Summary
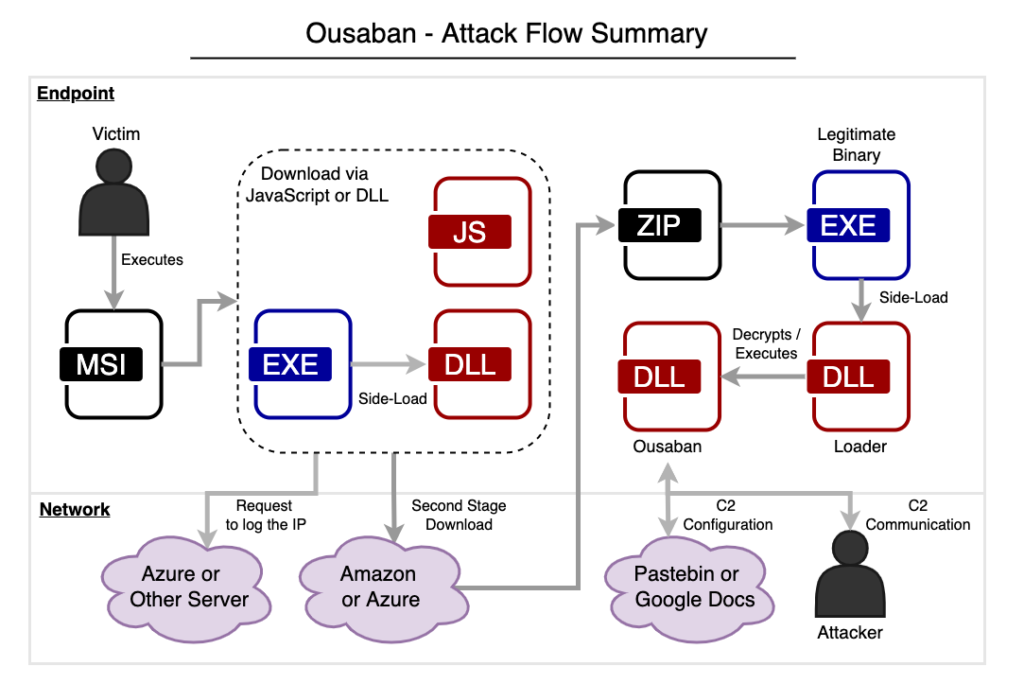
Ousaban (a.k.a. Javali) is a banking malware that emerged between 2017 and 2018, with the primary goal of stealing sensitive data from financial institutions in Brazil. This malware is developed in Delphi and it comes from a stream of LATAM banking trojans sourced from Brazil, sharing similarities with other families like Guildma, Casbaneiro, and Grandoreiro. Furthermore, the threat often abuses cloud services, such as Amazon S3 to download second stage payloads, and Google Docs to retrieve the C2 configuration.
Netskope Threat Labs came across recent Ousaban samples that are abusing multiple cloud services throughout the attack flow, such as Amazon or Azure to download its payloads and log the victim’s IP, and Pastebin to retrieve the C2 configuration. The malware is downloaded through MSI files either by a JavaScript or a Delphi DLL, and is targeting more than 50 financial institutions in Brazil. Furthermore, we also found Telegram abuse in the malware code, likely used for C2 communication via Webhooks.
In this blog post, we will analyze Ousaban, showing its delivery methods, obfuscation techniques, and C2 communication.
Delivery methods
Ousaban is delivered through malicious MSI files spread in phishing emails. In this campaign, we found that the MSI file downloads and executes the second stage either through JavaScript or a PE file.
Delivery by JavaScript
In the first scenario, the JavaScript is executed via CustomAction.
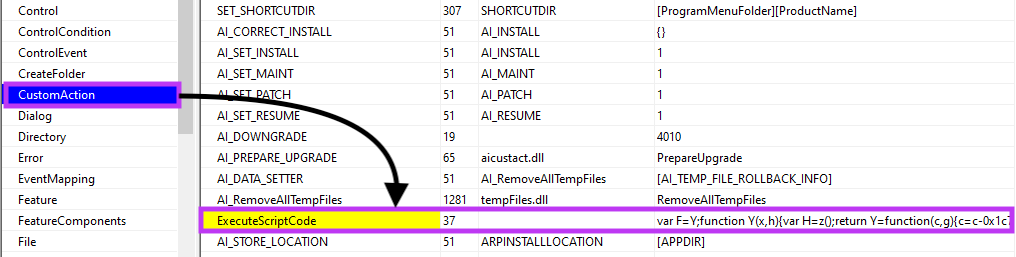
The JavaScript code is obfuscated, likely in an attempt to slow down analysis.
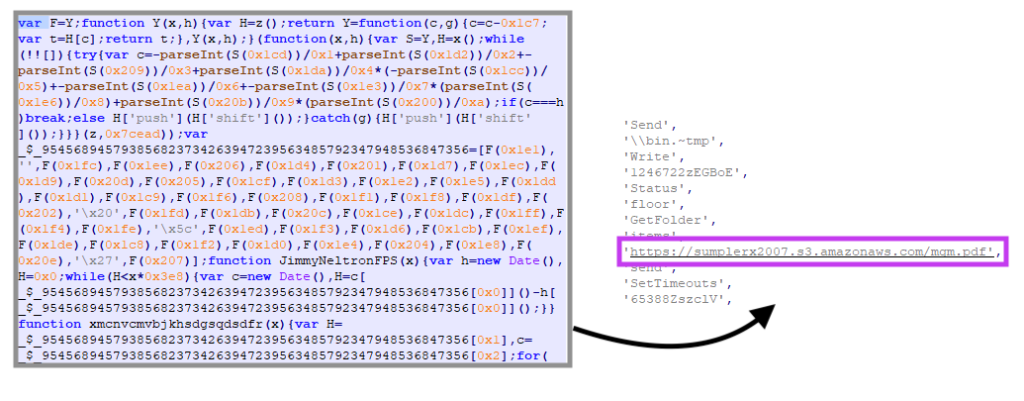
Looking at the deobfuscated code, these are the steps executed by the malware:
- Creates an empty file to be used as a flag in case the MSI is executed twice (similar concept as Mutex usage);
- Downloads the second stage from the cloud, either from Amazon or Azure;
- Decompress the ZIP file downloaded from the cloud and renames the main executable;
- Sends a simple GET request to another URL (Azure or another attacker-controlled server), alerting the attacker and logging the victim’s IP;
- Executes the main file via WMIC.

Delivery by File
We also found Ousaban being delivered without JavaScript. In this case, we can see a file named “avisoProtesto.exe” being executed via MSI CustomAction.
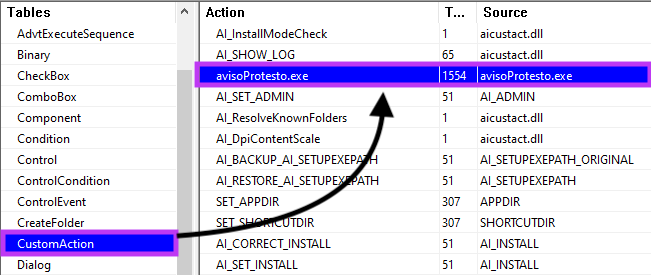
“avisoProtesto.exe” is a signed and non-malicious binary exploited to execute the malicious DLL via DLL search order hijacking.
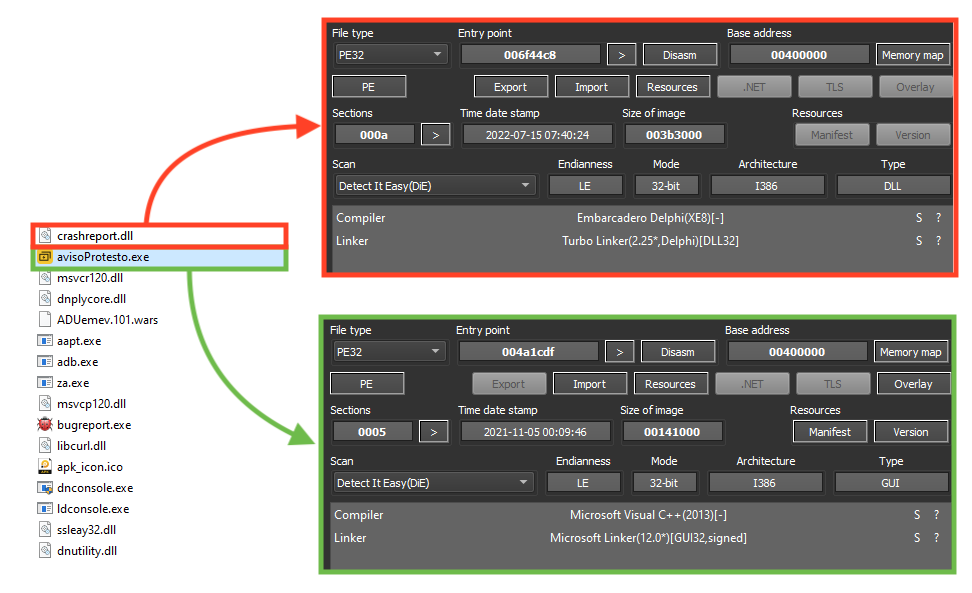
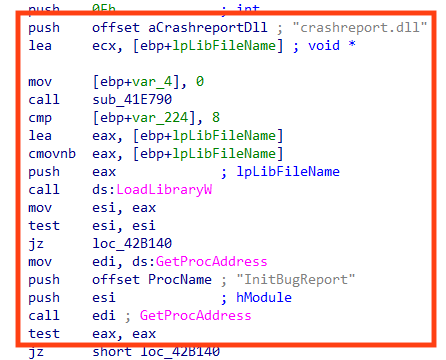
This is possible because the non-malicious binary loads a DLL named “crashreport.dll” without specifying the real path of the library. Therefore, the attacker places a DLL with the same name in the same folder of the executable, making it load the malicious DLL instead.
In this case, both next-stage and tracker URL are loaded from a text file, named “FileLinks”.
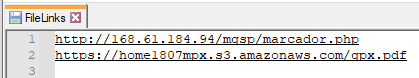
All the files we analyzed were downloading the next stage from the cloud, either Amazon or Azure. In some cases, the URL used to log the victim’s IP address was also from Azure. All the URLs can be found in our GitHub repository.
Loading the second stage
The binary downloaded from the cloud is a ZIP file containing the next stage payload, which is a Delphi DLL executed by a non-malicious binary.
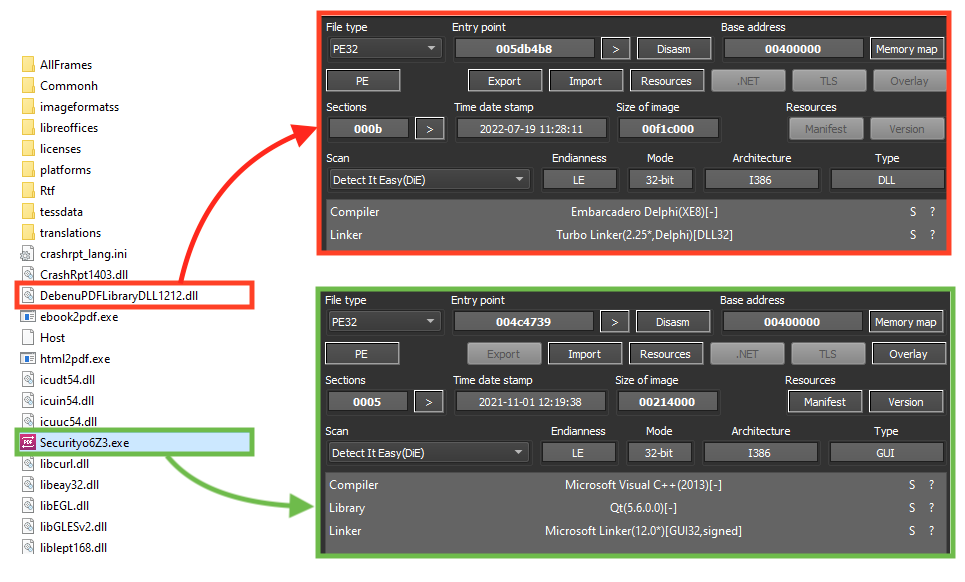
The file executed by the malware is a non-malicious executable with a valid signature (“Securityo6Z3.exe”).
The malicious DLL is then loaded by the non-malicious binary through a DLL search order hijacking vulnerability, the same technique that is used by some of the downloaders.
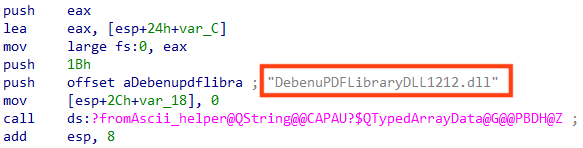
Second stage
The second stage is a Delphi malware responsible for decrypting and loading Ousaban’s payload in the following flow:
- Loads the encrypted bytes of Ousaban from disk;
- Decrypts Ousaban payload using a key stored in the “.data” section;
- Decrypts the code that runs Ousaban using the same key, stored in the “.data” section.

The encrypted payload of Ousaban is located among the files downloaded from the cloud, named “ZapfDingbats.pdf”.
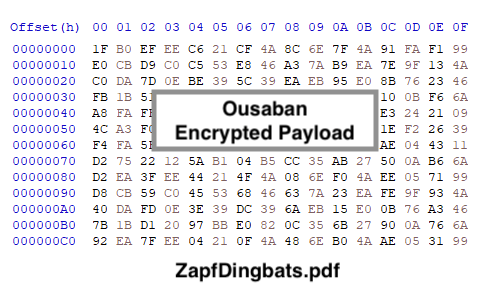
Once running, the second stage loads Ousaban’s encrypted bytes, which will be decrypted using the key stored in the PE “.data” section.
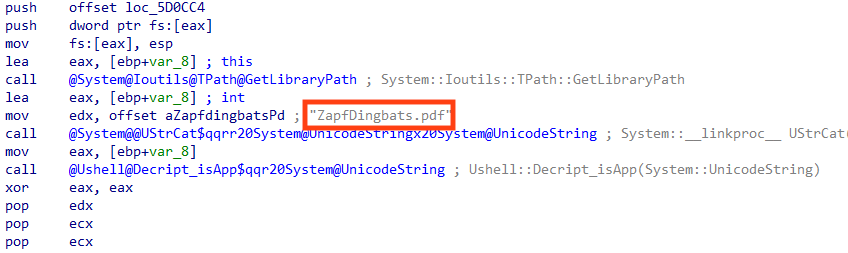
Aside from decrypting the payload, the second stage also decrypts the code that will execute Ousaban in runtime, probably to slow down reverse engineering.
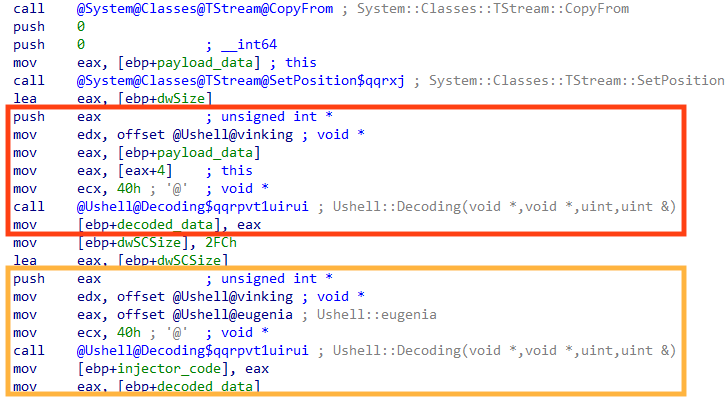
We created a Python script that can be used to statically decrypt Ousaban payloads, using the same algorithm found in the malware. The code can be found in our GitHub repository.
Important API calls used by this stage are also dynamically resolved, another common technique to slow down reverse engineering.
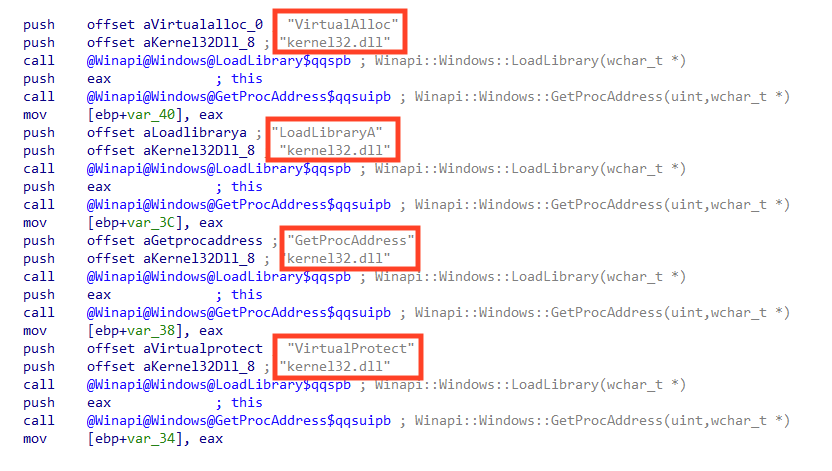
Ousaban payload
Ousaban is a Delphi banking trojan, mainly focused on stealing sensitive data from financial institutions in Brazil. As previously mentioned, Ousaban shares many similarities with other Brazilian banking malware, such as the algorithm to decrypt the strings and overlay capabilities.
Ousaban commonly packs/protects its payloads with UPX or Enigma.
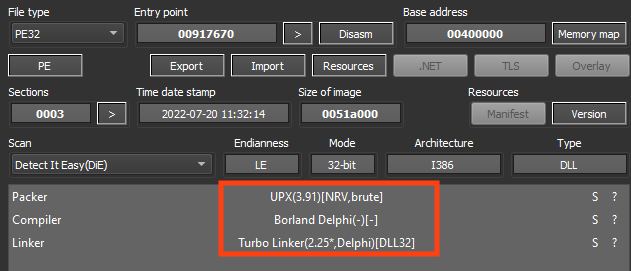
One of the most characteristic aspects of Brazilian-sourced banking malware is the algorithm used to encrypt/decrypt important strings.
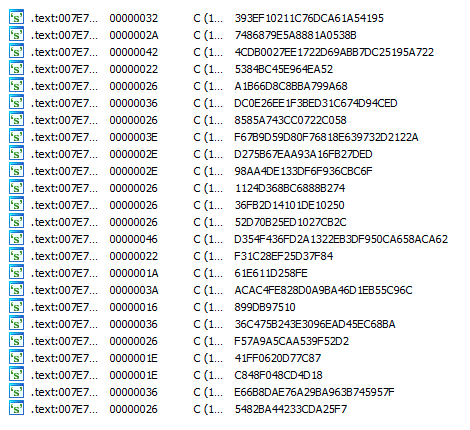
The algorithm used as a base by these trojans was originally demonstrated in a Brazilian magazine called “Mestres Da Espionagem Digital” in 2008. Simply put, it parses the hexadecimal string and uses a chained XOR operation with the key and the previous byte of the string.
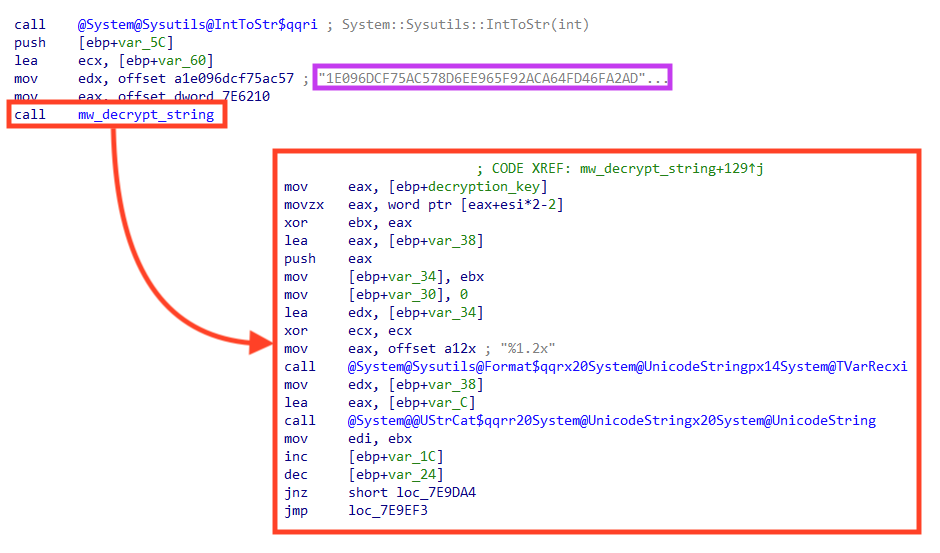
We created a Python script that can be used to decrypt strings from malware that uses this algorithm, such as Ousaban, Guildma, Grandoreiro, and others. The code can be used to decrypt a single string:
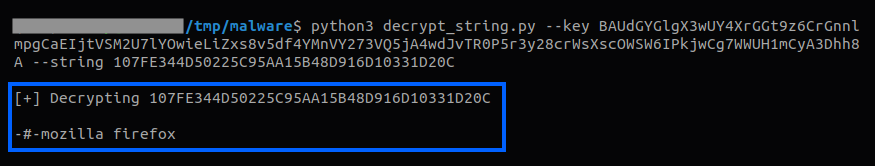
Or to decrypt multiple strings at once, saving the result in a JSON file and also providing the option to show in the console.
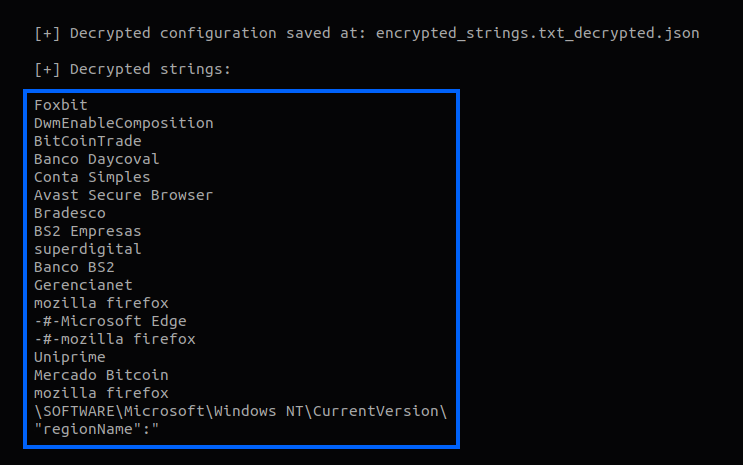
Like other Brazilian-sourced malware, Ousaban monitors the title text from the active window and compares it with a list of strings, to verify if the victim is accessing the website or an application of one of its targets.
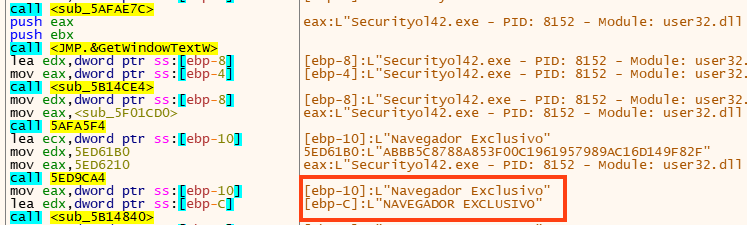
In the files we analyzed, we found Ousaban targeting over 50 different financial institutions. If the window title matches one of the targets, Ousaban starts the communication with the C2 address, providing the option to the attacker to access the machine remotely.
C2 communication
Ousaban stores the C2 address remotely. In this case, the malware is using Pastebin to fetch the data. In 2021, this malware was also spotted using Google Docs to fetch this information.
Within the files downloaded from the cloud by the first stage, there’s a file named “Host”, which stores the external location of the C2 configuration. The information is encrypted with the same algorithm used in the strings.
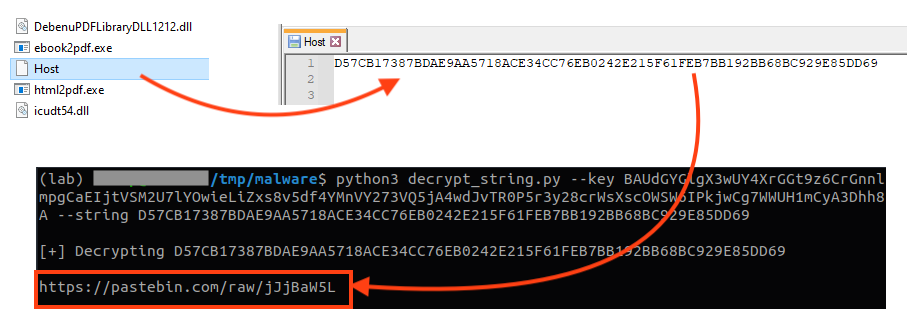
The data is stored in a dictionary, where the C2 host is also encrypted with the same algorithm used in the strings.
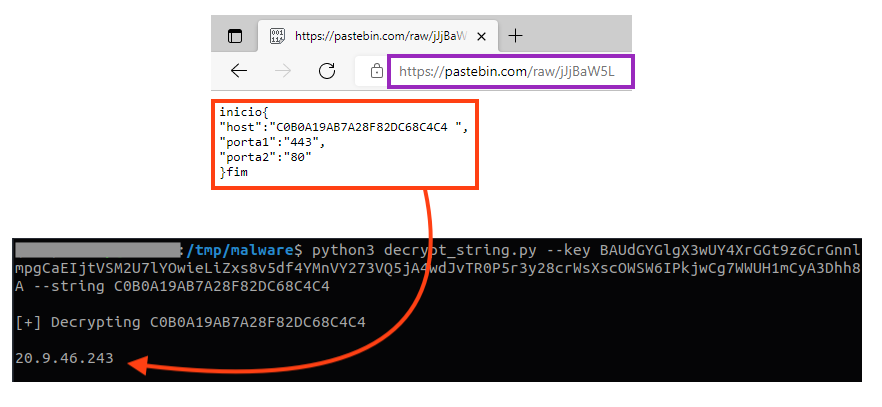
Ousaban only starts the communication once a targeted company is identified.
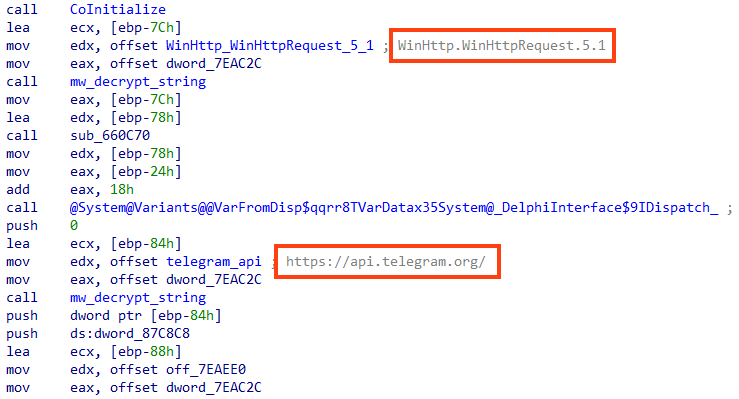
Lastly, the Ousaban samples we analyzed contain a routine to communicate via Telegram using Webhooks, likely to be used as a secondary channel.
Conclusion
Ousaban is a malware designed to steal sensitive information from several financial institutions, mainly based in Brazil. Ousaban shares many similarities with other Brazilian-based banking trojans, such as Guildma and Grandoreiro. Also, as we demonstrated in this analysis, the attackers behind this threat are abusing multiple cloud services throughout the attack chain. We believe that the use of the cloud will continue to grow among attackers especially due to cost and ease.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Win32.Malware.Heuristic
- Win32.Infostealer.Heuristic
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign and scripts can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Retour
Retour 















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog