Introduction
The insider story, whether it is a disgruntled or negligent employee, is one that is familiar to many organizations. The 2020 Securonix Insider Threat Report found that 60% of the insider threat cases they dealt with involved a “flight risk” employee, or an individual that is getting ready to leave their employment. In today’s cyber ecosystem identifying these threats has become more important than ever, since more organizations are responsible for personally identifiable information (PII) and intellectual property (IP) than ever before. Since every organization is likely responsible for sensitive data and has these “flight risk” users, a strategy for addressing insider threats is necessary.
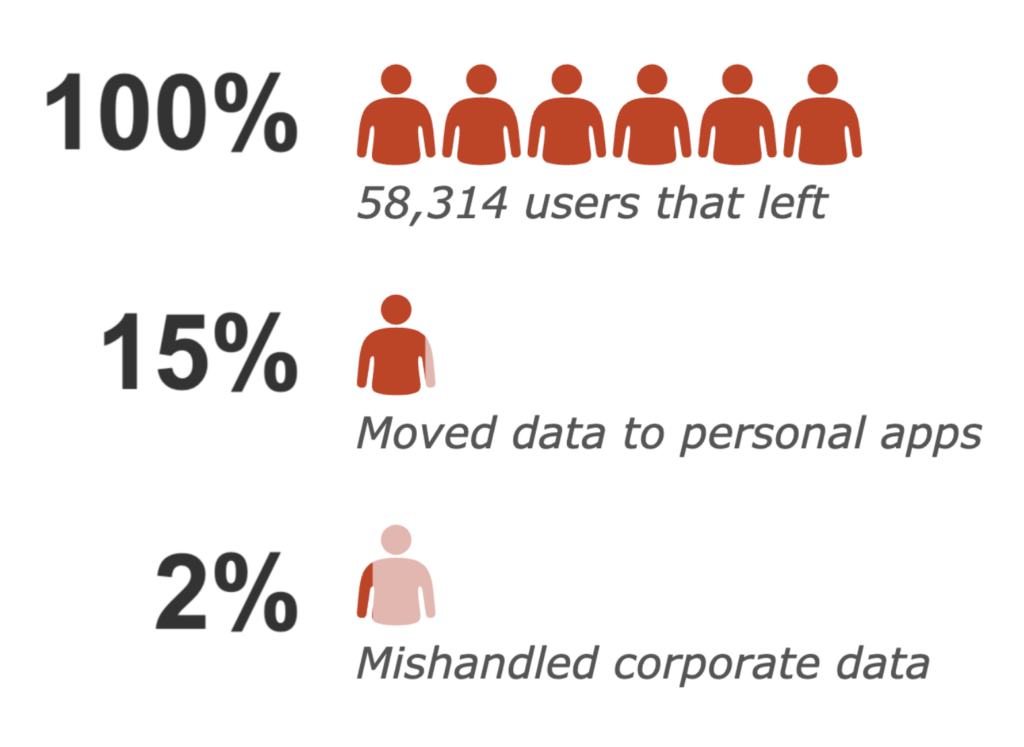
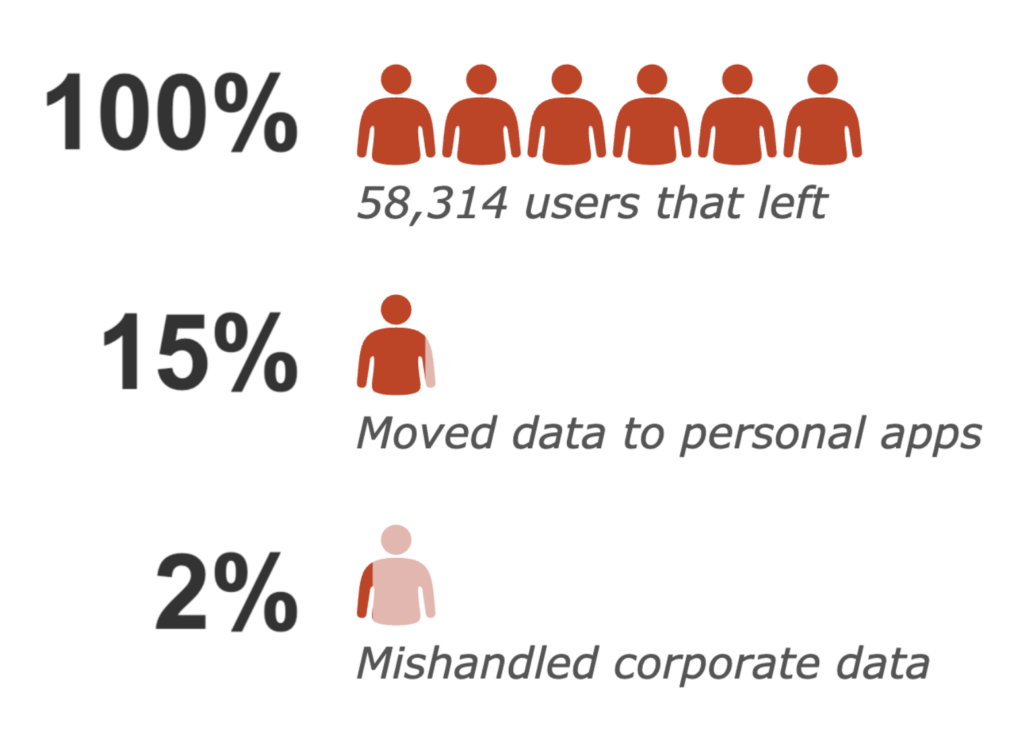
In this blog, we will summarize a study we conducted on 58,314 people that left their employment, the behaviors they exhibited before leaving, and the nature of the data they attempted to take with them. Furthermore, we will outline some techniques you can use in your own environment to find similar cases of data exfiltration via cloud apps.
