Over recent weeks, many organizations rapidly adopted new remote worker policies and practices without having the benefit of time or meaningful historical data to inform the architectural decisions needed. Coupled with the adoption of video, web and VoIP conferencing technologies, an unprecedented strain has been levied across IT resources which were built for a different time.
In this blog series, I’ll dive deeper into the architectural challenges to consider and provide perspectives on how we have been assisting organizations meet their immediate needs for secure connectivity, threat and data data protection from anywhere and for any device.
Traditional VPN Implementations
A traditional VPN configuration uses a single VPN concentrator/gateway for ingress to the network. This is because in the past, users were remotely accessing applications in a data center, so it makes sense to place the VPN concentrator in the data center as well.
Another advantage of this configuration is that traditional network perimeter designs also placed a variety of protections at the organization’s internet egress point. Therefore, by bringing traffic back to HQ, the organization was able to reuse the protections it put in place for on-premise users.
However, the use of a full tunnel to a single VPN gateway is not the optimal for cloud applications. This is especially true as organizations migrate their data center applications to the cloud. The network team is tempted to implement a split tunnel as an alternative to a full tunnel, which allows internet and cloud traffic to route over the user’s normal network connection. With split tunnel, the remote user has a shorter path to the internet and cloud, but the traffic would be uninspected.
Split-Tunnel vs. Full Tunnel Configurations
Most organizations size their VPN based on some assumptions of what their normal remote workload looks like. For example, a common model is to size your VPN requirements based on typical historical workloads, such as using an estimate that no more than 30% of your workforce is remote at a given time, and presuming that the trend will continue.
What happens if you deploy your remote access VPN with a full tunnel, and the number of remote workers or the application mix suddenly changes? A configuration based on past assumptions can quickly overwhelm the number of connections that you can support on the gateway and amount of bandwidth that’s available.
Route All Traffic through the VPN: The Bandwidth Challenge
VoIP and video collaboration tools are popular, mainstream applications that require bandwidth between users at a minimum (in peer to peer configurations) and to the cloud as well when using an application with a cloud server. Network teams normally have time to plan and implement capacity before the application’s rollout, based on the projected use.
Take Zoom for example, a popular choice for enterprise video conferencing. For one on one video calls, a Zoom session at 720p video requires 1.2 Mbps of bidirectional traffic for each user. A network architect planning the rollout might look at the number of total employees, and the number of people that need conferences on a given day.
These assumptions can be very misleading when dealing with application mixes and mobile populations that can rapidly shift. For example, with the prevalence of work from home policies now being implemented, and all meetings being done virtually, the amount of required bandwidth required no longer fits the assumptions of the original model. If we hypothetically take a 2000 person company, operating primarily in one geography, and each user spends half of his/her day in meetings (in other words, at any given time, the user has a 50% likelihood of being in a meeting), then the corresponding amount of bandwidth required thus becomes:
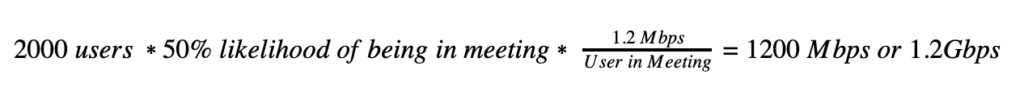
Thus, a surge in remote workers or change in application use could easily create a scenario that quickly consumes any headroom in a configuration that was normally working fine in the past. For example, suppose the company maintains a 2Gbps link at HQ.

It’s not Zoom’s fault that this change is happening, but rather a byproduct of its necessity as one of the key tools that enable the remote worker to be collaborative and stay productive. It’s a major jump in the amount of unexpected traffic that can change overnight under these circumstances. Not to mention, there is no additional security benefit for bringing this traffic through HQ, given that it’s certificate pinned and not inspectable with SSL decryption in the enterprise firewall.
Unfortunately, throwing more hardware or adding more software licenses to your existing VPN infrastructure may not help. If the organization switched to a configuration with multiple VPN concentrators, then it could distribute the ingress of VPN traffic, but introduces new issues:
- The problem of fixed resources is not addressed – each site has finite capacity and population shifts could still overwhelm a location.
- If the security stack is still at the corporate data center and all traffic still egresses from a single location, then the original bandwidth problem at egress still exists.
- If the network team adds additional egress points, then it must replicate the legacy appliance security stack at the new location or otherwise leave the organization vulnerable to cyberattack.
So in this scenario, there’s pressure from both the network teams to quickly move off of a full tunnel configuration, with no good option for how to do it. Quickly shifting to a new configuration might solve bandwidth issues but the security will suffer as a result.
Split-tunneling VPNs: The Security Challenge
If the organization switches to a split tunnel VPN, then the user’s Zoom traffic goes direct-to-internet over the local connection. The problem, however, is that it also lets all web and SaaS traffic out to the internet as well, with no visibility or enforcement of policy. What seemed like a solution to the organization’s networking problem introduces a major security problem.
It’s also now introduced a new access control problem as well. Hybrid cloud applications use a combination of the enterprise data center with virtual private cloud resources. It remains problematic to route the traffic to HQ to reach the virtual private cloud, but to do otherwise creates security challenges.
A Better Approach – Using the Netskope Security Cloud Platform
To use the applications that mobile workers need without the congestion problems that are often seen with traditional VPNs or the security gaps with a direct-to-internet strategy, use the Netskope Security Cloud. We deliver our services on a network architecture called NewEdge, which is a global, high-capacity private security cloud that delivers converged network access and network security. We share a design philosophy with Gartner Group’s Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), and we think it’s especially important when considering how to address security and networking requirements for your remote and mobile workforce.
Instead of connecting to a VPN concentrator, the remote worker connects to one of the global locations for NewEdge. Thus, customers have global coverage with multiple ingress points to NewEdge, without having to set up and maintain VPN concentrators. Users have direct access to all of the applications they need, including internet, SaaS, and private applications using an architecture designed to support the cloud and remote workers, without having to use the antiquated VPN hub & spoke architecture. Next Gen SWG provides threat protection and data protection across web and Saas applications. For private applications hosted in the data center, Netskope Private Access provides secure application-level access.
NewEdge delivers both optimized networking and the Network Security Cloud for fast and efficient inline security controls, including advanced threat protection, SSL/TLS inspection, adaptive access control, data loss prevention, and much more to make sure that the organization’s users, applications and data are safe.
While we touched on the tradeoffs organizations make when dealing with bandwidth issues, there are other considerations to think about as well. Look forward to more blogs as we dive deeper into how Netskope delivers a fast and secure user experience to remote workers.




 Back
Back 















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む