In this blog, we are going to discuss an attack vector that utilizes the STS AssumeRole and GetSessionToken API calls, and focus on what you have to do differently to detect, mitigate, and prevent abuse vs handling permanent access keys.
Imagine This
An attacker has just compromised one of your AWS credentials and gained access to your production AWS account. What do you do next? Revoke the credentials, of course. But just revoking the compromised credentials is not enough to keep the attacker out of your environment. In this blog post, we’ll explore temporary tokens and how they can provide an attacker continued access to your AWS environments, even after you have revoked compromised credentials.
Temporary tokens are provided by AWS Secure Token Service (STS) and are similar to permanent access keys in functionality and have been used to implement several common AWS features such as:
- Assuming roles, including the passing of roles to services
- Federated identities (e.g., single sign-on and cross-account access)
- Authentication of IoT devices
As with all security design, there are tradeoffs and security concerns from the use of temporary tokens:
- Temporary tokens can cause confusion during incident handling/response versus permanent access keys because their creation and use is logged in CloudTrail using different, somewhat confusing fields and values. As an example, there is no explicit json attribute that distinguishes a temporary token from a permanent API access key–you must infer from the access key id naming convention or other fields.
- The remediation options for Temporary Tokens can have with high impact; e.g., deletion of users
- Temporary tokens are harder to lock down since the creation of some types of temporary tokens cannot be restricted by policy.
- There is no tracking of which tokens have already been created, so auditing temporary token usage and identifying temporary tokens is difficult, as they must be derived from parsing CloudTrail logs. Further, there are no direct management functions (such as deletion) for temporary tokens. We’ll discuss in detail what mitigation steps apply later in the blog. This also makes it more difficult to assess exposure from credential risk because there is no easy way to list all temporary credentials that have been issued or are active/outstanding.
Temporary Tokens
Temporary tokens are implicitly created by AWS in the case of IoT device authentication or from assuming of roles by services. Temporary tokens can also be explicitly created by authenticated users calling STS AssumeRole or GetSessionToken, e.g.,
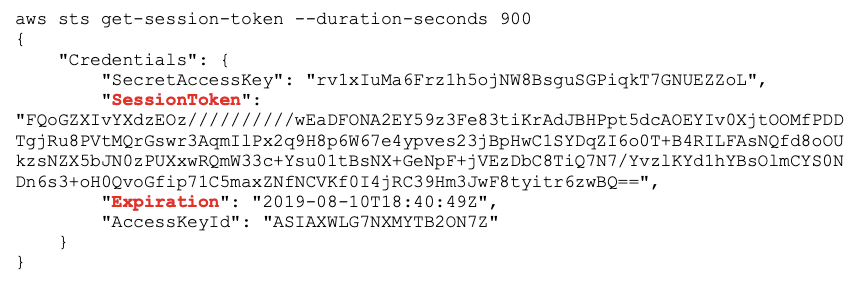
In addition to the access key id and secret, a temporary credential includes an expiration date and a session token, which must be included in any API calls (along with the access key and secret).
Temporary tokens essentially have the same functionality and similar security exposure as permanent access keys, but with a few differences:
- Expiration: Temporary tokens have an expiration, ranging from 15 minutes to 36 hours. This is good from a security viewpoint, as it reduces the time window for abuse in case of lost or stolen temporary tokens.
- API Access: Temporary tokens can call any service that the original credential (that created the temporary token) has privileges for, except that:
- within STS, temporary tokens can only call the
AssumeRoleAPI call. - within IAM, MFA is required.
These restrictions may not necessarily constrain attackers, since there are a large number of services that support AssumeRole [1], which combined with numerous techniques for escalating privileges [2], creates a large attack surface for lateral movement from temporary tokens to other privileged roles.
Attack Scenario
To highlight the challenges when temporary tokens are used in an attack, let’s look at a simple attack scenario. The environment has support personnel who must manage production S3 buckets, and the organization has created a specific role, MyBucketRole, that is assumed by support personnel whenever the need arises for S3 bucket support.
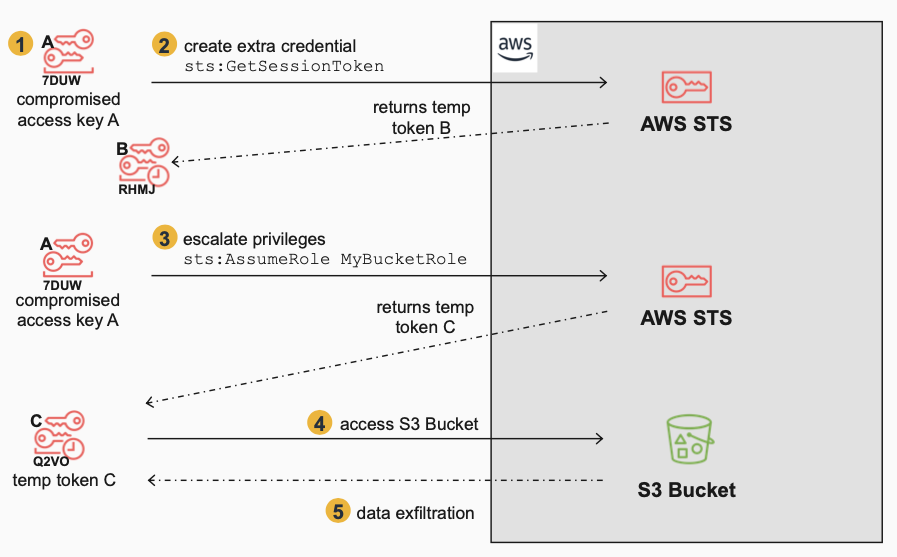
The Attacker:
- Gains initial access to the environment with stolen credentials (access key A) which was accidentally hard-coded into a script that was uploaded to Git by a support person.
- Generates a temporary token B using the stolen credentials (access key A) with a call to STS
GetSessionToken, for persistent access i.e., backdoor access. This is not used immediately but is saved for redundant access and will be used in a secondary attack, and we will see shortly why it has different challenges than permanent keys and other temporary tokens generated byAssumeRole. - Uses access key A to escalate privileges by assuming a role,
MyBucketRole, that has access to an S3 Bucket. This returns temporary token C, which when used will have the permissions ofMyBucketRole. - Accesses sensitive data on the S3 Bucket using temporary token C.
- Exfiltrates data from the S3 Bucket (e.g. S3 sync to another S3 bucket)
The initial compromise and attack vector in this scenario is the compromised credential. The use of temporary tokens does not change this risk profile but it will make the detection, mitigation, and prevention steps different or more challenging, which we cover in the next section.
Defender Viewpoint
Let’s look at this attack from the defender’s viewpoint to understand any challenges that stem from the use of temporary tokens by the attacker. We’re in the middle of the attack, we’re alerted to suspicious data access patterns during the exfiltration phase, and we’ve found out that a support user called AssumeRole and is performing data exfiltration.
Detection and Remediation
1 – Delete Compromised Key A
We immediately delete or make inactive the compromised access key A, regenerate new keys, ensure key rotation is enabled:
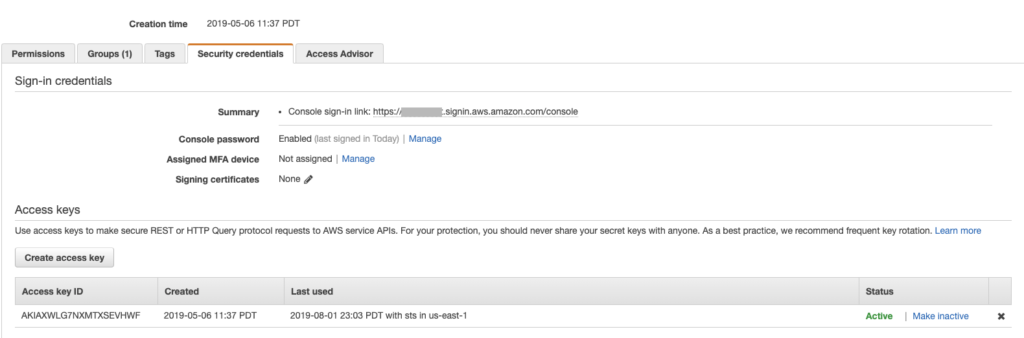
Additionally, we can discuss with the support user how they can better secure their API keys and send him/her to security training if necessary.
