One of the key tools at the center of social engineering attacks against organizations is phishing. According to the Anti-Phishing Working Group’s latest report, the number of unique phishing websites detected in December 2021 was 316,747, where they have detected between 68,000 and 94,000 attacks per month in early 2020, meaning that phishing attacks have more than tripled from 2020 to 2021.
Traditional phishing attacks will often clone a website or attempt to drop malware to compromise and steal sensitive data from the victim of phishing. However, the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) can mitigate cases where sensitive data is stolen, as this adds an extra layer of protection required to access the account or service. Also, a threat protection solution can mitigate cases where the phishing drops malware to the compromised machine. This is where a more modern phishing method comes into play, the man-in-the-middle (MITM) phishing attack.
To carry out an MITM attack, a malicious actor uses URLs that closely resemble the victim’s intended destination, which is used to direct the victim to a reverse proxy server. Usually, a reverse proxy server sits in front of a webserver to help balance the network load and provide increases in performance, reliability, and security. In MITM phishing attacks, the proxy server is used by the attacker to intercept the network communication between the victim’s computer and the real web server. Furthermore, the MITM server uses a TLS certificate generated by the attacker, allowing full HTTPS decryption, hence the ability to capture sensitive information such as credentials and MFA session cookies.
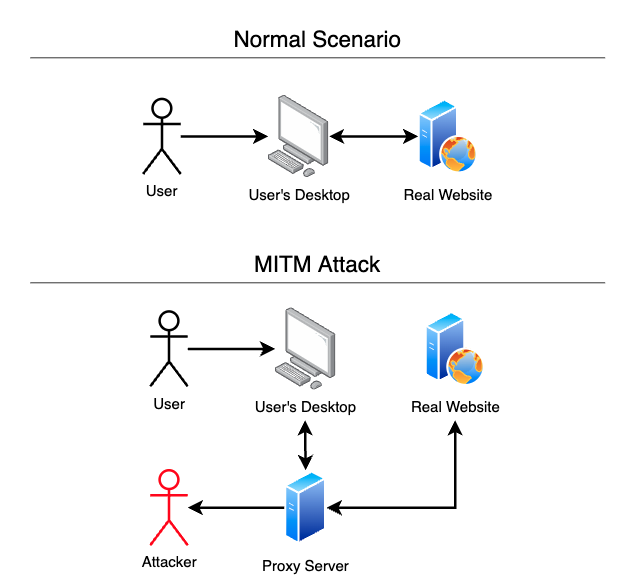
The mirroring of the legitimate site gives the phishing attack an appearance of legitimacy since the victim is browsing the real site through the attacker’s proxy server. However, although the victim is browsing the real website, the URL and the TLS certificate can be an indicator that something is off since they are not the same as the original. Furthermore, the user engaging with the legitimate website through the proxy also ensures that the captured MFA session cookies last longer, giving the attacker more time to perform malicious actions.
How MITM phishing works
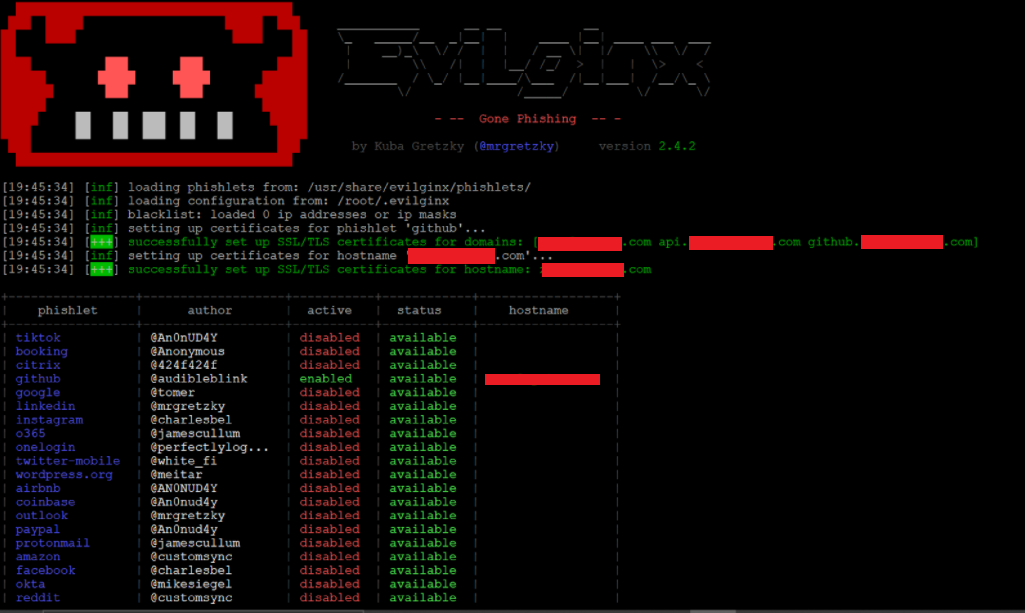
To demonstrate how MITM phishing works, we will set up a cloud infrastructure to intercept data from the GitHub login page. In this test, we used an AWS EC2 instance running Ubuntu 20.04 OS, installed with the open-source tools OpenSSL, keytool, certbot, and Evilginx2, which is a MITM phishing toolkit.
To resolve the attacker’s URL and ensure that victims get directed to the reverse proxy server, Evilginx2 provides a built-in DNS function. If using a cloud provisioned server, such as AWS EC2, the attacker must modify their AWS instance’s glue records to point toward their proxy server hosting the MITM toolkit, so that the reverse proxy server acts as a nameserver. This allows the attacker to route victims to the proxy server and then redirect the victim’s traffic to the real web server. Also, the SSL/TLS certificate will be set up for the registered domain as soon as the tool is running.
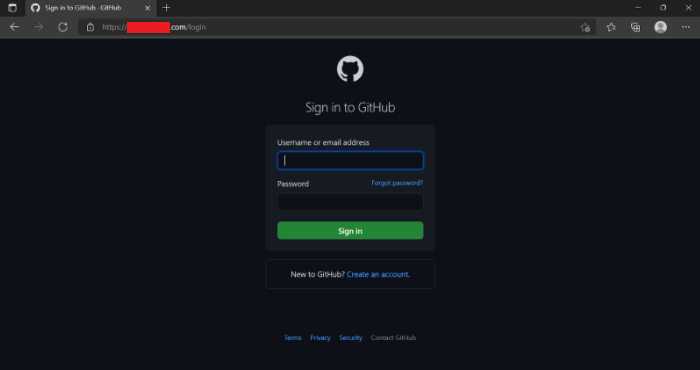
Once ready, the attacker needs to socially engineer the victim to access the desired service through the attacker’s URL, which is mirroring the real website. Aside from the URL and the TLS certificate, the rest is exactly the same, as the attacker is simply intercepting the traffic between the victim and the real website.
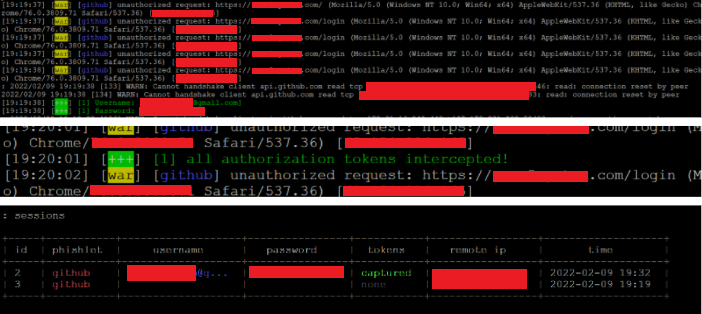
When the victim accesses the website through the attacker’s URL, the framework captures all the sensitive data, such as IP addresses, username, and password, which are redacted in the image below. Furthermore, all the session cookies are stored by the framework, allowing the attacker to re-use them for as long as they are valid, effectively bypassing MFA.
Mitigation against common MITM phishing tactics
The best way to avoid any form of phishing is end-user training to avoid falling for the social engineering used by the attacker. To mitigate MITM phishing attacks, the URL and the website certificate can be checked, as they are the most valuable indicators.
Other methods of mitigating phishing attacks include using password managers and email security services. Password managers will only autofill credentials if there’s an exact URL match. This level of protection is dependent on end-users not filling in the credentials themselves. Dedicated email security services can detect imposter domains that attackers may register hoping to trick users into thinking malicious emails are from legitimate sources. A Next Generation Secure Web Gateway (NG SWG) can protect users against phishing using a combination of URL filtering, content inspection, and activity detection.
While MITM phishing attacks do circumvent MFA by capturing the MFA session cookies, this should not deter MFA use. Multi-factor authentication is still a critical piece of any organization’s security since it is one more barrier of entry to threat actors.
Conclusions
MITM phishing attacks are an advanced way to steal sensitive credentials and bypass advanced security measures, like MFA. It is relatively easy to deploy this since there are many open-source toolkits available in the wild. Also, attackers can abuse cloud infrastructures to carry out this attack, as demonstrated in this blog, hence adding resilience to the scam.




 戻る
戻る
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む