Co-authored by James Robinson and Jeff Kessler
As rapidly as wide-area networking (WAN) and remote access strategies with associated technologies are changing, we’re always surprised by the amount of time some security professionals and auditors dedicate to the either/or debate between split tunnel and full tunnel connectivity.
History can partially explain how we got here. Long before COVID-19 reared its ugly head, corporate security teams were already grappling with how best to protect remote connectivity. First, they directed all employees working remotely to reach the corporate network via VPN, which meant all traffic was routed through the firewall/VPN concentrator in the enterprise data center. When these users were only, or primarily, accessing applications housed inside the corporate network, that made sense, although bandwidth limitations sometimes reduced application performance. A middle ground many of us found (we liked to call it splint-tunneling) was also to enable direct connections for “approved” cloud services while everything else was sent to the data center. However, this approach still had weaknesses including the abuse of these exposed cloud services and the lack of visibility by security teams. As cloud solutions became more and more prevalent, forcing traffic traveling from remote offices to cloud-based applications (and vice versa) to make a pitstop in the data center began to make less and less sense.
The easy solution was to reduce unnecessary backhauling to the data center by letting remote machines talk directly to the internet. Many security teams implemented “split tunneling,” by which traffic that needs to pass through the corporate network utilizes VPN connections, while traffic that is headed to the internet goes there directly without visiting the data center at all.
But easy is not security and split tunneling raises massive red flags for security teams. Internet browsers, software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications, and streaming technologies create new attack vectors for malware. Unless these solutions’ data streams flow through the corporate firewall, the company is relying solely on endpoint protection solutions for threat detection and mitigation. If a DNS or ICMP attack were to succeed in bypassing endpoint security, not only could it be used as a covert channel, but it could also be the entry point to the enterprise over the VPN connection. Historically security teams have not had good visibility into these kinds of attacks where the command and control traffic is asynchronous to the tunneled traffic that goes into the enterprise. Furthermore, these split-tunneled systems were mini-pivot points allowing the compromise of a system to be entry into data center secured systems and applications.
Split tunneling was already problematic and controversial before COVID. It was hard to manage the complexity of source to destination ports and protocols resulting in many companies using an all or none approach to accessing systems/apps or requiring jump boxes and other technologies to be offered up for end-users. Then the pandemic hit, leading businesses around the world to send large portions of their workforce home. And for companies that were still relying on full tunnel connectivity a year ago, backhauling all traffic through the data center, the sudden COVID-driven leap in traffic volume slowed performance to a crawl for WAN end users. Scalability was also hard to measure for the unexpected increase in volume. This rush for procuring and implementing additional infrastructure to support the increased volume of traffic didn’t allow for much time to secure, harden, and monitor this new infrastructure.
Secure multipoint tunneling offers another option
What, then, is a security team to do when Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and even teleconferencing applications like Zoom underpin almost every facet of corporate operations? Should security leaders insist on VPN backhauling, adding latency that may undermine employee productivity? Should they use PAC files and other technologies which add complexity and have complex models for management? Or should they eliminate filtering on internet traffic, with all the dangers that approach entails?
My answer, as a security leader who’s been tested plenty, is neither of the above. Instead, security teams should expand their horizons and consider a third solution to the dilemma—secure multipoint tunneling. It’s a model of network architecture in which remote traffic enters the corporate network only if the data center is its final destination. But unlike split tunneling, secure multipoint tunneling does not leave other traffic unprotected. As the name implies, secure multipoint tunneling routes communications to and from cloud-based resources through a second tunnel, which is protected by a cloud firewall.
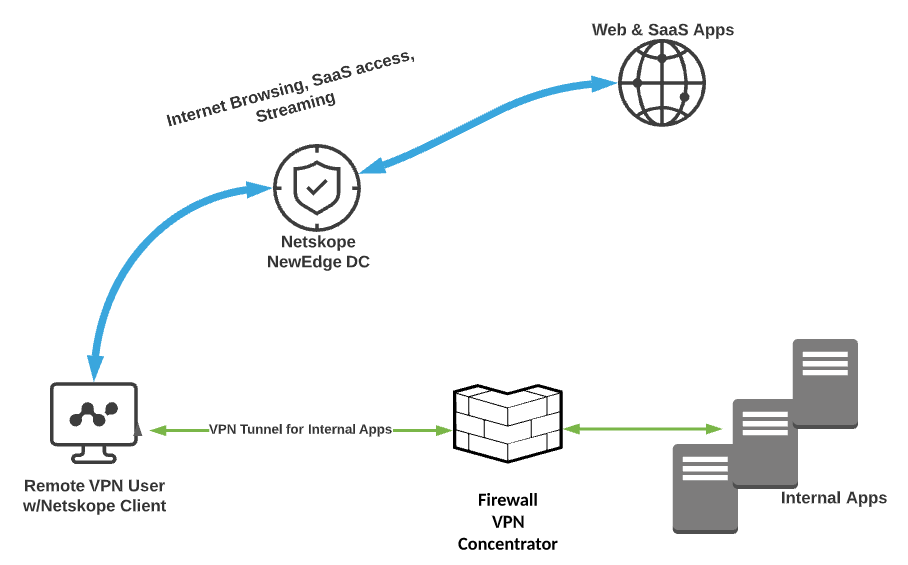
Essentially, in a modern organization with an assortment of different attack surfaces, this approach establishes a TLS connection to each network edge. On-premises and cloud-based resources are monitored by specialized security tools, and traffic reaches each destination through a separate secure tunnel. The security team can centrally monitor and apply controls to all traffic, whether or not it’s backhauled to the data center. In fact, I like to think of the traffic headed for the cloud firewall as being not backhauled but instead “uphauled.”
Shades of gray improve control and compliance
Such an architecture accelerates traffic headed to the corporate data center because far fewer communications are competing for that VPN bandwidth. At the same time, secure multipoint tunneling applies enterprise-grade security to direct-to-internet traffic, so the company isn’t relying on endpoint protection solutions to fully lock down cloud connections.
Perhaps most important, a well-designed security infrastructure utilizing secure multipoint tunneling should include a dashboard that provides the corporate security team with single-pane-of-glass visibility into security events across each of the tunnels. All ports, protocols, and telemetry should tie in, whether they lead to the data center or the cloud.
This approach gives end-users effective protection with minimal performance impact and offers security administrators greater confidence that remote systems’ controls are strong enough to fend off evolving threats. It also enables security teams to adopt Zero Trust and Adaptive Trust architectures that can help secure enterprises as well as appease auditors, who may have compliance concerns about a network architecture that leverages split tunneling with minimal security for cloud-direct traffic.
Many readers may agree with the use of secure multipoint tunneling as a solid approach to remote access however, our audit and third-party risk team do not understand the model or have not been given the guidance for when the model and approach should be used. In other cases as security professionals, we’ve gotten into the habit of seeing full tunneling and split tunneling as our only options. But WAN architecture is not limited to this oversimplified either/or. Like most things in life, WANs are available in a range of options. Selecting the right approach requires security pros to think beyond the binary.




 Retour
Retour
















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog