Netskope Threat Research Labs has observed a new wave of attacks on small- and medium-scale businesses in the Middle East and European regions using the Java-based Adwind RAT. In this new attack, the major targets include shipping and export industries where spam emails are sent containing Windows executable Pif file format as the weaponization file, which drops the Adwind payload. Netskope detects the attachment Pif file as Trojan.GenericKD.5562809 and the dropped Adwind Jar as Trojan.GenericKD.5561478.
We released an earlier blog where Adwind was used to target the hospitality industry to exfiltrate sensitive data. The spam based delivery mechanism is same in both the variants but the major difference is in the obfuscation techniques implemented in the new variant. The email sent to one of the targets is shown in Figure 1.
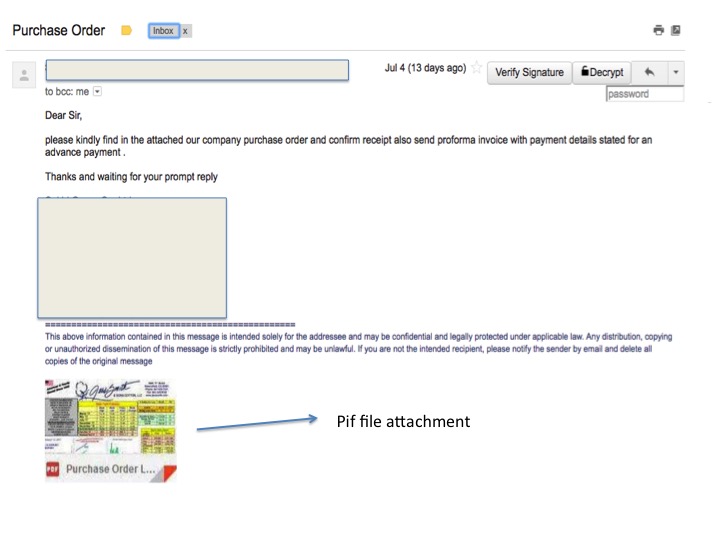
Figure 1 : Snapshot of a spam email containing Pif file attachment
It contained an attachment whose preview image looked like a PDF file but it was a Windows executable Pif file format.This file acts as the dropper for the main Adwind’s jar payload.
Brief Analysis of the Jar
Sample hash: 41c6aae5e303e7f3118af6a3ca2566a8
This new variant of Adwind has more obfuscation compared to the one we analyzed in our earlier blog, but the end functionality remains pretty much the same. The new variant uses multi-level obfuscation of class files by hiding the elements within TIFF files and by using AES encryption to thwart reverse engineering attempts.
The decompiled .jar file had very little information that could be deduced about the functionality since the code was heavily obfuscated. The Manifest file of the jar contained the entry point to execution: Main-Class: com.tool.Main
The main class then deduces string objects from multiple static classes defined in the form of :
static class N7034_ { static void N7034_() throws Throwable { Main.N5600_.N5577_[Integer.decode(((String)Main.N5600_.N5577_[0]).substring(1675, 1678)).intValue()] = ……
A snippet of the decompiled code of the dropped jar is shown in Figure 2,
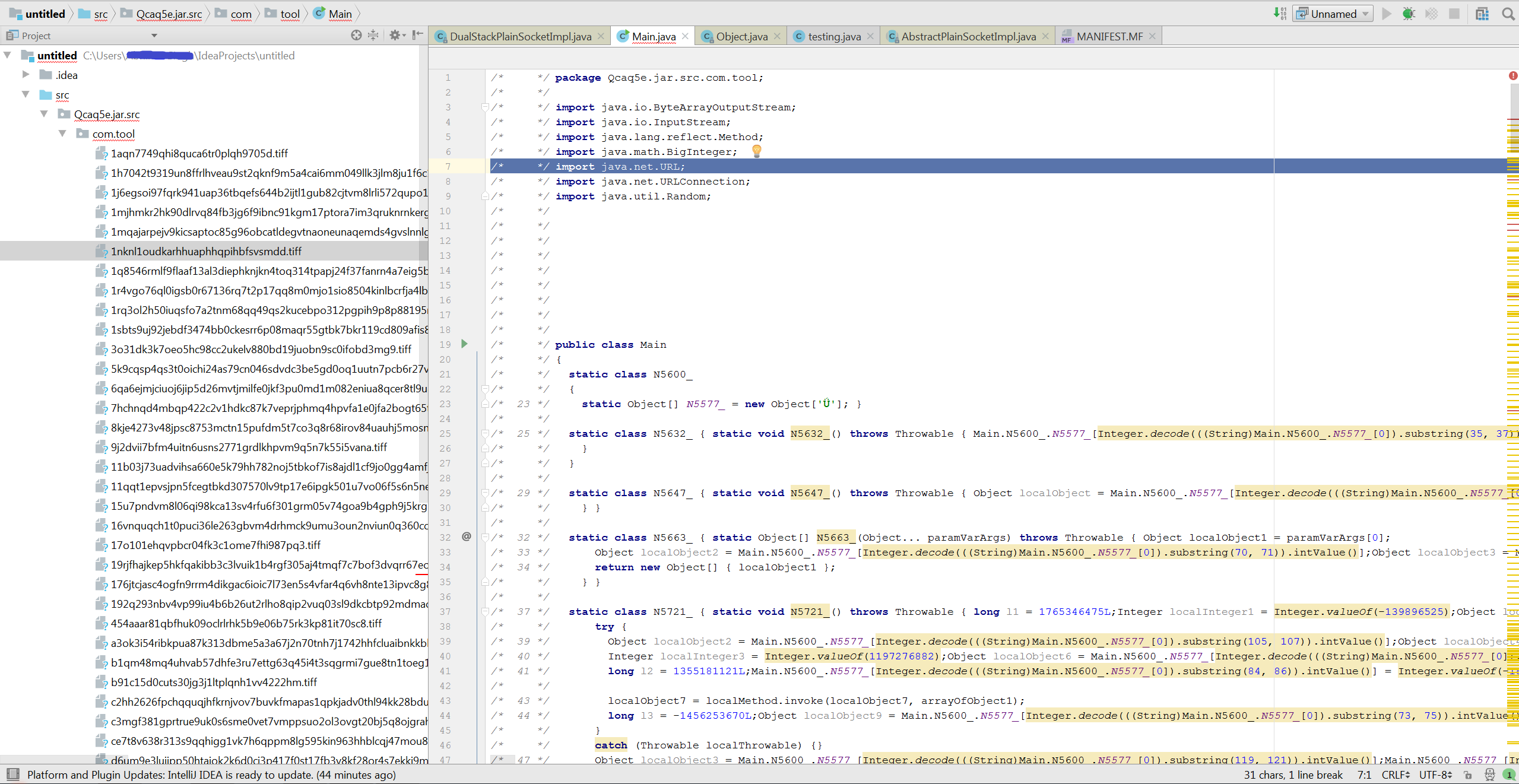
Figure 2: File structure of Adwind’s first level Jar file
Figure 2 shows the structure of decompiled jar file which contains various .tiff files that are bundled in the archive. The main class object refers to the bytes of these tiff files to construct a new jar as shown in figure 3 and 4.

Figure 3: getResource function accessing the .tiff files
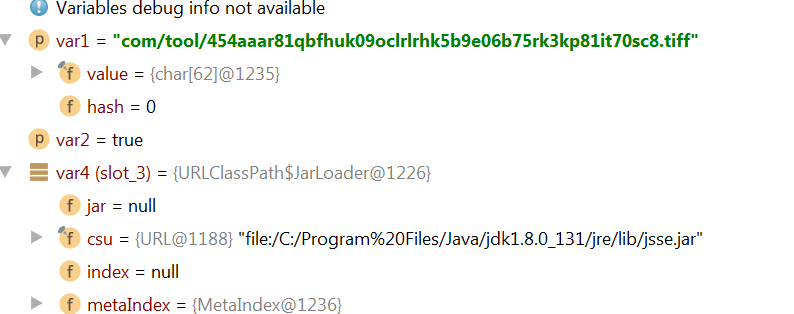
Figure 4: debug instruction showing byte access from tiff files.
This newly constructed jar file is then written in the user directory with an arbitrary extension. The constructed jar file is then executed by calling the Windows scripting engine as shown in Figure 5.
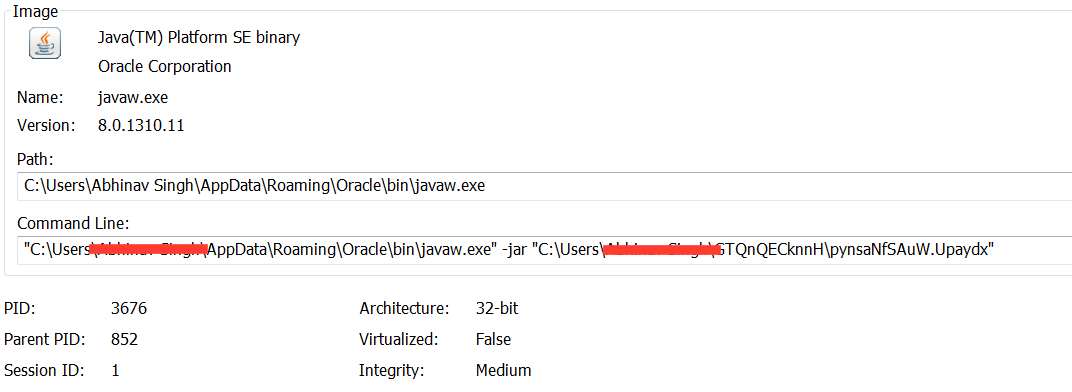 Figure 5: Next stage Jar file execution from the command line
Figure 5: Next stage Jar file execution from the command line
The jar also creates multiple VisualBasic scripts similar to the previously analyzed samples which perform basic enumerations for the jar like gathering information about the anti-virus and firewall installations on the infected machine. The jar also attempts to connect to its command and control IP 174[.]127[.]99[.]234 which was down at the time of this analysis.
The second level jar again contains heavily obfuscated class files which point to few other random named files in the archive namely: drop.box, mega.download, sky.drive (Figure 6)

Figure 6: 2nd level class file code snippet
These filenames are just used to store the encrypted data.The bytes are extracted from these randomly named files and then AES+RSA keys are applied to decrypt the data. This results in the construction of the final jar payload in a readable format. It also creates JSON config files and XML properties to access the private RSA and AES keys from Jrat[.]io server as shown in figures 7 and 8. T.
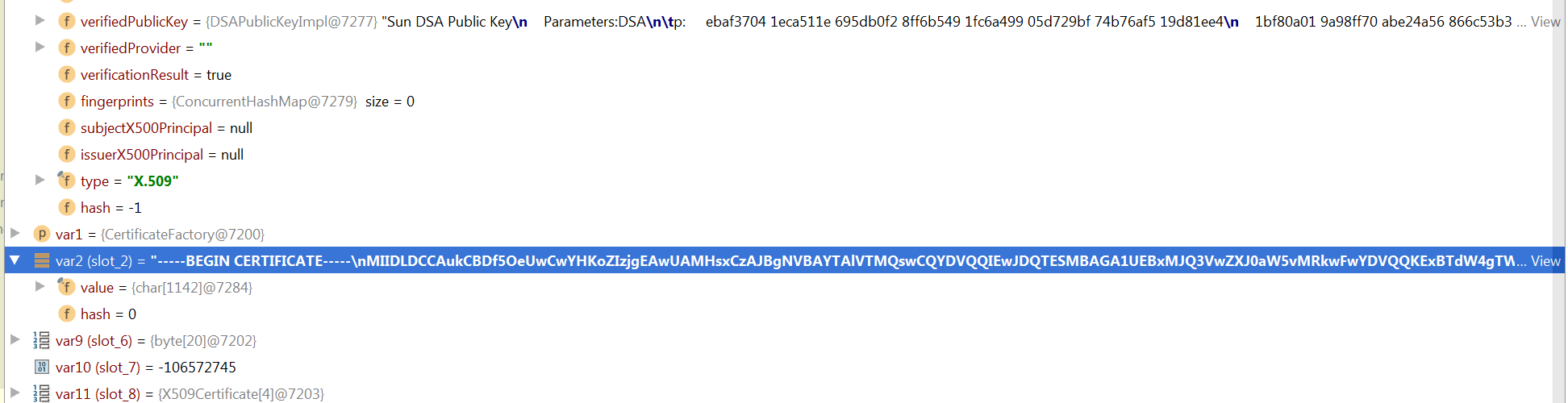 Figure 7: key exchange to connect with the Jrat server
