Summary
LockBit Ransomware (a.k.a. ABCD) is yet another ransomware group operating in the RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) model, following the same architecture as other major threat groups, like REvil. This threat emerged in September 2019 and is still being improved by its creators. In June 2021, the LockBit group announced the release of LockBit 2.0, which included a new website hosted on the deep web, as well as a new feature to encrypt Windows domains using group policy.
On August 11, 2021, the LockBit ransomware group announced in their deep web forum that they have infected the global IT consultancy company Accenture.

According to the company Cyble, the attackers have allegedly stolen about 6TB of data, and are demanding $50M (USD) as ransom. Also, Cyble mentioned that this attack was supposedly carried out by an insider, however, that has not been verified yet. The IT giant Accenture has confirmed the attack and also affirmed that the breach had no impact on their operations or systems.
The period established for Accenture to pay the ransom was August 11, 2021, which has now passed.
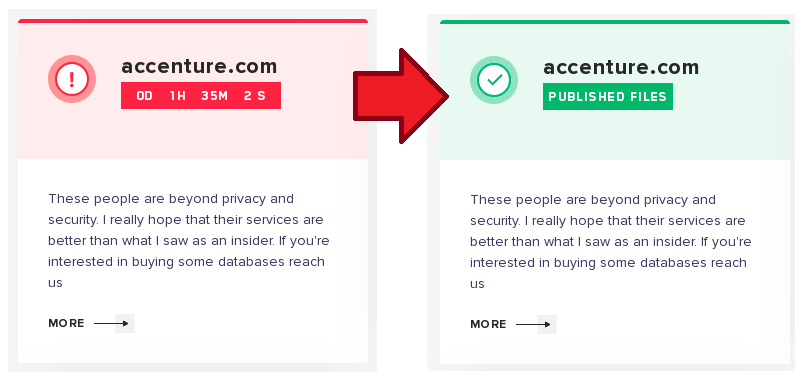
However, as I am writing this blog post, the period to pay the ransom was changed to August 12, 2021, at the end of the day.
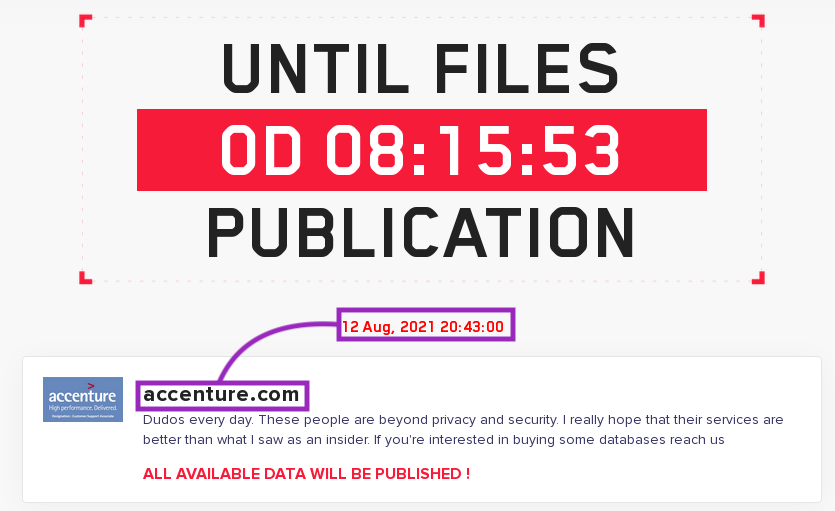
At this point, it’s unclear how the attack was carried out, or if LockBit really stole sensitive data from the company. In this threat coverage report, we will briefly show how LockBit works, describing some features used for anti-analysis.
Threat
LockBit ransomware is developed in both C and Assembly and uses AES + ECC to encrypt the files. The group operates in the RaaS model, and on their official website hosted on the deep web, we can find an advertisement trying to attract more affiliates into the scheme.

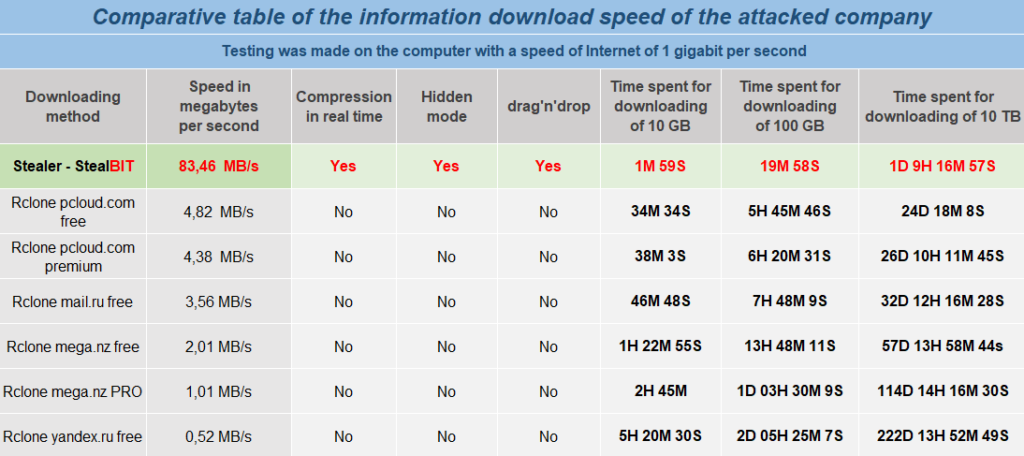
According to the page, the group is using a custom stealer named “StealBIT” to exfiltrate data from companies. They have even included a comparison between their service and other services, like MEGA and pCloud.
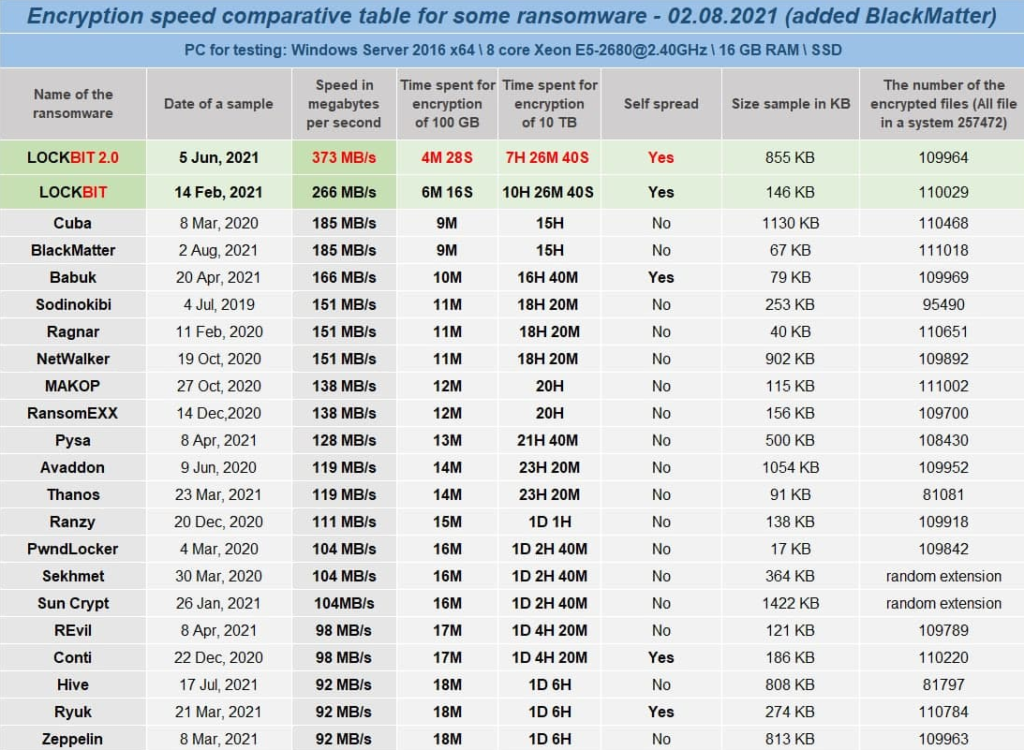
The website also includes an encryption speed comparative between LockBit and other ransomware families, such as Ragnar, REvil, Conti, and others.
Once the sample is executed, the code implements a very simple technique to detect if the process is being debugged, by checking the NtGlobalFlag value in the Process Environment Block (PEB) structure. This is usually done to avoid direct calls to the function CheckRemoteDebuggerPresent or IsDebuggerPresent.
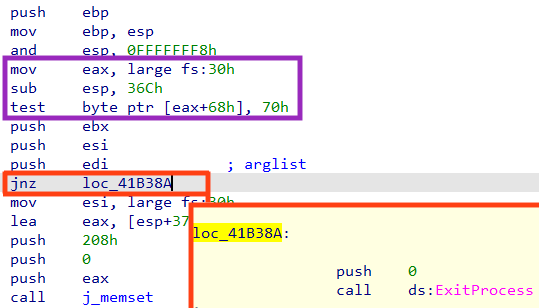
Also, LockBit verifies if the process is running with Administrator privileges by checking the return of the API OpenSCManagerA. If it’s not a privileged process, the function will fail, consequently reaching the ExitProcess call.
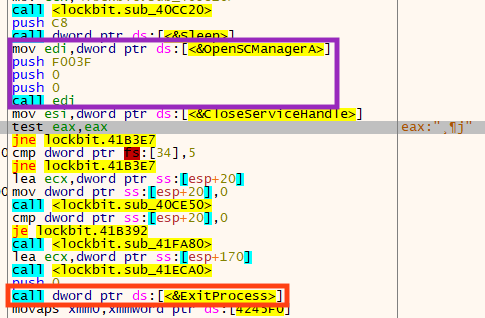
The sample also uses a Mutex to verify if there is another instance of LockBit running at the same time.

Looking at the PE .rdata section, we can see that LockBit attempts to protect some relevant information by encrypting the strings, which is just a basic protection against detection or quick analyses.
Furthermore, we can observe that LockBit is using Intel 128-bit XMM registers in the operations, probably to increase the performance of the code.
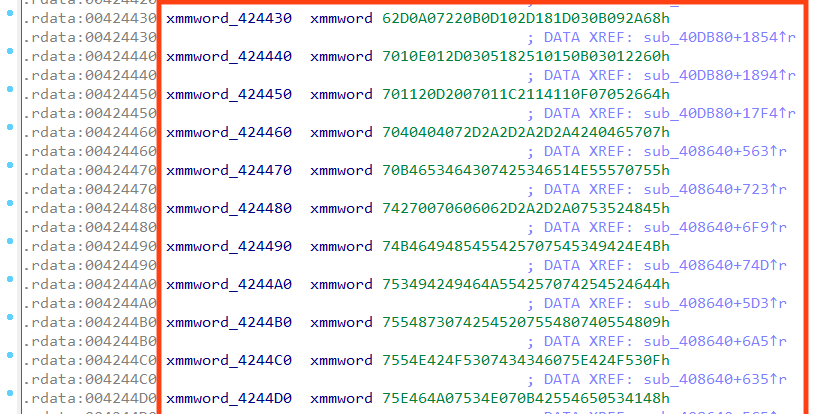
The algorithm is straightforward — it decrypts the string by doing a single byte XOR operation, using the first byte of the string as a key.
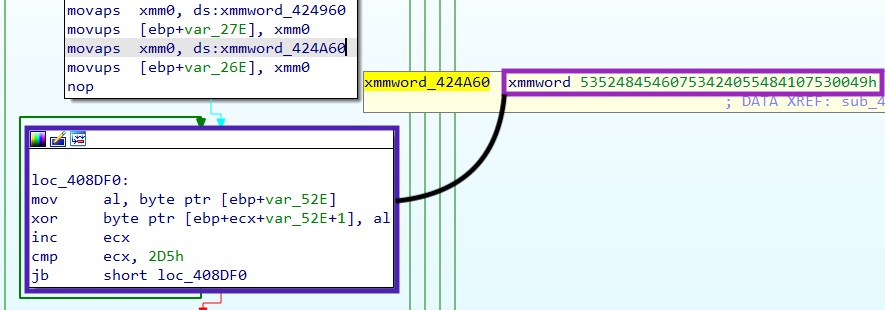
It should be possible to decrypt LockBit strings applying the same logic.
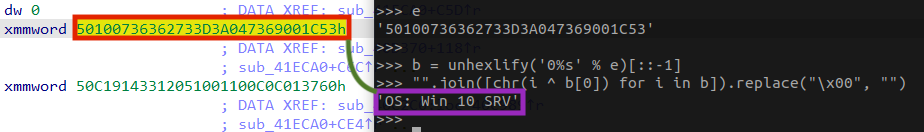
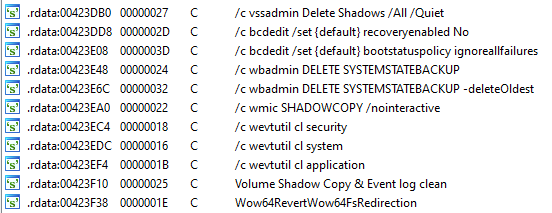
In addition, LockBit also executes a series of commands using the API ShellExecuteA to avoid any restoration of the files in the machine by disabling the system’s recovery mode and the Windows Shadow Copies.
After the files are encrypted, LockBit creates the ransom note in every single directory where there are encrypted files.
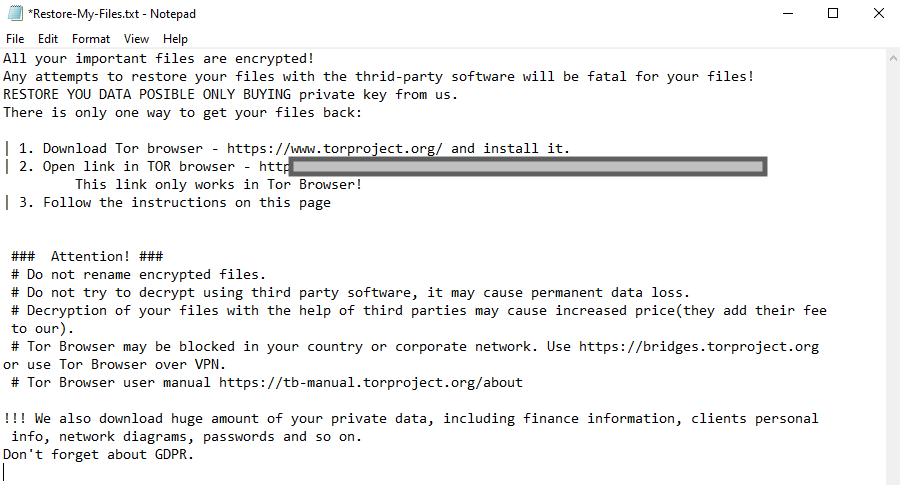
Lastly, the computer’s wallpaper is also changed by the malware, in case encrypting the files wasn’t enough to catch the victim’s attention.

Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Generic.Ransom.LockBit.19F98D1F
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
SHA256
6292c2294ad1e84cd0925c31ee6deb7afd300f935004a9e8a7a43bf80034abae
A full list of IOCs and a Yara rule are available in our Git repo.




 Back
Back
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む