Summary
“If a tree falls in a forest and no one is around to hear it, does it make a sound?”
If an unmanaged device is infected with ransomware, will the security operations team receive an alert? Consider a contractor or employee who uses their personal laptop for work. If that device becomes infected with ransomware, not only does it pose a risk to the organization’s data and a risk to other devices within the organization, but the device is not centrally managed. How does the security operations team know that an unmanaged device was infected with ransomware? In this blog post, we will illustrate how you can detect a ransomware infection on an unmanaged device by monitoring uploads to managed cloud apps.
Approach
In the past we have discussed the MO of multiple ransomware variants such as DearCry, Khonsari, LockBit, and Hive, to name a few. In most of these cases, ransomware operators deploy the malware on corporate devices, steal the information from these devices, and encrypt the contents before asking for a ransom.
While smaller organizations can effectively keep an eye on a small set of employees, a larger organization is going to have more of a challenge monitoring all of the devices within the corporation. This is something that plays to the ransomware operator’s advantage, and is exacerbated when the devices that access sensitive data are not managed. In these situations, the standard ransomware monitoring setup might encounter some detection challenges due to a lack of visibility.
However, there is a detection opportunity here via cloud applications. Users often install clients for the cloud applications they use on their machines, such as Microsoft OneDrive or Dropbox. These clients monitor the local file system for any file modifications and then sync the changes up to the cloud application. This is particularly useful for collaboration among teams that need to edit the same Word, Excel, or Powerpoint documents. When ransomware infects a machine that has a client installed and starts encrypting a large amount of files, these changes are also pushed up to the cloud provider.
Detection
Netskope detects ransomware on unmanaged devices by monitoring managed cloud apps for signs of a ransomware infection. Netskope’s Advanced UEBA platform uses a combination of heuristics, machine learning, and threat intelligence to identify two specific signs:
- A user suddenly uploads a large number of encrypted files to a managed cloud app. Netskope uses a combination of heuristics and machine learning to identify encrypted files. Because ransomware typically encrypts all of a victim’s documents very quickly, a sudden spike of encrypted files uploaded to a cloud app is a telltale sign of ransomware infection.
- A user uploads files that use a known ransomware extension. Many ransomware families use a file extension that is specific to that ransomware family and are rarely used otherwise. Netskope detects ransomware by monitoring file uploads containing these extensions.
As an example, Netskope recently detected an AvosLocker infection by identifying both of these signs:
- Multiple users uploaded thousands of encrypted files to a managed Microsoft 365 OneDrive account.
- All of the encrypted files had a file extension of avos2, a file extension associated with AvosLocker.
The diagram below shows how Netskope was able to detect the ransomware infection, even though it only affected unmanaged devices. The unmanaged devices uploaded the AvosLocker encrypted files to the managed OneDrive account. The OneDrive account was monitored by Netskope API Data Protection and Advanced UEBA which detected the ransomware-encrypted files and generated alerts for each of the infected users.
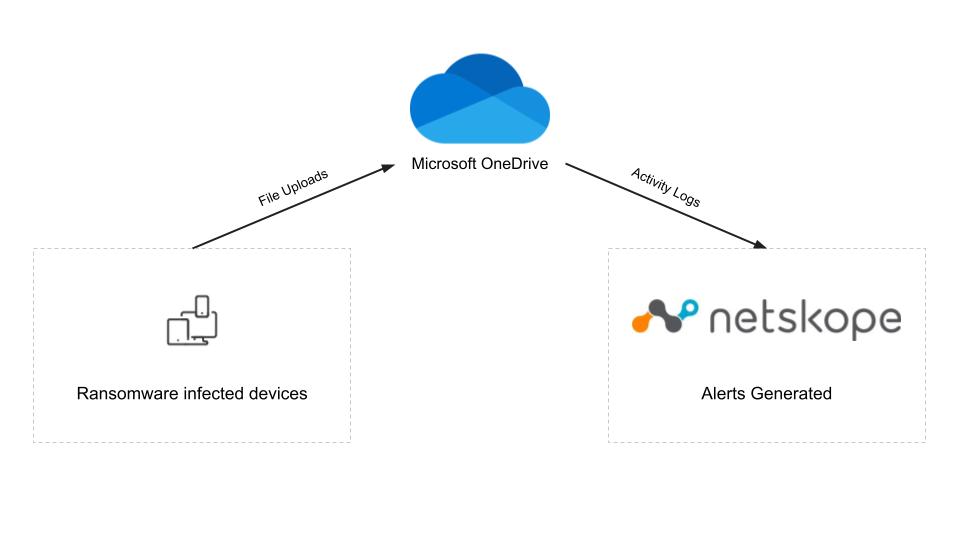
Protection
Below you will find a screenshot of the Netskope Advanced UEBA console, which includes a view of the User Confidence Index (UCI). The UCI is a risk score assigned to each user by Netskope. If the user presents no risk, then the score is 1,000, and each behavioral anomaly deducts some amount from that score to indicate the risk they pose to the organization.
The screenshot below shows the UCI at the top, and then it itemizes the anomalies below the timeline. In this example, the user’s confidence score goes from 1,000 to 0 in one day due to the ransomware infection, indicated by the uploads of encrypted files with ransomware extensions to a managed cloud app.
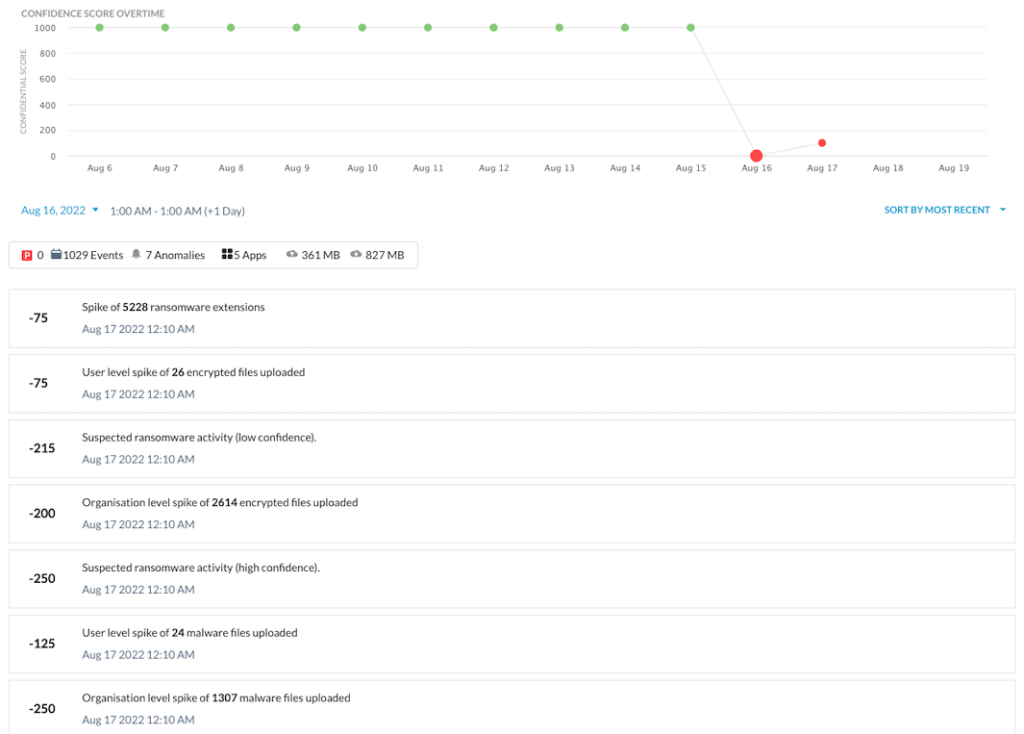
The UCI score changes may not always drop to zero, as it did in this example. Even slight changes in UCI can be used in adaptive access policies to provide real-time coaching on risky behaviors, limiting specific app activities, and controlling data movement between company and personal instances of managed apps.
Netskope’s Advanced UEBA has more than 55 detections for insiders, compromised accounts, and devices. Learn more about it here.




 Back
Back
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む