Security transformation is upon us, and the global pandemic further accelerated macro-trends such as work-from-anywhere that were already well underway. But with so many ideas now competing for airtime when it comes to describing that transformation and how to do it successfully, security professionals could be forgiven for thinking that the right moves and the good advice are getting buried under an avalanche of marketing, buzzwords, and acronyms.
Security Service Edge (SSE) is one of the newer ones. You likely already know about secure access service edge (SASE) as a framework for designing security and networking architecture to suit a business environment that increasingly relies on the cloud. SSE, which Gartner coined in 2021, encompasses a unified set of capabilities for the “security” side of SASE, including cloud access security broker (CASB), secure web gateway (SWG), zero-trust network access (ZTNA), firewall-as-a-service (FWaaS), data loss prevention (DLP), and remote browser isolation (RBI) among other security technologies that in the previous decade were delivered as separate services, but can now be delivered from a single platform.
But here we are getting into acronyms again, and you’re probably wondering to yourself, “How can SSE help me solve the issues my security team is facing right now?” Equally so, zero trust as a security paradigm is increasingly top of mind for both security executives and practitioners. So you might be wondering, should I implement one or the other or both? The answer is a resounding Yes.
Consider that the average security stack currently has 76 different controls currently in place. With a unified security solution consolidating what was once only available piecemeal, you have the opportunity to significantly simplify your security operations. As more organizations grapple with securing an increasingly remote, hybrid workforce amid an ever evolving threat landscape, granular visibility and continuous risk management become all the more important.
Simply put, SSE helps you simplify operations, better learn about your users, and apply zero trust principles to gain contextual knowledge of how your users interact with data—all of which will better protect you (and them) against risks, while also reducing your costs and providing more value to your business. But all solutions now marketed as SSE—or SASE, or zero trust—are not created equally.
Netskope Intelligent SSE
An “intelligent” solution, by definition, requires being able to acquire knowledge from that solution and use that knowledge to help it work better.
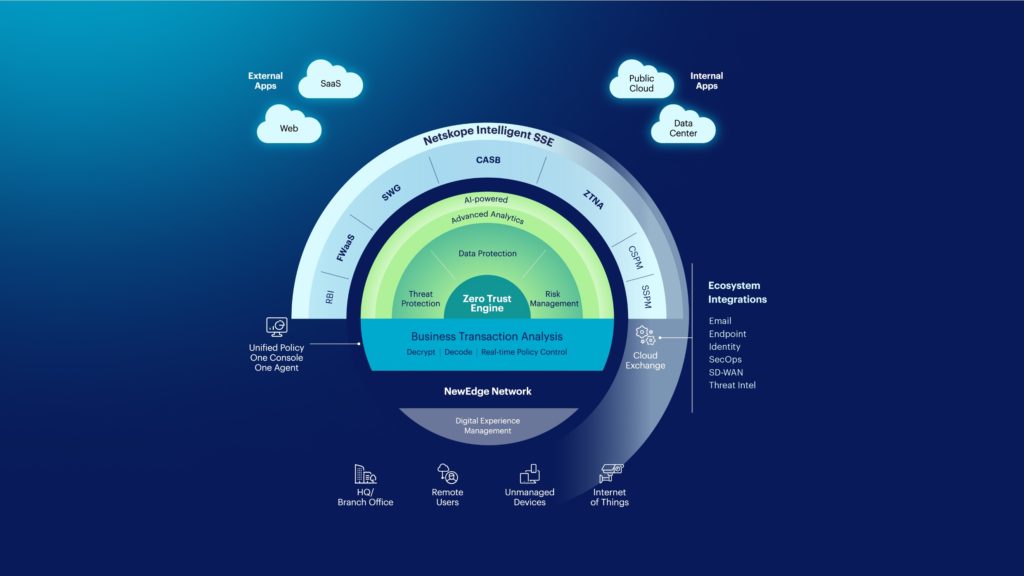
Netskope Intelligent SSE was designed from the onset to be a cloud-native and truly unified platform that quickly and safely connects users and devices to their destinations whether that was for web, SaaS, IaaS or private apps. We created this visualization of Netskope Intelligent SSE to help explain not only the individual components of a successful SSE solution, but also—crucially—how they work together in an intelligent way. Beyond specifically defined SSE components such as CASB, SWG, ZTNA, and FWaaS, Netskope can offer:
- Netskope NewEdge, the world’s largest and highest-performing carrier-class infrastructure extensively peers with leading web, content delivery networks (CDNs), and cloud and SaaS providers around the world to offer industry best SLAs of the lowest latency and the fastest access to traffic. NewEdge is further strengthened through the use of digital experience management, which helps notify users of risks, so they can identify and resolve the issue quickly with minimal impact to user experience or the business overall.
- Business transaction analysis, which decrypts and decodes what’s actually happening in your traffic, offering further visibility into the JSON API call. From there, Intelligent SSE can use the “big picture” data from this business transaction analysis to inform SSE capabilities like real-time granular policy control, threat protection, data protection, and cloud risk management.
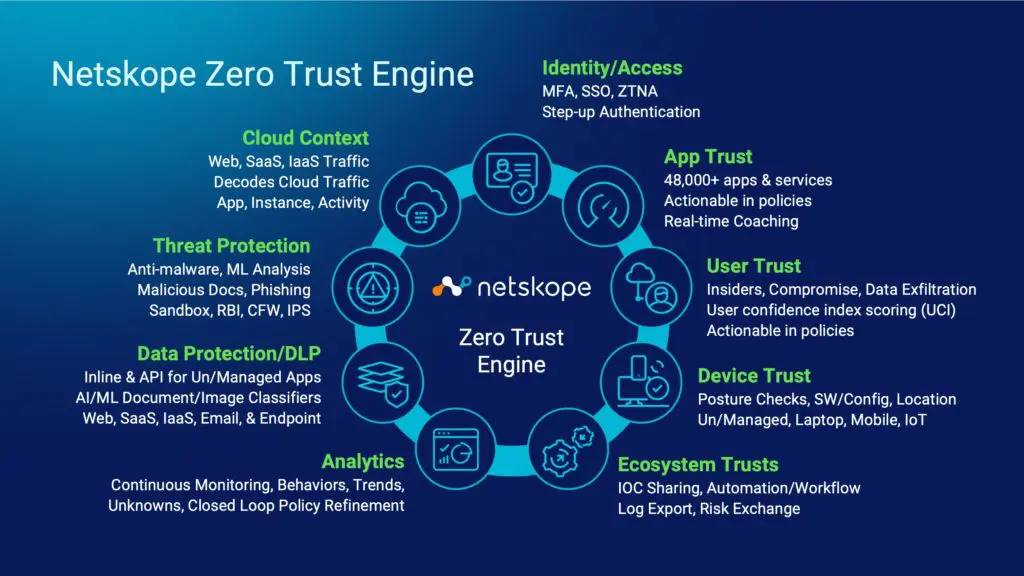
- Zero Trust Engine: This is the heart of the Netskope Intelligent SSE platform. The Zero Trust Engine is a combination of technologies that help to better understand cloud context. This stitches together the contextual story of the traffic, based around the particular app, instance (personal/corporate-managed), or activity being performed. What sets the Netskope Zero Trust Engine apart, is a rich set of telemetry that is used to define trust for a given use. This telemetry includes:
- Identity management – Utilizing multi-factor authentication and single-sign-on to verify that the user is who they claim to be.
- App trust – Pulling from a repository of more than 50,000 apps to calculate a cloud confidence index score the Zero Trust Engine can use these scores to make dynamic zero trust decisions. For example, if a user tries to upload sensitive information to a file-sharing app with a medium trust level, when the organization already has a high-trust file-sharing app, you have the opportunity to coach them to use the high-trust application.
- User trust – Similar to app trust, understanding characteristics of observed user behaviors to calculate a user confidence index. This allows you to make richer trust decisions, for example, when trying to determine whether a user is just naive to corporate security policies or if they’re in fact a malicious insider.
- Device trust – This is visibility into the device from which the access is being made, utilizing an understanding of the device posture, whether it is managed/unmanaged, vulnerability exposure, whether the device is infected with malware or clean, or even the device’s geographic location to determine how trustworthy it is. Further, these trust scores are not fixed but change over time based on a range of factors.
- Taken together, this dynamic context informs a more adaptive zero trust decision to be made as opposed to traditional binary zero trust (allow or block). The same context is leveraged to deliver advanced threat protection, data protection, and analytics for risk management. The various trust telemetry can also be exchanged with the rest of the security tools in a customer’s IT environment through the Netskope Cloud Exchange.
All of these SSE capabilities working together and communicating with each other to inform decisions, provide context around app and data usage, and recognize easily fixable misconfigurations is what makes Netskope SSE so intelligent. That intelligence makes this more than “marketecture”—you use it to solve the challenges of transformation and protect your most important assets: people and data.
Real business value
None of this—not even our recognition by Gartner as a clear Leader in SSE—would matter if we weren’t able to provide demonstrable business value to our customers. Netskope customers realize that SSE is a key part of their security transformation journey, and are already beginning to see the results.
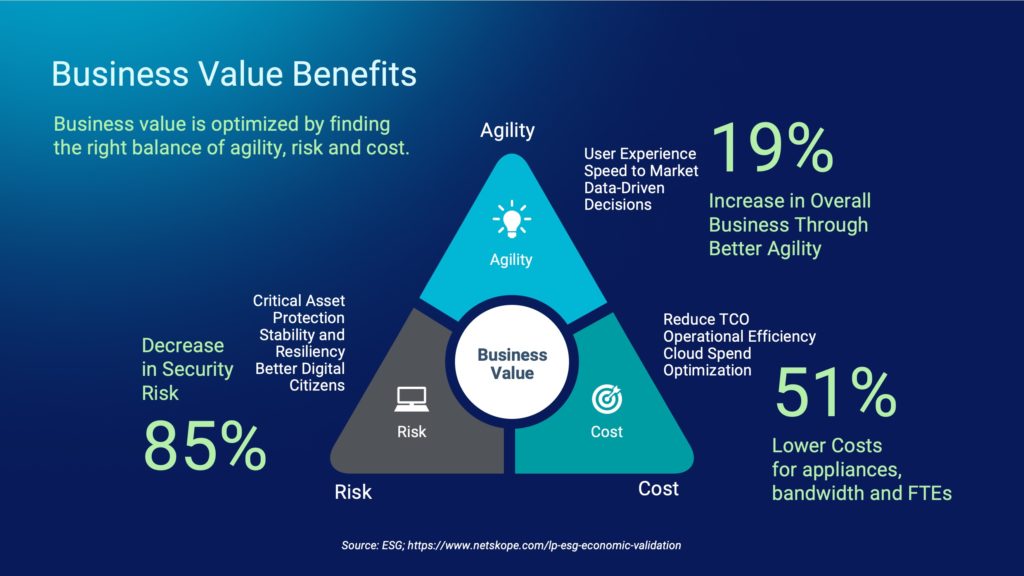
A recent ESG validation study showed that an example mid-size customer using the Netskope platform, which includes Netskope Intelligent SSE, saw an 85% decrease in security risks and exposures, as a result a tighter, more aligned security stack. Additionally the same example customer also saw a 51% decrease in cost of appliances, bandwidth, and operational costs, as a result of this consolidated, cloud-native security. This decrease in risk and cost showed that the example customer reported seeing a 19% increase in existing business through using Netskope. These numbers are a testament to the value, rich visibility, and security that comes baked into the Netskope Intelligent SSE platform.
See how your organization can benefit from using Netskope Intelligent SSE. For more information, please visit our Netskope Intelligent SSE page.




 戻る
戻る
















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む