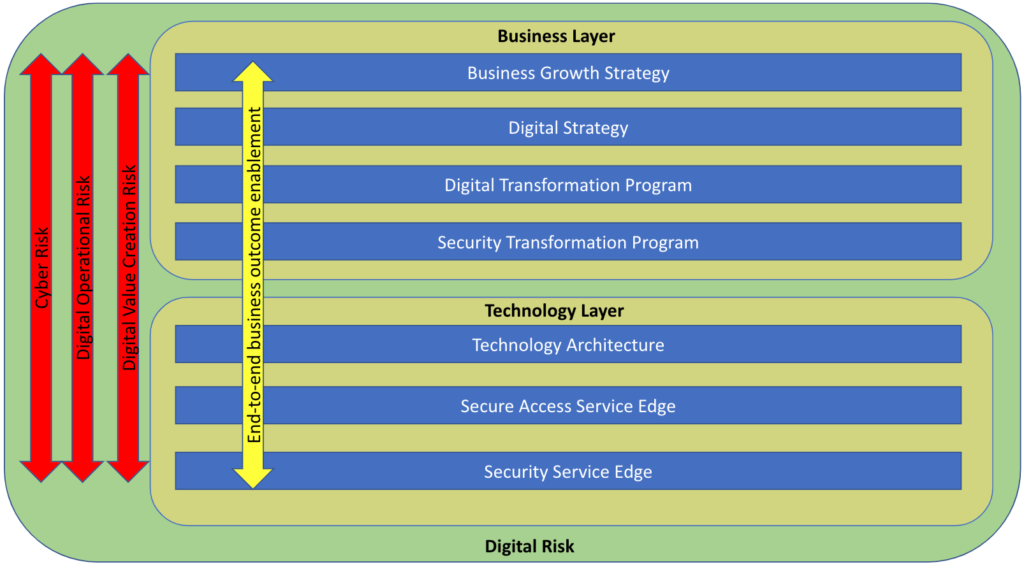
In the first part of this blog series, I took a look at how an understanding of digital strategy and digital risk is key to starting a security transformation journey. In this post, I am digging further into how a secure access service edge (SASE) architecture with security service edge (SSE) capabilities and zero trust principles can help mitigate the types of digital risk I outlined in part one.
SASE: a core component of security transformation
A core element of security transformation is the secure access service edge (SASE) architectural framework, coined by Gartner in 2019 to refer to a cloud-based architecture that delivers network and security services meant to protect users, applications, and data.
SASE, as an architecture, creates a highly resilient, highly performant security cloud that allows organizations and security teams to re-architect how data and information assets have traditionally been protected with every user and every device accessing services and data via a SASE framework. This cloud-based architecture sees the traditional controls that we are familiar with, move the controls closer to the data—the critical asset.
The technology and platform that implements the security components of SASE is referred to as security service edge (SSE). The core components of SSE include threat protection, cloud and SaaS security posture management (CSPM & SSPM), data leakage protection (DLP), remote browser isolation (RBI), Next Gen Secure Web Gateway (NG-SWG), cloud firewall (CFW), and zero trust network access (ZTNA). The networking side of SASE is called WAN Edge, and is primarily powered by software defined WAN, or SD-WAN.
SSE and SASE allow security teams to holistically support the digital objectives of their organization and play a key role in managing those three top level digital risks I discussed in my previous post. Here’s how:
Digital Operational Risk
The very nature of the highly resilient, highly performant security cloud upon which a SASE framework is built, clearly addresses the risk of disruption of digital services stemming from technology failure or human errors. Furthermore, the inclusion of threat protection works to prevent disruption via cyber threats.
Cyber Risk
The core SSE controls and capabilities enable security teams to adapt traditional approaches to managing cyber risk to support cloud adoption and the organization’s digital transformation. Traditional controls are still relevant but they need to be cloud-native,, which means these controls have moved closer to the data and users.
Digital Value Creation Risk
It is also worth taking a moment to consider how value is created from data through digital services. Value is created in a number ways, for example:
- Streamlining and automating existing processes and taking cost out of the business
- Faster onboarding and faster delivery of services, providing superior customer experience
- Enabling users to access digital services and data sources required to collaborate and share data with third parties, exchange information with customers, conduct research, enrich data from external sources, all of which are required to gain greater business insights, allows a deeper understanding of the customer and the ability to provide that personalized service and personalized pricing, achieving the customer expectation, and ultimately leading to growth.
When users are prevented from accessing digital services and external data sources, and collaborating or exchanging information with third-parties and customers, value creation is stifled which ultimately impacts business growth.
While a SASE architecture and SSE capabilities are key to managing these digital risks, a strong foundation in zero trust principles is also necessary.
Zero trust
The term “zero trust” can have many different meanings, depending on who you’re talking to. To level set for this conversation, zero trust is defined as the ability to continuously assess the context of various conditions to enable adaptive risk-based decision making. A zero trust approach creates a capability that allows an organization to make risk-based decisions, under an assumed breach condition of the network (i.e. the network cannot be trusted), grant minimal access to resources and data, enforcing least privilege, and limiting the blast radius.
The principles of zero trust must be embedded into the technology fabric and security architecture in order to create a capability that enables both agility and security. For an organization to apply a zero trust approach in an environment, contextualized risk decisions need to be continuously evaluated and access adaptively applied, commensurate to the risk, without exposing the organization to excess risk. The various data sources (data points) that can be continuously assessed are threat, identity, user behavior, application risk, data, and device. With the right technical capabilities, organizations can be very surgical with how they allow access to data and resources and balancing that commensurate with the risk.
Zero trust can become an enabler for digital transformation and value creation through digitalization, but in order to to do this successfully, the underlying architecture and technology must meet certain criteria:
- Instance and action awareness helps to enforce the principle of least privilege, the system must be able to distinguish between instances of the same cloud service or application (corporate or personal) as well as be able to control what actions an end user is taking. Without both instance and action awareness, the principle of least privilege can not be enforced.
- Advanced threat protection offers the ability to detect threats and changes in threats during the course of a digital transaction or session, and will drive an action to adapt access granted during that session or transaction.
- ZTNA offers the ability to apply the same, consistent set of security policies for both on-prem and cloud infrastructures (IaaS), as applied to cloud services (SaaS) and limit the blast radius by only exposing a small portion of the technology stack.
- Data context is important because data is the true value creation asset of organizations today, understanding data risk and the type of data in use is a key data point in the risk decision.
- Ecosystem integration means there must be broad integration between technology stacks so that the various data points (e.g. endpoint, identities, user behaviors, etc) can be ingested into the risk decision engine so that risk-informed actions can be taken continuously and adaptively.
WIth all of these criteria in mind, it’s easy to see that zero trust principles are a fundamental building block of a successful SASE architecture with SSE capabilities.
Now that I’ve covered how SASE, SSE, and zero trust all play into managing the risks that come along with transformation, the third and final part of this series will dig into some of the key use cases with each of these elements in action.




 Zurück
Zurück
















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen