Netskope Threat Labs publishes a monthly summary blog post of the top threats we are tracking on the Netskope platform. The purpose of this post is to provide strategic, actionable intelligence on active threats against enterprise users worldwide.
Summary
- Attackers continue to attempt to fly under the radar by using cloud apps to deliver malware, with 61% of all malware downloads in February originating from 161 cloud apps, both six-month highs.
- Malicious plain text files, especially malicious LNK and PowerShell files, are on the rise and accounted for 12% of malware downloads in February, a six-month high.
- Trojans continue to represent the majority of malware downloads, used to deliver payloads such as the infostealers AgentTesla and ClipBanker, and the backdoors Zusy and Farfli.
Cloud Malware Delivery
Attackers attempt to fly under the radar by delivering malicious content via popular cloud apps. Abusing cloud apps for malware delivery enables attackers to evade security controls that rely primarily on domain block lists and URL filtering, or that do not inspect cloud traffic. In February 2023, 61% of all HTTP/HTTPS malware downloads originated from popular cloud apps, increasing for the fourth consecutive month.
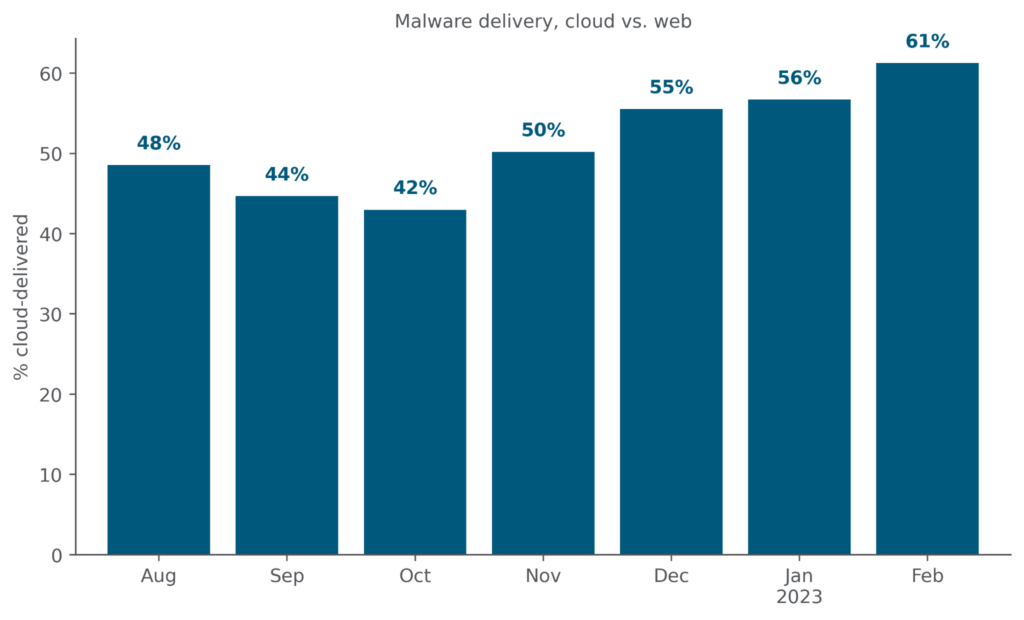
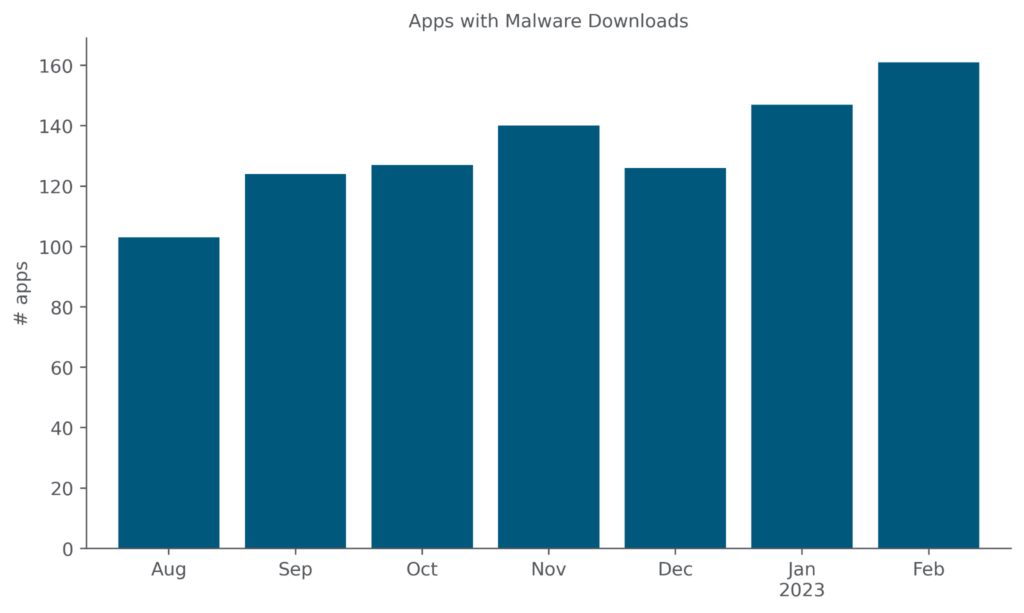
The increase in cloud malware downloads is driven partially by an increase in the number of distinct cloud apps from which malware are being downloaded. In February 2023, Netskope detected malware downloads from 161 distinct cloud apps, increasing for the second consecutive month.
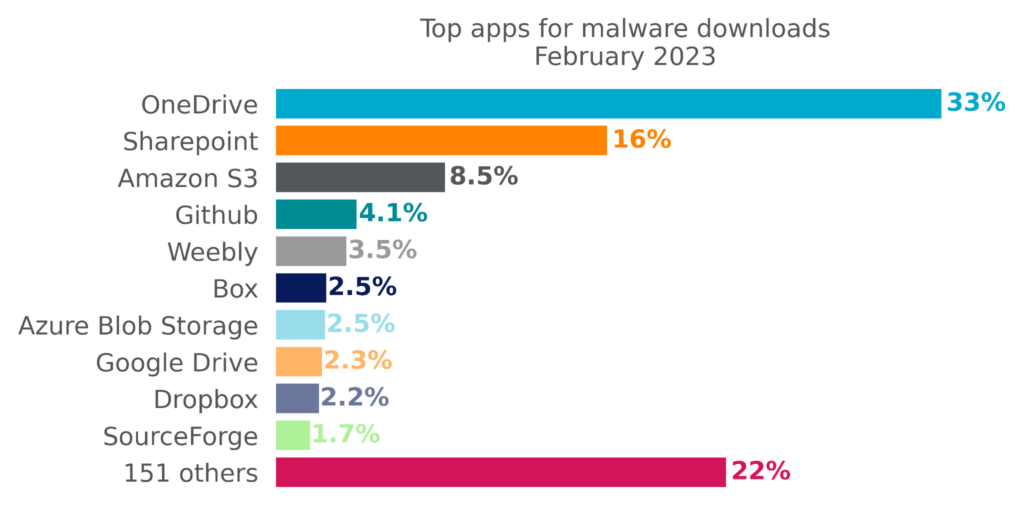
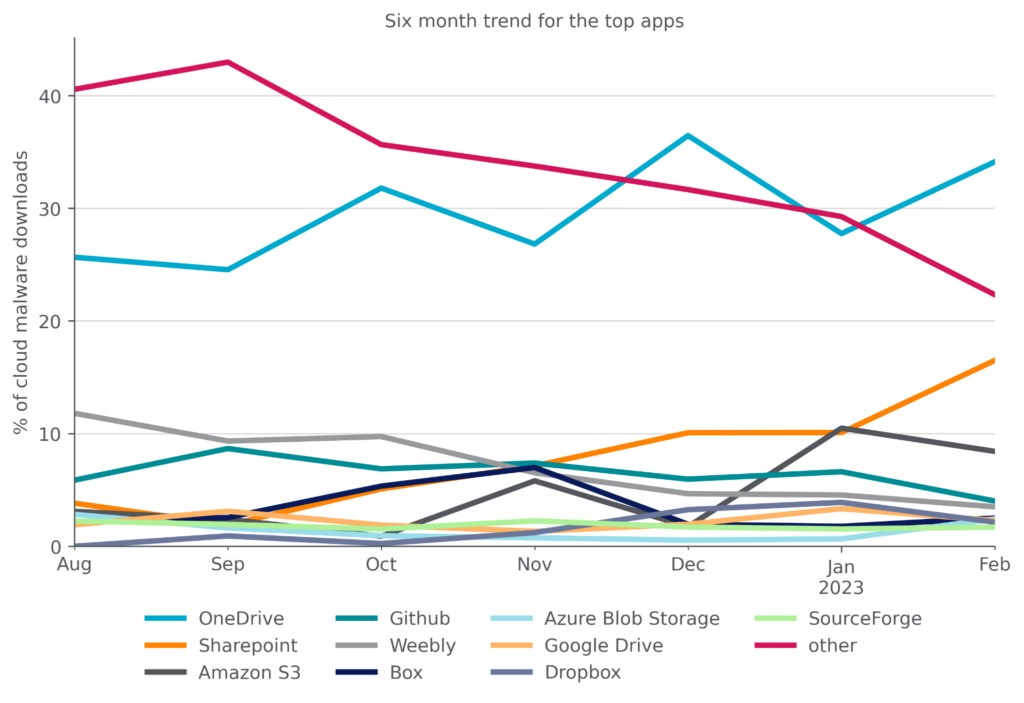
Attackers achieve the most success reaching enterprise users when they abuse cloud apps that are already popular in the enterprise. Microsoft OneDrive, the most popular enterprise cloud app, has held the top spot for the most cloud malware downloads for more than six months. The other top apps for malware downloads include collaboration apps (Sharepoint), cloud storage apps (Amazon S3, Box, Azure Blob Storage, Google Drive, DropBox), free web hosting services (Weebly), and free software hosting sites (GitHub, SourceForge).
Microsoft Sharepoint continues an upward trajectory, hitting a six-month high of 16% in February. The top ten apps accounted for 78% of cloud malware downloads in February, also a six-month high. While the number of apps with malware downloads continues to increase, the downloads are becoming increasingly concentrated in the most popular apps. For the first time in six months, no webmail apps appeared in the top ten list. The top ten list is a reflection of attacker tactics, user behavior, and company policy.
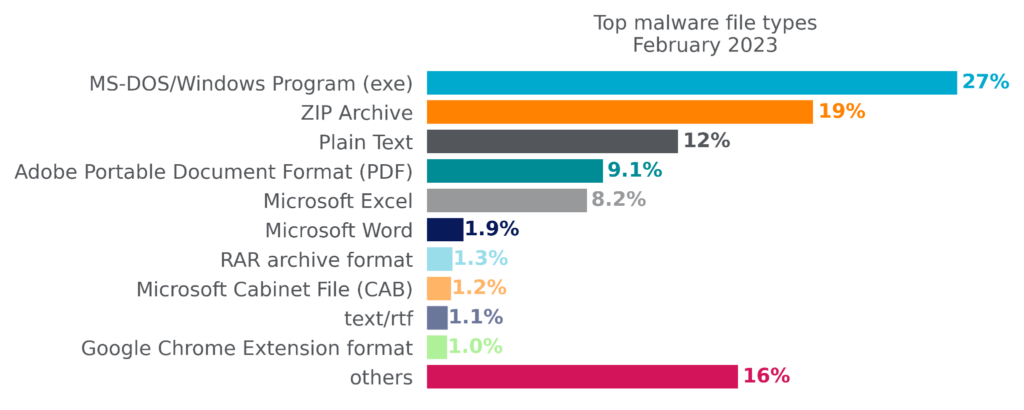
Top Malware File Types
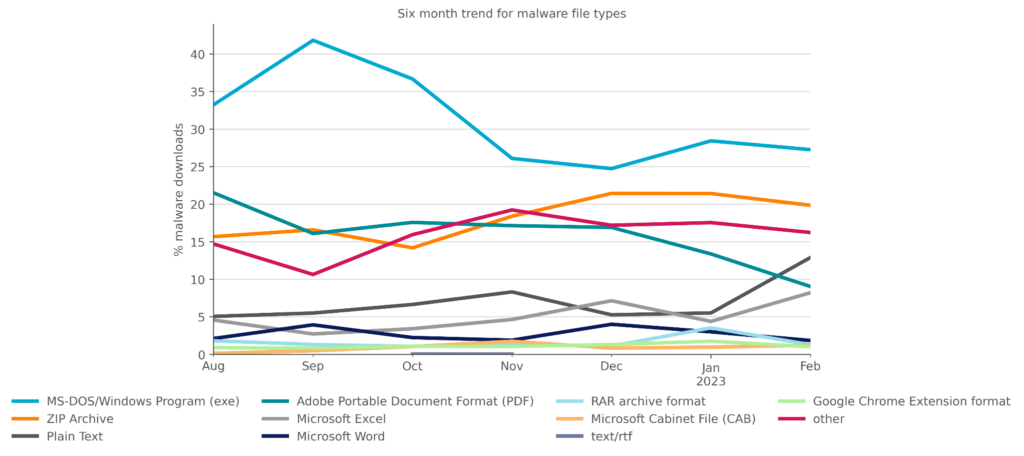
By file type, Microsoft Windows Portable Executable files (EXE/DLL) accounted for the plurality of malware downloads in February, as they have for at least the past six months. Delivering malware in archive files, particularly ZIP files, had been gradually increasing but appears to have plateaued in February. PDF files have been exhibiting the opposite trend, gradually decreasing and hitting a six-month low in February. Malicious Plain Text files, particularly malicious PowerShell scripts and LNK files, hit a six-month high in February. The popularity of other file types remains largely unchanged, as attackers continue to use a wide variety of file types to target their victims.
Top Malware Families
Attackers are constantly creating new malware families and new variants of existing families, either as an attempt to bypass security solutions or to update their malware’s capabilities. In February 2023, 67% of all malware downloads detected by Netskope were either new families or new variants that had not been observed in the preceding six months. The other 33% were samples that had been previously observed during the preceding six months and are still circulating in the wild.
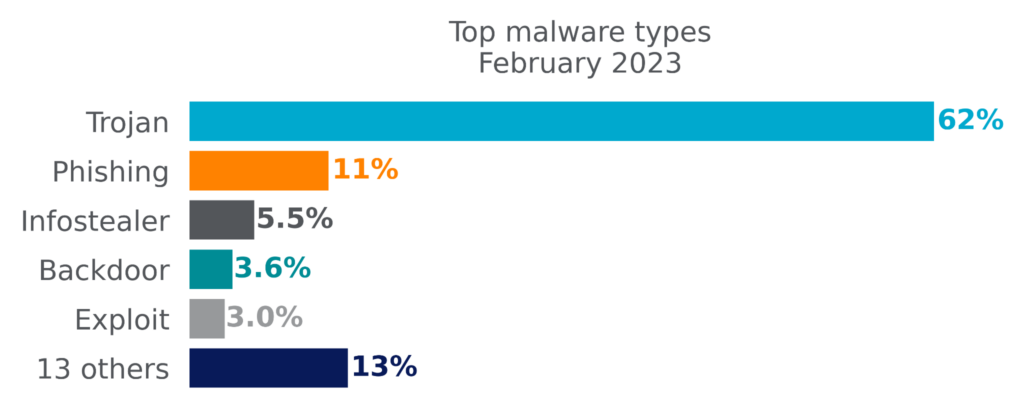
By volume, Netskope blocks more Trojans than any other malware type. Trojans are commonly used by attackers to gain an initial foothold and to deliver other types of malware, such as infostealers, Remote Access Trojans (RATs), backdoors, and ransomware. Other top malware types include phishing lures (typically PDF files designed to lure victims into phishing scams), infostealers whose primary purpose is stealing information (especially passwords, tokens, and cookies), backdoors that provide clandestine remote access, and file-based exploits.
The following list contains the top malware and ransomware families blocked by Netskope in February 2023:
- Backdoor.Farfli (a.k.a Gh0st RAT, PCRat) is an old remote access tool associated with multiple APT groups that continues to be modified by APT groups for use in new attacks. Details
- Backdoor.Zusy (a.k.a. TinyBanker) is a banking Trojan based on the source code of Zeus, aiming to steal personal information via code injection into websites. Details
- Infostealer.AgentTesla is a .NET-based Remote Access Trojan with many capabilities, such as stealing browsers’ passwords, capturing keystrokes, clipboard, etc. Details
- Infostealer.ClipBanker is an infostealer that steals banking information among other data and is typically spread via emails and social media Details
- Infostealer.Fareit (a.k.a Siplog, Pony) is both an infostealer and botnet, stealing credentials from VPNs, browsers, and more. Details
- Phishing.PhishingX is a malicious PDF file used as part of a phishing campaign to redirect victims to a phishing page.
- Ransomware.DarkBit is a ransomware variant first discovered in early 2023 targeting organizations in Israel. Details
- Trojan.Razy is a Trojan typically distributed via malicious ads disguised as legitimate software, often used to steal cryptocurrency data. Details
- Trojan.Ursnif (a.k.a. Gozi) is a banking Trojan and backdoor, which had its source code leaked on GitHub in 2005, allowing attackers to create and distribute many variants. Details
- Trojan.Valyria (a.k.a. POWERSTATS) is a family of malicious Microsoft Office Documents that contain embedded malicious VBScripts usually to deliver other malicious payloads. Details
Recommendations
Attackers have always sought to evade detection and avoid suspicion in delivering malware. Two strategies that attackers have been using increasingly in the past six months are to deliver malware by abusing cloud apps and to package malware in ZIP files. Netskope Threat Labs recommends that you review your security posture to ensure that you are adequately protected against both of these trends:
- Inspect all HTTP and HTTPS downloads, including all web and cloud traffic, to prevent malware from infiltrating your network. Netskope customers can configure their Netskope NG-SWG with a Threat Protection policy that applies to downloads from all categories and applies to all file types.
- Ensure that your security controls recursively inspect the content of popular archive files such as ZIP files for malicious content. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection recursively inspects the content of archives, including ISO, TAR, RAR, 7Z, and ZIP.
- Ensure that high-risk file types like executables and archives are thoroughly inspected using a combination of static and dynamic analysis before being downloaded. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection customers can use a Patient Zero Prevention Policy to hold downloads until they have been fully inspected.
- Configure policies to block downloads from apps that are not used in your organization to reduce your risk surface to only those apps and instances that are necessary for the business.
- Block downloads of all risky file types from newly registered domains and newly observed domains.
In addition to recommendations above, Remote Browser Isolation (RBI) technology can provide additional protection when there is a need to visit websites that fall in categories that can present higher risk, like Newly Observed and Newly Registered Domains.
About This Report
Netskope provides threat and data protection to millions of users worldwide. Information presented in this report is based on anonymized usage data collected by the Netskope Security Cloud platform relating to a subset of Netskope customers with prior authorization. This report contains information about detections raised by Netskope’s Next Generation Secure Web Gateway (SWG), not considering the significance of the impact of each individual threat. Stats in this report are based on the period starting August 1, 2022 through February 28, 2023. Stats are reflection of attacker tactics, user behavior, and organization policy.




 Indietro
Indietro 















 Leggi il blog
Leggi il blog