This should at least kick out our attacker, right? Not quite.
2 – Alerts on Continued Access with Temporary Token C
We find that the data exfiltration continues because the temporary token C created by AssumeRole still exists and is valid for up to 36 hours.

Any access key ids will start with “ASIA”, which is the naming convention that distinguishes temporary tokens from permanent tokens (”AKIA”). [3] There is no explicit attribute to distinguish a temporary token vs access key. There is also nothing in this event that ties the temporary token back to the principal that created it — that information is contained in a different event that captures the creation of the temporary token.
3 – Mitigate by Revoking Active Sessions for Temporary Token C
Although there is no way to list, directly delete, or deactivate temporary tokens, there is a workaround. We can revoke active sessions associated with a Role i.e., sessions started by AssumeRole. The policy can be set in the Revoke sessions tab for the role assumed by the attacker (IAM service):
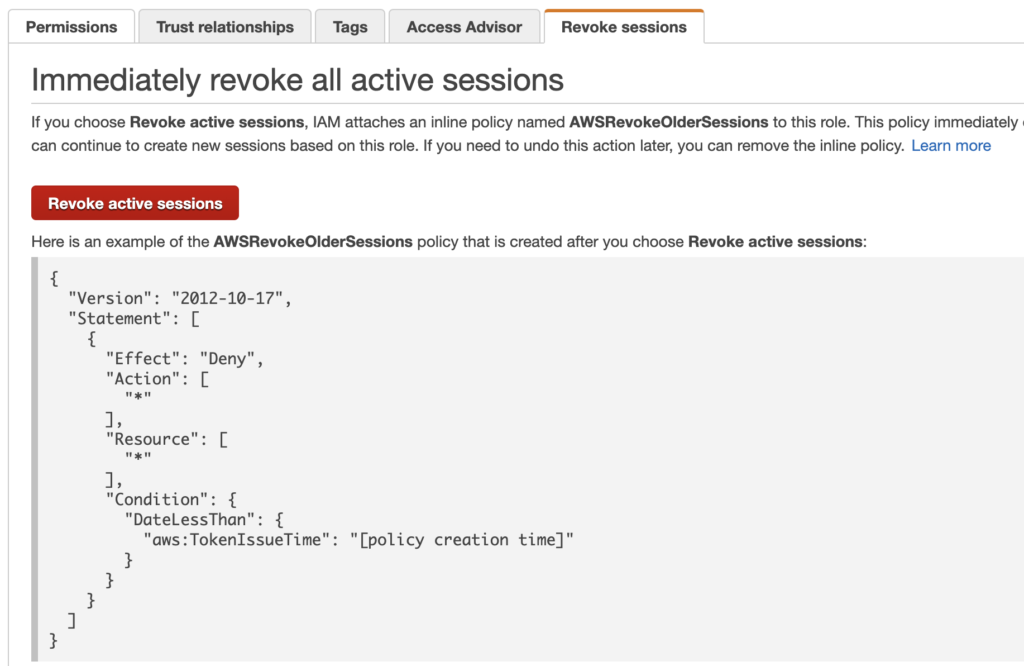
It implements a policy condition that denies any API call if the token was created earlier than the time you put the policy in place [6].
We should be done now, right? Not yet.
4 – Alerts on Continued Access with New Temporary Tokens
We continue to see data exfiltration using an AssumedRole temporary token but that is different from temporary token C:

Where are these coming from?
5 – Discover Temporary Token B
The problem is temporary token B, which is repeatedly calling AssumeRole to generate new tokens:

AssumeRoleThese new temporary tokens have creation timestamps that are newer than what was set in the Revoke active sessions policy in step #3, so they are not denied.
We could do the Revoke active sessions step again (step #3) which will update the timestamp to the current time, but that doesn’t stop the attacker, who can keep calling AssumeRole.
Should we delete temporary token B, as in step #1? Unfortunately, we can’t because it’s not a permanent key, and there are no API calls or Console actions to list or delete temporary tokens.
Should we try to contain it using Revoke active sessions, which worked in step #3? Unfortunately, Revoke active sessions works only for Roles i.e. it’s only available to control sessions from tokens created with AssumeRole. It doesn’t apply to or work for temporary tokens created by GetSessonToken.
What now?
6 – Delete User or Change Permissions
The recommended ways to remediate temporary tokens created by GetSessonToken, are to:
- Change/restrict the privileges (policies) for the user or role that created the token since the temporary token creates a session with the current privileges of the user/role at the time of use (not creation) [4].
- Delete the user [5], which will immediately delete all temporary tokens associated with that user.
The user in question is the IAM user who created the temporary token i.e. the support user. So, in order to be safe, we delete the user. Hopefully, we have Cloud Formation Templates or other ways to recreate the user easily. For a single user, this may be ok. However, if the IAM User is used as a service account and has many active sessions, then deleting the user will immediately cancel all active sessions, which can have a large negative impact.
We have finally kicked the attacker out of our AWS environment by deleting or mitigating all compromised credentials! Now, let’s look at how we can lockdown the environment to prevent this happening in the first place.
Prevention
1 – Prevent Creation of Temporary Tokens by AssumeRole
We can use IAM policies to limit who can call AssumeRole by limiting the trust relationship of the role.
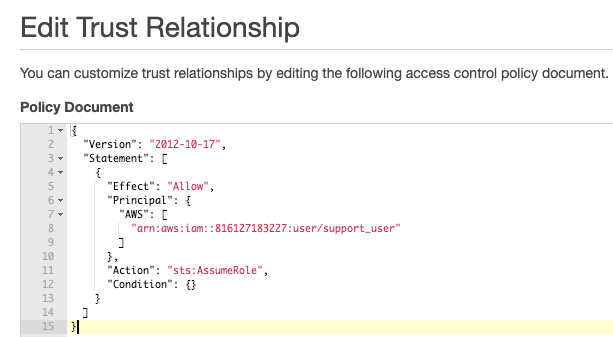
In this example, only support_user is able to assume MyBucketRole — no other roles, users, or other principals can assume this role.
2 – Alert on Creation of Temporary Tokens by GetSessionToken
How about preventing GetSessionToken? Unfortunately, we cannot restrict or prevent calls to GetSessionToken, as explained in the IAM User Guide [7]:
IAM users can also call GetSessionToken to create temporary security credentials. No permissions are required for a user to call GetSessionToken. The purpose of this operation is to authenticate the user using MFA. You cannot use policies to control authentication. This means that you cannot prevent IAM users from calling GetSessionToken to create temporary tokens.
Instead, we can focus on alerts based on early detection. Since GetSessionToken‘s primary use is to MFA enable a token that can be used to call MFA-protected API calls, it should occur much less frequently in your environment.

You can distinguish MFA GetSessionToken calls by looking for the existence of requestParameters.serialNumber.
Note: Alerting on sts:AssumeRole calls is not useful because of false positives since it is validly and widely used by many services [1].
3 – Mitigate Compromised Permanent Keys
Using MFA and/or IP/VPC allow listing in IAM policies will reduce the probability of downstream abuse from temporary tokens.


4 – Mitigate Compromised EC2 Temporary Tokens
Dynamic allow listing the source IPs of temporary tokens generated by sts:AssumeRole (see example from the Netflix Security team[8]) can help contain and minimize the impact of stolen temporary tokens since the tokens can only be used from the EC2 instance. The tradeoff is the time and resources required to maintain additional code, which may introduce additional security bugs or vulnerabilities. Additionally, this does not prevent the stolen credentials from being used from the EC2 instance itself.
Summary
Temporary tokens are just one way an attacker can maintain persistence, evade defenses, and escalate privileges in your environment. Because they differ from permanent keys in how they are detected, remediated, and prevented, you want to take appropriate measures to manage this risk.
In the attack scenario above, you need to detect whether temporary tokens have been used by an attacker and what type of tokens they are. For those created by AssumeRole, you can revoke active sessions. For those created by GetSessionToken, you must delete the user or restrict its permissions. To prevent credential compromise, restrict the use of permanent keys with source IP allow listing and/or MFA, restrict the trust relationships for roles that are assumed, and consider a metadata proxy (IP allow listing) for EC2-generated temporary credentials.
This table summarizes the specific defensive measures you can use to prevent, detect, and remediate temporary tokens (AssumeRole and GetSessionToken) as well as permanent keys:
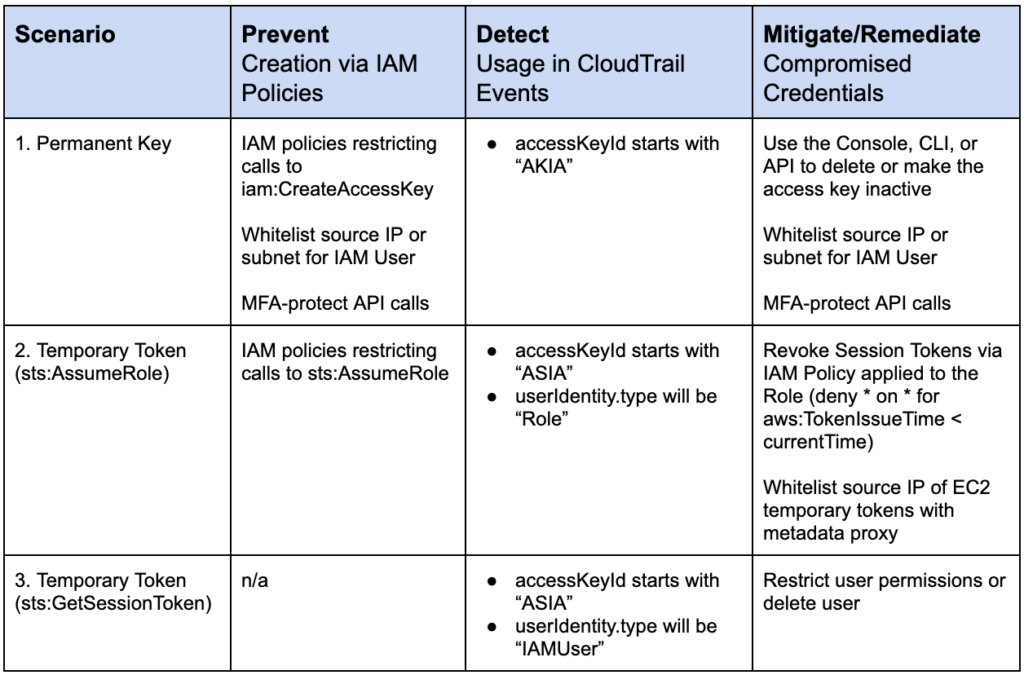
Netskope provides support in preventing abuse with continuous security assessment checks, detection with inline and API introspection, and custom auto-remediation commands.
For an attack chain perspective on managing Temporary Tokens, see our blog post: MITRE Att&ck View: Securing AWS Temporary Tokens.
This blog post is based on talks given at:
- Defcon 27 on August 10, 2019. Slides are linked here.
- AWS Community Day 2019, Bay Area on September 13, 2019. A recorded video of the presentation is here.
References
[1] AWS Identity and Access Management: AWS Services That Work with IAM
[2] “AWS IAM Privilege Escalation – Methods and Mitigation,” S.Gietzen, Rhino Security Labs.
https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/aws-privilege-escalation-methods-mitigation/
[3] “Managing Access Keys for IAM Users: Auditing Access Keys,” AWS Identity and Access Management User Guide, AWS.
[4] “Disabling Permissions for Temporary Security Credentials,” AWS Identity and Access Management User Guide, AWS.
[5] “My AWS account might be compromised,” Knowledge Center, AWS, October 2019.
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/potential-account-compromise/
[6] “Revoking IAM Role Temporary Security Credentials,” AWS Identity and Access Management User Guide, AWS.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_use_revoke-sessions.html
[7] “Granting Permissions to Create Temporary Security Credentials,” AWS Identity and Access Management User Guide, AWS.
[8] “Netflix Information Security: Preventing Credential Compromise in AWS,” W.Bengtson, Netflix Security Tools and Operations, November 2018.




 Voltar
Voltar
















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog