Introduction
“The more things change, the more they stay the same.“
In the recent Equinix breach in September 2020, 74 RDP servers were exposed to the Internet. Any publicly exposed ports are a risk but remote access protocols such as RDP have had their share of critical vulnerabilities (e.g., BlueKeep in 2019).
In this blog, we will look at remote access statistics of public cloud workloads based on 287,877 compute instances across 327 anonymized production environments in AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. The focus will be on a few common ports/protocols used for remote access or management of workloads, namely: SSH, RDP, and to a lesser extent, VNC.
What we will find is that:
- Direct Access is Still Very Common
Direct access to compute instances is still very common (35-85%+ of public workloads depending upon cloud provider environment)—allowing inbound traffic to ports from public CIDRs for SSH/RDP. Although this finding is not necessarily surprising, the high percentage of workloads is, from 35% up to 85%. Unsurprisingly, SSH is the most common due to the popularity of Linux workloads, followed by RDP, then VNC.
- Broad Internet Exposure is Alarmingly Common
Additionally, a fair number of network configurations allow broad source IP CIDRs to access these same ports (SSH/RDP) e.g. from the entire public Internet (0.0.0.0/0). Over 13% of AWS public instances allow inbound access to All Destination Ports from any public Internet address, 71% of AWS public instances allow SSH from any public Internet address, and 14% of AWS public instances allow RDP from any public Internet IP address.
- Better Secure Access Alternatives Not Deployed
The implication from the above is that better secure access alternatives from the cloud service providers or other vendors are not being deployed. These alternatives are more secure than direct access or bastion hosts in almost every area (credential/key management, authorization, auditing, protocol/port attack surface, protocol vulnerabilities) and are referenced later in this blog.
Direct remote access
To identify direct access, we looked at public compute instances (with at least one assigned public IP address) that have a network security group or firewall ruleset that allows inbound traffic to a port range that included any of: 22 (SSH), 3389 (RDP), or 3800/3900 (VNC) and from a public source IP range. We counted separately the All Port range (0-65535).
We might guess that remote access directly to public instances is still common in the cloud, but the frequency of occurrence is eye-opening:
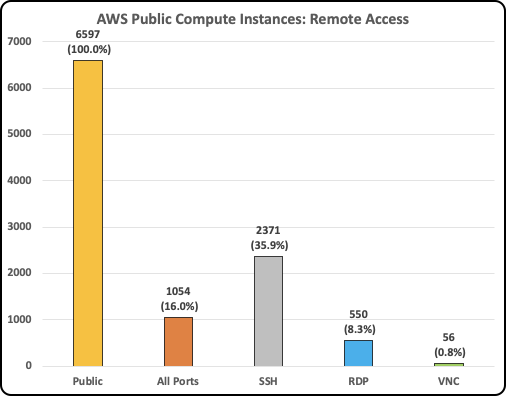
- In AWS, out of 6,597 public EC2 instances, 16% allowed inbound traffic to All Ports, 36% to SSH, 8% to RDP, 1% to VNC.
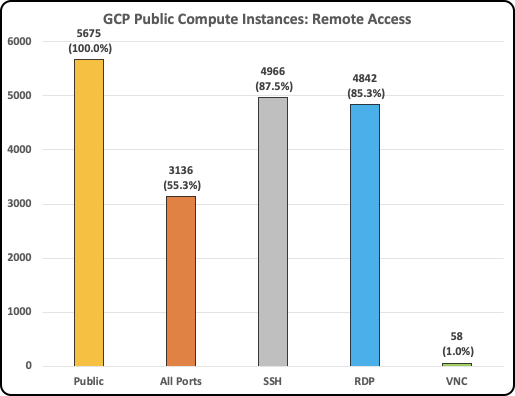
- In GCP, out of 5,675 public compute instances, 55% allowed inbound traffic to All Ports, 88% to SSH, 85% to RDP, and 1% to VNC.
- In Azure, out of 15,432 public compute instances, 53% allowed inbound traffic to SSH.
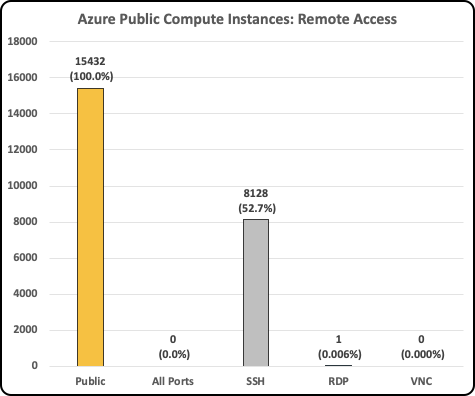
As we can see, direct inbound access from the Internet to public compute instances is very common, regardless of cloud service provider. This reflects bad security practices since there are better alternatives mentioned below.
In addition, allowing traffic to all All Destination Ports (0-65535) is commonly found in AWS (16%) and GCP (55%) public compute instances. Overly broad port access only increases the risk of port scans and exploits of other services running on the compute instances that normally should not be exposed to the Internet.
Internet exposure
In the inbound traffic rules and data above, narrow IP allow lists restricting traffic from a single IP address (/32) would normally mitigate some of the risks above. To provide more context, we break down the source IP ranges for these same public instances and protocols. Since VNC counts were negligible, we will focus on SSH and RDP.
We see that there are a significant number of compute instances with networking rules allowing traffic from any public Internet address.
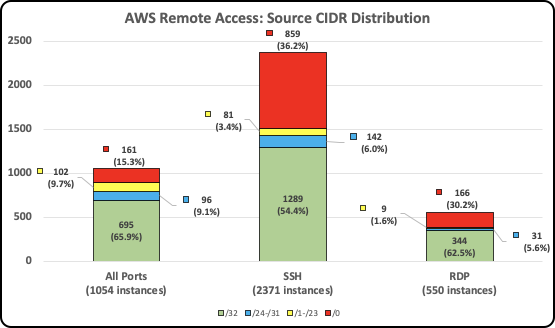
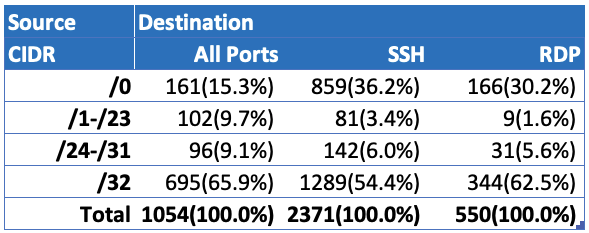
- In AWS, out of 1,054 public compute instances allowing All Destination Ports, more than 15% (161) of these can be scanned/attacked from any public IP address. For those instances allowing SSH, more than 36% (859) are reachable from any public IP address. And for RDP, more than 30% (166) of the compute instances are reachable from any public IP address.
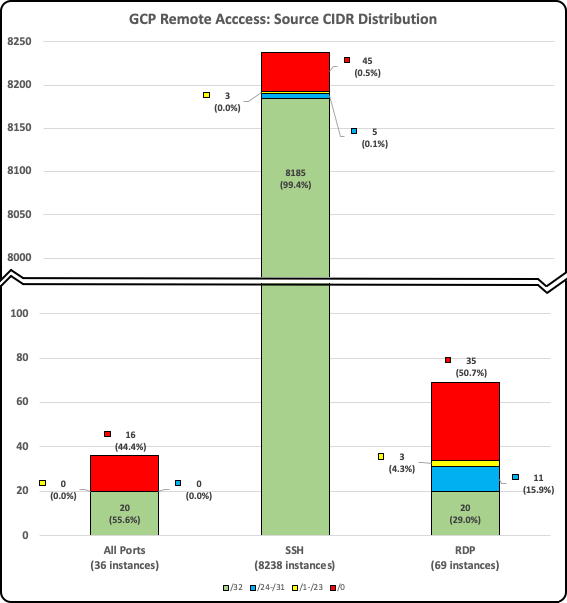
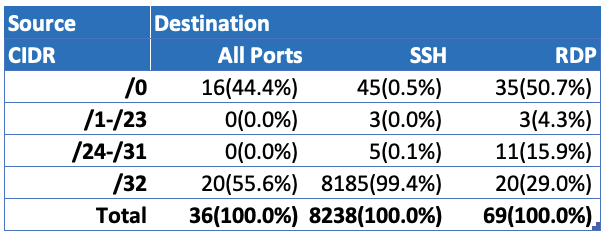
- In GCP, similarly, more than 44% of the compute instances have rules allowing inbound traffic from any public Internet address to All Destination Ports. Instances allowing SSH are minimally exposed to the whole Internet (only .5%). But for those instances allowing RDP, more than 50% are reachable from any Internet address.
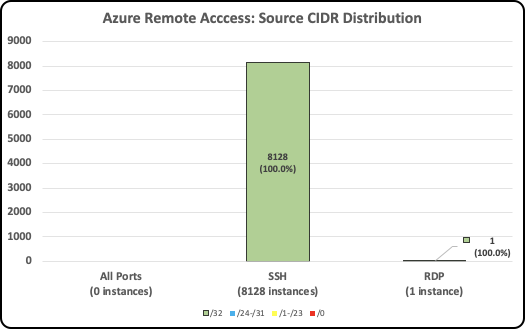
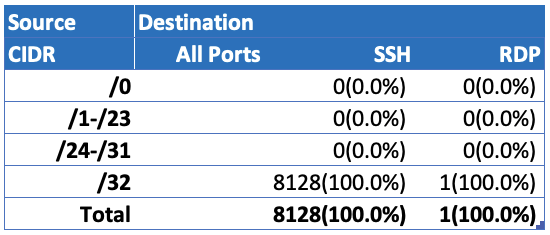
- In contrast, the Azure compute instances in this dataset have tighter network controls. All Destination Ports, RDP and VNC were tightly restricted, and out of the 8,128 instances allowing SSH and the one instance allowing RDP, all (100%) of the instances were restricted to traffic from a single source IP address (/32).
Conclusions
In the above environments, there are clearly some security concerns:
- Compute Instances: A significant number of public compute instances allow direct remote access to either SSH or RDP from the Internet. This ranges from more than 40% of public instances in AWS, 50% in Azure, and more than 85% in GCP that allow this traffic.
- Ports Exposed: It is not only the number of instances, but the number of ports exposed in each instance. In AWS, 16% (1,054) of the public compute instances have All Destination Ports open to inbound traffic from the Internet, and in GCP, more than 55% (3,136) expose All Ports as well.
- Internet Exposure: Additionally, the breadth of source IP ranges that are allowed to contact compute instances is overly broad. In AWS, 15% up to 36% of the public compute instances expose All Ports, SSH, or RDP to the entire Internet. in GCP, 44% to 51% expose All Ports or RDP similarly.
- Protocol Vulnerabilities: There is more risk due to multiple protocols e.g. SSH and RDP and VNC. Hardening practices differ, and it’s more difficult to manage access consistently due to differences in authentication (keys/AD/password), authorization (AD/OS-level), logging (different local logs). In addition, all three protocols (SSH, RDP, VNC) have had numerous vulnerabilities and CVEs such as RDP BlueKeep etc. In addition, there are specific attacks such as SSH multiplexing that are protocol dependent.
Fortunately, there are several, relatively simple measures that can be taken to reduce these risks:
- Secure Access over HTTPS: Better alternatives for remote access exist including cloud provider alternatives and Netskope Private Access, which provide more consistent/clear/secure credential management, auditing, access control, and less exposure to protocol vulnerabilities.
Cloud provider alternatives are explained in detail here:
Leaving Bastion Hosts Behind Part 1: GCP
Leaving Bastion Hosts Behind Part 2: AWS
Leaving Bastion Hosts Behind Part 3: Azure
These solutions reduce the number of ports exposed (reducing it to 443/HTTPS) and the vulnerability risk associated with multiple protocols (SSH/RDP/VNC).
- Audit/Configuration Checks: Compute instances and their security groups or firewall rules can be regularly audited for insecure settings, such as All Destination Ports allowed or overly broad Source IP CIDR ranges including 0.0.0.0/0. This can be done DIY with API/CLI scripts or with commercial offerings such as Netskope for AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Data analysis and methodology
The analysis presented in this blog post is based on anonymized usage data collected by the Netskope Security Cloud platform relating to a subset of Netskope customers with prior authorization.
A compute instance was determined to be public if the instance had an assigned public IP address. Network routability or other intervening controls were not considered.
Protocols were inferred from common default ports for the major remote access protocols (SSH = tcp/22, RDP = tcp/udp/3389, VNC = tcp 3800/3900). Compute instances that allowed All Destination Ports (0-65535) were counted once only, while double-counting among protocols were allowed especially if ranges were used (e.g. allowed destination port range: 0-5000 would count for both SSH, RDP, and VNC).




 Zurück
Zurück
















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen