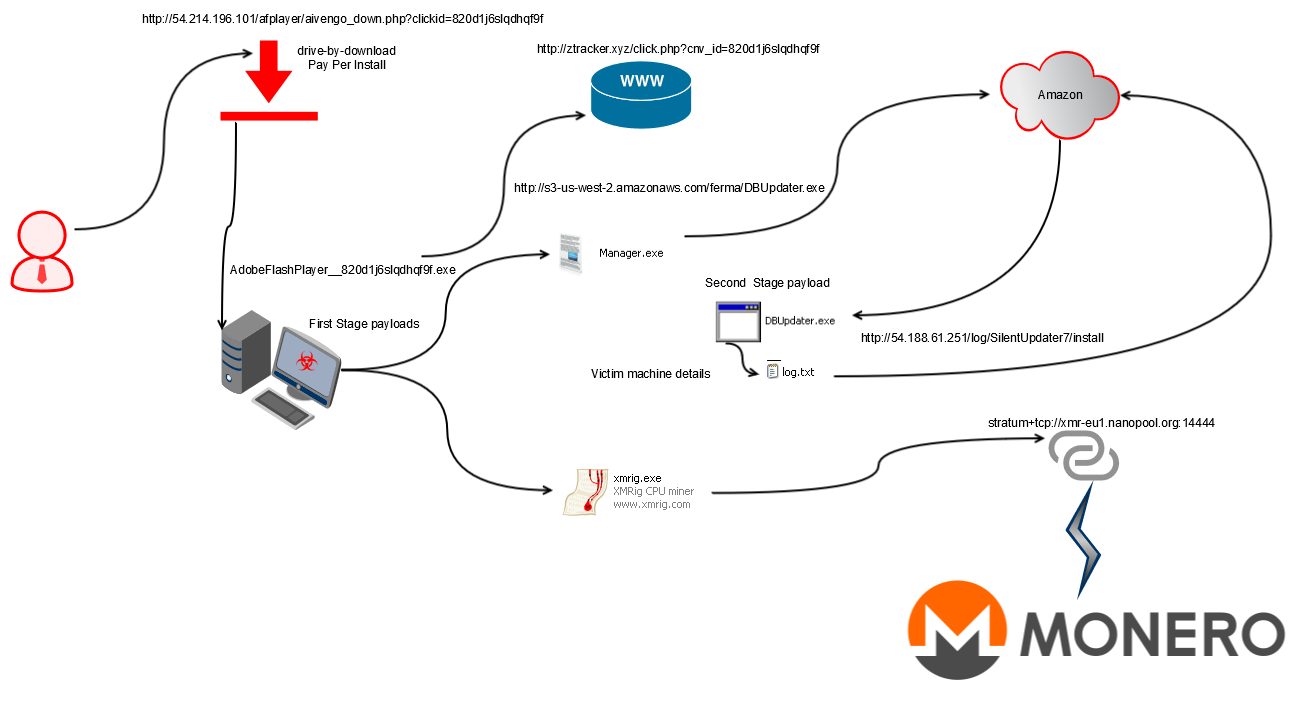
Figure 3: Initial version of the Xbooster Attack Kill chain
The depiction illustrates the use of pay-per-install” (PPI)/ “pay-per-click” (PPC) drive-by-download model for the distribution of xbooster. PPI / PPC models charge money based on the number of successful installations. The downloaded executable drops two executables named xmrig.exe and manager.exe. Xmrig.exe performs the monero mining operation. Manager.exe downloads DBupdater.exe from Amazon S3 which exfiltrates the infected host details recorded in a file named, ‘log.txt’, to a C&C server within AWS.
The visual depiction of the attack kill chain of the latest version of the xbooster Monero miner that downloaded a zip file from Amazon S3 with the similar working is shown in Figure 4.
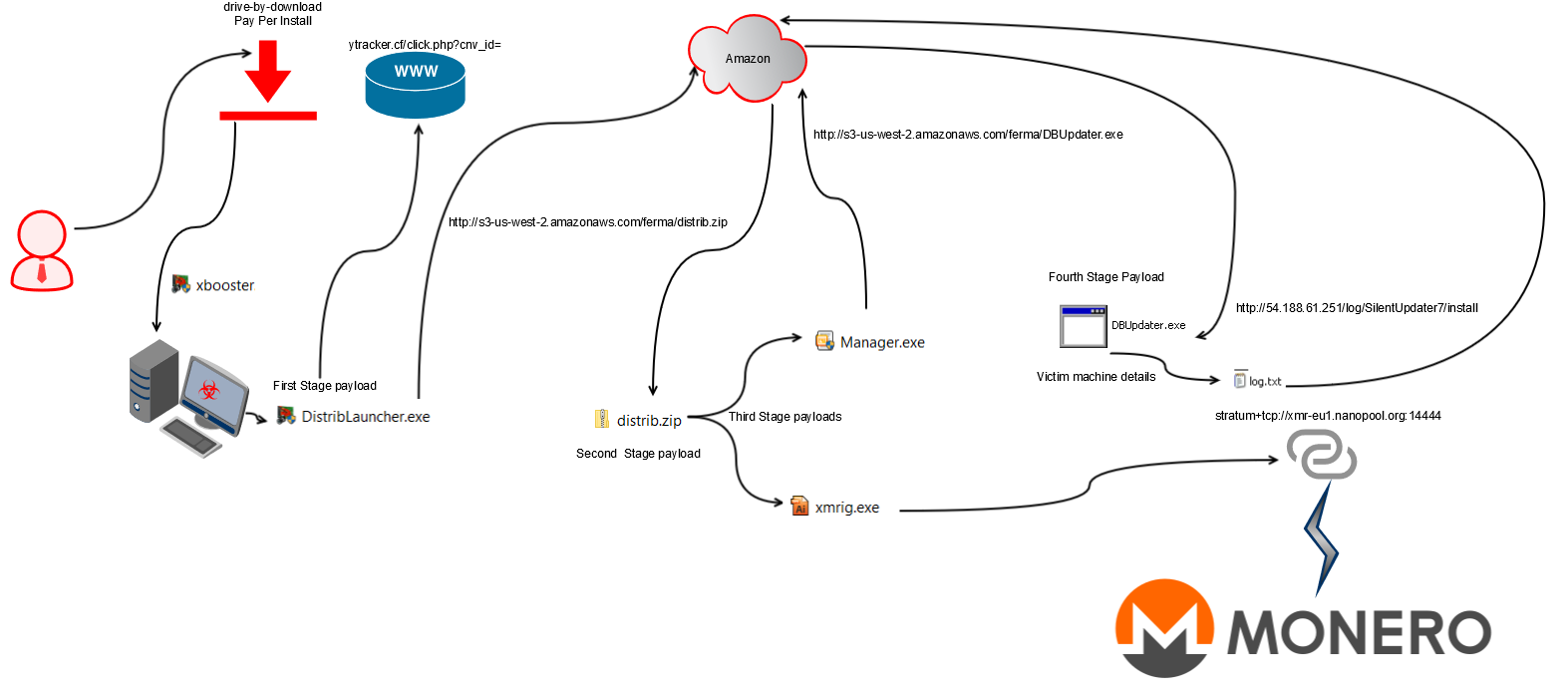
Figure 4: Latest version of the xbooster Monero miner
Conclusion
Leveraging the computing power for Monero coin mining is turning out to be a lucrative business model for threat actors and adware vendors. The advantage of being anonymous with Monero has induced this adoption as threat actors always prefer to stay under the radar. The coin miner eats away CPU cycles thereby hogging the CPU usage. The mining attacks always lead to drastic consequence in a corporate environment that is always equipped with robust hardware and have an abundant power supply.
The high CPU usage of corporate resources can potentially lead to disruption of critical business as the infrastructure becomes slow or unresponsive and may even result in an unexpected shutdown. Since Monero miners with mining pools have been most commonly deployed by threat actors, users can consider blocking the Monero mining pools in the corporate environment.
Netskope has disclosed the AWS attack elements to the concerned entities. Netskope for web armored with multi-layered threat protection capabilities like advanced heuristic analysis and dynamic cloud sandbox offers protection from parasitic mining attacks. We will continue to monitor the coin mining attacks and trends and also ensure our solutions provide robust defense from these attacks.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Employ a threat aware, unified platform like Netskope that can assemble the pieces and find hybrid threats and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/ well-known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Administrators can create firewall rules to block bitcoin pools documented in the Wikipedia article
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Back
Back 























 Read the blog
Read the blog