Summary
Emotet is undoubtedly a very resilient botnet. Even though its operation was disrupted by Europol in January 2021, Emotet came back a few months later and continues to spread. In May 2022, shortly after Microsoft released new controls related to malicious macros, Netskope Threat Labs analyzed an Emotet campaign where they were testing a new delivery method, by using LNK files. Later, Netskope Threat Labs found a new campaign in June 2022 where Emotet continued to use Microsoft Office files to spread its payloads.
After another brief hiatus, a new Emotet campaign was spotted in March 2023, where attackers are still using Microsoft Office files as a delivery method. While there are also no notable differences in its main payload, the attackers behind Emotet have added a technique that increases the file size to bypass security solutions that do not scan large files. In this blog post, we will analyze this Emotet campaign from the delivery mechanism to the last payload.
Analysis
While Emotet continues to abuse Microsoft Office to deliver the second stage through malicious macros, attackers are now using a technique known as binary padding, where junk bytes are added at the end of the file to increase its size, to evade security solutions that do not scan large files.
This example Emotet sample contains many zero bytes at the end of the file, increasing its size to over 500 MB. To spread this file, the attackers are compressing the word document in a ZIP file and attaching it to spam emails.
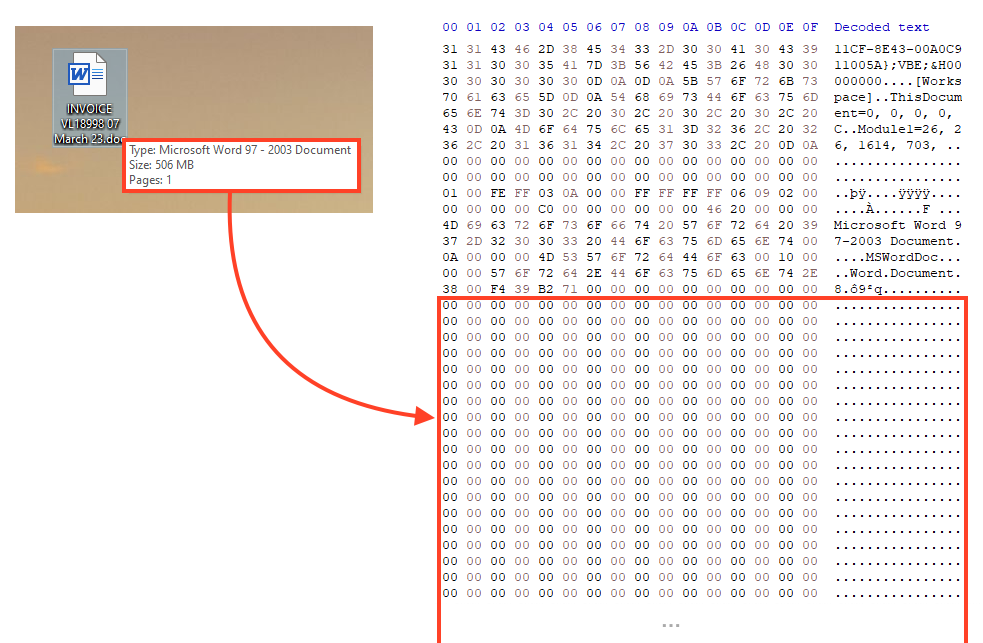
Emotet continues to use the same Office template that it has used since 2021, luring users to bypass Microsoft Office controls to enable malicious macros.
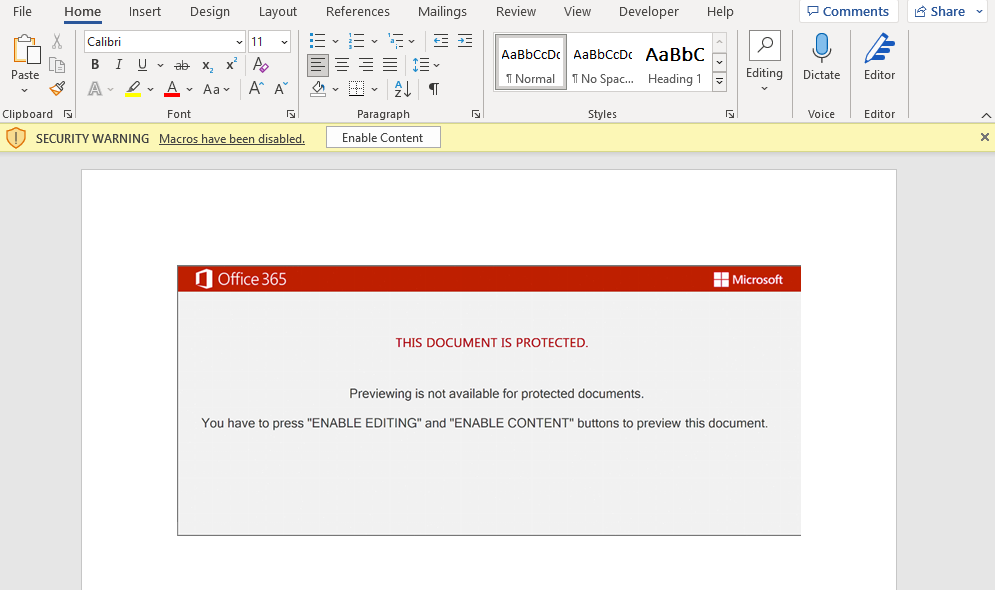
As usual, Emotet contains multiple URLs to download the second stage, which are obfuscated within the malicious macros. The code iterates through this URL list and tries to download the file. If the URL is offline, then it moves to the next one until it finds an online payload.
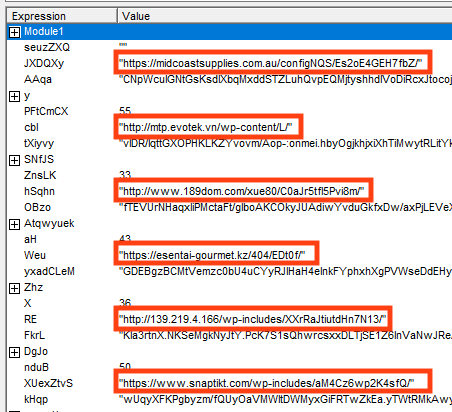
Netskope Threat Labs found three online URLs delivering two distinct payloads. Emotet attackers are also using the binary padding technique in the second stage payloads. These files were likely compiled on March 8 and March 9, 2023.
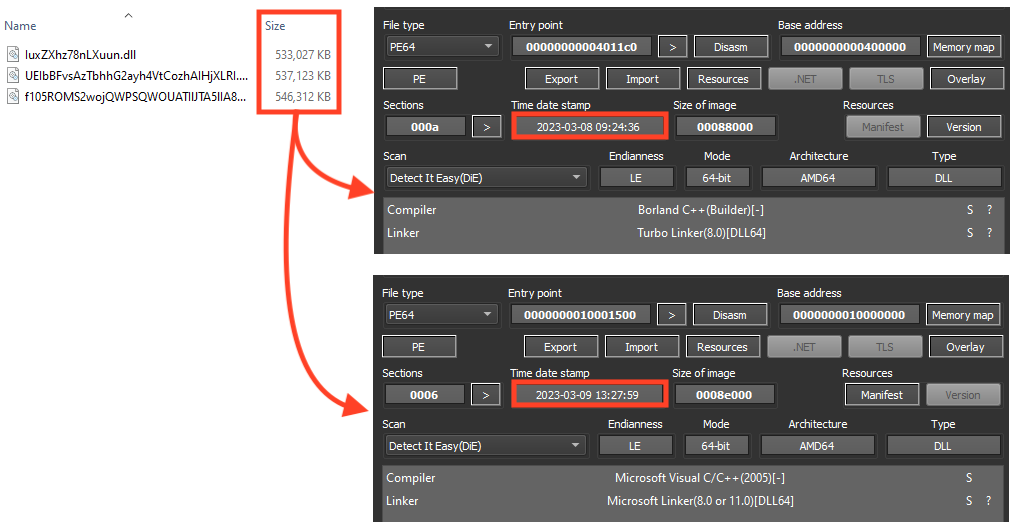
Like previous campaigns analyzed by Netskope Threat Labs, Emotet continues to store its main payload, and the shellcode that runs the payload, encrypted as resources in the second stage PE file.
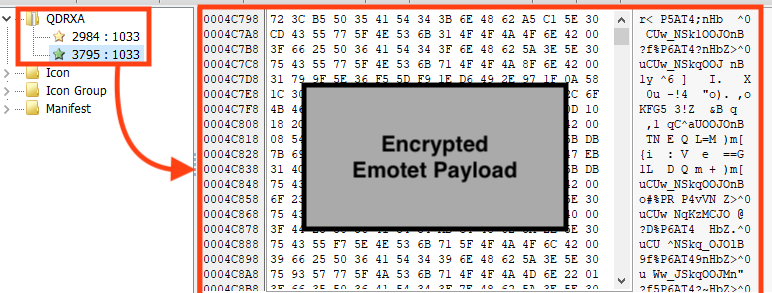
Once running, Emotet first decrypts the shellcode from the PE’s resources and then, using the same algorithm, decrypts its main payload to the process memory.
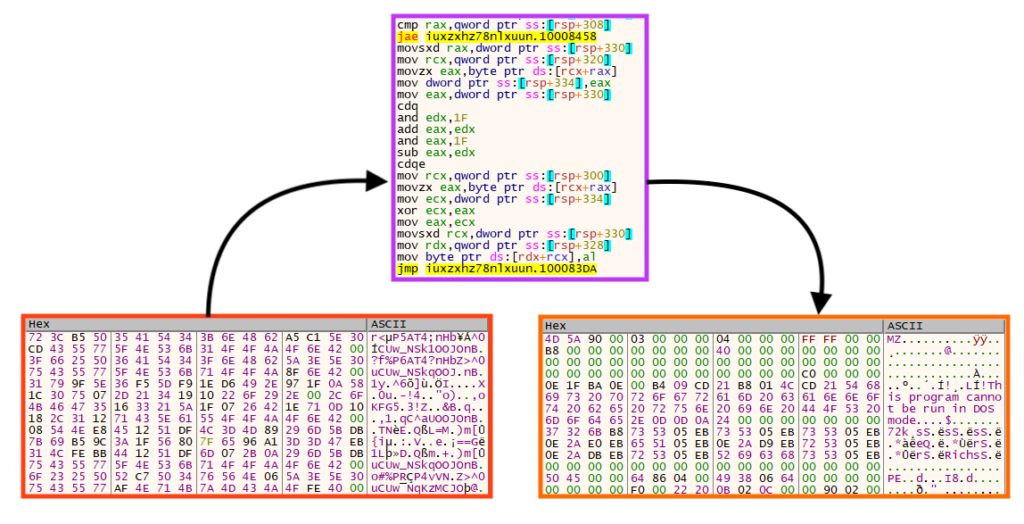
Once both resources are decrypted and allocated in the process memory, Emotet executes the main payload using the shellcode.
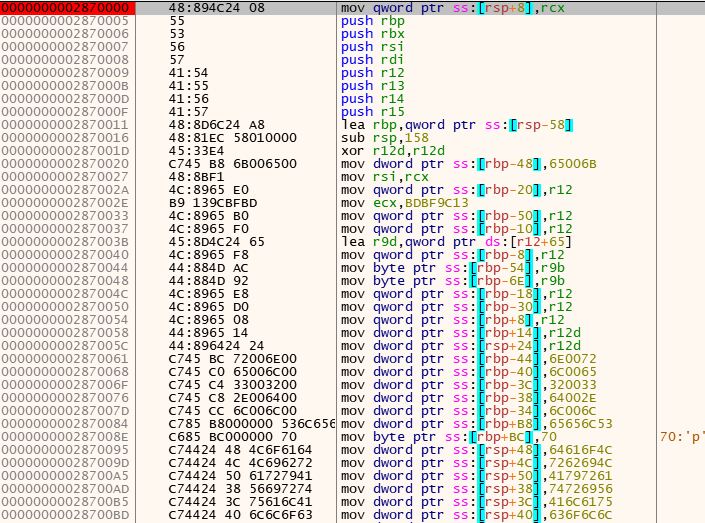
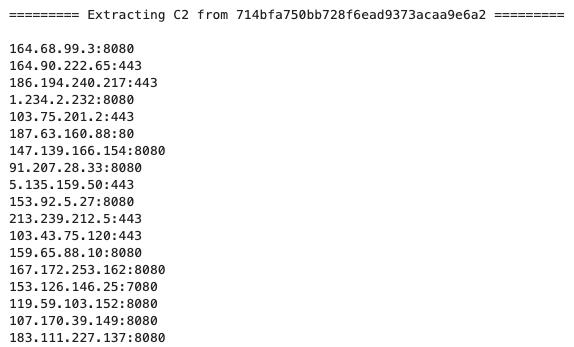
The final payload is very similar to the payloads analyzed by Netskope Threat Labs in May 2022. The encrypted strings and all the C2 server addresses can be retrieved by debugging the file manually or by using a script to virtually execute Emotet’s functions.
Conclusions
Aside from the binary padding technique, Emotet attackers are still using the same techniques as older campaigns, such abusing Microsoft Office files with the same template, spreading itself through spam emails, and using multiple URLs to download the second stage. There are also no notable differences in its main payload, so it’s possible to fetch strings and C2 server addresses through reverse engineering using the same process used in older payloads. Netskope Threat Labs will continue to monitor Emotet’s campaigns to track any notable differences in their TTPs.
Protection
- Netskope Threat Protection
- VBA:Amphitryon.683
- Win64.Trojan.Emotet
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
As an additional measure, Netskope customers can mitigate this attack by blocking large files from untrusted sources (e.g. Microsoft Office documents and PE files above 400 MB).
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign, scripts, and the Yara rules can be found in our GitHub repository.




 戻る
戻る 















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む