We found that the last 50 days of employment is when a majority of the data movement occurs.
The analysis presented in this blog post is based on anonymized usage data collected by the Netskope Security Cloud platform relating to a subset of Netskope customers with prior authorization.
Scope
Insider threat can mean a vast array of things, but for the sake of scoping this research, when we say insider, we mean an individual that has exfiltrated sensitive corporate data using cloud apps, where sensitive data is defined as data that could hurt an organization if it were to be leaked to the public or a competitor.
We are not focused on insiders doing any of the following:
- Using a USB drive to move data
- Printing out documents and walking out of the building with them
- Taking pictures of a monitor with their phones
Overview of our approach
Our approach to addressing this threat can be broken down into three elements:
- Having the correct architecture to monitor cloud traffic
- Applying labels to the data being moved
- Analyzing the data for anomalous behavior
Architecture
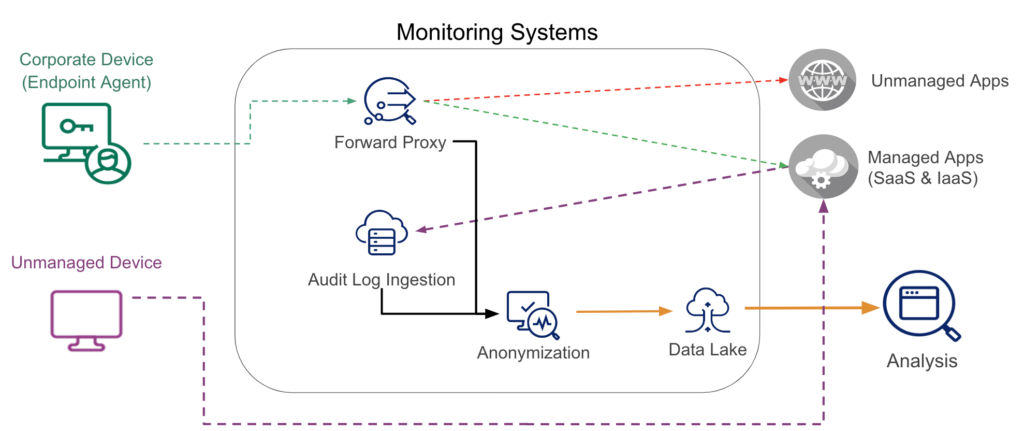
To successfully identify data movement to the cloud from the corporate environment, we monitor both inline forward proxy logs and API audit logs. The inline forward proxy logs are able to identify data movement to managed and unmanaged cloud applications. And the audit logs identify access from managed and unmanaged devices. All of this information is then anonymized and analyzed for anomalies.
Applying labels
The cloud traffic needs to be labeled via two mechanisms so we can gain the most insight from the logs.
Applying Instance Labels
We apply instance labels by looking at the application itself, the name of the instance extracted by the proxy, and the domain of the username used to log into the application. For example, a user named John working at Acme uses Google Gmail for personal correspondence, and Acme provides him a Google Gmail account for business correspondence. We consider these two instances of the same app; John’s personal instance and the Acme organization instance.
| Application | Domain | Label |
|---|---|---|
| Google Drive | acme.com | Business |
| Google Drive | gmail.com | Personal |
| Google Drive | foobar.com | Unknown |
Applying Data Labels
To apply data labels, the files in the traffic are sent to the DLP module to ensure compliance with organization-configured DLP policies. When files that violate the policies set by the organization are moved, an alert is raised.
When these labels are applied to the data, the result looks something like the following:
| User | App | App Instance label | Activity | File Name | DLP Violation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [email protected] | Google Drive | personal | upload | black_project.docx | Secret project code names |
Anomaly Detection
All of the above events are then sent to an anomaly detection component that identifies unusual deviations from the individuals’ baseline behavior. This behavior is focused on data movement anomalies that violate corporate DLP policy.
Anomaly detection looks for spikes in activities that are different from the user’s baseline behavior. For example, if a user usually uploads under 2 MB to their personal applications but suddenly uploads 2 TB to their personal Google Drive in one day, this would be anomalous behavior.
The key to accurately detecting insider threats exfiltrating data to cloud apps is to have all three components, instance labels, data labels, and anomaly detection. Omitting one or more of these components results in a significant decrease in detection efficacy.
Data Exfiltration
15% of the “flight risk” employees moved data to personal cloud applications, but only 2% of the “flight risk” employees violated corporate policies.
The 2% of “flight risks” that violated corporate policies moved:
- 94% of the files in the last 91 days
- 84% of the files in the last 49 days
- 74% of the files in the last 28 days
- 49% of the files in the last 14 days
So, if you were to monitor the last 14 days of employment, you may detect about half of the files being exfiltrated. In order to catch the full 2% of users, you would need proactive analysis for a longer period.
Conclusion
In this blog, we reviewed the insights we gathered by looking at more than 58k users that left their employment. We saw that about 2% of individuals that leave their employment mishandle corporate data before leaving. While 2% might not seem like a lot, the data that these individuals target ends up being about 70% IP and PII. To mitigate this, we need to:
- Understand that 2% of “flight risks” take sensitive data with them
- And that 75% of data is uploaded in the last 50 days, before the typical 14 day notice
- But by monitoring the nature, volume, and direction of data moved we are able to detect these cases
If you enjoyed the insights from this blog post, keep up with the latest from Netskope Threat Labs here.




 Back
Back

















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む