In my previous blog, I covered the many different types of cyber threat intelligence and why gathering CTI is beneficial to security teams. In this post, I will dig into the cyber threat intelligence lifecycle framework and a model to help correlate and contextualize your findings.
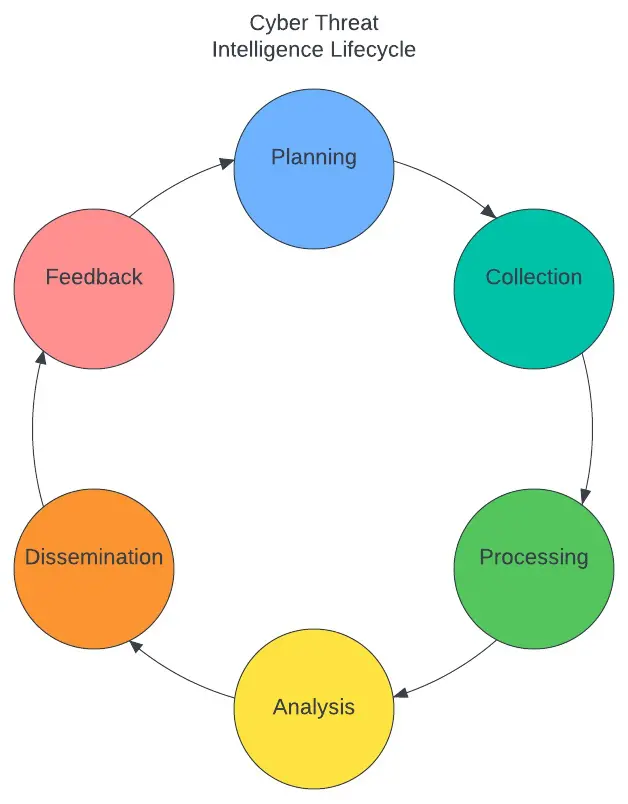
Cyber threat intelligence lifecycle
Performing cyber threat intelligence gathering should be approached with a method in mind. This is where the CTI lifecycle can help provide a framework for how to accomplish CTI. Similar to the scientific method, CTI can be broken into six phases, each with a specific goal to enhance either the CTI process or the information gathered while performing CTI.
- Planning – Set requirements, goals, and methods for intelligence gathering to answer a specific question.
- Collection – The process of gathering information from sources.
- Processing – Organizing information gathered in the Collection phase.
- Analysis – Examining information to place relevance, priority, and potential actional items
- Dissemination – Delivering information to the teams that can best utilize it.
- Feedback – Asking did the information gathered answer the question, help or enhance a team’s objective? What information does the team still need?
Here at Netskope one of the many ways teams utilize the CTI lifecycle, and multiple other intelligence gathering tools, is to feed data into the Netskope Cloud Threat Exchange platform, providing up-to-date threat intelligence, including IoCs. This way Netskope and Netskope customers can detect, alert, and block the latest threats. To start the process, the analyst plans to ingest accurate and relevant IoCs that are found in the wild. Collection then occurs with tools curating intelligence and the analyst building automation to go to the next stage of processing. Processing provides context through other threat intelligence gathered, such as threat actors and TPPs, along with the IoCs. In the Analysis phase, IoCs are enriched and then, depending on relevance, formatted to share with different teams. Dissemination is where these IoCs are then shared through intel channels built between teams in the format that works best for their objective. With Feedback regular team meetings ensure any gaps within the intelligence shared are discovered and a plan is formulated to fill these gaps.
Diamond model
While it is important to have a process to methodize intelligence gathering, it is just as important to have a model that helps correlate and contextualize that information gathered. One such model that can help consumers of threat intelligence is the diamond model (pictured below).
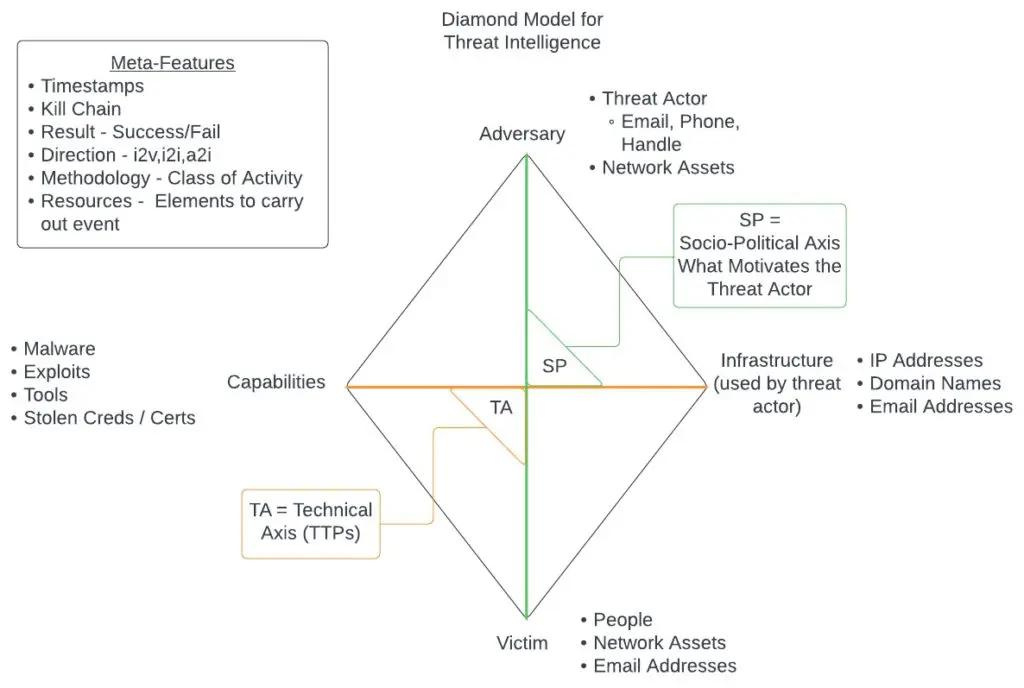
One important aspect of the diamond model for threat intelligence is that it allows analysts to easily pivot from one piece of intelligence to another, which helps either fulfill the full picture while gathering, or show blindspots in intelligence. The main focus of the model is to track adversaries, capabilities, infrastructure, and victims over time. This activity is shown through the use of an activity thread which correlates trends of attackers, TPPs, and infrastructure across attacks against multiple different victims. The activity thread is helpful in building out potential future paths threat actors could take, which allows defenders and responders to take a proactive approach to security and not reactive.
Another key aspect of the diamond model is the ability to form activity groups and activity-attack graphs. Activity groups are groupings of common identifying behavior such as particular APT activity or a common attack pathway used by threat actors signaling a specific type of attack. Activity-attack graphs are graphical representations of actual attacks occuring in the threat landscape along the cyber kill chain. This allows CTI analysts to track current activity in the threat landscape and correlate the MITRE ATT&CK TPPs to the cyber kill chain in order to formulate scenarios an organization may face. Using these attack graphs, security teams can formulate specific threat hunt scenarios and ensure their security stack protects against attacks found in the wild.
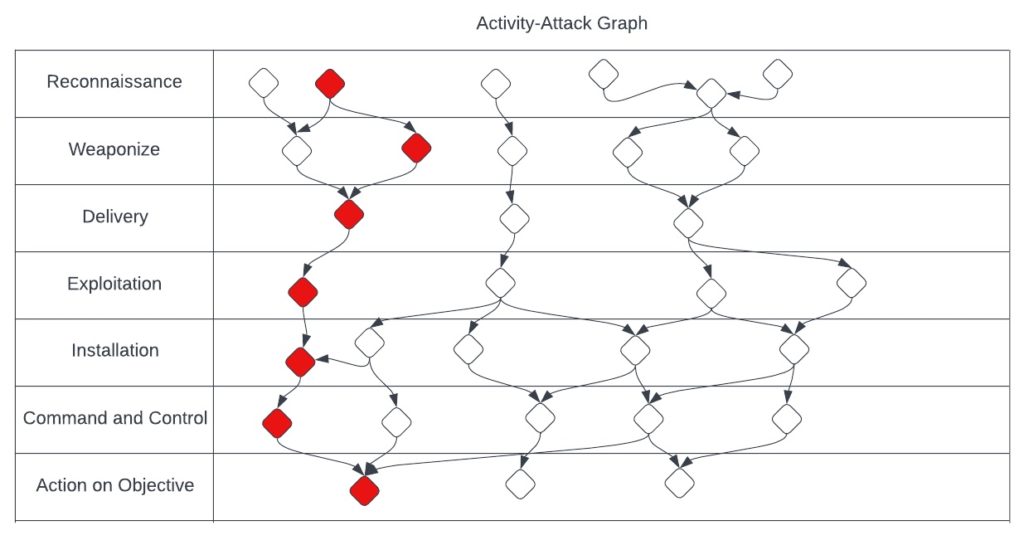
For more information on the diamond model and activity-attack graphs with the diamond model see the original paper by Sergio Caltagirone, Andrew Pendergast, and Christopher Betz here.
Here the diamond model is used to put together intelligence on the threat actor FIN7. I started with formulating a diamond based on the known adversary and then doing a high-level analysis of capabilities, infrastructure, and victims of the threat actor’s previous attacks.
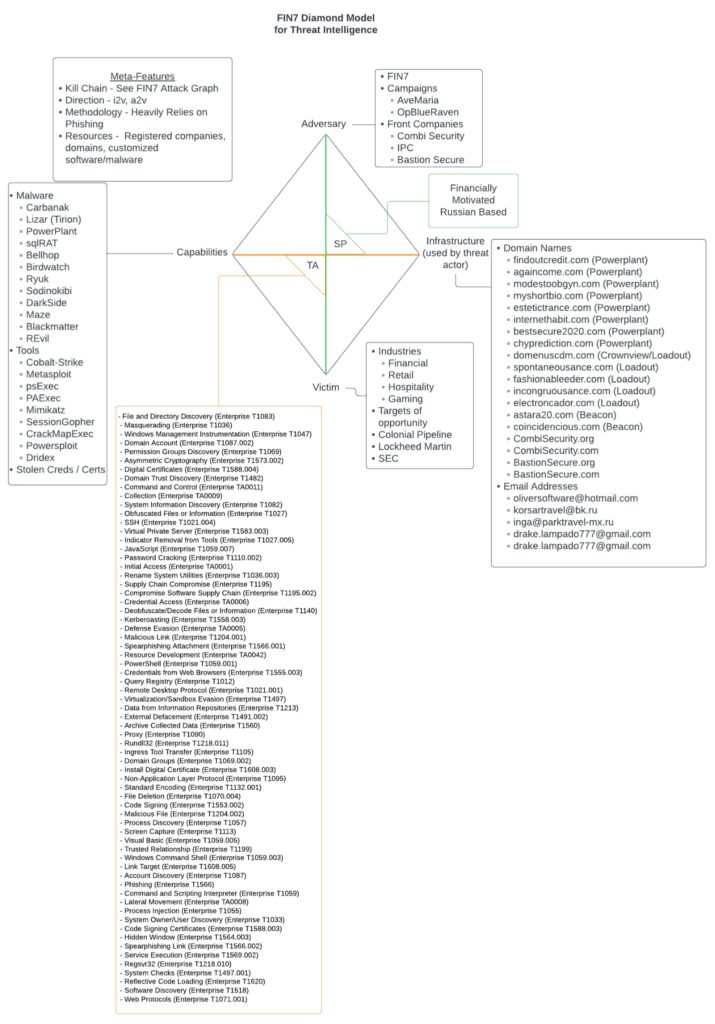
Using this graph I was then able to build out a high-level activity-attack graph based on how the threat actors operate in the wild. Building the attack graph allowed me the ability to pull out an activity grouping specific to FIN7 as well in which they favor the use of phishing, powershell scripts, and their own PowerPlant backdoor.
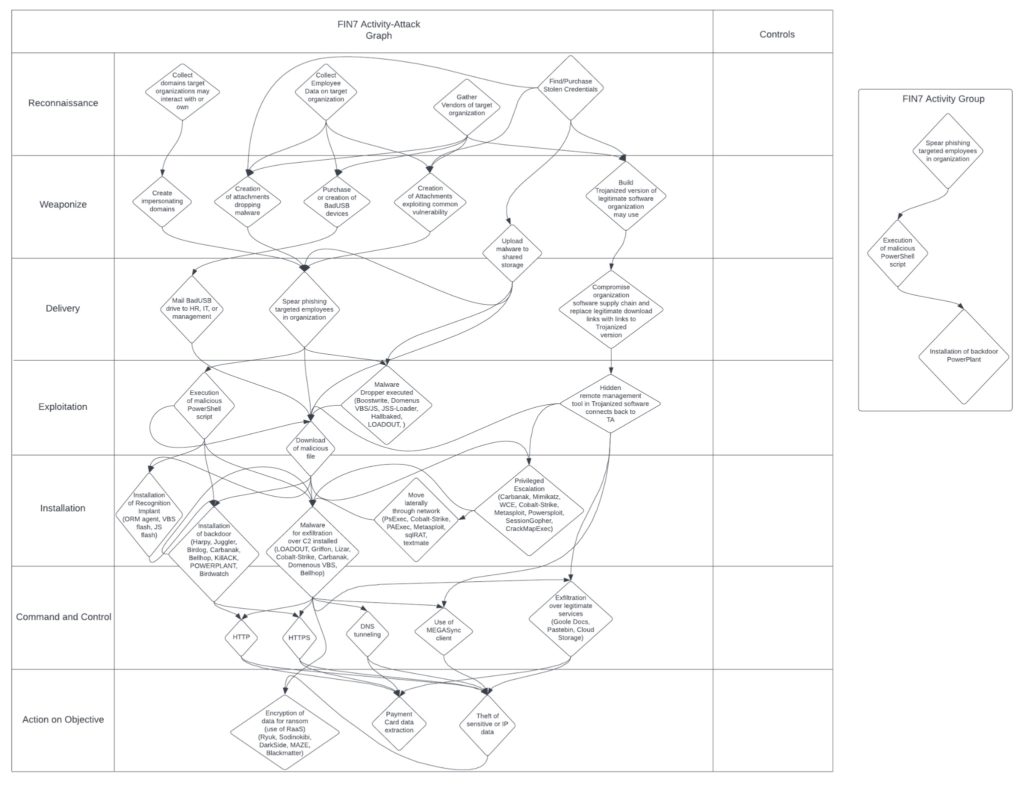
With the activity-attack graph, the ability for security teams to be responsive to FIN7 attacks is greatly enhanced. The SOC can now reference this when implementing controls to close gaps or understand where lack of visibility occurs, threat hunters can easily come up with the hypothesis needed to begin hunting, and incident response can reference it when doing IR to help provide context to the forensic artifacts that are uncovered.
Learn more here about how cyber threat intelligence is a key part of Netskope Cloud Threat Exchange




 Retour
Retour 















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog