Summary
The number of cloud apps being used in the enterprise increased by 20% in 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sudden and dramatic shift to remote work for knowledge workers worldwide. Individuals, teams, and organizations all turned to cloud apps to help address some of the new challenges of remote work. The increase in the number of cloud apps was led by an increase in consumer and collaboration apps, the fasting spreading of which included Discord, Zoom, Lumin PDF, and…Xbox LIVE? That’s right, the shift to remote work led to the rapid adoption of new apps to enable remote work and a blurring of lines between work and home that included an increase in personal use of managed devices.
This blog post accompanies the release of our February 2021 Cloud and Threat Report, which analyzes 2020’s most interesting trends in enterprise cloud and web security. In addition to highlighting the increase in cloud app usage, the Cloud Threat Report also highlights four other noteworthy trends from 2020:
- Cloud-delivered malware continues to increase, now representing 61% of all malware.
- Malicious Office documents increased dramatically, now representing 27% of all malware downloads.
- Cloud phishing continues to increase, with 13% of phishing campaigns hosted in the cloud and 33% targeting cloud app credentials.
- Personal app usage in the enterprise continues to increase, with 83% of users accessing personal apps from managed devices.
Update Feb 28, 2021 – Netskope calculates its CCI ratings based on publicly available information and questionnaire responses from app vendors. This article originally mentioned iLovePDF had a “Poor” CCI rating. Thanks to new information that has been made available to Netskope, the iLovePDF CCI rating has increased.
Cloud apps increase
Netskope is deployed inline for millions of managed devices worldwide, with our secure web gateway monitoring cloud and web activity to secure our customers and their data. Netskope Threat Labs leverages anonymized usage data collected from the Netskope Security Cloud platform to gain visibility into cloud app usage on managed devices. Each month, we count the total number of distinct cloud apps in use in each organization and compute the average across all organizations of similar size, using the following bins:
- Small organizations with <500 users
- Medium organizations with 500 – 2000 users
- Large organizations with 2000 – 4000 users
- X-Large organizations with >4000 users
The number of apps increases with organization size, with the smallest organizations averaging 258 apps and the largest organizations averaging 1,265 apps in December 2020.
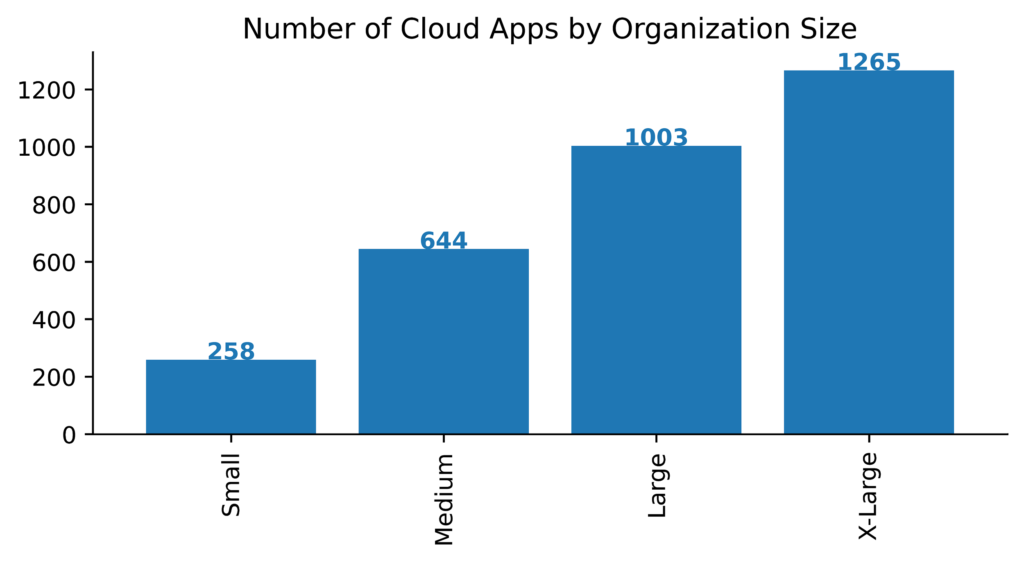
The number of apps also tends to increase over time, as new apps are regularly introduced into the market and gain popularity among enterprise users. However, in 2020 we observed faster than usual growth, with the number of apps increasing by 20%. The following shows the monthly trend for medium-sized organizations throughout the year, starting at 535 apps and spiking to 733 in October before ending the year at 644.
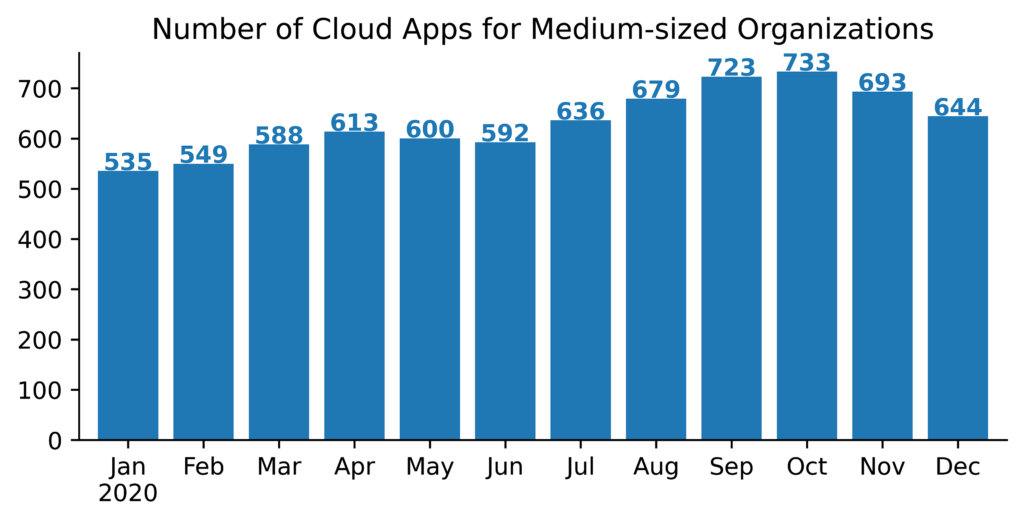
There were four months when the average number of cloud apps was actually lower than the previous month, and we ended the year nearly 100 apps below the peak. Why the monthly fluctuations? These are driven primarily by one-off app usage by individual users. For example, a user might turn to an online PDF editor in a pinch, but that app isn’t part of their normal workflow or commonly used in the organization. Across an organization, these one-offs add up and lead to short-term fluctuations.
2020 ended with users in medium-sized organizations using 109 more apps on average than when it started. What types of apps drove this overall growth? In total, we saw growth in 25 different cloud app categories. In most categories, the gains were modest, averaging between 1 and 5 new apps. However, there were two categories that stood out, collaboration apps and consumer apps, together accounting for 30% of the overall increase. We attribute both of these increases to the COVID-19 pandemic and sudden shift to remote work. The increase in collaboration apps was driven by a now mostly remote workforce’s need to stay connected. The increase in consumer apps was driven by that same workforce’s blurring of the lines between work and home, with more managed devices being used for personal reasons. In the next section, we look at some of the fastest spreading apps contributing to the increase.
Fastest-spreading apps
We define “fastest-spreading” as those apps that were adopted by the most new organizations over the course of the year. We do this to identify the apps that contributed most to the growth in the number of apps. For example, Discord is one of the fastest spreading collaboration apps because it was used in 21% of all organizations at the beginning of the year and 48% at the end of the year, a 27 point increase in the number of organizations with Discord users.
Contrast this with a different metric, “fastest-growing.” We define the “fastest-growing” apps as those apps for which we saw the biggest increase in the number of users. For example, Microsoft Teams was the fastest-growing collaboration app, used by 12% of users at the beginning of the year and 21% of users at the end of the year, a 9 point increase. It is not, however, one of the fastest spreading apps. It was used by 69% of organizations at the beginning of the year and 70% at the end of the year, an increase of only 1 point.
In other words, don’t expect to see many of the big-name enterprise apps in the fastest-spreading list. The fastest-spreading apps will instead be up-and-comers and other apps that just haven’t historically seen much use on managed devices.
Fastest-spreading collaboration apps
The fastest-spreading collaboration apps represented a wide range of functionality. The following list provides some examples of the fastest-spreading collaboration apps and the functionality each of them provides.
- Discord – Chat
- Lumin PDF – PDF editing
- Monday.com – Project management
- Mentimeter – Interactive presentations
- Miro – Online whiteboarding
- Zoom – Video conferencing
- Loom – Video messaging
Most of the fastest-spreading collaboration apps are ostensibly business-related, driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and shift to remote work. Groups seeking to stay connected have turned to these apps to provide a facsimile of the in-person interactions they used to have before the pandemic started. Apps in this class include Mentimeter, Miro, Zoom, and Loom. Others, like Discord, are commonly used for both business and personal reasons. For example, multiple conferences in the past year used Discord as a chat platform, but Discord’s primary user base is gamers. This leads us into the next section about the fastest-spreading consumer apps…
Fastest-spreading consumer apps
Many people who suddenly shifted to remote work saw the lines between work and home begin to blur. This is made evident by the list of the fastest-spreading consumer apps. Many of these are apps that have been popular for a long time but were rarely used on managed devices in the enterprise. This set of apps represents the blurring of lines; managed devices once used primarily for work only are now being used for personal reasons, with gaming, video, and image sharing apps leading the way.
- Xbox LIVE
- LEGO
- Dailymotion
- Hulu
- Imgur
- Giphy
A second class of consumer apps was also highly represented in the fastest-spreading consumer apps, online file converters. This represents a different phenomenon. For many organizations, the sudden shift to remote work meant issuing laptops to users who previously used desktops in the office. If those laptops weren’t equipped with the same software, those users sought out alternatives. These apps represent users seeking apps to support their day-to-day work:
- PDF2Go.com
- PDF to PNG
- CloudConvert
- Smallpdf
- iLovePDF
- Pdf2jpg.net
Cloud apps as shadow IT
The growth in cloud apps we saw in 2020 was not an IT-led endeavor. In the examples shared in this blog post, Zoom is most likely to have been part of an IT-led effort. Overall, we found that 97% of the cloud apps in use in the enterprise are not managed by a centralized IT or security function. Instead, these are apps that are freely adopted within business units or by individual end-users. In other words, 97% of the cloud apps in use in the enterprise are cloud shadow IT.
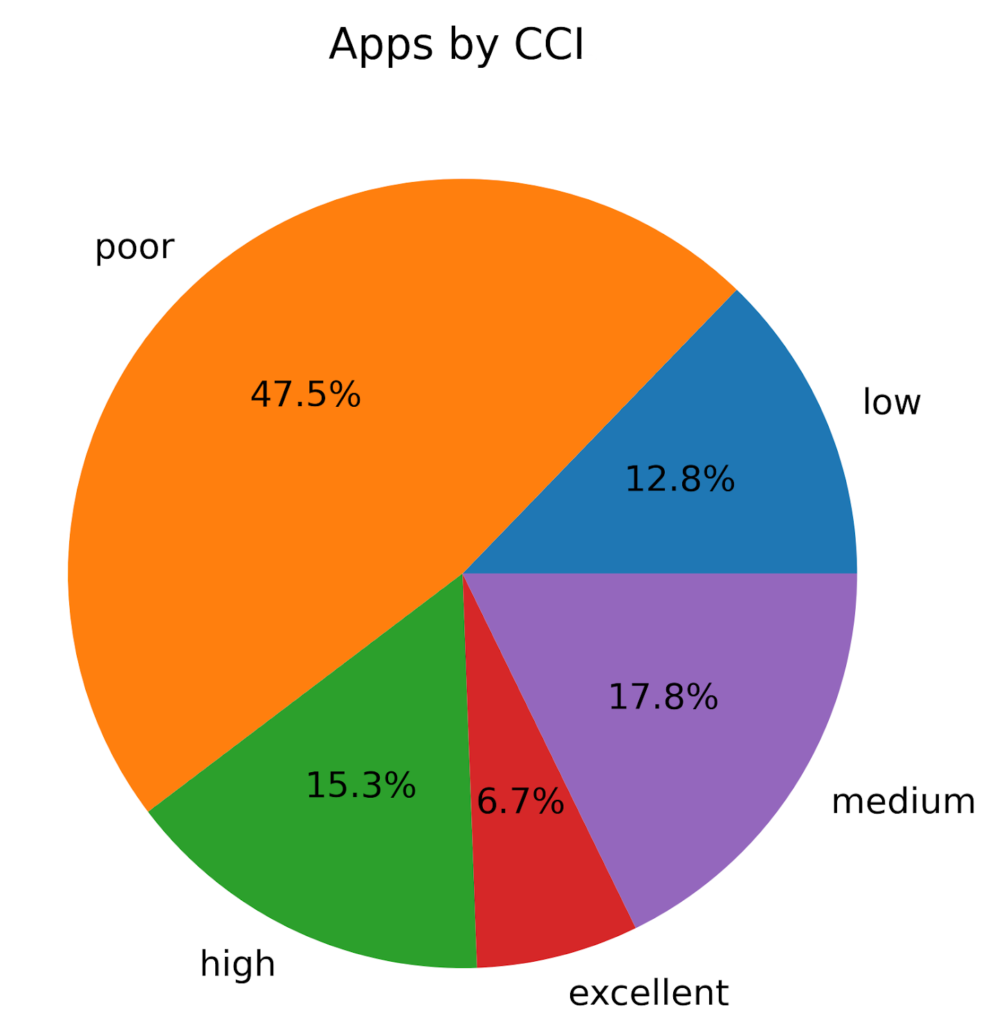
This becomes problematic when users and business units start uploading sensitive company data to apps that aren’t designed to handle sensitive data. Overall, we found that 47.5% of apps in use in the enterprise have a Cloud Confidence IndexTM (CCI) rating of “Poor,” a rating that Netskope assigns to apps that enterprises that put sensitive data at risk—apps enterprises should avoid using and instead migrate to safer alternatives.
Netskope scores apps based on publicly available information and responses to questionnaires submitted by the app vendors. We score the apps based on multiple dimensions across data protection, certifications, access control, auditability, disaster recovery, business continuity, legal, and privacy. Reasons contributing to an app’s “Poor” rating include:
- Not having compliance certifications
- Not having any data center certifications
- Not encrypting data at rest
- Not having any disaster recovery support
- Not having offsite backups
- Not allowing customer-managed encryption keys
- Claiming ownership of user-uploaded data
Among the “Poor” apps to which we saw the most data uploaded from managed devices were personal email providers and online file editing services, including:
- Yahoo Mail
- PDF to PNG
- PDF2Go.com
- AOL Mail
At the other end of the spectrum, a combined 22% of all apps used in the enterprise have a “High” or “Excellent” rating, indicating that they are ready for enterprise use.
Addressing the issues
Cloud traffic now represents 53% of web gateway sessions driven by app adoption. The Netskope Cloud Security platform working with integrated identity service provider solutions can provide the following to address app security issues:
- Provisioning with AD and SCIM to share users and groups with Netskope
- Monitoring to define and track federated identities where Netskope can extend SSO/MFA to over 28,000 apps and cloud services with CCI ratings
- Policy-driven actions to request step-up authentication based on content and context
- Enforcement to place users into a high-risk group based activity/events until investigated
- Extend SSO/MFA across SASE architecture including Netskope Private Access (ZTNA) for private apps
Data analysis
The analysis presented in this blog post is based on anonymized usage data collected by the Netskope Security Cloud platform relating to a subset of Netskope customers with prior authorization.
Conclusions
The number of cloud apps in use in the enterprise increased by 20% in 2020, led by collaboration apps (to stay connected to their coworkers) and consumer apps (to unwind and to fill gaps in tooling). 97% of apps in use in the enterprise are shadow IT, apps freely adopted by end-users and business units. This becomes problematic when apps with a “Poor” CCI rating—nearly half of all apps—are used to process sensitive data, putting that data at risk. Read more in our February 2021 Cloud and Threat Report.




 Retour
Retour
















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog