Summary
67% of the malware downloads Netskope blocks come from popular cloud applications being abused by attackers. One of the services commonly abused by threat actors is Discord, which is abused to host malware such as TroubleGrabber using public attachment URLs.
In this blog post, we will analyze a recent DBatLoader (a.k.a. ModiLoader) sample that uses this technique on Discord to deliver a malware known as Warzone (a.k.a. Ave Maria), a Remote Access Trojan created in 2018.
This malware is actively being sold on the internet, through a dedicated website:
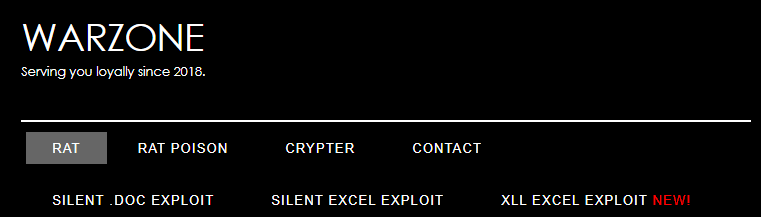
It offers a long list of capabilities, such as:
- Remote Desktop
- WebCam Live Stream
- Download/Upload Files
- Password Grabber (Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Edge, Outlook, etc.)
- Offline/Online Keylogger

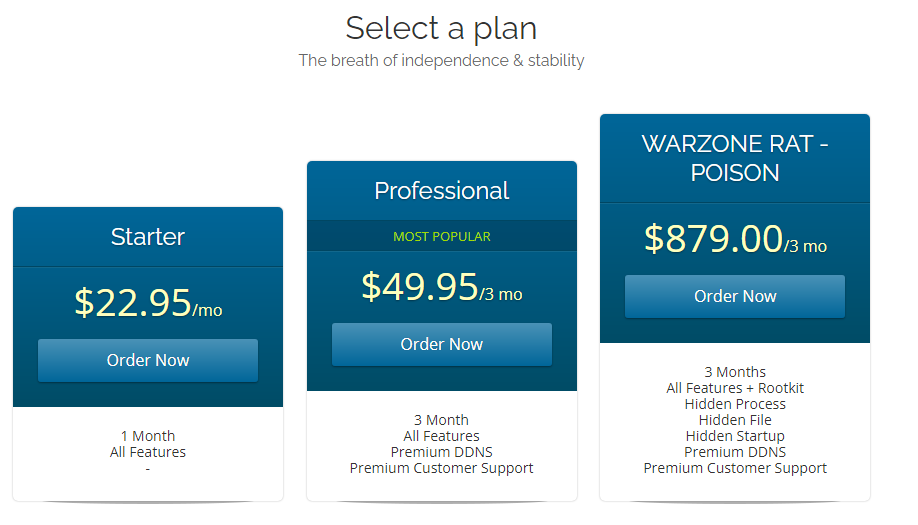
The malware is being sold under many prices, depending on the selected plan:
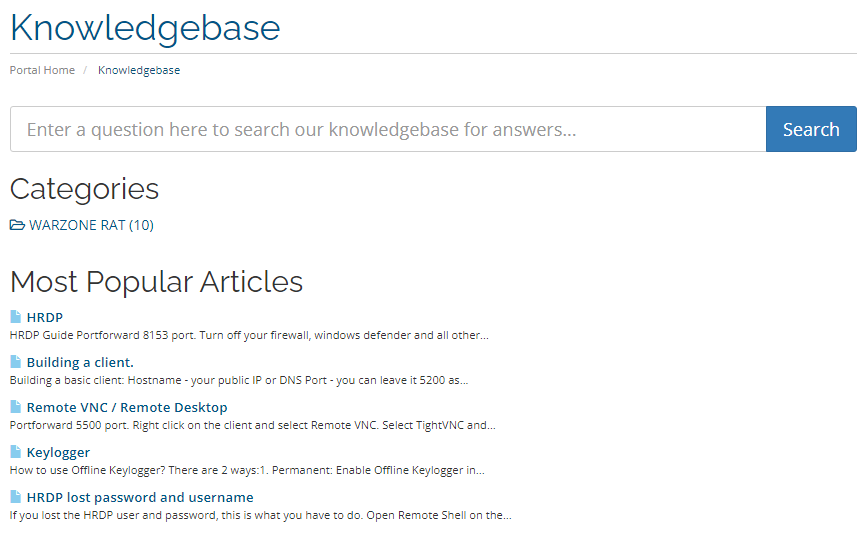
The website even includes a knowledge base that contains information about the usage of Warzone RAT.
Analysis
It all starts with the first stage of DBatLoader, which is known for abusing cloud services, like Google Drive and Discord, to retrieve its second stage, both of which are developed in Delphi.
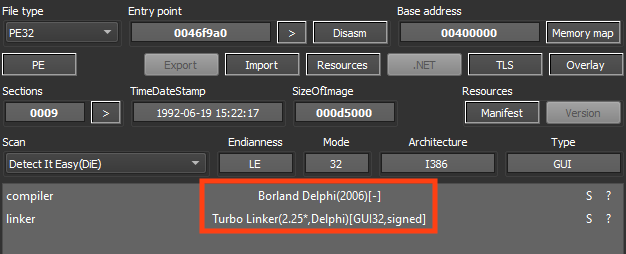
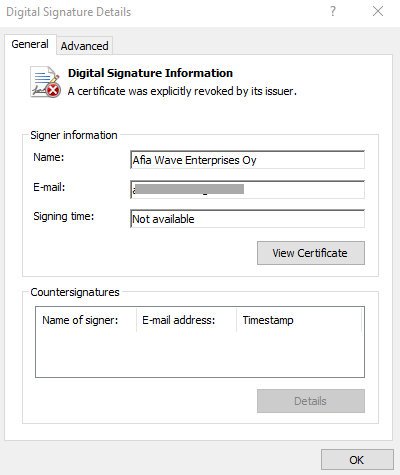
The sample is signed with a revoked certificate from “Afia Wave Enterprises”.
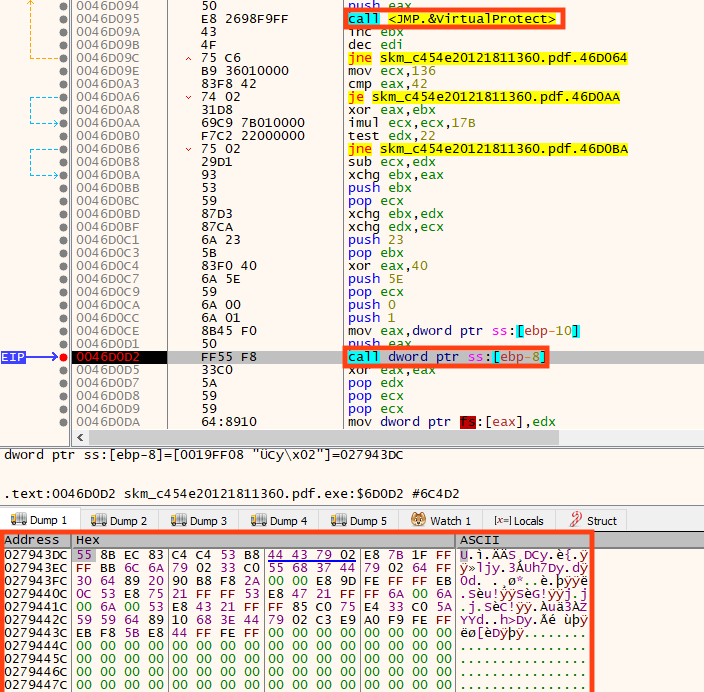
Once running, the malware allocates and executes a shellcode, which is responsible for downloading the second stage.
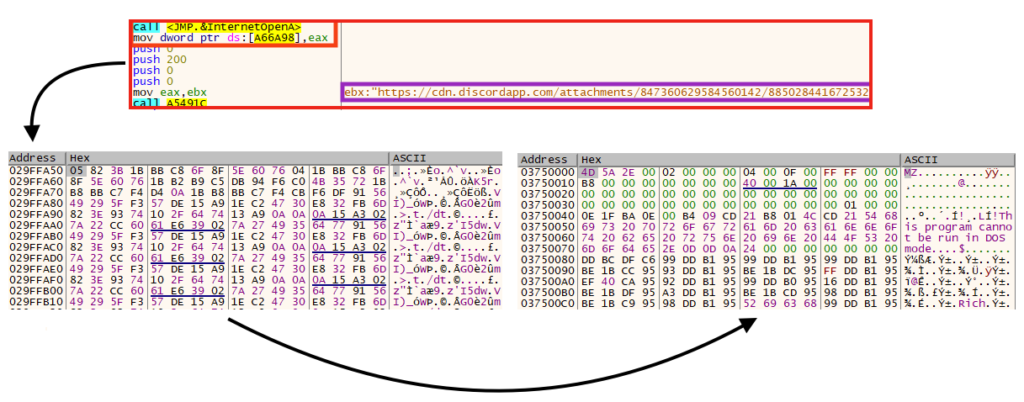
Later, the second stage is downloaded from Discord, which is eventually decrypted and executed in memory.
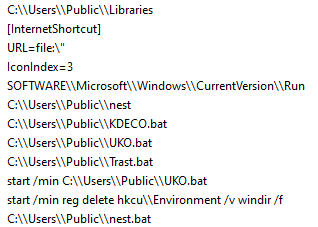
Looking at the decrypted file strings, we can see references to a few batch scripts that are usually created and executed by this malware to accomplish small tasks, like disabling Windows Defender. However, this sample doesn’t contain the routines to run these files.
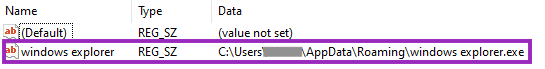
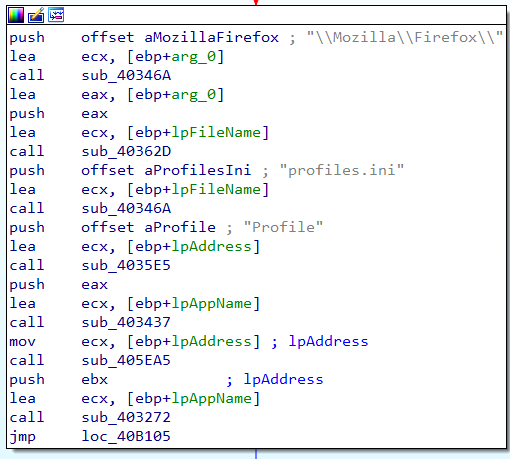
The loader then copies itself to “%AppData%” as “windows explorer.exe” and creates a very simple persistence technique through Windows Registry.
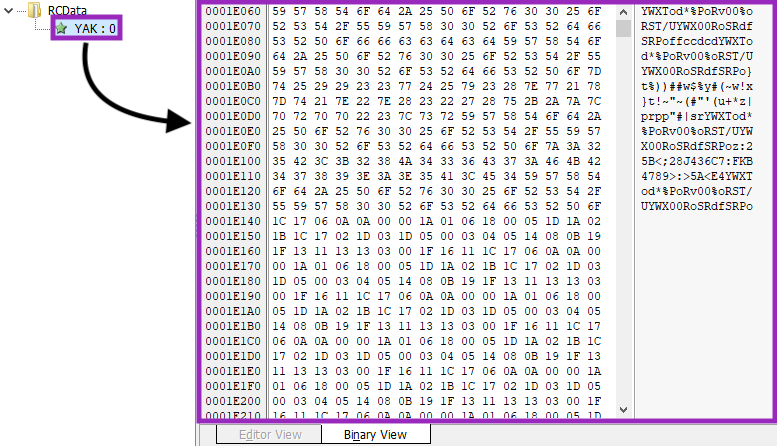
The final payload is encrypted and stored in DBatLoader’s resources, named “YAK”.
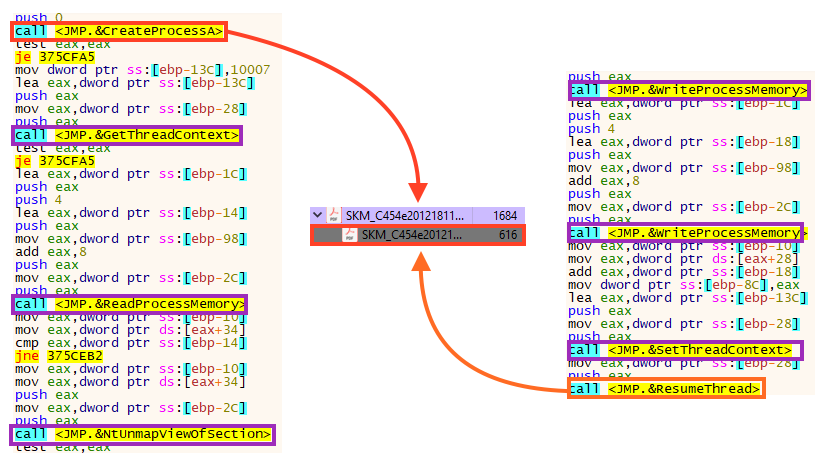
After decrypting these bytes, the payload is executed using a technique known as Process Hollowing. Simply put, the code is injected through the following steps:
- The target process is created in a suspended state with CreateProcessA;
- The original process’ code section is removed with NtUnmapViewOfSection;
- New space is allocated in the process with VirtualAllocEx;
- The malicious code is written using WriteProcessMemory;
- Finally, the code is resumed with SetThreatContext and ResumeThread.
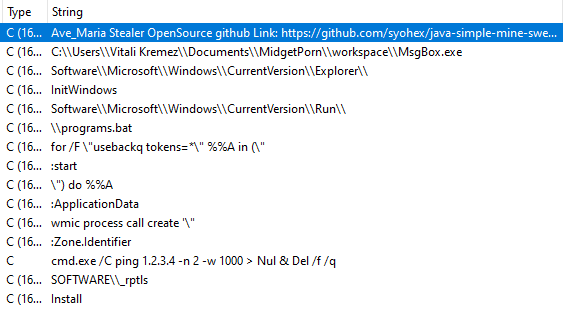
This is a very common process injection technique, used by many malware such as Astaroth, Cobalt Strike, and Trickbot. After injecting Warzone RAT, DBatLoader exits the process without further actions.
The final payload can be dumped from memory using a debugger or the pe-sieve tool.
As we mentioned earlier in this blog post, Warzone provides full access to the infected machine and is also able to steal passwords from many browsers and email clients.
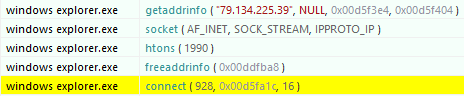
The malware communicates to its C2 server via TCP using sockets, through the port 1990 in this case.
This information is encrypted and stored within the PE file in a section named “.bss”. The first 4 bytes of the section are the key length, followed by the key and the encrypted data.
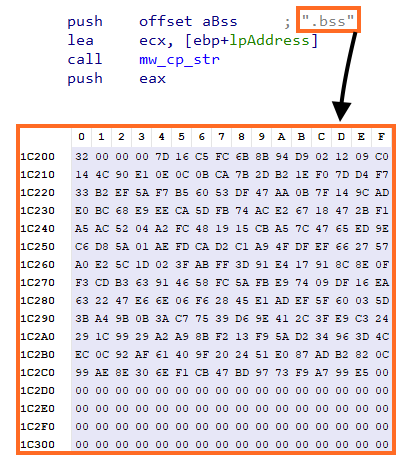
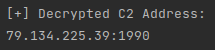
The data is encrypted with RC4 and, once we understood this structure, we created a python script that is able to parse and decrypt the C2 address from Warzone.
Conclusion
Using Discord to host malicious payloads isn’t something new, as we saw in TroubleGrabber in 2020. However, we should expect more malware to abuse not only Discord but other cloud services as well, as it can be more reliable and harder to detect. Netskope is actively monitoring attackers abusing cloud apps for malware delivery.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Win32.Trojan.Modiloader
- Win32.Trojan.WarzoneRAT
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
SHA256 Hashes
| DBatLoader First Stage | 07915b1a44803fc9bd86d2d9ddad19434440b3d73f5c77f3400c84a935dd0255 |
| DBatLoader Second Stage | 8f1d0ba030b897786c9ad6b68bb9165e539371648a8a60e2a6f1136647b5104e |
| Warzone RAT | e89c137a4faa31d639492b045a78dd115468f9191143c302d165aefe85b3c06a |
The full list of IOCs, the script that decrypts Warzone configuration, and a Yara rule can be found in our Github repository.




 Voltar
Voltar
















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog