Co-authored by Yihua Liao, Ari Azarafrooz, and Yi Zhang
Ransomware attacks are on the rise. Many organizations have fallen victim to ransomware attacks. While there are different forms of ransomware, it typically involves the attacker breaching an organization’s network, encrypting a large amount of the organization’s files, which usually contain sensitive information, exfiltrating the encrypted files, and demanding a ransom. Therefore, a sudden increase of encrypted data movement in the corporate network traffic can be a strong indication of ransomware infection. To effectively detect such behavior patterns, at Netskope, we have developed the capability to detect encrypted files using machine learning (ML) and generate encrypted data movement alerts as part of Advanced UEBA (user and entity behavior analytics). This has helped our customers to identify ransomware attacks as they unfold in their network. One example is to detect ransomware on unmanaged devices. In this blog post, we will explain the technology behind encrypted file detection and Advanced UEBA, which is part of a pending patent application.
ML-based encrypted file detection
The sequence of bytes in an encrypted file tends to be more random than unencrypted files, which is often manifested in some statistical measures of randomness and information density in the file. Therefore, these statistical tests can be helpful in determining whether a file is encrypted or not. We have explored various statistical tests, including:
- Chi-square Test
- Entropy
- Arithmetic Mean
- Monte Carlo Value for Pi
- Serial Correlation Coefficient
However, our analysis shows that using any of these statistical tests alone is not sufficient to identify encrypted files and can generate excessive false positives. For example, some compressed files also look random according to some of these tests.
To reduce the false positives from individual statistical tests, we developed a classification ML model to classify whether a file is encrypted or not. The model takes all of the statistical tests and other characteristics of the file as input features, based on millions of real and synthetic files of different file types. The model uses LightGBM, a decision tree-like ML algorithm, to automatically learn the difference between encrypted files and unencrypted files. In our experiments, the ML model was able to achieve good accuracy with low false positives.
UEBA alerts
The encrypted file classification ML model determines whether an individual file is encrypted or not. In a ransomware attack, there are usually hundreds or thousands of encrypted files involved. To further reduce false positives and help our customers identify the user accounts that were involved, we use Advanced UEBA to generate user-level alerts to flag users with anomalous encrypted data movements that are indicative of ransomware attacks.
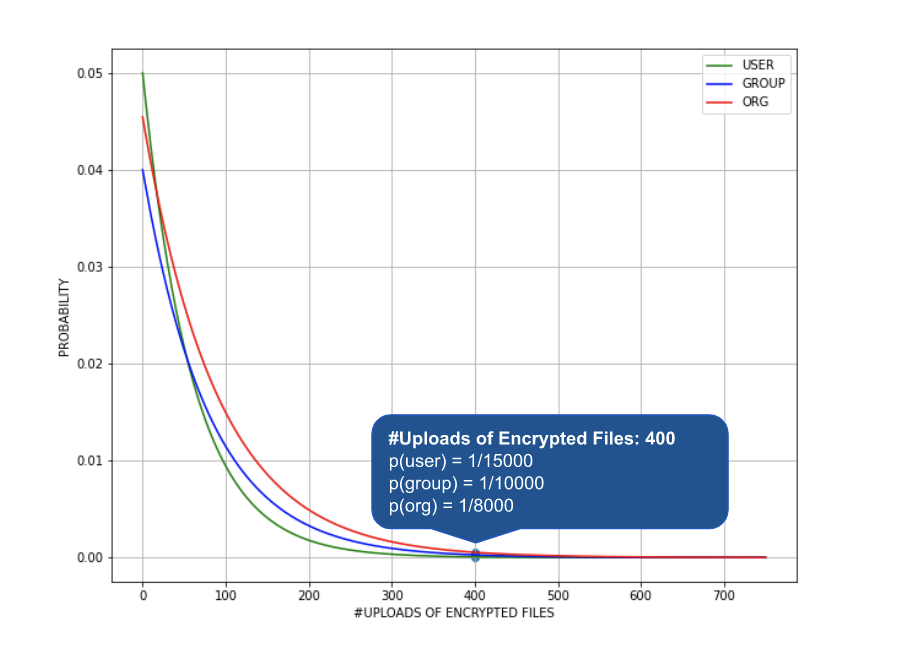
The goal of behavior analytics is to detect anomalous user behavior that indicates potential threats such as malicious insiders, compromised accounts, data exfiltration, ransomware, and other threats, through machine learning and statistical analysis. The figure below shows examples of ransomware detection policies in Advanced UEBA.

In the case of ransomware attacks, an infected user may upload a large number of encrypted files to a managed cloud app. This can be deemed anomalous and highly unlikely when compared to the normal behavior profile of the same user, their peer groups, and all other users in the same organization. This is illustrated in the figure below. As a result, an UEBA alert is generated for this user.
Netskope UEBA uses a scoring metric, User Confidence Index (UCI), to holistically evaluate the riskiness of users. The UCI Score helps security administrators easily identify the top risky users and take remediation actions based on the score.
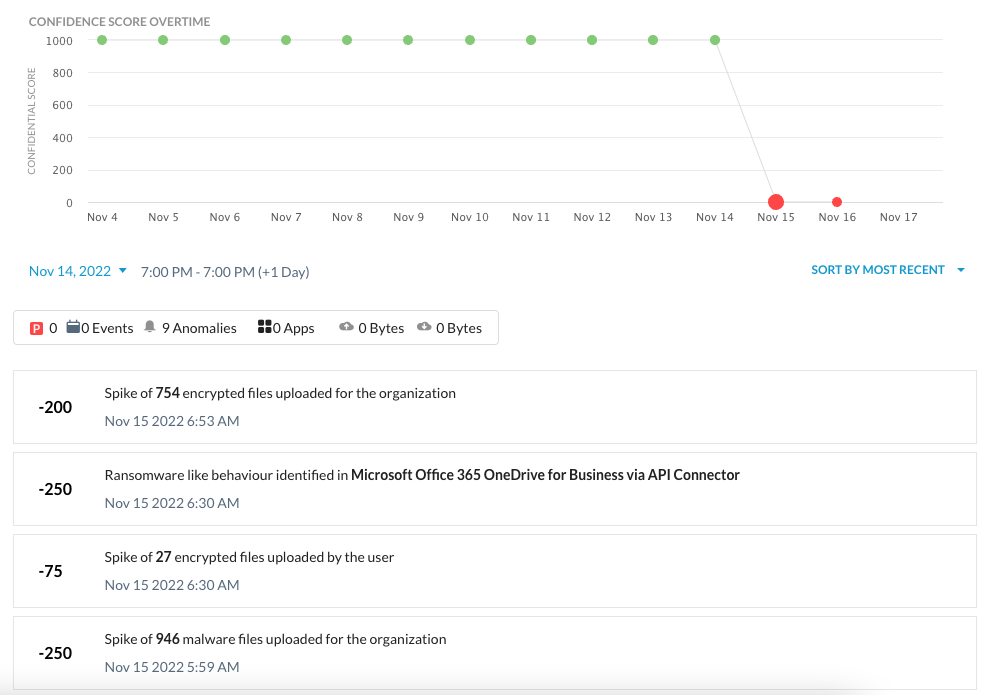
UCI is calculated based on all the alerts associated with a user that occurred in the past, weighted by the severity and abnormality of the alerts, as well as the time decay factor. UCI ranges from 0 to 1000, the higher the score, the less risky the user. In the UCI dashboard, users are rank-ordered by the UCI score so that it’s easy for security administrators to view the riskiest users. As part of the adaptive access control feature, security administrators can configure policies based on the UCI score to block or alert the user’s access or activities. Below is an example of a user’s confidence score drop due to the ransomware infection, indicated by the uploads of encrypted files with ransomware extensions to a managed cloud app.
Netskope’s Advanced UEBA has more than 100 detections for insiders, compromised accounts, and devices. As threat patterns change over time, we will add more detection capabilities to make Advanced UEBA more powerful. Please visit here to learn more about Netskope’s Advanced UEBA.




 戻る
戻る
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む