Figure 7: key exchange to connect with the Jrat server
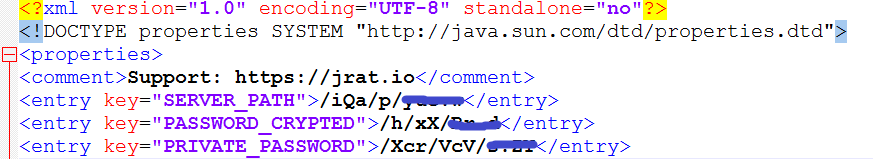
Figure 8: Hard coded location to access private keys from Jrat server
This domain claims to be selling Jrat for educational purposes only, but most of the popular browsers consider this domain as hostile
Looking at the plain crafted Jar, we can deduce the similarities in the code from its previous versions. There have been very few changes made to the functionality and the attackers have laid more focus on keeping the core functionality hidden by implementing multiple layers of obfuscation and encryption mechanisms. The decompiled code illustrating the functionality of the RAT is shown in Figure 9
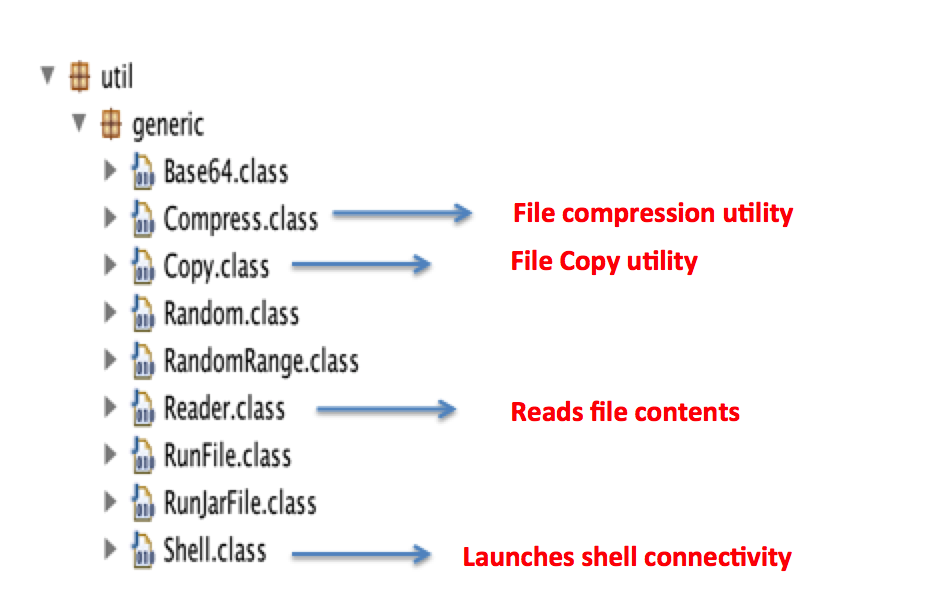
Figure 9: RATs functionalities defined in the decompiled code
Conclusion
Changes in the obfuscation techniques and keeping the core functionality same points in the direction that the Adwind actors are attempting to find new ways of defeating signature and network based engines which forms the core layer of security in small and medium scale enterprises. In a cloud ready environment, such threats can easily propagate inside the corporate environment through the syncing and sharing of files.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Voltar
Voltar















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog