Co-authored by James Robinson and Nathan Smolenski
2020 was a tough year. As security leaders, we faced new challenges in protecting applications and users who were shifting rapidly off-premises and into the cloud, and our security teams’ workloads grew at an unprecedented rate. In 2021 and 2022, CISOs need to prioritize ensuring that we’re focused on the right things. With Blackhat and DefCon shaping up to be the first large, in-person cybersecurity event, it’s a great time to ask what threats are we facing now, and what do we expect to be coming at us in the next 18 to 24 months?
Currently, most CISOs are firmly focused on the threats right in front of our faces, not on leveraging known intelligence to understand what may be just past the horizon. The majority of security professionals are just now beginning to realize that most threats entering companies these days are coming through cloud infrastructure—already a reactive approach to security in this time of transition will not reflect well on us over the next few years. Many of the models we use such as MITRE ATT&CK are robust, but too often can quickly fall behind the times, while not focused on the future. Meanwhile, our teams, the news, and the intel community see newer methods that are on the edge of becoming new attack vectors.
To support better communication with our teams and leadership, security leaders need to develop a systematic process for understanding the threats we faced yesterday and will face today, tomorrow, and beyond. There are a variety of approaches to threat modeling. At Netskope, we have a regimented process. At least once a year, our security team systematically measures our threat exposures. We make sure we thoroughly understand each one, rating its relevance, velocity, and potential impact on infrastructure and business operations. Then, we generate a graphical depiction of the threat landscape specific to our company—a visual tool that can be understood by staff and management at every level, regardless of technical expertise.
This doesn’t guarantee that we won’t be blindsided—no model does—but the three-step exercise outlined below helps us understand, communicate, and prepare for the threats we will likely face in the near future. These threats help us to focus our efforts, communicate clearly, understand our position, as well as use this as an update to our risk register and matrix. It’s a threat assessment model I often suggest security teams pursue if they haven’t yet developed their own such models or capabilities.
1. Collect existing and emerging threats
The first step is to list all the threats we’re seeing, as well as those that we’re not seeing yet but are anticipating. The prior year’s threat model is a useful jumping-off point, but the cybersecurity environment is continuously evolving, so we intentionally seek out changes from year to year.
This is a group exercise that encompasses many perspectives. We consider:
- What attacks has Netskope faced over the past year?
- What new types of attacks have we read about since our last threat modeling exercise?
- What exposures are our peers, competitors, and software providers talking about?
- Are there updates to the MITRE ATT&CK framework that may create exposures for our business in the near future?
- What geopolitical, physical, environmental or other emerging risk areas, need to be considered when creating and updating our collection of threats to analyze?
Then, we model each threat on the list, to make sure we understand where and how it poses risk to our business. There are a lot of different forms of modeling. Some are very detailed, while others are simple flowcharts that can be put together in a team-building exercise. Here is a model that Netskope developed to describe threats to a specific technology that we are no longer using.
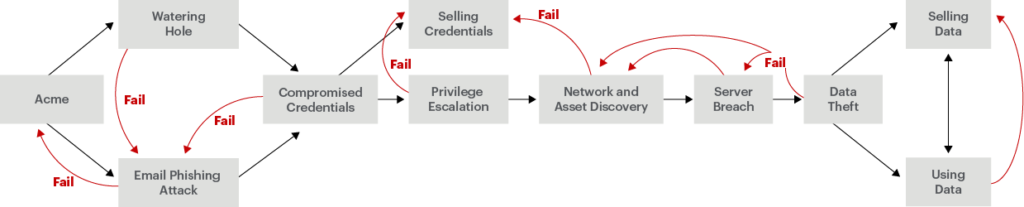
The gray arrows represent information flows, and the red arrows indicate points where potential failures re-emerge or can pivot. For example, a watering hole or a phishing attack might gather user credentials. Attackers might sell those credentials or utilize them to access the application in question. From there, they might be able to discover and access resources on the network, potentially moving from the application we’re modeling to internal servers that hold sensitive data.
Developing this type of model ensures that everyone within the security team shares a common understanding of the threats posed to our organization. It is standard practice within our team to build these out for each threat identified in our assessment and to refer to it as needed throughout the year.
2. Describe the threats
Our next step is to evaluate each threat in terms of several characteristics. We use a rubric similar to this:
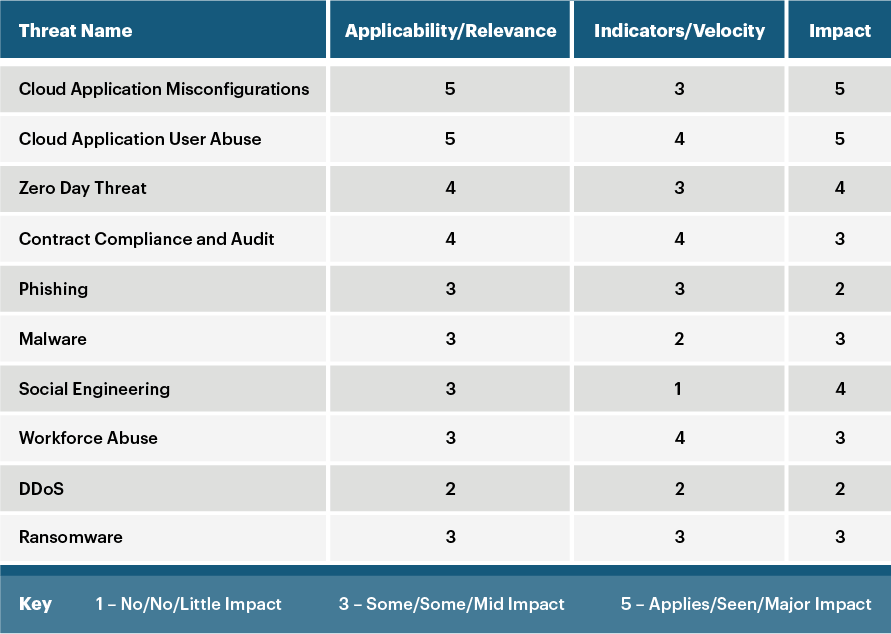
To make it easy we rate the threat from 1 to 5 on three different facets that affect its risk to the organization, answering a number of questions as we determine the appropriate rating.
Applicability/relevance. To what degree does this threat apply to us? Are there any indicators that the threat has been exploited against us over the past year (or another timeframe)? Have Netskope’s peers or partners seen it? Has a trusted source either reported its occurrence or predicted its emergence over the next 12 months? Alternatively, does the threat have certain prerequisite conditions—such as location in a floodplain—that make it irrelevant to our facilities?
Velocity. Is this threat currently a problem for us? Do we expect it to grow in reach over the next year? If it hasn’t yet emerged, is it right around the corner? At what point do we expect it to pick up steam? (For instance, software supply chain attacks—like the huge SolarWinds breach—are starting to happen with increasing frequency.)
Impact. How much impact would a successful attack have on our business? Would it cripple our supply chain? Would it lead to a customer relations disaster? Or would its most likely outcome be a continuation of business as usual if we just tighten certain defenses or pay a modest fine to regulators?
3. Communicate risk information, update detection and mitigation strategies
After completing the rubric, Netskope determines what controls we have in place to deal with each threat deemed applicable and relevant to our organization. We consider whether those controls give us adequate visibility and/or protect us from attacks along this particular threat vector. We also evaluate what actions we are prepared to take in the event that our controls detect an attack.
Then, we consolidate all this information into a visual “organization risk summary” that maps the threats we’re facing, as well as the mitigation efforts and countermeasures we’re adopting. The graphic looks something like this:
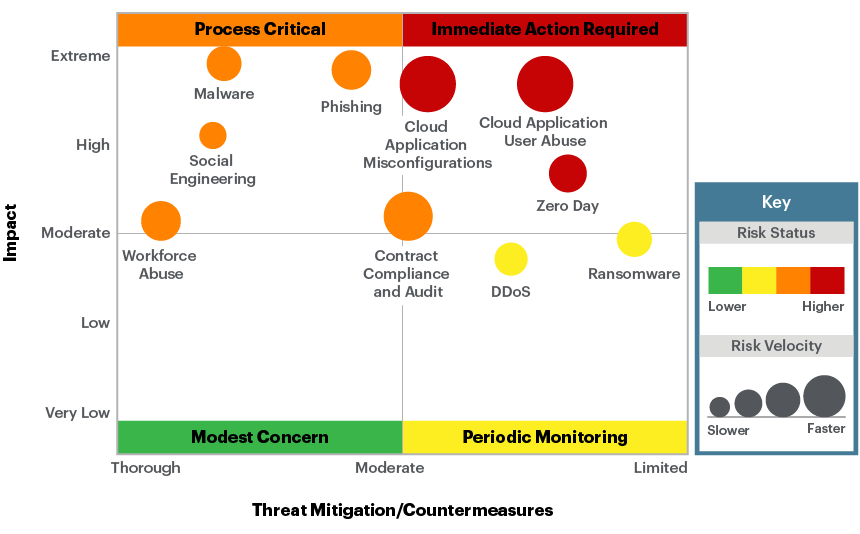
Threats in the top right quadrant have the potential for an extreme impact to carry to our business, and we have limited countermeasures in place. Anything that appears there presents a high risk, and threats represented by a large circle are rapidly evolving. These threats should command a great deal of our security team’s attention over the next year. By contrast, we expect that successful attacks of a type in the chart’s bottom-left corner would have a low impact on our organization, and we are confident in our countermeasures. Thus, these threats are green in color.
The visual format of our risk summary report makes it accessible for everyone up and down our organizational chart. For the C-suite and board, we do this by using relatable examples like food safety or operations threats. The savvy security leader always has stories in their back pocket to support scenarios covered in the analysis. The security team can use this analysis to prioritize projects over the coming year. They can see where technical or procedural enhancements are most critical, and update the organization’s detection and mitigation strategies for each type of threat.
The prioritization can also be used for budgetary purposes. When technical and procedural enhancements require additional investment in people, process, or technology spending, the threat models can help to dictate, in a risk-based manner, where investments can make the biggest impact to reduce risks and or close identified gaps.
At the same time, the CEO and board can easily understand which threats we’ve identified as our biggest concerns and why. They will have confidence in the organization’s approach to cybersecurity and have a helpful guide to making the right investments in relevant resources to reduce or better manage identified risks.
This also allows security leaders to be more illustrative about what our teams are focusing on, as opposed to just answering the broad question of “Are we secure?” When thinking about the planning and execution of activities such as validating IR plans, red/blue/purple team activities, and engaging executives for tabletop exercises; framing those activities on the basis of the modeled threats will enable much more effective, real-life scenarios for preparedness. This all helps us drive a better understanding of what threats our organizations actually focus on, as opposed to the perception of what we protect against.
Vigilance is vital
The threat landscape will continue to evolve rapidly, and security teams are constantly at risk of being overwhelmed. A systematic approach to regularly evaluating, prioritizing, and understanding the organizational threat landscape provides a tool for clear communication company-wide and is crucial for cutting through the noise to make sure that threats the CISO prioritizes are clear and thoroughly explained to every stakeholder.




 戻る
戻る
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む