Summary
LockBit (a.k.a. ABCD) emerged in September 2019 and became one of the most relevant RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) groups among others like REvil, BlackMatter, Night Sky, Maze, Conti and Netwalker. The group targets many organizations around the world with a double-extortion scheme, where the attackers steal sensitive data and threaten to leak everything if the ransom is not paid.
The LockBit group was recently the target of two important events. The first one was a DDoS attack that took their websites down for a couple of days. And the second was a leak of the LockBit 3.0 (a.k.a LockBit Black) ransomware builder, which allows anyone to generate the necessary files to build LockBit payloads, such as the encryptor and decryptor. This blog will cover both the timeline and the details of this leak.
Timeline
In June 2021, the RaaS group announced LockBit 2.0, which included a redesigned leak website and code improvements, such as automatically encrypting Windows domains using Active Directory group policies. LockBit was also actively trying to recruit insiders that could help them breach and infect corporate networks.
In June 2022, LockBit announced a 3.0 version (a.k.a. LockBit Black) becoming the first RaaS group to offer a bug bounty program, paying security researchers between $1,000 up to $1 million for security vulnerabilities found in the website or in the ransomware software. They also announced a payment for any “brilliant ideas” that could aid the group to improve their operation.

Furthermore, the third version also introduced code in the website that was indicating a new extortion model, where people would be able to buy stolen data leaked on their website. This new version also included code improvements, such as new anti-analysis features.
In August 2022, LockBit suffered a DDoS attack that shut down their websites for an entire weekend, supposedly in response to an attack made against the Entrust company, according to a message left in DDoS HTTPS requests. In the same month, LockBit announced improvements in their defenses against DDoS attacks, such as using unique links in the ransom notes for the victims. Also, they announced that they were taking the operation to a triple extortion method, by performing DDoS attacks against victims who refuse to pay the ransom on top of leaking or selling the stolen data.

In September 2022, a newly registered Twitter account claimed that their team was able to hack LockBit servers and find the LockBit 3.0 ransomware builder, sharing a download link to the files. It was found later that this leak was not the result of an attack, but leaked by a developer who was disappointed with LockBit leadership.
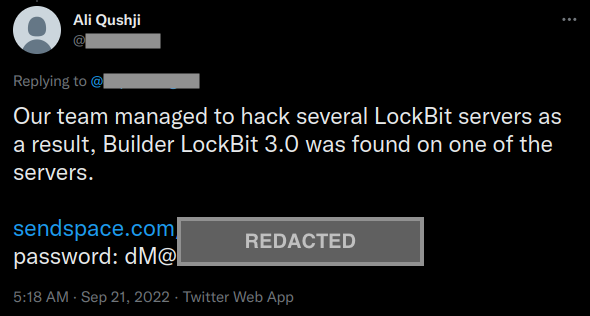
Netskope Threat Labs confirmed that the files leaked by this Twitter account are indeed the builder of LockBit 3.0, as we will show later in this post. LockBit 3.0 remains active despite this leak, as we can still observe recent activities on their website.
LockBit’s Website
The leaked LockBit 3.0 website (a.k.a. “wall-of-shame”) is still online. We can observe recent activities on the website, where the group adds information about breached companies along with the ransom deadline, which is the same behavior we documented previously.
The website also contains a page with information about the affiliate program.

This page contains the affiliate program rules, the description of LockBit’s functionalities, allowed and forbidden types of companies to target, affiliate profit percentage, and more.

According to the website, the affiliates receive 80% of the ransom and the remaining 20% should be paid to the LockBit group.

As previously mentioned, LockBit also offers a bug bounty program that offers remuneration based on:
- Website bugs;
- Locker bugs;
- TOX messenger vulnerabilities;
- Tor network vulnerabilities;
- Doxing (whoever finds the affiliate program boss);
- Brilliant ideas;

Furthermore, the website has a counter that shows how many days LockBit has been operating.

Leaked LockBit 3.0 Builder
The ZIP file leaked by the Twitter user contains the necessary files to build the encryptor and decryptor of LockBit 3.0, being:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| builder.exe | Executable used to generate both encryptor and decryptor of LockBit. |
| keygen.exe | Executable used to generate the RSA public and private key pair. |
| config.json | LockBit’s JSON configuration. |
| Build.bat | Batch script that executes the required files to build LockBit files. |
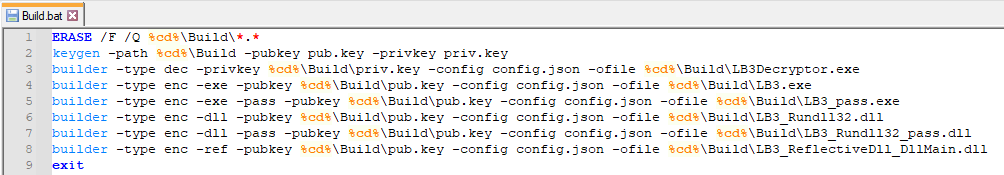
The batch script is used to simply execute the necessary files to build LockBit’s encryptor and decryptor. This is done by first generating the RSA key pair and then calling the builder executable.
All the files are created within a folder named “Build”.
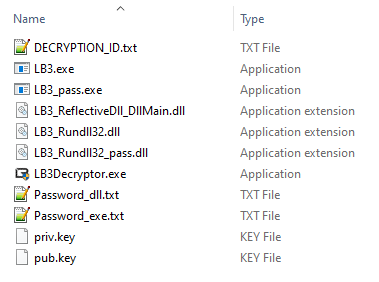
The folder contains the RSA key pair and the decryption ID, which is required to access the victim’s website to contact LockBit support.
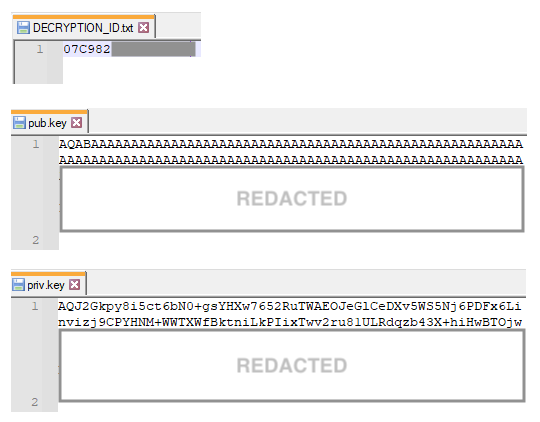
It also contains instructions on how to execute LockBit.
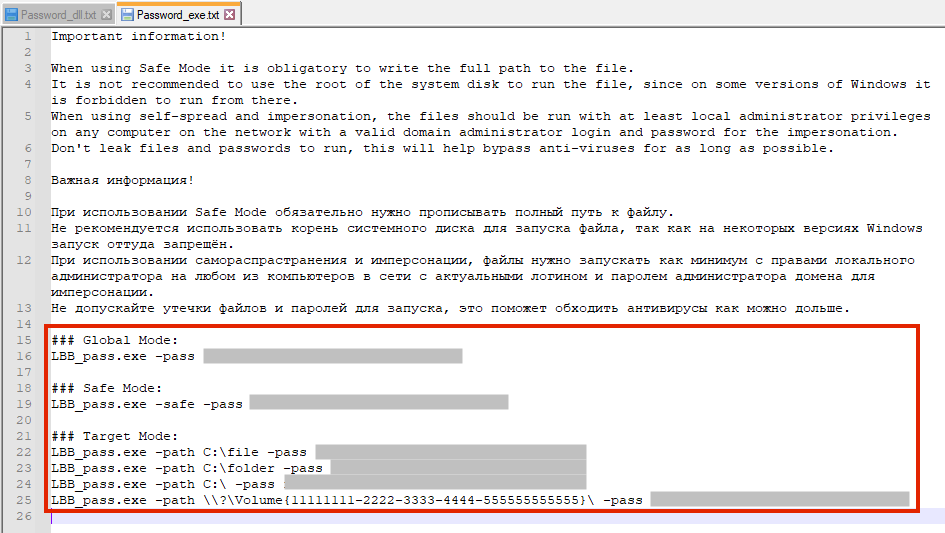
We tested the encryption process by running the same command line as suggested in the text file above.
Like other ransomware, LockBit also changes the wallpaper with the ransom message.

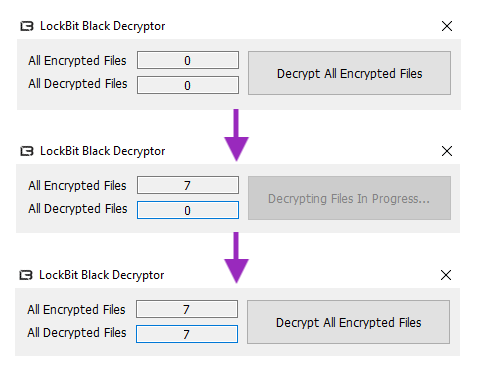
Lastly, we tested the decryptor executable and we confirmed that it was able to decrypt all the files using the key generated previously.
Conclusions
This is not the first time that details and files of a ransomware group have been leaked by members, as we can remember with the Conti ransomware case, where individuals decided to leak inside information after the group declared support to Russia in the Ukraine invasion.
This leak likely caused an impact on LockBit, since one could try to build and deploy a ransomware payload without being an affiliate by using the leaked files. However, we believe that this is not something that will disrupt the group, as the RaaS model is more appealing to affiliates, since they can use the “official” website and the support infrastructure provided by the group.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring LockBit and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Gen:Variant.Ransom.Lockbit3.10
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox




 Back
Back
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む