Sharing data is the basis for all business processes and what drives operations and productivity. Today, more than 50% of organizations’ data is in the cloud and the typical enterprise now deploys more than 2,400 cloud applications. Concurrently, data protection remains the nexus between cloud apps, web services, and an increasingly larger number of remote users in support of modern business initiatives. These business trends create increased data dispersion in the web and cloud, across personal, private, and corporate instances, increasing the risk of data exfiltration and inadvertent, or intentional, exposure. Saying that data protection is more difficult today than ever before is a big understatement.
Challenges
Netskope Threat Labs research reveals that sensitive data increasingly moves laterally across cloud applications such as from Microsoft Teams to OneDrive or SharePoint. A growing trend is employees exchanging data between corporate and personal app instances. Netskope research finds that 83% of employees use personal app instances on managed devices and average 20 file uploads each month to these personal apps.
- Top personal apps users upload sensitive data to via managed devices include:
- Microsoft OneDrive
- Google Drive
- Google Gmail
- iCloud
- WeTransfer
Based on the above, IT Security teams need greater visibility into and, subsequently, control over data between cloud applications and instances, regardless of the access method users employ, whether direct-to-internet, using a mobile app, web browser, or sync client, or via managed (corporate) or unmanaged personal devices. And let’s not forget email. While collaboration tool use is rapidly increasing and introduces new data loss vectors to organizations (e.g. chat, screenshot captures), email is still the leading threat vector for organizations today. Even if modern attacks need other channels like the web to compromise a client, email is commonly used to deliver the initial URL, in the form of a link to an exploit kit or phishing website, an attachment in the form of a malicious payload, or the starting point for a credential phishing attack. Thirty percent of email attacks are only the entry point for a more sophisticated attack.
Modern data protection
To address these evolving challenges, IT security teams need to modernize their data protection. Beyond simply being cloud-smart, data protection has to be web-smart, email-smart, user-smart, and more in order to be effective at reducing the potential attack surface while detecting and preventing any data loss or exposure.
Realize, however, that the modern Data Protection model involves more than data loss prevention (DLP) tools and techniques. Data protection is a process and DLP is one of several key components in it, specifically for inspection. Visibility, identity, applications, and remediation/response all comprise this model, complementing inspection. As part of a data protection strategy, it’s imperative to reduce your attack surface as much as possible, prior to implementing DLP inspection tools.
Think of this process as a funnel, with identity and access control of users being the first stage: involving strong access authentication, user and device risk assessment, and behavior analytics. Next in the funnel is application knowledge: whereby application risk assessment, application instance awareness, adaptive access controls (AAC), and granular activity controls, such as share, post, sync, allow, join, download, and shutdown, are essential to further reduce an organization’s attack surface and minimize risk exposure. This is where contextual awareness benefits an organization’s data protection strategy. It goes beyond ”allow” or “block” controls and enables safe business productivity by providing restrictions on certain activities (e.g. only allow downloading of data to a managed device).
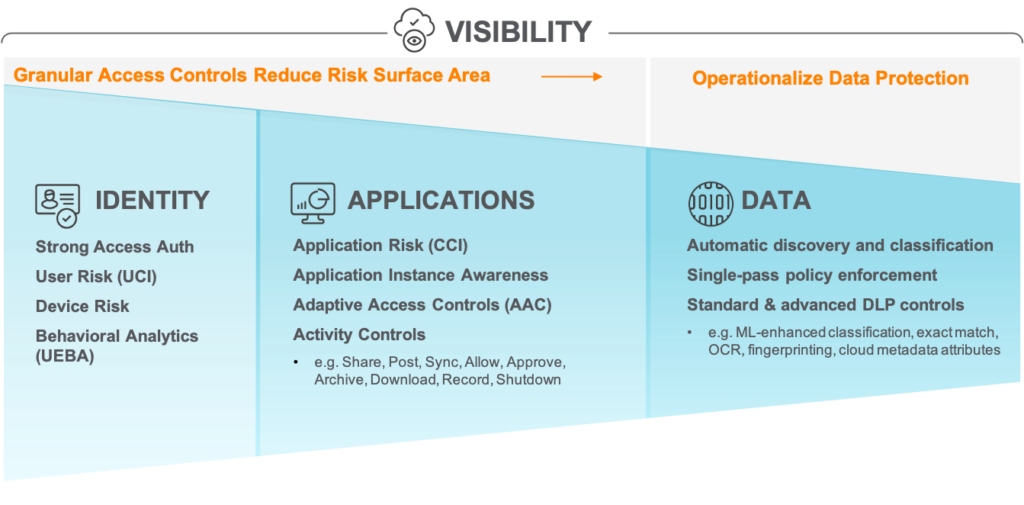
Then, following this stage, you introduce the inspection of data after the two prior stages have reduced the relevant, targeted data significantly. This involves well-known DLP capabilities like regular expressions, pattern and keyword matching, as well as predefined and customizable dictionaries. DLP efficiency can further be enhanced with advanced capabilities like exact data matching, fingerprinting, and optical character recognition (OCR) for detecting sensitive data in images. Applying DLP after employing identity and app controls, dramatically decreases your false-positive rate and frees up cycles for other security and data protection initiatives. Furthermore, innovative scanning and classification techniques can be applied at this stage using machine learning (ML) capabilities. Sensitive data is increasingly hidden in and exfiltrated through images. Think about it: with today’s work-from-home, shelter-in-place norm, how many times have you captured a screenshot of a slide or whiteboard drawing in a Zoom or Microsoft Teams meeting? This happens all the time and represents a growing potential sensitive data loss vector. ML-enhanced scanning can reliably detect and classify images that may contain sensitive data, such as screenshots, whiteboard diagrams, and passports; ultimately increasing detection accuracy and reducing false positives for your overall DLP engine.
Overall, the most effective way to protect your growing amount of data from the risk of exfiltration is through inline tools. While API-enabled controls provide data protection for managed SaaS and IaaS applications like Microsoft OneDrive and Amazon S3 buckets, inline controls augment APIs with real-time inline protection across both managed and unmanaged apps, the latter of which we know comprises thousands of apps. These tools detect and see the traffic traversing cloud apps and services—both managed and unmanaged as well as between app instances like corporate and personal. A perfect example is having the ability to see and prevent users from exfiltrating sensitive content from their corporate email to their personal email instances (e.g. [email protected] -> [email protected]).
Last, but not least, is the visibility component of this operational funnel. Deep visibility of data utilized by your users and applications is imperative regardless of location (e.g. remote or on-prem), access method (e.g. web or mobile app) or service/app type (e.g. SaaS app or email or web). Visibility extends across the funnel emphasizing that you can’t control or protect it if you can’t see it. What’s required to detect this modern, cloud-driven movement of data is deep, real-time visibility with a contextual awareness of data across users, apps, devices, data type, activity, instance, and more. Not putting data in context ultimately leads to blind spots in your security strategy, increasing risk. Using legacy, on-premises security tools also provides no value as they can’t see, and are therefore, functionally unaware, of the intra- and inter-cloud communications.
Call to action
As you update and modernize your business—whether adopting new cloud apps or supporting the safe growth of your remote workforce—do the same with your security strategy. Review all of the ways data traverses and can leave your organization, and then work to detect and control it. Consider the following questions to ask yourself/your IT security team:
- Do I know where all of my sensitive data is? Who can access it and how?
- Can I detect and control intra- and inter-cloud data movement—both authorized and unauthorized? Does this apply to data between managed and unmanaged/shadow IT apps and instances?
- Can I easily and consistently configure and enforce data protection policies across all of our traffic/access methods: SaaS app, IaaS services, web, and email?
- Do I have the tools to effectively secure data in all the ways that users in my organization work: email, chat, video, web forum posts, social media, and more, via managed and unmanaged devices?
- Does my organization have an established remediation and incident response strategy for data breaches and violations?
Netskope solution
The Netskope Security Cloud is a scalable, context-aware, cloud-smart platform that seamlessly protects your data and users no matter where they are. Netskope has just extended its data protection portfolio by adding outbound SMTP email DLP for Microsoft Office 365/Exchange Online and Google Gmail environments. This solution also complements and integrates with Secure Email Gateway (SEG) products by vendors like Mimecast, who is a Netskope Technology Alliances partner.
Whether using Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, Slack, or a combination of these and numerous other cloud applications and services, Netskope provides unmatched 4-in-1 data protection (i.e. SaaS, IaaS, web, and now, email) for your users everywhere while helping you reduce risk and maintain compliance.
For more information on how Netskope can help you protect your sensitive data, go to: https://www.netskope.com/products/capabilities/data-protection
For access to the latest Netskope Cloud and Threat Report, go to: https://resources.netskope.com/cloud-reports




 Voltar
Voltar
















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog