Summary
RedLine Stealer is a malware that emerged in 2020, discovered in underground forums being sold in different plans, starting from $100 per month. The malware offers many capabilities for device reconnaissance, remote control, and information stealing, including:
- Data from browsers (e.g. login, passwords, credit cards, cookies, etc.);
- Data from Discord and Telegram (e.g. chat logs, tokens, etc.);
- VPN and FTP Credentials;
Since its discovery, attackers have used many different vectors to spread this stealer, including through fake installers and fake game hacking tools. Also, RedLine Stealer was found in compromised devices by the DEV-0537 hacking group (a.k.a. lapsus$).
In April 2022, Netskope Threat Labs identified a new RedLine Stealer campaign spread on YouTube, using a fake bot to buy Mystery Box NFT from Binance. The video description leads the victim to download the fake bot, which is hosted on GitHub.
In this blog post, we will analyze this campaign, showing how it’s being spread and how the fake bot leads to RedLine Stealer.
YouTube Videos
The malware is spread through YouTube videos that lure victims into downloading a fake bot to automatically buy Binance NFT Mystery Boxes. At this point, we found five videos across multiple channels that are part of the same campaign. All the URLs can be found in our GitHub repository.
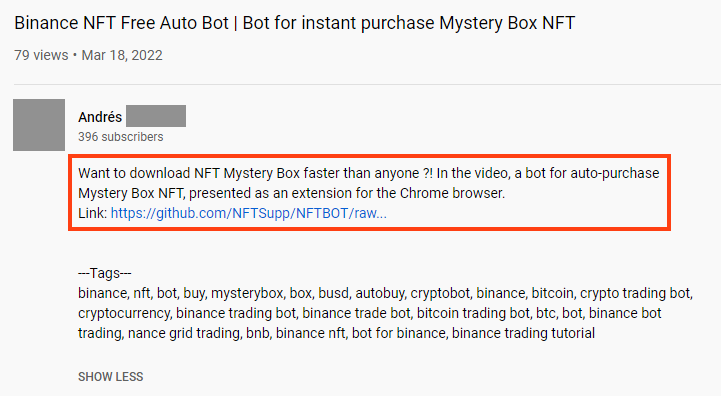
The video description provides details and the download link for the fake bot, which is supposed to be presented as a Chrome extension.
The video description also contains different tags, probably to increase its visibility, including:
binance, nft, bot, buy, mysterybox, box, busd, autobuy, cryptobot, binance, bitcoin, crypto trading bot, cryptocurrency, binance trading bot, binance trade bot, bitcoin trading bot, btc, bot, binance bot trading, nance grid trading, bnb, binance nft, bot for binance, binance trading tutorial
Stage 01 – Loader
All the videos we found are pointing to the same GitHub URL, downloading a file named “BinanceNFT.bot v.1.3.zip”.
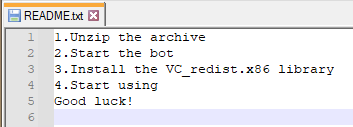
Once we decompress the ZIP file, we have the packed RedLine sample (“BinanceNFT.bot v.1.3.exe”) and a Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable installer (“VC_redist.x86.exe”).
The “README.txt” file contains the instructions that should be followed to run the fake NFT bot, including installing the Microsoft Visual C++. This is probably needed as RedLine is developed in .NET and it is also unpacked and injected into an executable from this framework.
The first stage was likely compiled on April 5, 2022, and it’s responsible for decrypting and loading RedLine Stealer into another process.
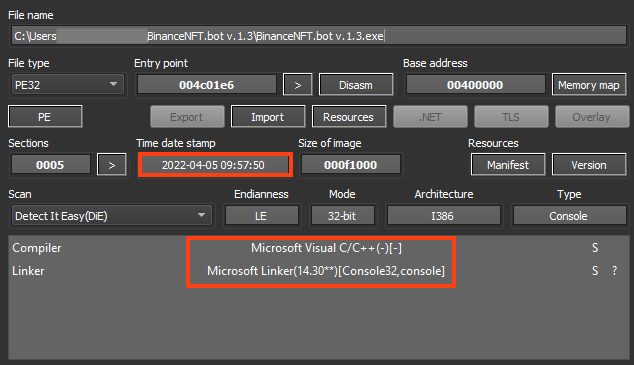
The binary details also include values that seem to be copied from another executable, using “LauncherPatcher.exe” as the original filename.
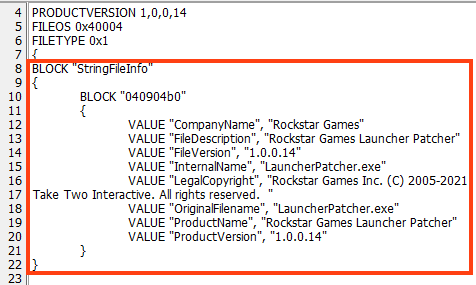
Many malware families use a trick to delay the execution of its functions, often to delay the execution inside sandboxes, which usually contain limited time of operation. As a result, there are sandboxes that are able to bypass this technique, by patching or hooking Sleep functions, for example.
This RedLine Stealer loader contains a simple trick to evade sandboxes with such functionality. Upon execution, it tries to delay the execution by 15 seconds and compares the timestamp (GetTickCount) before and after the Sleep API execution. If the elapsed time is less than 15 seconds, it exits the process.
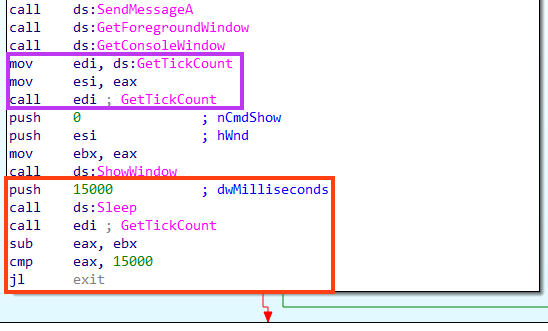
This can be tested by patching the Sleep function in a debugger.
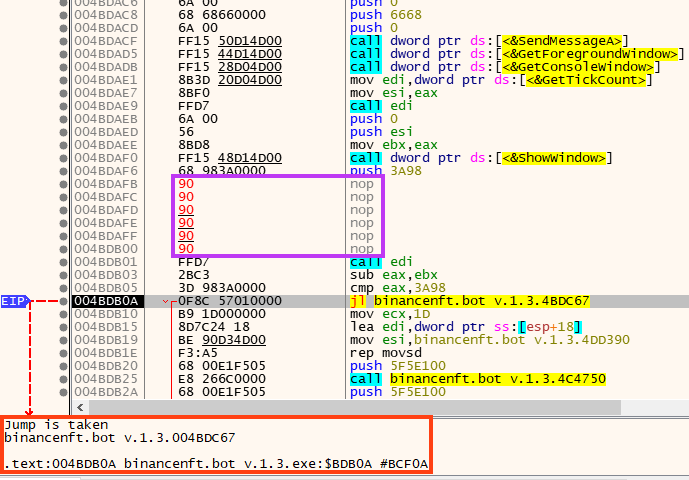
If the sandbox is not detected through this simple trick, it then decrypts the next stage using a simple rolling XOR algorithm with “OdoAAtK” as the key.
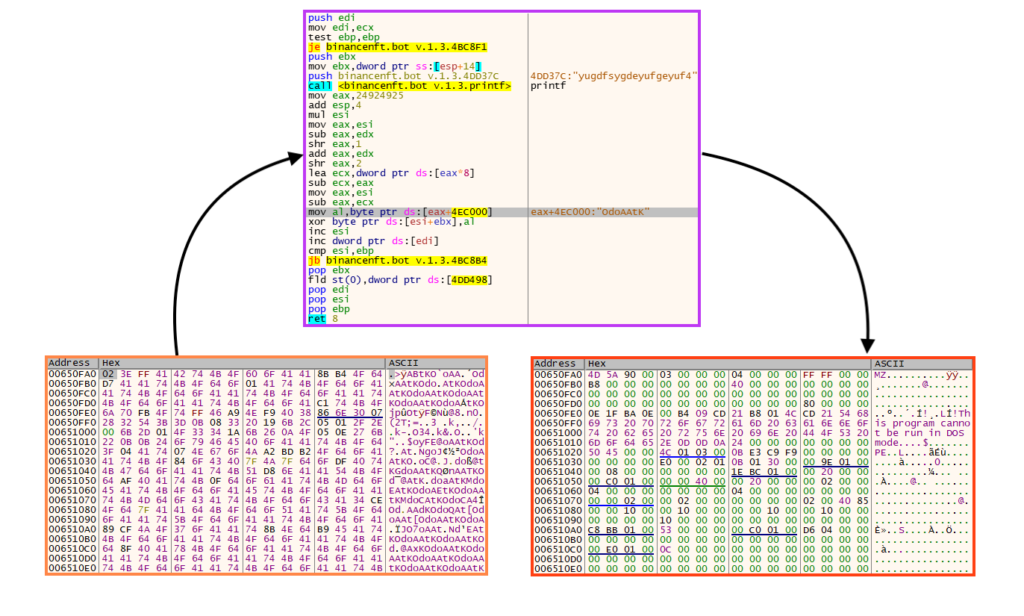
Then, it executes a shellcode, which is decrypted using the same algorithm.
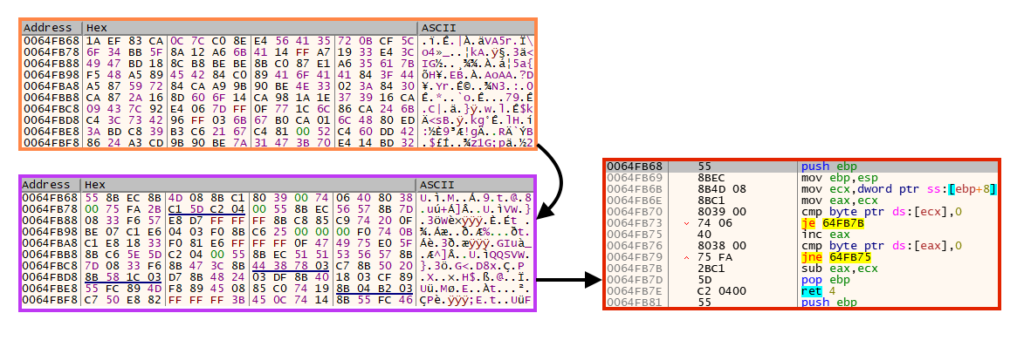
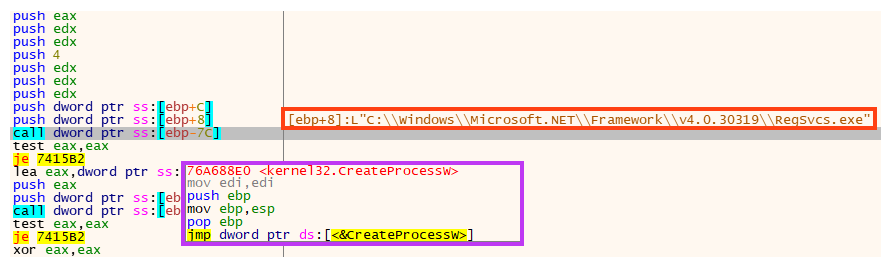
And finally, the payload is injected to “RegSvcs.exe” using a simple process injection technique, similar to RunPE. We also found cases where a similar loader injects RedLine Stealer into “AppLaunch.exe”, as we will describe later.
Stage 02 – Payload
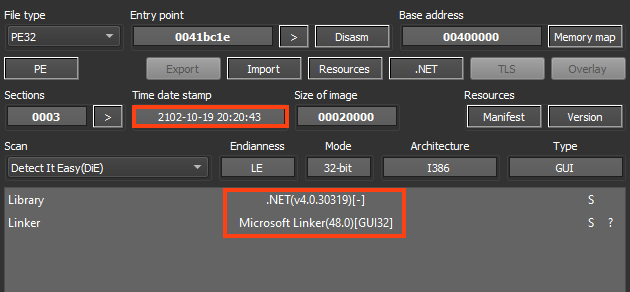
RedLine Stealer is developed in .NET, and the compilation timestamp was altered in the binary, showing a date from the year 2102. Formbook was also using altered timestamp dates in its payloads, which is a common behavior for malware authors to deceive analysts/researchers.
Fortunately, RedLine Stealer uses a very nonsense date, which can be used for detection in Yara rules, for example.
Once executed, the infostealer calls a function named “Check”. If this function returns true, the malware exits its process.
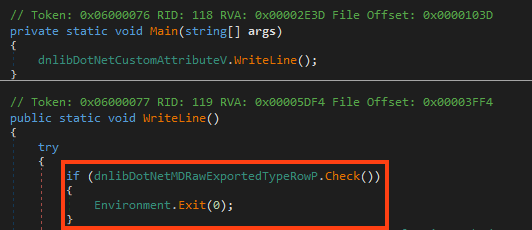
In summary, this function verifies if the malware is running in blocklisted countries, by comparing the country name with the OS region information.
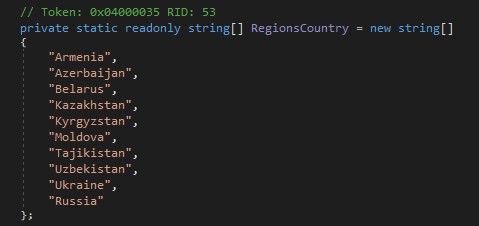
This malware does not execute if any of these countries is detected:
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Moldova
- Russia
- Tajikistan
- Ukraine
- Uzbekistan
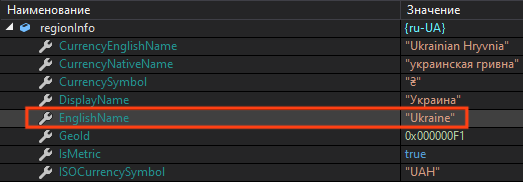
We tested this by changing the OS language to Ukrainian. The malware uses the field “EnglishName” from the .NET RegionInfo Class to compare with the blocklist.
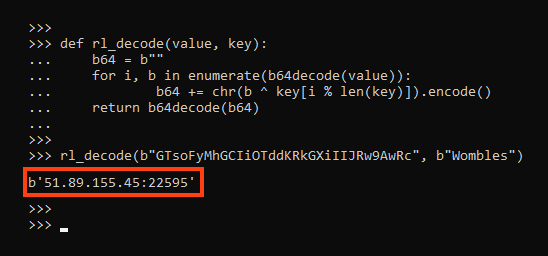
RedLine Stealer maintains a simple configuration, where the values are base64 encoded and encrypted with a rolling XOR algorithm.
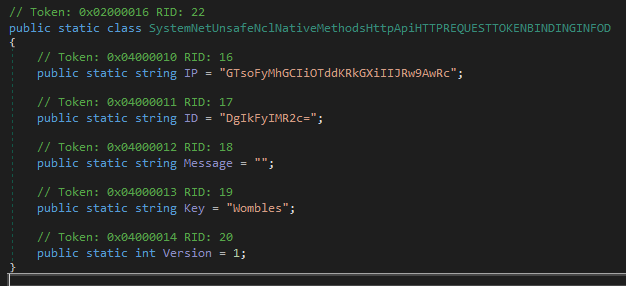
The decryption key used by this sample is “Wombles”, and we can use a simple Python script to retrieve the C2 address value:
The “ID” value also uses the same algorithm:
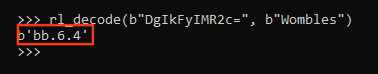
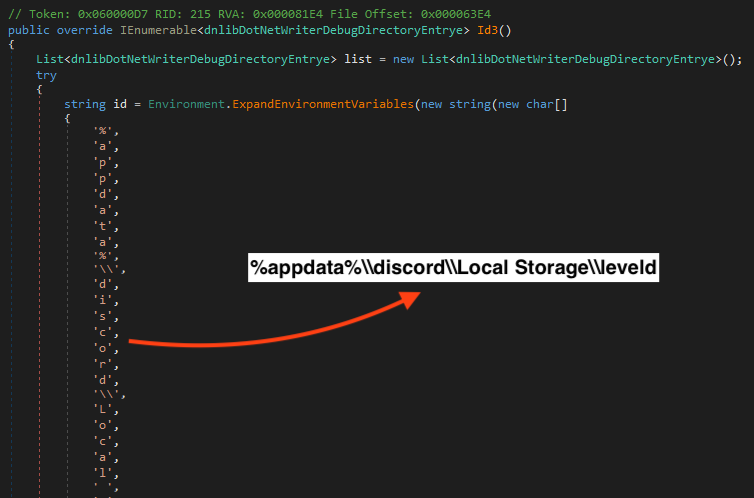
As previously mentioned, RedLine Stealer offers many capabilities to the attacker, including stealing Discord tokens.
More Files From the Same Campaign
Looking at the GitHub account (“NFTSupp”) that owns the repository where the file linked on the YouTube videos is hosted, we can see that the activities started in March, 2022.
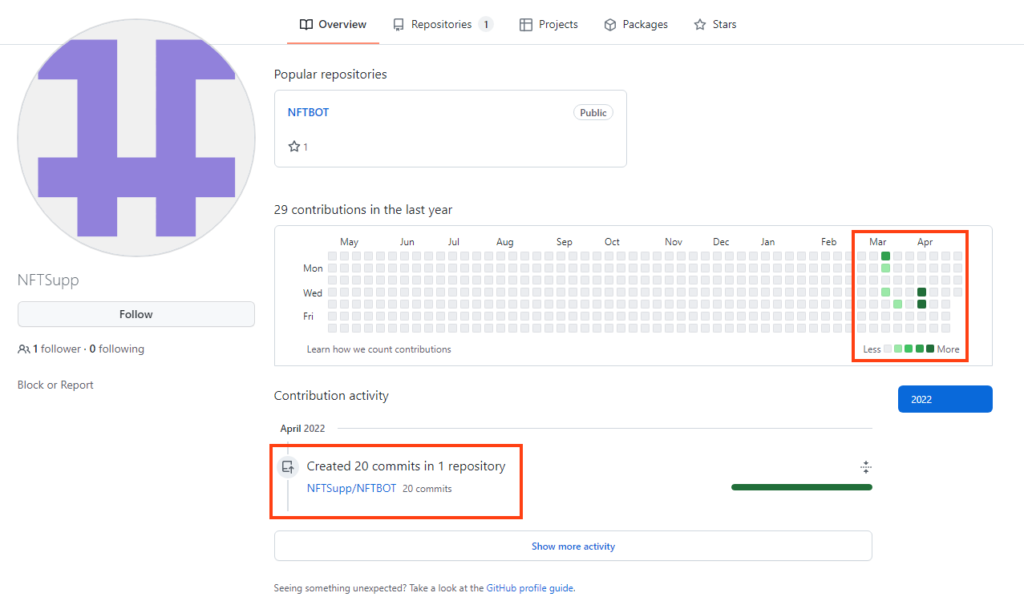
Aside from the files we analyzed in this blog post contained within “BinanceNFT.bot v.1.3.zip”, there are 15 additional compressed files hosted in the same repository (“NFTBOT”), where two of them are password protected (“45.rar” and “Upload.Openbot.rar”).
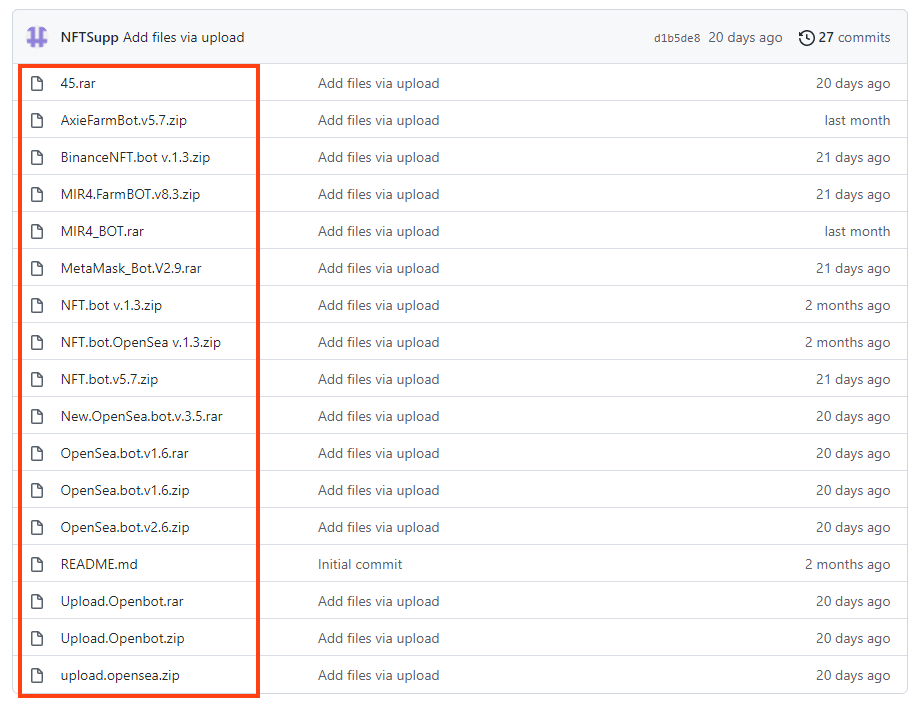
Within these compressed files, we found five distinct RedLine Stealer loaders.
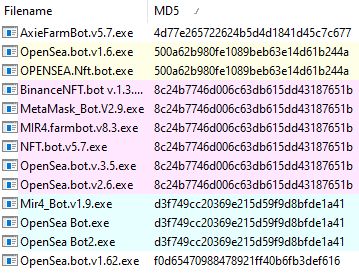
All five loaders we analyzed are slightly different, but they all unpack and inject RedLine Stealer in a similar way, as we described earlier in this analysis. The oldest sample we found was likely compiled on March 11, 2022 and the newest one on April 7, 2022.
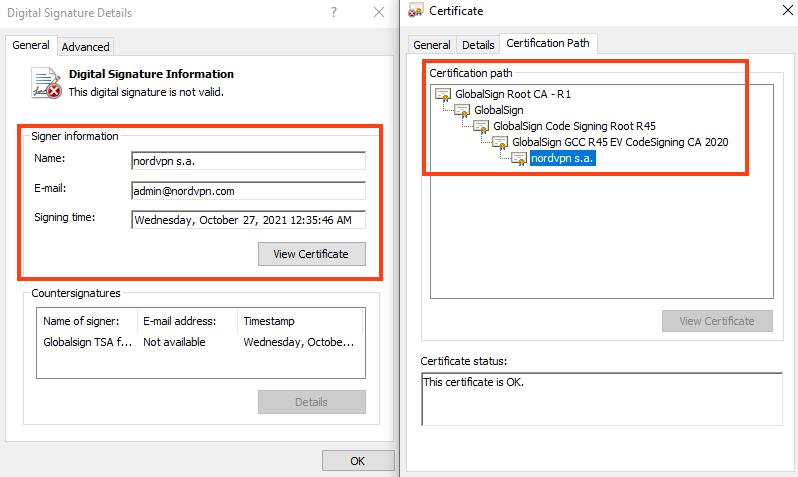
Furthermore, two out of five files are digitally signed, which may bypass some antivirus engines. The first one seems to be using a signature from “NordVPN S.A.”
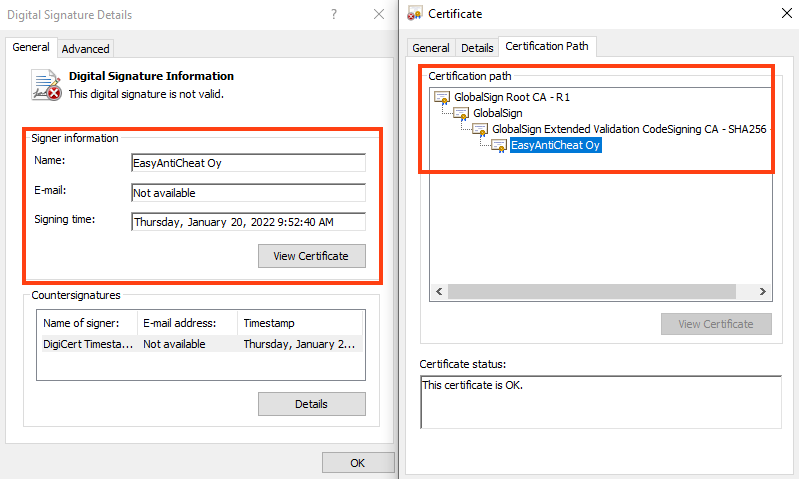
And the second is signed for “EasyAntiCheat Oy”.
Also, one of the loaders is injecting the payload into “AppLaunch.exe” instead of “RegSvcs.exe”.
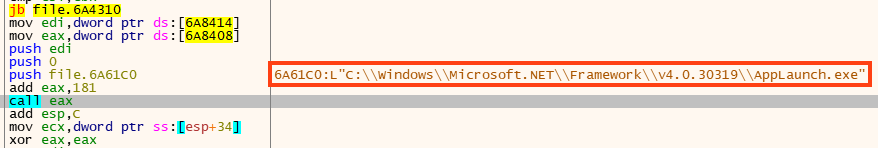
We found four distinct RedLine Stealer payloads from these five loaders, which are all sharing the same C2 address.
Conclusions
Although RedLine Stealer is a low-cost malware, it offers many capabilities that could cause serious damage to its victims, such as the loss of sensitive data. RedLine Stealer was already known for abusing YouTube videos to spread through fake themes, however, we saw in this campaign that the attacker is also abusing GitHub in the attack flow, to host the payloads.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Win32.Trojan.RedLineStealer
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign and the Yara rules can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Zurück
Zurück
















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen