Introduction
The Internet was buzzing yesterday over a rapidly spreading attack involving malicious apps masquerading as Google Docs which gained permission to victims’ Google Gmail accounts and extracted confidential information. Netskope considers these type of attacks as CloudPhishing, as they are significantly more sophisticated than a traditional phishing attack, and exploit the implicit trust users have in well-known cloud services. With the enterprise adoption of cloud services and user trust in them becoming more ubiquitous, using cloud services for an attack has become irresistible to hackers. Netskope Threat Research Labs has observed and published analysis of many attacks in the last year that have used cloud services.
Yesterday, Google acted very quickly and mitigated the attack, but some users had already been compromised. Netskope Introspection customers can identify if any of their enterprise users had granted access to the malicious apps (yes, there were multiple apps) prior to Google mitigating the attack.
Additional details of previous CloudPhishing fan-out attacks detected by Netskope can be found in our original blog
How the attack worked
This attack involved only Google Gmail. A GIF animation detailing the attack was posted by a twitter user.
To start, the victim receives an email from one of their contacts who are also using Google Gmail. The subject as well as the body of the email references the sender with name and indicate that a Google document is available for viewing as shown in Figure 1.
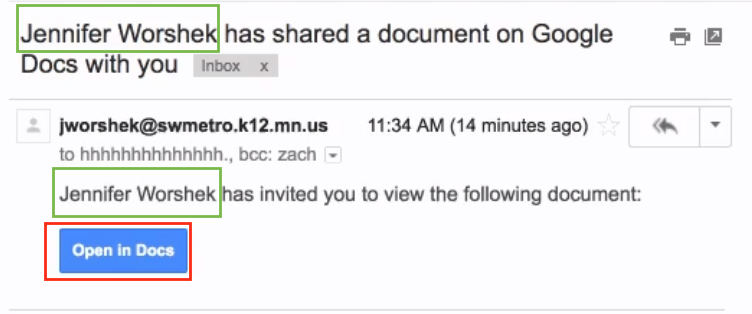
Figure 1: Targeted nature of CloudPhishing attack.
The email arrives from legitimate Google SMTP mail servers and also from a legitimate sender, therefore it is not detected by Gmail as a phishing email as shown in Figure 2. The use of the legitimate sender name along with the content of the email make it difficult for victims to identify that it is a phishing attempt.
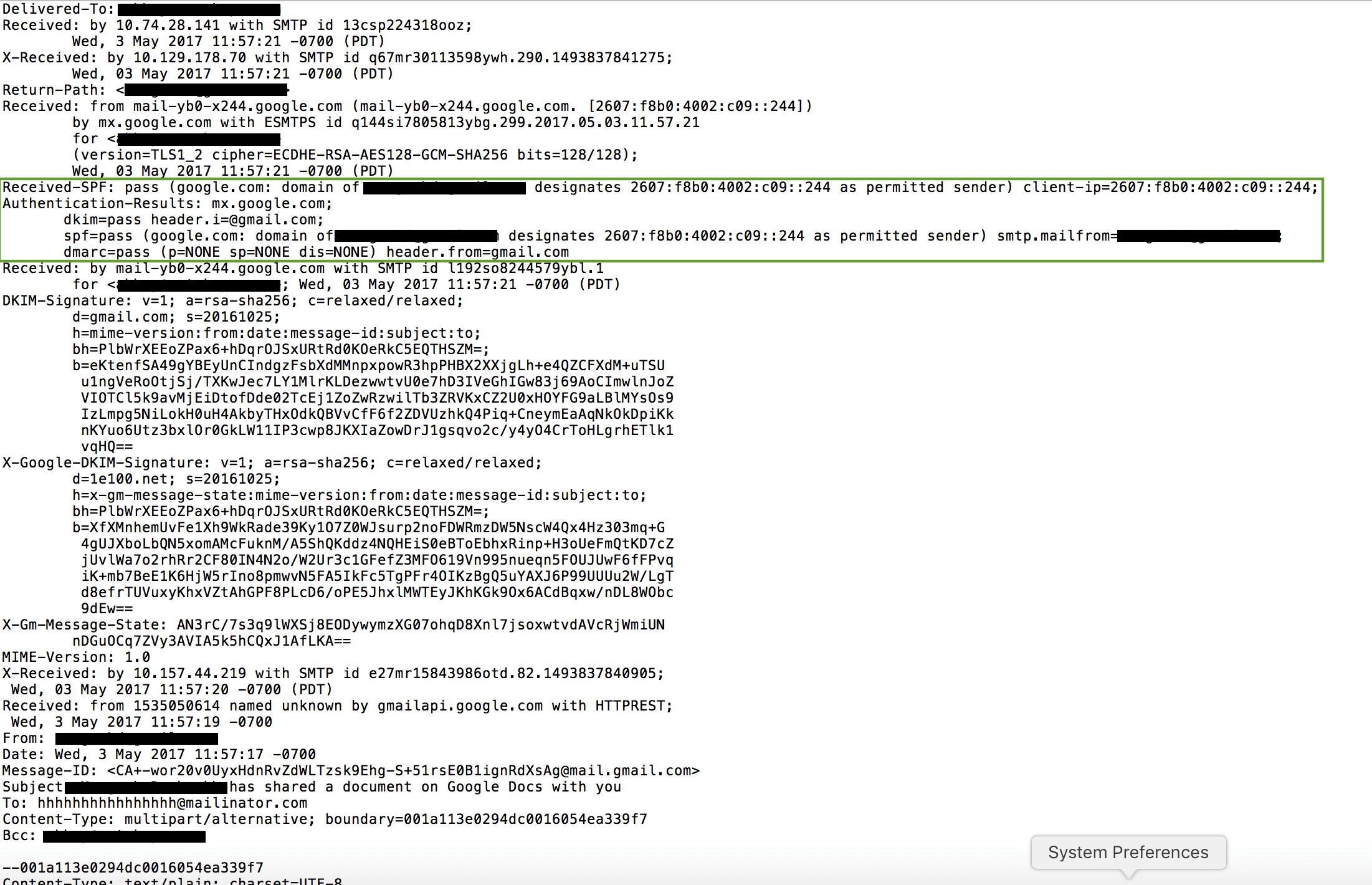
Figure 2: CloudPhishing message header showing use of legitimate servers
Once the user clicks on the “Open in Docs” button (link), they are taken through various HTTP redirects in the browser that eventually attempt to install a Google Gmail app developed using the Google Gmail API. Prior to asking the permission levels for the app during the installation, if the user is logged into multiple Gmail accounts or Gmail-hosted email accounts in the same browser, it would ask the user to select the Google account which they would like to grant the permission level as shown in Figure 3. As shown in the red box in Figure 3, the name of the app displayed is “Google Docs” which give the false sense of trust to the user that they are indeed installing a Google-built app.
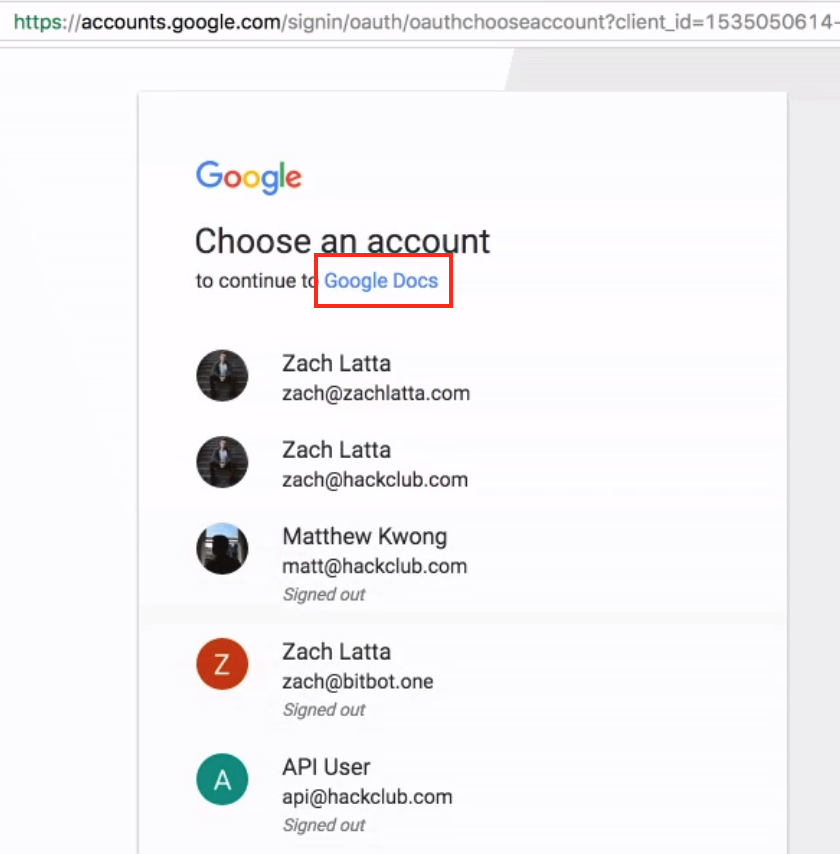
Figure 3: Crossing the trust barrier in a CloudPhishing attack.
Upon selecting one of the accounts, the app installation process now requests several different permission levels as shown in Figure 4. As we can notice in the red box within Figure 4, the app installation is requesting access to read, send, delete, and manage the user’s email.
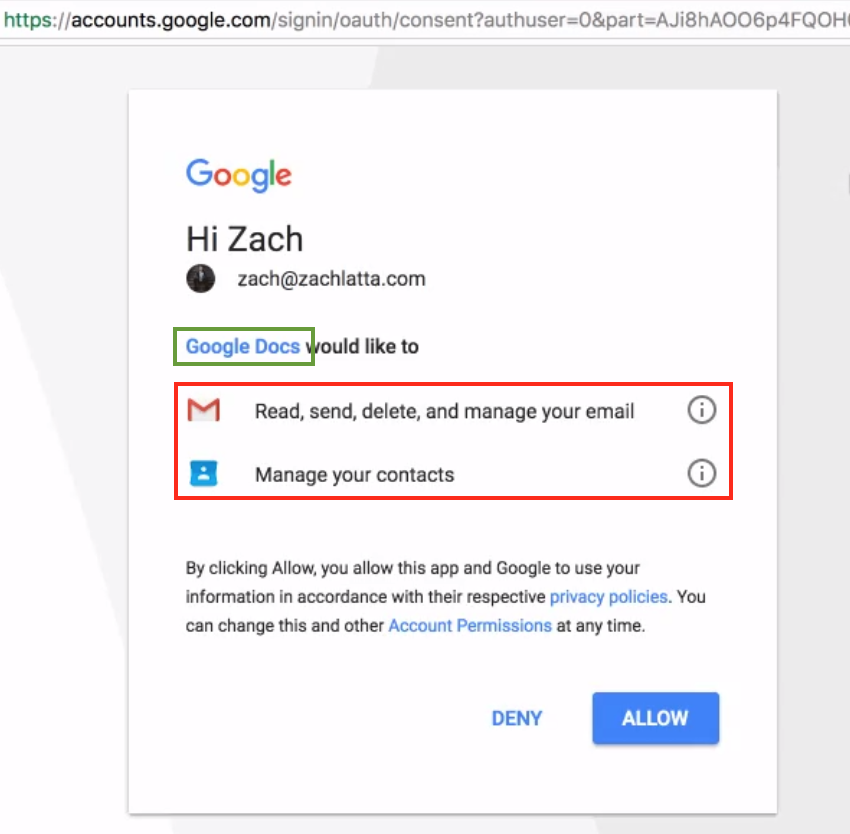
Figure 4: Tricking the user into granting open permissions
Once the victim has clicked “Allow” they have granted full permissions to their email account to the attackers. This complete process is typically referred to OAuth-based app installation which — in simple terms — means granting a token to the app author without giving them the actual password. This token can then access various resources within the email account based on the granted permission levels.
Upon clicking the “Allow” button, the victim is redirected to the attacker’s website along with the respective OAuth tokens. All of the final redirects are to a php page called “g.php” on the domains listed below in Table 1.
| docscloud[.]download |
| docscloud[.]info |
| docscloud[.]win |
| gdocs[.]download |
| docscloud[.]info |
| g-docs[.]pro |
| gdocs[.]pro |
| gdocs[.]win |
| docscloud[.]download |
| g-cloud[.]win |
| g-cloud[.]pro |
Table 1: Domains associated with this CloudPhishing attack
The source code to the redirect page “g.php” seems to have been leaked on pastebin. The review of the code identifies the logic where the attacker is subsequently using the OAuth token to access the victim’s email account to read all the “gmail.com” contacts. Subsequently, the script sends each of the victims’ “gmail.com” contacts the phishing email again using the OAuth token. The use of legitimate OAuth token make the emails received appear legitimate and are not identified as Phishing emails by Google Gmail itself.
What makes this attack so unique?
Though the motive behind the attack cannot be ascertained at this time, it is very evident that the use of cloud technologies and also the adoption of cloud services has created a completely new vector in the ever-changing threat landscape. In this scenario, there has been no use of any malicious file for infecting, propagating, or data exfiltration. In this particular attack, all these phases have now transformed into using Google Gmail application and all the network traffic looks legitimate proving traditional network security devices incapable of protection. There is absolutely no role of endpoint security products to detect and protect against such an attack.
Another important aspect is the rise of a new class of threats leveraging OAuth protocol implementations called “Cross App Instance Grant”. As seen in the attack flow Figure 3 above, the phishing attempt that was happening on a particular Google account can transform into a user granting permissions to the app on a completely different Google App Instance. This could be the very reason that we were able to identify a number of enterprise users that used Google G Suite with their custom domains (not gmail.com) have granted permissions to this app (though as per pastebin source code mentioned above the attack was targeting only Google “gmail.com” domain email accounts).
The implicit trust that users place on the SaaS app vendor names used in various contexts such as app names, email subjects, icons, etc. make these users so much more gullible for phishing attacks. In this particular attack, the ease with which such trust was exploited is of big concern to individual users as well as enterprises. For example using few clicks and code we were able to create and demonstrate a fake Google Drive API-based app with the name “Google Sheet” as shown in Figure 5 and 6.
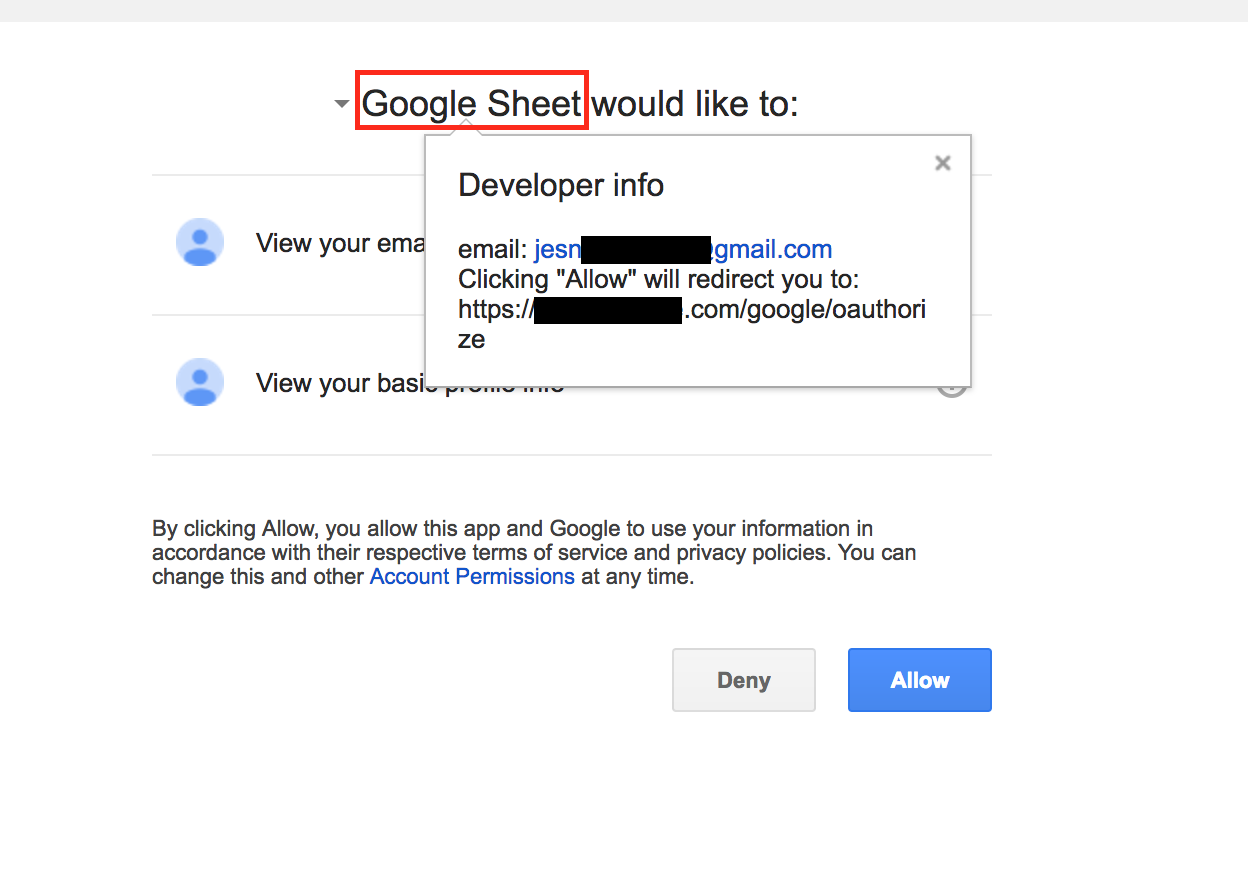
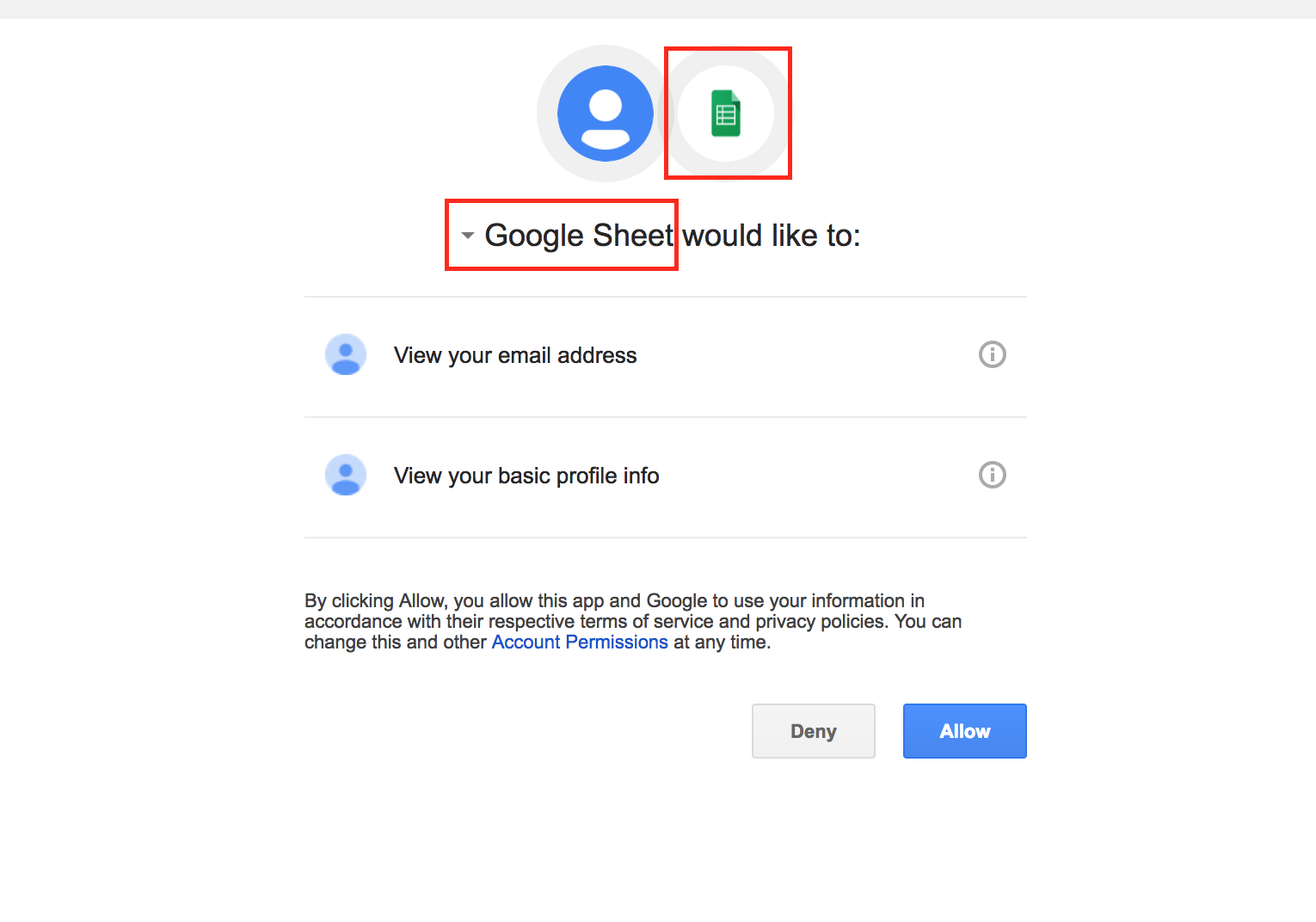 The use of one of the top cloud app types, Email, along with an OAuth based app that used the final redirect URI page to automate the exfiltration of email addresses and further propagate by sending phishing emails that enticed even more users has demonstrated the next evolution of worm propagation.
The use of one of the top cloud app types, Email, along with an OAuth based app that used the final redirect URI page to automate the exfiltration of email addresses and further propagate by sending phishing emails that enticed even more users has demonstrated the next evolution of worm propagation.
Netskope findings, impact, and steps for remediation
Netskope Threat Research Labs identified a number of enterprise users across multiple verticals that had granted permissions to the malicious apps. It is interesting to note that the attackers had created at least 9 different apps using the Google Gmail API.
Though Google has quickly mitigated the attack, the time between when a victim granted permission to the app to when Google mitigated the attack could have been used for data theft including reading/copying emails, reading/copying contacts, downloading email attachments, etc. If an enterprise has identified that their users have granted access to the app in this attack, we recommend they conduct a full audit of the activities that were performed in Google Gmail after the permissions were granted to the app.
Best Practices
Netskope recommends the following to combat CloudPhishing and malware threats:
- Use a threat-aware cloud access security broker to continuously monitor the scope of app permissions granted by enterprise users
- Detect and remediate all threats, even for data at rest, across all the sanctioned instances of cloud services using a threat-aware cloud access security broker
- Detect and remediate all threats being downloaded from permitted cloud services, including unsanctioned instances, using a threat-aware cloud access security broker solution
- Actively track usage of unsanctioned cloud services and enforce DLP policies to control files and data enroute to or from your corporate environment
- Conduct regular CloudPhishing tests of the end user to ensure that users are able to recognize the attack and act appropriately
- Disallow users from authorizing apps, and disable allowing less secure apps
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Uncheck the option “Remember this action for this site for all PDF documents” in the PDF reader software
- Hover your mouse over all hyperlinks to confirm them before clicking on the link
- Actively track URL links added to the “Always Allow” list in PDF reader software
- Avoid executing any file unless you are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users to avoid opening untrusted attachments regardless of their extensions or file names
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Zurück
Zurück















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen